Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Moment of A Force
Uploaded by
Robin Biswas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views27 pagesIn Case 1, applying a force at the end of the wrench results in the greatest torque on the nut since it has the longest moment arm. Case 3 has the shortest moment arm and therefore the lowest torque. Case 2 has an intermediate torque.
Original Description:
Original Title
Moment of a Force
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIn Case 1, applying a force at the end of the wrench results in the greatest torque on the nut since it has the longest moment arm. Case 3 has the shortest moment arm and therefore the lowest torque. Case 2 has an intermediate torque.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views27 pagesMoment of A Force
Uploaded by
Robin BiswasIn Case 1, applying a force at the end of the wrench results in the greatest torque on the nut since it has the longest moment arm. Case 3 has the shortest moment arm and therefore the lowest torque. Case 2 has an intermediate torque.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 27
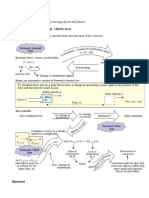
Concept Question
The picture below shows three different
ways of using a wrench to loosen a stuck
nut. Assume the applied force F is the
same in each case.
In which of the cases is the torque on the
nut the biggest?
1. Case 1
2. Case 2
3. Case 3
Rigid Objects in
Equilibrium
A system is in equilibrium if and only
if:
pivot
d
Turning effect about pivot Center of gravity
due to gravity: W=-mg
(gravity acts at center of gravity)
This object is NOT in equilibrium.
Not in equilibrium Equilibrium
pivot
ot
d
Center of gravity
W=-mg
Center of gravity
Torque about pivot 0 Torque about pivot = 0
A method to find center of gravity of an irregular object
KINDS OF EQULIBTIUM
a) stable:
A body is said to be in a state of equilibrium ,if it regains its
original equilibrium position after being slightly disturbed.
b) unstable:
If the body does not regain its original equilibrium position
after being slightly disturbed , the equilibrium is said to be
UNSTABLE.
c) neutral :
If after being slightly disturbed, the body does not have any
tendency either to regain its original equilibrium position or to
tilt further from its new position ,the equilibrium is said be
Neutral.
So, the stability of a body can be
increased :
1) The centre of gravity should be as low
as possible.
2) The area of base is as large as possible
so that the vertical line through which the
COG of the body passes through its base.
Examples……….
a) Table lamp ,burner ,flask, bottle have a heavy
and large base as to have lower the COG and more
stable equilibrium.
b) A ship is loaded near the bottom , to lower the
COG.
c) persons in a small boat are not allowed to
stand.
d) In a double-decker bus ,the conductor advises
the passengers to occupy the lower deck at first.
e) self erecting toy’s base is heavily loaded.
You might also like
- Centre of Gravity and Stability PDFDocument29 pagesCentre of Gravity and Stability PDFkonincoNo ratings yet
- Principle of MomentsDocument18 pagesPrinciple of Momentsmelissa50% (2)
- Chapter 4 Equilibrium PF Rigid Body & ForceDocument61 pagesChapter 4 Equilibrium PF Rigid Body & ForceIsabelNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 15 TheTurningEffectOfForcesDocument29 pagesIGCSE 15 TheTurningEffectOfForcessalmanNo ratings yet
- Turning Effect of Forces: Chapter 5 NotesDocument5 pagesTurning Effect of Forces: Chapter 5 NotesHryan MahajanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 15 TheTurningEffectOfForcesDocument23 pagesIGCSE 15 TheTurningEffectOfForcesAnkush Malik100% (1)
- Turning EffectDocument40 pagesTurning Effectrobin biswasNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Mechanics Lecture Notes 3 For StudentsDocument21 pagesIntroduction of Mechanics Lecture Notes 3 For StudentsjianghuiNo ratings yet
- Centreofgravity 161103174228Document32 pagesCentreofgravity 161103174228rodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- 8 EquilibriumDocument10 pages8 EquilibriumSelwah Hj AkipNo ratings yet
- 2 (1) .Physics MechanicsDocument35 pages2 (1) .Physics MechanicsNo PainNo ratings yet
- Turning Effects of Forces MomentsDocument7 pagesTurning Effects of Forces Momentsanwar9602020No ratings yet
- AP Physics Notes - Newton's Laws of MotionDocument9 pagesAP Physics Notes - Newton's Laws of MotionAndy HeNo ratings yet
- GP3 Mass, Inertia, C.GDocument3 pagesGP3 Mass, Inertia, C.GKatlo MokgethiNo ratings yet
- Forces at RestDocument67 pagesForces at RestOdaneNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 MomentDocument9 pagesTopic 4 MomentgoldphishNo ratings yet
- General Physics PDFDocument5 pagesGeneral Physics PDFsimi sanuNo ratings yet
- 5-Turning Effect of Forces-2Document15 pages5-Turning Effect of Forces-2Essie KutisariNo ratings yet
- TorqueDocument3 pagesTorquerf08dNo ratings yet
- N ' L M I: Ewton S Aws of OtionDocument8 pagesN ' L M I: Ewton S Aws of OtionSamyak JainNo ratings yet
- Torque and Moments QuizDocument6 pagesTorque and Moments QuizMohammad Yasir MuneebNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium and Centre of GravityDocument20 pagesEquilibrium and Centre of GravityWaleedNo ratings yet
- Center of Gravity FinalDocument28 pagesCenter of Gravity FinalEira DizonNo ratings yet
- Moments and EquilibriumDocument6 pagesMoments and Equilibriumogenrwot albertNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - Newtons Laws Lecture Notes PDFDocument12 pagesCH 4 - Newtons Laws Lecture Notes PDFLilyNo ratings yet
- 10 1425 Web Lec 07 UsingNewtonsLawsDocument18 pages10 1425 Web Lec 07 UsingNewtonsLawsAK CreationNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Friction-1Document43 pagesLecture 3 Friction-1Maro IdehNo ratings yet
- 440 B4 D 01Document26 pages440 B4 D 01divasusti0% (1)
- 11 2 Center of GravityDocument18 pages11 2 Center of GravityluisynonNo ratings yet
- ENGD1106D Mechanical Principles-Dynamics: Week 7 Mass, Gravity, Weightlessness Circular MotionDocument21 pagesENGD1106D Mechanical Principles-Dynamics: Week 7 Mass, Gravity, Weightlessness Circular MotionHalaaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Buoyancy and StabilityDocument6 pagesUnit 5 Buoyancy and StabilityMOJALEFA JACOB MOLEFINo ratings yet
- MomentsDocument38 pagesMomentsaslaym607No ratings yet
- Applied Fluid Mechanics 05 Bouyancy and Stability PDFDocument29 pagesApplied Fluid Mechanics 05 Bouyancy and Stability PDFYilber Roa0% (1)
- Igcse 15 TheturningeffectofforcesDocument23 pagesIgcse 15 TheturningeffectofforcesHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- Program of "Physics": Lecturer: Dr. DO Xuan Hoi Room A1. 503 E-MailDocument14 pagesProgram of "Physics": Lecturer: Dr. DO Xuan Hoi Room A1. 503 E-MailThu HòaNo ratings yet
- Center of GravityDocument21 pagesCenter of GravityIra AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Physics 101:: Physics 101: Torque and EquilibriumDocument16 pagesPhysics 101:: Physics 101: Torque and Equilibriumriyantrin_552787272No ratings yet
- 2023-2024-Class XI-Physics-Part 4-AWDocument15 pages2023-2024-Class XI-Physics-Part 4-AWjimmyemandeeNo ratings yet
- Q 1: Define Like and Unlike Parallel Forces?: A B OA AB OB AB B OB OA AB R A BDocument3 pagesQ 1: Define Like and Unlike Parallel Forces?: A B OA AB OB AB B OB OA AB R A BRiaz Hussain LaghariNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyDocument20 pagesEquilibrium of A Rigid BodywaqarNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Rigid Body & FrictionDocument54 pagesEquilibrium of Rigid Body & Frictionmuhammad adnielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8-Phy220Document42 pagesChapter 8-Phy220Jordan TuckerNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionconsolidatedDocument8 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionconsolidatedAditya VijayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 & 4Document30 pagesChapter 3 & 4Junyi JiNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law in Motion1Document7 pagesNewton's Law in Motion1Chan LieslNo ratings yet
- CBSE-XI Physics - Chap-4-6Document43 pagesCBSE-XI Physics - Chap-4-6himeshs298No ratings yet
- Chapter - 11 - Equilibrium - and ElasticityDocument10 pagesChapter - 11 - Equilibrium - and Elasticitypbreddy42No ratings yet
- 4 Buoyancy 2023 W6&W7Document60 pages4 Buoyancy 2023 W6&W7saramelissa1192No ratings yet
- Torque & Equilibrium ConditionsDocument13 pagesTorque & Equilibrium ConditionsJohn Dale IbaleNo ratings yet
- Center of Gravity and Moment of ForceDocument17 pagesCenter of Gravity and Moment of ForceLeonidas RocksNo ratings yet
- Upthrust and Archimedes Principle Moments and Equilibrium PDFDocument11 pagesUpthrust and Archimedes Principle Moments and Equilibrium PDFAlisa DowningNo ratings yet
- Force & FrictionDocument53 pagesForce & FrictionJerald MagcalasNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Force and Newton's Laws-FinalDocument52 pagesChapter - Force and Newton's Laws-Finalraie saadNo ratings yet
- Nsejs 2015 SOLUtION PDFDocument7 pagesNsejs 2015 SOLUtION PDFamit kumarNo ratings yet
- Centre of Gravity and Stability of An Object: GCSE PhysicsDocument29 pagesCentre of Gravity and Stability of An Object: GCSE PhysicsQuinella TuitionNo ratings yet
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 6: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #6From EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 6: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #6No ratings yet