Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1-Function (Lexical, Auxiliary) 2 - Form (Finite, Nonfinite) v. Categories 3 - Meaning (Stative, Dynamic) 4-Complementation (Intensive, Extensive)
Uploaded by
Ahmed Falah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesVerb elements can be realized through function, form, meaning, and complementation. Finite verbs show tense, mood, and aspect, while nonfinite verbs do not show tense or mood but can indicate aspect and voice. Subjects and adverbs can be single words or phrases. Verb phrases can consist of a head verb preceded by one or more auxiliary verbs. Subjects can be clauses. Noun phrases can be pronouns, proper nouns, or complex structures including modifiers and relative clauses.
Original Description:
Original Title
9
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentVerb elements can be realized through function, form, meaning, and complementation. Finite verbs show tense, mood, and aspect, while nonfinite verbs do not show tense or mood but can indicate aspect and voice. Subjects and adverbs can be single words or phrases. Verb phrases can consist of a head verb preceded by one or more auxiliary verbs. Subjects can be clauses. Noun phrases can be pronouns, proper nouns, or complex structures including modifiers and relative clauses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pages1-Function (Lexical, Auxiliary) 2 - Form (Finite, Nonfinite) v. Categories 3 - Meaning (Stative, Dynamic) 4-Complementation (Intensive, Extensive)
Uploaded by
Ahmed FalahVerb elements can be realized through function, form, meaning, and complementation. Finite verbs show tense, mood, and aspect, while nonfinite verbs do not show tense or mood but can indicate aspect and voice. Subjects and adverbs can be single words or phrases. Verb phrases can consist of a head verb preceded by one or more auxiliary verbs. Subjects can be clauses. Noun phrases can be pronouns, proper nouns, or complex structures including modifiers and relative clauses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
2.11: Elements Realization types: how do we realize a v.
1- function ( lexical, auxiliary)
2- form (finite, nonfinite)
v. categories
3- meaning (stative, dynamic)
4-complementation ( intensive, extensive)
Verb element is always a verb phrase.
What do we mean by finite & non finite?
• Finite verbs: showing tense, mood, aspect, voice
• Nonfinite verbs: not showing tense, or mood but still capable of indicating
aspect and voice.
we mean by mood is(verb action) (Verbs have three moods
—indicative, imperative, and subjunctive).
statements questions.
requests commands
hypothetical statements
conditional statements
• By Verbal aspect we mean timing of the verb it consists of simple, progressive,
perfect, or perfect progressive.
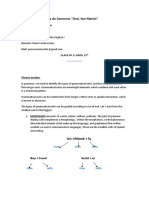
• Mary wanted (to be a student at a large university.) TO+ infinitive
V. Cs A
Od
• (Carefully searching the room), John found a ring. ING participle
A. V. Od
A.
• (Made the chairman every year), he was very busy. ed form
V. Co A.
A.
• Finite: e.g. He may be growing happier.
• Non finite: as in: 1- to infinitive ,2- ing participle and 3 -ed participle
e.g. :
-To talk like that must be dangerous.
-Having been offended before, he was sensitive.
-Called her early, he will be here.
How do we realize subject and adverb
1 word (pronoun) as: He
• Subject proper noun as: John
can be complex structure as: phrase, clause
- The girl with long hair is beautiful.
-what I need is a long holiday. finite
-Being a chairman is a huge responsibility. infinite
adverb phrase - John very carefully searched the room.
Adverbs noun phrase - They make him the chairman every year.
Can be prepositional phrase - She studied at a large university.
clause finite - non finite
- He grew happier, when his friend arrived.
- Seeing the large crowd, John stopped his car.
• Verb phrase can be of one word or more than one word, in which case the verb
phrase consists of a head verb preceded by one or more auxiliary verbs as in the
following:
• He had given the girl an apple.
• He may be growing happier.
• He may been challenged rudely.
• The subject of the sentence may be a clause as in:
• That she answered the question correctly pleased him.
• Concerning nouns, a noun phrase may be of a pronoun such as(they) or a proper
noun such as (john). But it may also be a long and complex structure of: a noun as
a head, preceded by other words as an article, an adjective, or another noun, and
followed by a prepositional phrase or by a relative clause but it is rare.
• The new gas stove in the kitchen which I bought last month has a very efficient
oven.
You might also like
- SpeechLanguage Development ChartDocument10 pagesSpeechLanguage Development ChartFelipe Apablaza Campos100% (1)
- Basic Grammar and ConversationDocument56 pagesBasic Grammar and ConversationAfaf Mahmoud50% (2)
- The Sentence - A Complete ThoughtDocument37 pagesThe Sentence - A Complete Thoughtshakeelamjad100% (2)
- Basic English Grammar (Final)Document133 pagesBasic English Grammar (Final)Dariah MeitazaNo ratings yet
- Tenses Review PDFDocument5 pagesTenses Review PDFTraduçãoSimultânea100% (3)
- Power English 2Document143 pagesPower English 2Deaf CanuckNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Part of Speech (Noun, Pronoun, Verb, Adjective)Document39 pagesWeek 2 - Part of Speech (Noun, Pronoun, Verb, Adjective)Anisa LarasNo ratings yet
- Gramatyka Opisowa - Język AngielskiDocument29 pagesGramatyka Opisowa - Język Angielskiap.filang2018100% (1)
- Carte Gramatica Limbii Engleze in Scheme, CataragaADocument70 pagesCarte Gramatica Limbii Engleze in Scheme, CataragaACaterin CuculescuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Parts of SpeechDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Parts of Speechkuranji ruriNo ratings yet
- The Pushto Manual by Henry George RavertDocument278 pagesThe Pushto Manual by Henry George RavertBilal AfridiNo ratings yet
- (123doc) - De-Cuong-On-Thi-Mon-Ngu-Phap-Tieng-Anh-Hay-Ngan-GonDocument20 pages(123doc) - De-Cuong-On-Thi-Mon-Ngu-Phap-Tieng-Anh-Hay-Ngan-GonPhạm Kim HiềnNo ratings yet
- Morphology - Lexical WordsDocument5 pagesMorphology - Lexical WordsĐặng Lê Khánh LinhNo ratings yet
- Naoual Derraz - GrammarDocument28 pagesNaoual Derraz - GrammarfatimernitNo ratings yet
- Sentences 2023Document31 pagesSentences 2023mgenimkubwa85No ratings yet
- For Example A) Noun Phrase As SubjectDocument20 pagesFor Example A) Noun Phrase As SubjectMarcusKlahnTokoeJr.No ratings yet
- Phrases & Sentence TypesDocument34 pagesPhrases & Sentence Typeseaonyinye13No ratings yet
- Summary of Grammar MaterialDocument5 pagesSummary of Grammar Materialmalimaksum1234No ratings yet
- Adjective, Adverb, Noun Clauses Gerund, Participial and Infinitive P PhrasesDocument19 pagesAdjective, Adverb, Noun Clauses Gerund, Participial and Infinitive P PhrasesRoman Tilahun100% (1)
- Summary and ResponsesDocument57 pagesSummary and Responsesapi-534944980No ratings yet
- SyntaxDocument56 pagesSyntaxLes SircNo ratings yet
- The SentenceDocument5 pagesThe SentenceBediako EzekielNo ratings yet
- Listing of The Parts of SpeechDocument10 pagesListing of The Parts of SpeechVân AnhNo ratings yet
- Personal Letter by Miss: Materi 3Document12 pagesPersonal Letter by Miss: Materi 3Pak BosNo ratings yet
- B. Inggris Tentang AdverbDocument14 pagesB. Inggris Tentang AdverbM JodinNo ratings yet
- Morphology Unit4Document25 pagesMorphology Unit4ferasORVNo ratings yet
- Notes For Assignments Sem 2Document28 pagesNotes For Assignments Sem 2soufwa18No ratings yet
- B.ingg MateriDocument48 pagesB.ingg MateriNia AiniyaNo ratings yet
- Phrase, Clause and SentenceDocument26 pagesPhrase, Clause and SentenceDikla Sasta WijaksaNo ratings yet
- TAT1 S2 THANH Eight Word ClassesDocument38 pagesTAT1 S2 THANH Eight Word ClassesHải LinhNo ratings yet
- Morphology: Prof. K.T.KhaderDocument50 pagesMorphology: Prof. K.T.KhaderHani QarmootNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document28 pagesChapter 42321000101No ratings yet
- English Syntax I Facultad de Filosofía Y Letras UNT - Año 2020Document24 pagesEnglish Syntax I Facultad de Filosofía Y Letras UNT - Año 2020Victoria del Rosario MaidanaNo ratings yet
- 1º Año Clase 3 - 13 Abril - Grammar 1Document9 pages1º Año Clase 3 - 13 Abril - Grammar 1Jo O ConnorNo ratings yet
- Phrase, Clause, N SentenceDocument24 pagesPhrase, Clause, N SentenceHassan ali SayedNo ratings yet
- Enla 1012 Sentence Structure: Sentence TypesDocument54 pagesEnla 1012 Sentence Structure: Sentence TypesNurye NigusNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument25 pagesMorphologysrilankamuslimaid1No ratings yet
- Post-Modifiers (Cont'd) : Do Exercise 4.1, 4.2Document17 pagesPost-Modifiers (Cont'd) : Do Exercise 4.1, 4.2twy113No ratings yet
- Grammar 3Document49 pagesGrammar 3ABDELLAH RGUIBINo ratings yet
- CS 8 Aspect, Verb Tenses, ClausesDocument30 pagesCS 8 Aspect, Verb Tenses, ClausesDinanath DahalNo ratings yet
- John 2. The Girl 3. His Brother 4. It 5. He 6. They: Parts of A SentenceDocument40 pagesJohn 2. The Girl 3. His Brother 4. It 5. He 6. They: Parts of A Sentencesaadi mziriNo ratings yet
- PhraseDocument13 pagesPhrasenandiniNo ratings yet
- Unit.1 - Phrase - Clause - SentenceDocument26 pagesUnit.1 - Phrase - Clause - SentenceUyển NhiNo ratings yet
- Sem 2 H Words and Word ClassesDocument7 pagesSem 2 H Words and Word ClassesAgnesNo ratings yet
- SyntaxTypes of Sentences According To The Type of CommunicationDocument3 pagesSyntaxTypes of Sentences According To The Type of CommunicationVanya NikolovaNo ratings yet
- ELT122-Week 1-3 (pg.14-19)Document38 pagesELT122-Week 1-3 (pg.14-19)Becira LiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Elements of The Sentence 2.1Document88 pagesChapter 2 Elements of The Sentence 2.1Yousif johnNo ratings yet
- VerbsDocument51 pagesVerbsJelena JelenaNo ratings yet
- Syntax (Clause)Document12 pagesSyntax (Clause)YouniverseNo ratings yet
- VERBSDocument204 pagesVERBSChenwie Mother of GodNo ratings yet
- VHU - Syntax ContextDocument22 pagesVHU - Syntax ContextkhangtammedNo ratings yet
- Lcture 2 On Phrse ClseDocument75 pagesLcture 2 On Phrse ClseMahmudur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Semi-Composite SentenceDocument24 pagesSemi-Composite SentenceЮлия БеловаNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 - Parts of SpeechDocument9 pagesUNIT 1 - Parts of SpeechNurul MandulangiNo ratings yet
- 7 Phrases and ClausesDocument27 pages7 Phrases and Clausesjangauci123No ratings yet
- Active Voice and Passive VoiceDocument8 pagesActive Voice and Passive VoiceClarise Vera Simangan NabennegNo ratings yet
- Verbs: What Is A Verb?Document8 pagesVerbs: What Is A Verb?Jughead Mithy100% (1)
- English 111 ReviewerDocument7 pagesEnglish 111 ReviewerCharles IldefonsoNo ratings yet
- De Juan - Written Activity No. 1 (English)Document15 pagesDe Juan - Written Activity No. 1 (English)J.L Gaming YTNo ratings yet
- Writing Skills 1 Week 2Document15 pagesWriting Skills 1 Week 2Aysha AlmamariNo ratings yet
- Syntax OutlinesDocument10 pagesSyntax OutlinesТаняNo ratings yet
- BasicDocument46 pagesBasicTNo ratings yet
- How To Make Your Own English SentenceDocument19 pagesHow To Make Your Own English SentenceiizzzaaaNo ratings yet
- Parts of A SentenceDocument6 pagesParts of A Sentencesatria yudaNo ratings yet
- Tiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3From EverandTiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3No ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument1 pageParts of SpeechAhmed FalahNo ratings yet
- 8Document4 pages8Ahmed FalahNo ratings yet
- 7Document2 pages7Ahmed FalahNo ratings yet
- 3Document2 pages3Ahmed FalahNo ratings yet
- Organs Which Produce The Human Speech Sounds.: Organs of Speech (Articulators) : Represent A Set ofDocument4 pagesOrgans Which Produce The Human Speech Sounds.: Organs of Speech (Articulators) : Represent A Set ofAhmed FalahNo ratings yet
- Can/ Could CanDocument4 pagesCan/ Could CanAhmed FalahNo ratings yet
- 3.50: Shall: ShouldDocument4 pages3.50: Shall: ShouldAhmed FalahNo ratings yet
- 1, 2Document5 pages1, 2Ahmed FalahNo ratings yet
- Phonetics (Description)Document18 pagesPhonetics (Description)Ahmed FalahNo ratings yet
- صوت الفصل الرابعDocument16 pagesصوت الفصل الرابعAhmed FalahNo ratings yet
- تعاريف وملخصات الصوتDocument12 pagesتعاريف وملخصات الصوتAhmed FalahNo ratings yet
- Consonant Sequences .. @haidouri1Document2 pagesConsonant Sequences .. @haidouri1Ahmed FalahNo ratings yet
- Basics of English Grammar: Progressive and Perfect TenseDocument2 pagesBasics of English Grammar: Progressive and Perfect TenseElisa GerNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus - Basic Grammar 2Document13 pagesCourse Syllabus - Basic Grammar 2Thúy HiềnNo ratings yet
- Inglés Primaria Quinto 2 PDFDocument25 pagesInglés Primaria Quinto 2 PDFmargantoniNo ratings yet
- Count Nouns and Non-Count Nouns. Simple Present VS Present Continuous.Document3 pagesCount Nouns and Non-Count Nouns. Simple Present VS Present Continuous.Blanca CamposNo ratings yet
- Dependent Prepositions: Inglés Profesional 2 Frida Pongo HuamánDocument43 pagesDependent Prepositions: Inglés Profesional 2 Frida Pongo Huamángady Marmanilla SanchezNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument6 pagesActive and Passive VoiceÁngel Sánchez IbáñezNo ratings yet
- Used To and Would For Past Habits PDFDocument2 pagesUsed To and Would For Past Habits PDFLG GL100% (1)
- Compound Words and Phrasal Words: MorphosyntaxDocument11 pagesCompound Words and Phrasal Words: MorphosyntaxSelmaKSelma0% (1)
- Concord Verb AgreementDocument3 pagesConcord Verb AgreementSatu SisiTerhapusNo ratings yet
- 14.voice (Common Error)Document6 pages14.voice (Common Error)Aditya KumarNo ratings yet
- EXAM QsDocument2 pagesEXAM QssafyshNo ratings yet
- The Syntax of The DP Mihaela Tanase-Dogaru Fall Semester 2013Document12 pagesThe Syntax of The DP Mihaela Tanase-Dogaru Fall Semester 2013nochefNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument10 pagesProject ReportgraciousNo ratings yet
- Ingles Basico de 9no GradoDocument3 pagesIngles Basico de 9no GradoMalory GamarraNo ratings yet
- Sentence Types PDFDocument2 pagesSentence Types PDFMaureen MactalNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Present Passive Voice, Past Passive Voice, Phrasal VerbsDocument13 pagesUnit 9 Present Passive Voice, Past Passive Voice, Phrasal VerbsTiền NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Elective Course: Control in English & Romanian: The Infinitive/Subjunctive Divide Course 4: Expanding Control: Control in RomanianDocument5 pagesElective Course: Control in English & Romanian: The Infinitive/Subjunctive Divide Course 4: Expanding Control: Control in RomanianAndrei BobeicăNo ratings yet
- Embedded QuestionsDocument2 pagesEmbedded Questionsmaria estevezNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Reference LessonsDocument4 pagesEnglish Grammar Reference LessonsGiovanni M BertoliniNo ratings yet
- Orthography Syntax and Morphemes in CebuanoDocument34 pagesOrthography Syntax and Morphemes in CebuanoHarvey PalaoNo ratings yet
- Skillful CEFR Mapping Listening and Speaking 1Document7 pagesSkillful CEFR Mapping Listening and Speaking 1Tin DangNo ratings yet
- Latin Crossword SamplesDocument7 pagesLatin Crossword SamplesGabriel De Souza FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Discovery Invention Possible Future Inventions: Fire HoneyDocument9 pagesDiscovery Invention Possible Future Inventions: Fire HoneyJackie ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Possessives and ApostrpheDocument6 pagesPossessives and Apostrphelauramates100% (1)
- What Are DeterminersDocument31 pagesWhat Are DeterminersSaisudeep Das100% (1)