Professional Documents
Culture Documents
KS4 Forces - Forces
Uploaded by
Hakim AbbasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
KS4 Forces - Forces
Uploaded by
Hakim AbbasCopyright:
Available Formats
KS4 Forces – Forces
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
What is a force?
A force is a push, pull or twist.
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
Say if the following are pushes, pulls or twists:
Push Writing on paper
Push Typing on a keyboard
Tug-of-war Pull
Twist Unscrewing the top off a bottle Twist
Push Posting a letter through a door
Putting on a pair of socks Pull
Twist Turning a door handle Twist
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
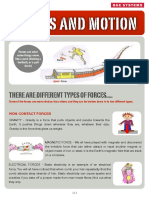
Types of force you need to know……
Friction Gravity
Air resistance
Magnetism
Tension
Electrostatic
Nuclear
Compression
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
Describing the forces
The force you get when two
Magnetism material rub together
The force you get when a
Friction material is being stretched
Compression The force you get when a
material is being squashed
The force that enables
Tension compasses to work
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
Describing the forces
Gravity The force that holds the particles
in a nucleus together
Nuclear The force you get when an
object moves through air
The force that exists between all
Air resistance objects with mass
The force you get between two
Electrostatic charged objects
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
Attractive or repulsive?
Gravity? Attractive, always
Magnetism? Attractive and repulsive
Electrostatic? Attractive and repulsive
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
Contact and non-contact
If two objects or materials need to be touching for the
ONTACT force.
force to have an effect then it is a C________
Examples: Friction
Air resistance
ouching
If two objects or materials do not need to be t______
for the force to have an effect then it is a NON
CONTACT force.
Examples: Gravity
Electrostatic
Magnetic
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
Gravity
Gravity is an attractive f____
orce that exists
asses Gravity is always
between all m_____.
ttractive
a_______.
arger the mass is, the greater the
The l____
urther away a
gravitational attraction. The f_____
mass is, the less the gravitational attraction.
Your w____ is the pull of the Earth’s gravity
on youreight
body. The Moon is kept in
orbit around the
If you stood on the M___ you would weigh Earth due to gravity.
less than on Earth. oon
This is because the Moon has less mass
than Earth, so the Moon’s g_________ pull
is weaker than the Earth’s. ravitational
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
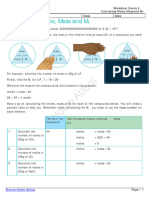
Mass and weight
What is the difference between mass and weight?
Your mass is a measure of Your weight is a measure of
how many particles there are in the pull of gravity on your
your body. It does not matter body. Your weight depends
where you are in the Universe, upon what planet you are
your mass does not change. standing on.
You would weigh less on
What is mass measured in? Mercury than on Earth
Kilograms because Mercury is smaller
than Earth.
Mass = 10kg
10kg What is weight measured in?
Newtons
Weight = 100 N
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
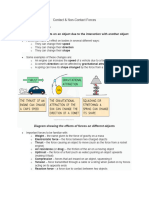
Force diagrams
Force diagrams show Draw a force diagram for a falling
you the direction a force object when it first starts to fall.
is acting in. It shows you
the direction an object is Air resistance
being pushed, pulled or
twisted. The direction of
the arrow shows you the
direction of the force. The
sizes of the arrows can
be used to compare the
sizes of the forces.
Weight
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
Unused homework diary on a table
What force pulls down on the book?
Gravity
The diary does not move, so there
must be an equal and opposite force
pushing up on the diary.
What do we call this force?
Reaction force
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
Forces on a speeding fish?
What is thrust?
A forward push
What is upthrust?
The upwards force on a body in a liquid or a gas
Upthrust
Thrust Friction
Weight
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
Label the forces acting on the moving ship shown:
Upthrust or
buoyancy
Air
resistance
Thrust Friction
Weight
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
A ship arrives at port and is loaded with cargo:
What happens to the weight of the ship? Increases
What happens to the upthrust on the ship? Increases
Which is the largest force, weight or upthrust? Both equal
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
Forces and motion
If an object is stationary and an unbalanced
force acts on it, it will start to move.
If an object is moving and an unbalanced force acts
on it there are three possibilities…
The object could speed
up.
The object could slow
down.
The object could change
direction.
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
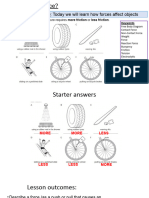
In which direction, if any will the following
stationery objects move?
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
What is friction?
If you rub your hands together there is resistance to the
motion.
What do we call this force?
Friction
What causes it?
Even though your hands
look smooth, on a
microscopic level it is not,
so when your hands rub
together you get the
resistive force of friction.
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
Direction of friction
Friction always acts in the For the following moving
opposite direction to the way objects, mark with an
an object is moving. arrow, the direction
friction is acting in.
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
Friction effects
Friction always acts in the o______
pposite direction to
which an object is moving in.
orce
Friction is a type of f____.
Whenever you get friction between two objects
eat and w_____.
you always get h___ earing
You can reduce the effect of friction by using a
ubricant O_
l______. il is a lubricant used in car engines to
reduce friction effects.
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
Starting moving…
An object will only start to move if the forces applied to it
overcome any frictional forces. For the examples shown say
if the stationary objects will move or not, and if they do move,
say in which direction.
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
Friction - useful or hindrance?
Write down three instances where friction is useful and three
where it is a hindrance.
Discuss your ideas with the class and then have a vote on
what the class thinks are the top three for each.
Useful Hindrance
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
Which of the following is not a force?
A. Heat
B. Gravity
C. Tension
D. Friction
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
For a man standing up, in which direction
does gravity act?
A.
B. C. D.
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
For a fish in water, what do we call force Z?
A. Friction
Z
B. Air resistance
C. Gravity
D. Upthrust
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
In what units is force measured in?
A. Joules
B. Metres
C. Newtons
D. Seconds
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
What device is used to measure force?
A. Clock
B. Voltmeter
C. Joulemeter
D. Newtonmeter
© Boardworks Ltd 2003
You might also like
- Forces and Their EffectsDocument24 pagesForces and Their EffectsLee TeckBee50% (2)
- Power Profile - Gravity Powers PDFDocument6 pagesPower Profile - Gravity Powers PDFJeff HobbsNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion RotDocument53 pagesLaws of Motion RotGyrot Gan100% (1)
- Knorr Bremse Tebs G2Document86 pagesKnorr Bremse Tebs G2Adrian Rusu100% (3)
- Linked PDFDocument422 pagesLinked PDFBander ShtatNo ratings yet
- Summary 7KDocument2 pagesSummary 7KTHJNo ratings yet
- BMW 5HP19Document54 pagesBMW 5HP19Leonardo Rodriguez100% (4)
- Audi Q2 Owner ManualDocument364 pagesAudi Q2 Owner ManualSnap Blue75% (4)
- AURLTX103 Student Assessment - ramAN ComDocument22 pagesAURLTX103 Student Assessment - ramAN ComRAMANdeep kaurNo ratings yet
- Form 1y Phy Notes. From MR WafulaDocument21 pagesForm 1y Phy Notes. From MR WafulaJoy TechNo ratings yet
- KS4 Forces - ForcesDocument31 pagesKS4 Forces - Forcesjt100% (1)
- Laws of Motion v1.1Document42 pagesLaws of Motion v1.1Ramesh IyerNo ratings yet
- 13.3 RadioactivityDocument117 pages13.3 RadioactivityHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Friction and the Laws of Motion - Physics Made Simple - 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandFriction and the Laws of Motion - Physics Made Simple - 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- A Push or A Pull - The Definition of Force - Physics Book Grade 5 | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandA Push or A Pull - The Definition of Force - Physics Book Grade 5 | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Suffix of BearingDocument14 pagesSuffix of BearingPirnandoTariganNo ratings yet
- ks4 Forces - ForcesDocument31 pagesks4 Forces - ForcessalmaNo ratings yet
- 1.5.1 Newton Laws of Motion (Effects of Forces)Document102 pages1.5.1 Newton Laws of Motion (Effects of Forces)Law PeterNo ratings yet
- JS What Is A ForceDocument21 pagesJS What Is A Forcej.sandNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 1.discovering ForcesDocument16 pagesGrade 7 1.discovering Forcesselimhussein2758No ratings yet
- Complete Physics Classnotes Midterm Sprint - 8th PDFDocument60 pagesComplete Physics Classnotes Midterm Sprint - 8th PDFIbad ur Rehman gamerNo ratings yet
- FORCESDocument11 pagesFORCESJennieNo ratings yet
- Forces and Their EffectDocument27 pagesForces and Their EffectvinaazfianaNo ratings yet
- P1 Chapter 1Document1 pageP1 Chapter 1Rehan ShahNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument56 pagesForcesMais MarwanNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument144 pagesForcesVasanthaNo ratings yet
- 1 of 9 © Boardworks LTD 2012Document9 pages1 of 9 © Boardworks LTD 2012Yuni MuliaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 8:ForCES - Tansi International College, AwkaDocument6 pagesWEEK 8:ForCES - Tansi International College, AwkaOgechi ohajianyaNo ratings yet
- 2 - IGCSE-Forces and ShapeDocument35 pages2 - IGCSE-Forces and ShapeHoracio FerrándizNo ratings yet
- A Push or Pull: Force and Motion ForceDocument22 pagesA Push or Pull: Force and Motion ForceAbu Sheikh100% (1)
- Pod HandlerDocument90 pagesPod HandlerJanaina ProençaNo ratings yet
- Gse 1Document3 pagesGse 1Nayan PaulNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Reviewer 2nd MonthlyDocument2 pagesSCIENCE Reviewer 2nd MonthlyRaizza Mae NovelaNo ratings yet
- Force & Pressure 1Document28 pagesForce & Pressure 1Kyna MustafaNo ratings yet
- L1 Forces Contact Non ContactDocument19 pagesL1 Forces Contact Non ContactNgọc BùiNo ratings yet
- Forces - Notes From SLSDocument2 pagesForces - Notes From SLSVanessa OngNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument14 pagesForcesMaria IezhitsaNo ratings yet
- Forces: Newtons (N)Document4 pagesForces: Newtons (N)rajsacksNo ratings yet
- Types of Load Failure and Properties of MaterialDocument5 pagesTypes of Load Failure and Properties of Materialdummy staticNo ratings yet
- KS3 Physics: Forces and Their EffectsDocument18 pagesKS3 Physics: Forces and Their EffectsCinara RahimovaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 LGDocument34 pagesCH 2 LGThaw ThawNo ratings yet
- Mass and WeightDocument17 pagesMass and WeightibanathinkomboniNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 (Summary Notes)Document7 pagesUnit-1 (Summary Notes)chellykuukiNo ratings yet
- Machinery Shaft Failure AnalysisDocument4 pagesMachinery Shaft Failure Analysisعين العربNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - KODocument1 pageTopic 5 - KOAmani A. YusefNo ratings yet
- Y07 Forces P1Document36 pagesY07 Forces P1Mulki MohamedNo ratings yet
- LAB VIVA Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesLAB VIVA Questions and AnswersNilambar YadavNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion WorksheetDocument7 pagesForces and Motion WorksheetGuidong ReyesNo ratings yet
- Force and EnergyDocument19 pagesForce and EnergyAarnav KejriwalNo ratings yet
- P Forces Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesP Forces Knowledge Organiserc.sproatNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE ForcesDocument62 pagesCIE IGCSE ForcesRudi HartonoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Prop Part 1Document13 pagesMechanical Prop Part 1eslamezzat21061990No ratings yet
- Materials Part 4 - The Young ModulusDocument30 pagesMaterials Part 4 - The Young Modulusobvo heckienNo ratings yet
- A Push or A Pull That Acts On An Object Due To The Interaction With Another ObjectDocument7 pagesA Push or A Pull That Acts On An Object Due To The Interaction With Another ObjectM. ShayanNo ratings yet
- S2 Applying Force NotesDocument18 pagesS2 Applying Force NotesDIONYSUSNo ratings yet
- What Are Forces?Document94 pagesWhat Are Forces?GARO OHANOGLUNo ratings yet
- KS3 Physics: Forces and PressureDocument56 pagesKS3 Physics: Forces and PressureozmanNo ratings yet
- 3 Igcse-Cam - Chp-3-Forces and MotionDocument39 pages3 Igcse-Cam - Chp-3-Forces and MotionSadik AbrarNo ratings yet
- Force and PressureDocument36 pagesForce and PressureBhuvaneswari BalaNo ratings yet
- What Are ForcesDocument9 pagesWhat Are ForcesjtNo ratings yet
- Frictional ForceDocument6 pagesFrictional ForceSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Fisica U1 Vocab.Document1 pageFisica U1 Vocab.Noemí Arenas GarcíaNo ratings yet
- 03 ForceDocument67 pages03 ForcegodiewamuchuNo ratings yet
- FORCESDocument4 pagesFORCESNirvana SuggieNo ratings yet
- Center Aligned Title Page With PretitleDocument64 pagesCenter Aligned Title Page With PretitleLei Ann MendozaNo ratings yet
- 2 - FrictionDocument16 pages2 - FrictionSav LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Motion and Force GlossaryDocument3 pagesMotion and Force GlossaryLi OliviaNo ratings yet
- WS9 Moles, ReactionsDocument1 pageWS9 Moles, ReactionsHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- WS14 Net Ionic Equation WorksheetDocument1 pageWS14 Net Ionic Equation WorksheetHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- WS8 Moles, Molecules and GramsDocument2 pagesWS8 Moles, Molecules and GramsHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- WS5 Mole Calculation Practice MassDocument2 pagesWS5 Mole Calculation Practice MassHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- WS15 Calculating Moles Mass and MR Bronze Activity SheetDocument4 pagesWS15 Calculating Moles Mass and MR Bronze Activity SheetHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- WS15C Moles Solutions Practice Questions 2Document1 pageWS15C Moles Solutions Practice Questions 2Hakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 0.1 Table of Contents-ChemDocument1 page0.1 Table of Contents-ChemHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- WS5 Mole Calculation Practice Mass MsDocument2 pagesWS5 Mole Calculation Practice Mass MsHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- WS15G Moles Practice Questions 3Document1 pageWS15G Moles Practice Questions 3Hakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Anic Chemistry QPDocument78 pagesAnic Chemistry QPHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- WS3 Chemical Equations OldDocument2 pagesWS3 Chemical Equations OldHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 8.2 Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument59 pages8.2 Electromagnetic SpectrumHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Force - Scalars & VectorsDocument10 pages3.4 Force - Scalars & VectorsHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 6.chemical Changes QPDocument25 pages6.chemical Changes QPHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 3.atoms, Elements and Compounds - QPDocument40 pages3.atoms, Elements and Compounds - QPHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 6.1 States of MatterDocument11 pages6.1 States of MatterHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument119 pagesMagnetism and ElectromagnetismHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 10.3 Practical ElectricityDocument73 pages10.3 Practical ElectricityHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 10 ElectricityDocument26 pages10 ElectricityHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Turning Effect of ForcesDocument86 pagesTurning Effect of ForcesHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 3.1. Hook's Law - NotesDocument2 pages3.1. Hook's Law - NotesHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- LightDocument12 pagesLightHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Elastic DeformationDocument36 pages3.2 Elastic DeformationHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Carnot Engine TheoremDocument4 pagesCarnot Engine TheoremMisc BagNo ratings yet
- Asme Sec Viii d2 Art D-1Document17 pagesAsme Sec Viii d2 Art D-1DieguitoOmarMoralesNo ratings yet
- Fib Bulletin 57 ContentsDocument2 pagesFib Bulletin 57 Contentshilander2k2No ratings yet
- Grease Trap DetailDocument1 pageGrease Trap Detaildan PioquintoNo ratings yet
- Long Pile - t10-031Document16 pagesLong Pile - t10-031mNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard:-IS 12701:1996 Date of Manufacturing: - 14.06.2020 Date of Testing: - 16.06.2020Document2 pagesIndian Standard:-IS 12701:1996 Date of Manufacturing: - 14.06.2020 Date of Testing: - 16.06.2020abhishek sharmaNo ratings yet
- ExtremeServiceBook HardwiredDocument92 pagesExtremeServiceBook HardwiredfrostyfoleyNo ratings yet
- LB 7 300 - Antwerp - Datasheet - EN - 2935082041 2Document2 pagesLB 7 300 - Antwerp - Datasheet - EN - 2935082041 2Ayman MedaneyNo ratings yet
- Tabl r407c enDocument1 pageTabl r407c enRudy YoussefNo ratings yet
- BOUNDS-Analysis of Properties of Fiber Composites With Anisotropic Constituents PDFDocument8 pagesBOUNDS-Analysis of Properties of Fiber Composites With Anisotropic Constituents PDFRaghavendra PrasadNo ratings yet
- PSV - General GuidelinesDocument60 pagesPSV - General GuidelinesamrazamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 021Document94 pagesChapter 021Gims BuafNo ratings yet
- Castrol Agri MP Plus 20W-40Document2 pagesCastrol Agri MP Plus 20W-40RayNo ratings yet
- Pressure Boosting SetsDocument102 pagesPressure Boosting SetsAmazon tecNo ratings yet
- Hte TransmissionDocument60 pagesHte TransmissionLuis MeleroNo ratings yet
- LT32559 - FH230 Series - Fuel ProDocument2 pagesLT32559 - FH230 Series - Fuel ProShananda SoniNo ratings yet
- JpaDocument2 pagesJpajacklyn ade putraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 Application of Work Energy Method: OverviewDocument6 pagesLesson 10 Application of Work Energy Method: OverviewNadjer C. AdamNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Rotary CompleteDocument22 pagesLab Report Rotary CompleteSyed Farid100% (1)
- Nps Tables For Selected Sizes NPS To NPS 3Document4 pagesNps Tables For Selected Sizes NPS To NPS 3POWERNo ratings yet
- Brochure TrunnionDocument52 pagesBrochure TrunnionZts MksNo ratings yet
- Flow of FluidDocument28 pagesFlow of FluidJamal JalalaniNo ratings yet
- Aero Masters Thesis Delft NLDocument103 pagesAero Masters Thesis Delft NLRichard HilsonNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Different Shapes of 50 Storeys High Rise Building Under Different Loading ConditionDocument6 pagesDesign and Analysis of Different Shapes of 50 Storeys High Rise Building Under Different Loading ConditionEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet