Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LEC - 1a
Uploaded by
Khalid Abdirashid Abubakar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views19 pagesOriginal Title
LEC- 1a
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views19 pagesLEC - 1a
Uploaded by
Khalid Abdirashid AbubakarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
Power electronics
• Power Electronics refers to an interdisciplinary
subject within electrical engineering that deals
with the design, control and conversion of
power in its electric form. A system that
converts electric energy to an electric load
through a control circuit is known as a Power
Electronic System.
Purpose
• The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce and
explain the main concepts in Power
Electronics, which include Power Semi-
Conductor Devices, Phase-Controlled
Converters, DC to DC Converter, Inverters and
AC to AC Converters.
Introduction
• Power Electronics refers to the process of
controlling the flow of current and voltage and
converting it to a form that is suitable for user
loads. The most desirable power electronic
system is one whose efficiency and reliability
is 100%.
Take a look at the following block diagram. It
shows the components of a Power Electronic
system and how they are interlinked.
• A power electronic system converts electrical
energy from one form to another and ensures
the following is achieved-
Maximum efficiency
Maximum reliability
Maximum availability
Minimum cost
Least weight
Small size
Applications of Power Electronics
are classified into two types:
Static Applications and Drive
Applications.
Static Applications
• This utilizes moving and/or rotating
mechanical parts such as welding, heating,
cooling, and electro-plating and DC power.
Drive Applications
• Drive applications have rotating parts such as
motors. Examples include compressors, pumps,
conveyer belts and air conditioning systems.
• Air Conditioning System
• Power electronics is extensively used in air
conditioners to control elements such as
compressors. A schematic diagram that shows
how power electronics is used in air
conditioners is shown below.
Power semiconductor
• Materials that permit flow of electrons are called
conductors (e.g., gold, silver, copper, etc.).
• Materials that block flow of electrons are called
insulators (e.g., rubber, glass, Teflon, mica, etc.).
• Materials whose conductivity falls between those
of conductors and insulators are called
semiconductors.
• Semiconductors are “part-time” conductors
• whose conductivity can be controlled.
• Some common power devices are the power
diode, thyristor, power MOSFET and IGBT
(insulated gate bipolar transistor). A power
diode or MOSFET, for example, operates on
similar principles as its low-power
counterpart, but is able to carry a larger
amount of current and typically is able to
support a larger reverse-bias voltage in the
off-state.
Cont…
• Silicon is the most common material used to
build semiconductor devices.
• • Si is the main ingredient of sand and it is
estimated that a cubic mile of seawater
• contains 15,000 tons of Si.
• Germanium is another semiconductor
material with four valence electrons.
Control characteristics of power device
• The power semiconductor devices can be
operated as switches by applying control
signals to gate terminals of thyristors (and to
the base of bipolar transistors).
• The required output is obtained by varying the
conduction time of these switching devices.
• Showing the figure [Pdf]
LOOK AT BDF
Classification of power semiconductor
• Uncontrolled turn on and off (diode)
• Controlled turn on and uncontrolled turn off (SCR).
• Controlled turn on and off characteristics
(BJT,MOSFET,GTO,SITH,IGBT,SIT,MCT);
• Continuous gate signal required (BJT,MOSFET.IGBT,SIT);
• Pulse gate requirement (SCR,GTO,MCT)
• Bipolar voltage withstanding capability (SCR,GTO);
• Unipolar voltage withstanding capability (BJT,MOSFET,GTO,IGBT,MCT)
• Bidirectional current capability (TRIAC,RCT)
• Unidirectional current
capability(SCR,GTO,BJT,MOSFET,MCT,IGBT,SITH,SIT,DIODE)
Ideal characteristics
The characteristics of an ideal switch
• In the On state when the switch on, it must have :
• 1- Able to carry any value of forward current .
• 2-has zero voltage drop.
• 3-has zero on state resistance.
• 4-has zero power dissipation.
• In the Off state when the switch off, it must have :
• 1-Able to withstand infinite open- circuit voltage
• 2- has zero leakage current.
• Has infinite off state resistance
Types of power electronic circuit
• 1) diode rectifiers
• 2) Ac to Dc converters (controlled rectifier)
• 3)Ac to Ac converters (Ac voltage controllers)
• 4)Dc to Dc converters (Dc choppers)
• 5) DC to Ac converters (inverters)
• 6) Static switches
You might also like
- Concept of Power ElectronicsDocument23 pagesConcept of Power ElectronicsMuttoju VaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Advanced Power Electronics Course Contents and ApplicationsDocument36 pagesAdvanced Power Electronics Course Contents and Applicationsmuhammad haseebNo ratings yet
- ELG4139: Power Electronics Systems: Power Supplies and Motor Drives!Document25 pagesELG4139: Power Electronics Systems: Power Supplies and Motor Drives!bitew ayalewNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - CombinedDocument194 pagesUnit 1 - CombinedNINJANo ratings yet
- Power Electronics SeminarDocument25 pagesPower Electronics Seminarsreemukhi100% (3)
- Types of Static SwitchesDocument55 pagesTypes of Static SwitchesSubhash MurkuteNo ratings yet
- MCT4320 Power Electronics Reference and EvaluationDocument38 pagesMCT4320 Power Electronics Reference and EvaluationOmar Bin ShehabNo ratings yet
- Introduction Unit1Document34 pagesIntroduction Unit1senthilku marNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics IntroductionDocument18 pagesPower Electronics Introductionsagar378No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document31 pagesUnit 1bilal alkhNo ratings yet
- Control of Electrical Converters: Course 1Document26 pagesControl of Electrical Converters: Course 1Gara BrasovNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 AspDocument52 pagesUnit - 1 AspGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- PowerElec-Course Outline Intro Assign1Document15 pagesPowerElec-Course Outline Intro Assign1Ndunya WestleyNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics: Anela L. SalvadorDocument148 pagesIndustrial Electronics: Anela L. SalvadorJames SuarezNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument59 pagesPower ElectronicsbojjasaigowthamiNo ratings yet
- @1b - Semiconductors Diodes and ApplicationsDocument269 pages@1b - Semiconductors Diodes and Applicationsminh vũNo ratings yet
- 1) Power Switching Devices EE-442-642Document17 pages1) Power Switching Devices EE-442-642Mehmet DALNo ratings yet
- Basics of Power Electronics ComponentsDocument22 pagesBasics of Power Electronics ComponentsAtif SaleemNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document27 pagesPart 1Mustafa AlhumayreNo ratings yet
- Class PEDocument90 pagesClass PEAlex WaxanNo ratings yet
- EE4532 Part A Lecture - pdf0Document83 pagesEE4532 Part A Lecture - pdf0Denise Isebella LeeNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1aaDocument164 pagesUNIT 1aaDr.K.Krishna Veni ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document30 pagesModule 1Sathya Prakash PNo ratings yet
- Ele4363 Lo1Document93 pagesEle4363 Lo1Shashe gNo ratings yet
- ME8791 Actuation SystemsDocument52 pagesME8791 Actuation SystemsJkl MahanthNo ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument6 pagesPower Semiconductor DevicesNassor Nassor ANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power Electronics SystemDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Power Electronics Systemrakesh_pal_3No ratings yet
- EE 442 642 Power Switching DevicesDocument16 pagesEE 442 642 Power Switching Devicesthienvuong90No ratings yet
- Mechatroncis UNIT 5Document28 pagesMechatroncis UNIT 5Mayank GijreNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power SystemsDocument17 pagesElectrical Power SystemshasanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Overview of Power ElectronicsDocument64 pagesUnit 2 - Overview of Power ElectronicsKakumbi Shukhovu ChitiNo ratings yet
- Iare Pe Lecture NotesDocument177 pagesIare Pe Lecture NotesShewan DebretsionNo ratings yet
- Unit - IIDocument35 pagesUnit - IIthota nagajyothiNo ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor Devices: An Overview of Key Components and Their ApplicationsDocument31 pagesPower Semiconductor Devices: An Overview of Key Components and Their ApplicationsLai Yon Peng50% (2)
- Introduction to Power ElectronicsDocument17 pagesIntroduction to Power ElectronicsAbdullrahman Al-ShammaaNo ratings yet
- MCS3304 4Document11 pagesMCS3304 4Muhammad Ibrahim IsahNo ratings yet
- Variable Speed DrivesDocument16 pagesVariable Speed Drivesfaizan123khanNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Introduction: 1.0 Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument30 pagesUnit-1 Introduction: 1.0 Introduction To Power ElectronicsAishwarya PKamatagiNo ratings yet
- Module-I 3 Con TopoDocument4 pagesModule-I 3 Con TopoLalbahadur MajhiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics R19 - UNIT-1Document51 pagesPower Electronics R19 - UNIT-1Emmanuel BathulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Switching ConceptDocument97 pagesChapter 2 - Switching ConceptAbdullatif AlbattatNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Guide Covering Rectification, Inverters, Choppers & MoreDocument276 pagesPower Electronics Guide Covering Rectification, Inverters, Choppers & MoreBikrant PoudelNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: P.Karthikeyan, BE (EEE), SmecDocument19 pagesPower Electronics: P.Karthikeyan, BE (EEE), SmecKrishnamoorthy AyyasamiNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Applications of Power ElectronicsDocument7 pages1.2 Applications of Power ElectronicsSwamy100% (1)
- Power Switching DevicesDocument31 pagesPower Switching DevicesFercho Collahuazo VNo ratings yet
- Elect Q1Wk1 Electrical and Electronic ComponentsDocument25 pagesElect Q1Wk1 Electrical and Electronic Componentsquackity obamaNo ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument2 pagesPower Semiconductor Devicessaakhi4135No ratings yet
- Power Elecrtoincs and InstrumentationDocument119 pagesPower Elecrtoincs and InstrumentationMeenuNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentDocument10 pagesElectronic ComponentVimalaChristinalNo ratings yet
- a) MOSFETb) GTO c) MOSFETd) IGBTe) BJTf) GTOg) IGBTQs#2 Which of the following power semiconductor device has bidirectional blocking capability?a) SCR b) MOSFETc) IGBTd) GTODocument49 pagesa) MOSFETb) GTO c) MOSFETd) IGBTe) BJTf) GTOg) IGBTQs#2 Which of the following power semiconductor device has bidirectional blocking capability?a) SCR b) MOSFETc) IGBTd) GTOyougogwencoco 7No ratings yet
- Power Cis The Application of SolidDocument20 pagesPower Cis The Application of SolidsharathVEMNo ratings yet
- U1 l1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument5 pagesU1 l1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsRasedulIslamNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument20 pagesPower ElectronicsJohn Paul BaquiranNo ratings yet
- Over and Under Voltage Protection RelayDocument44 pagesOver and Under Voltage Protection RelaySeven Hills100% (3)
- Overview and Power Devices PDFDocument48 pagesOverview and Power Devices PDFSebastian LangkahNo ratings yet
- Induction RelayDocument15 pagesInduction RelayEE166Srushti Vibhute.No ratings yet
- Unit-I 1Document14 pagesUnit-I 1Federico AldoNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and Energy Conversion Systems, Fundamentals and Hard-switching ConvertersFrom EverandPower Electronics and Energy Conversion Systems, Fundamentals and Hard-switching ConvertersNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Lecture Notes of Power Electronics CourseFrom EverandPower Electronics: Lecture Notes of Power Electronics CourseNo ratings yet
- Lecturer 11 PMDocument12 pagesLecturer 11 PMKhalid Abdirashid AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Lecturer 10-PMDocument19 pagesLecturer 10-PMKhalid Abdirashid AbubakarNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument33 pagesUntitledKhalid Abdirashid AbubakarNo ratings yet
- CCCM Dashboard - Sep 2022Document1 pageCCCM Dashboard - Sep 2022Khalid Abdirashid AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Final Schedual 2022 by AdminDocument2 pagesFinal Schedual 2022 by AdminKhalid Abdirashid AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Part 1Document55 pagesChapter 6 Part 1Khalid Abdirashid AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Lec - 2Document22 pagesLec - 2Khalid Abdirashid AbubakarNo ratings yet
- What is a Thyristor? Understanding Semiconductor DevicesDocument44 pagesWhat is a Thyristor? Understanding Semiconductor DevicesKhalid Abdirashid AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Production Engineering: Somali National UniversityDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Production Engineering: Somali National UniversityKhalid Abdirashid AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Part 2Document26 pagesChapter 6 Part 2Khalid Abdirashid AbubakarNo ratings yet
- 1 Heritage InstituteDocument3 pages1 Heritage InstituteKhalid Abdirashid AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Call For ProposalsDocument3 pagesCall For ProposalsKhalid Abdirashid AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Rca-40822 - Dual Mosfet - DatasheetDocument1 pageRca-40822 - Dual Mosfet - DatasheetmauriciosaddamNo ratings yet
- Design Rules and Technology File OverviewDocument22 pagesDesign Rules and Technology File OverviewNguyen Van ToanNo ratings yet
- Thyristors PDFDocument53 pagesThyristors PDFKashyap ChintuNo ratings yet
- Proyecto Final ExcelDocument7 pagesProyecto Final ExcelKennyi Adan Mamani MaytaNo ratings yet
- RGVPV Logic Families Seminar ReportDocument13 pagesRGVPV Logic Families Seminar ReportMukesh SandanNo ratings yet
- 2N-crossReference DBDocument305 pages2N-crossReference DBYahel BronNo ratings yet
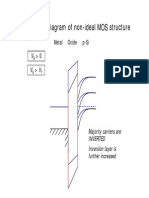
- Energy Band Diagram of Non-Ideal MOS Structure Gy G: 0 Metal Oxide P-Si 0Document12 pagesEnergy Band Diagram of Non-Ideal MOS Structure Gy G: 0 Metal Oxide P-Si 0LimLamGhaiNo ratings yet
- Combinational Mos Logic Circuits: Basic ConceptsDocument41 pagesCombinational Mos Logic Circuits: Basic Conceptsflampard24No ratings yet
- CMOS IC Design for Analog CircuitsDocument2 pagesCMOS IC Design for Analog CircuitsVijay UrkudeNo ratings yet
- Common Emitter Amplifier CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesCommon Emitter Amplifier CharacteristicsAswin VengatNo ratings yet
- Vl9213 Solid State Device Modeling and Simulation LT P CDocument1 pageVl9213 Solid State Device Modeling and Simulation LT P CSoma SundarNo ratings yet
- BUT11AX SavantICDocument3 pagesBUT11AX SavantICGabriel LatiuNo ratings yet
- Centurion C ServiceDocument18 pagesCenturion C ServicebioservanesNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation & Power Electronics: Lecture 13 & 14 ThyristorsDocument43 pagesInstrumentation & Power Electronics: Lecture 13 & 14 Thyristorsarjay08No ratings yet
- EE Course Notes: BJTs Chapter 5 SummaryDocument7 pagesEE Course Notes: BJTs Chapter 5 SummarybkrebtelNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 MOS Field Effect Transistors v1Document33 pagesLecture10 MOS Field Effect Transistors v1Dr-Suraj Kumar SawNo ratings yet
- The Cascode Amplifier: DC ACDocument8 pagesThe Cascode Amplifier: DC ACRamanaButterfly83% (6)
- TransistorDocument23 pagesTransistorRonny PrajitnoNo ratings yet
- P5506BDG UnikcDocument5 pagesP5506BDG UnikcYessenia PerezNo ratings yet
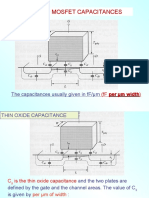
- Review of Mosfet Capacitances: The Capacitances Usually Given in FF/ MDocument46 pagesReview of Mosfet Capacitances: The Capacitances Usually Given in FF/ MSalim SanNo ratings yet
- Air University: Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Lab TitleDocument5 pagesAir University: Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Lab TitleAMMAD MAHMOODNo ratings yet
- Component List For Powercom BNTDocument4 pagesComponent List For Powercom BNTanoop.ashu9376No ratings yet
- Transistor As A SwitchDocument12 pagesTransistor As A Switcharjuna4306No ratings yet
- Bipolar transistor early effect and storage timeDocument9 pagesBipolar transistor early effect and storage timeozcarlosaNo ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor Devices: EE 3036 D: Presented byDocument10 pagesPower Semiconductor Devices: EE 3036 D: Presented byShubham ranjanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - MOS Transistor DynamicsDocument60 pagesLecture 9 - MOS Transistor DynamicsRogin Garcia GopezNo ratings yet
- Silicon NPN Darlington Power Transistors: DescriptionDocument3 pagesSilicon NPN Darlington Power Transistors: DescriptionDaniel Jesus LozanoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6Document12 pagesAssignment 6Harshita AnandNo ratings yet
- Embedded DRAM Using C-Axis-Aligned Crystalline In-Ga-Zn Oxide FET With 1.8V-Power-Supply VoltageDocument8 pagesEmbedded DRAM Using C-Axis-Aligned Crystalline In-Ga-Zn Oxide FET With 1.8V-Power-Supply VoltageRabbi HasnatNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design Module - 5Document30 pagesVLSI Design Module - 5PavitraNo ratings yet