Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 5 - KO
Uploaded by
Amani A. YusefOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 5 - KO
Uploaded by
Amani A. YusefCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 5 – Forces and their Effects.
Important Formulae
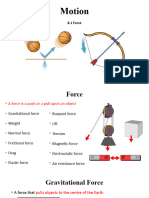
Types of Forces Pushing force, pulling force & turning force. Forces can change the speed of something, the direction it is Speed = distance travelled ÷ time taken
moving in or its shape. Unit: meter per second (m/s)
Force Diagrams We can show the forces acting on an object using a force diagram. The arrow shows the size of the force (the
longer the arrow, the bigger the force) and the direction in which the force acts.
Moment = size of force x distance of force
from the fulcrum
Newton The unit of force (N), measured using a force meter, also called a newton meter. Unit: newton meters (Nm)
Weight The weight of an object is the gravitational force between the object and the Earth. The more mass the object
has the greater its weight will be. Weight is a force and is therefore measured in newtons (N).
Gravity All objects have a force that attracts them towards each other. This is called gravity.
Mass The mass of an object is the amount of matter it contains. It is measured in kilograms (kg).
Newton’s Third Every action has an equal and opposite reaction. When an object exerts a force on something else its is called
Law of Motion an action force. There is always an equal and opposite force called a reaction force.
Hooke's Law The extension of an elastic object is directly proportional to the force applied to it.
Elastic Limit When a material is stretched or compressed too far and it is not able to return to it’s original shape the
stretching or compressing force is beyond the elastic limit.
Friction Force that resists one object moving through or over something. An example is air resistance on a car. Describe the forces:
Lubricant A substance, such as grease or oil, that reduces friction when applied as a surface coating to moving parts. • There is a force of air resistance which
slows the arrow down.
Air Resistance A force of friction produced when an object moves through the air. • Gravity/the weight of the arrow makes the
Water Resistance A force of friction produced when an object moves through the water. Water is denser than air so the ‘drag’ is arrow fall to the ground.
larger.
Terminal Velocity The max speed of an object, reached when the forces moving the object are balanced by its frictional forces.
Streamlined An object that has a special smooth shape to reduce the air resistance acting on them.
Balanced Forces If the forces on an object are balanced, an object that is not moving stays still and an object that is moving
continues to move at the same speed and in the same direction.
Unbalanced Forces If the forces on an object are unbalanced, an object that is not moving starts to move and an object that is
moving changes speed or direction.
Moment A moment is the turning effect of a force around a fixed point called a pivot, measured in newton meters.
Lever A large load can be moved by a smaller effort using a lever, for example pliers or crowbar. The crane has a counterweight on the non-
Fulcrum The point where the load is pivoted. lifting end this allows the crane to lift heavy
loads safely. The counterweight moves
Load The object you are trying to move. further from the tower when the crane is
Effort The force applied to move the load. lifting a heavy load.
You might also like
- SCIENCE Reviewer 2nd MonthlyDocument2 pagesSCIENCE Reviewer 2nd MonthlyRaizza Mae NovelaNo ratings yet
- Motion and Force GlossaryDocument3 pagesMotion and Force GlossaryLi OliviaNo ratings yet
- Forces: by Georgina HolmesDocument16 pagesForces: by Georgina HolmesGeorgina HolmesNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument56 pagesForcesMais MarwanNo ratings yet
- Physics - Unit 1Document7 pagesPhysics - Unit 1michaela menzelNo ratings yet
- Science: Unit 10 ForcesDocument3 pagesScience: Unit 10 ForcesahmedNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 and 5Document11 pagesUnit 3 and 5RayyanNo ratings yet
- Science Notes For Forces and MotionDocument6 pagesScience Notes For Forces and Motiontoe masterNo ratings yet
- Physics DefinitionDocument6 pagesPhysics DefinitionMin Aung KyawNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument18 pagesForcesRoqaya BadawyNo ratings yet
- Force Work EnergyDocument28 pagesForce Work EnergyRitam DasNo ratings yet
- Force Causes Change in Motion By: Avigael MarayaDocument18 pagesForce Causes Change in Motion By: Avigael MarayaHazel LiporadaNo ratings yet
- 5 Newtons LawsDocument1 page5 Newtons LawsShashi KanthNo ratings yet
- 2324 T1 Physics 3 and 4 Forces Motion Turning EffectsDocument38 pages2324 T1 Physics 3 and 4 Forces Motion Turning EffectswilsonconcepcionNo ratings yet
- Esc 17 1Document21 pagesEsc 17 1elaco56No ratings yet
- FORCESDocument11 pagesFORCESJennieNo ratings yet
- DLR-Fizik Konu AnlatımıDocument18 pagesDLR-Fizik Konu Anlatımıugurhan96No ratings yet
- Physics PPT 9knyDocument18 pagesPhysics PPT 9knyÉva HuszárNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 General Physics 2 SLM EditedDocument7 pagesLesson 1 General Physics 2 SLM EditedDIANNE PLANANo ratings yet
- Physics - NotesDocument12 pagesPhysics - Notesdagakabbier1718No ratings yet
- GED Physics Note1 (Motion and Forces)Document4 pagesGED Physics Note1 (Motion and Forces)Shahadat Hussain Parvez100% (2)
- 9 Application of Forces & Transfer of Energy - 2023Document83 pages9 Application of Forces & Transfer of Energy - 2023Tarun Rana Rajdevar (Victoriasch)No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 MotionDocument4 pagesLecture 2 MotionAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- St. Louis Review Center, Inc-Davao Tel. No. (082) 224-2515 or 222-8732 1Document8 pagesSt. Louis Review Center, Inc-Davao Tel. No. (082) 224-2515 or 222-8732 1Earshad Shinichi IIINo ratings yet
- 5 G8 Science Q1 - Week 2 - ForcesDocument27 pages5 G8 Science Q1 - Week 2 - ForcesMary Ann BarquioNo ratings yet
- Physics Sec QuarterDocument4 pagesPhysics Sec QuarterLaurence MatthewNo ratings yet
- CH 2 LGDocument34 pagesCH 2 LGThaw ThawNo ratings yet
- Group3 PhysicsDocument26 pagesGroup3 PhysicsCarl Eric Amora Velasco IINo ratings yet
- Forces, Vectors, Work, Energy, PowerDocument43 pagesForces, Vectors, Work, Energy, Poweranwar9602020100% (1)
- FORCEDocument10 pagesFORCEsspanda19999No ratings yet
- Class 8 Force and FriDocument8 pagesClass 8 Force and FriSourabh RanaNo ratings yet
- Quick Check: Work = Force - displacement W=F - d W=F cos (Ө) dDocument6 pagesQuick Check: Work = Force - displacement W=F - d W=F cos (Ө) dRowindeNo ratings yet
- F2 SC 8.1 ForceDocument22 pagesF2 SC 8.1 Forcekaozhiqi0717No ratings yet
- Y10 Science Notes Semester 1Document3 pagesY10 Science Notes Semester 1Oscar ReinitzNo ratings yet
- 18 2f19 Motionanddesignvocab Updated7-2-15Document3 pages18 2f19 Motionanddesignvocab Updated7-2-15api-393389803No ratings yet
- Chapter 1:Physics:An IntroductionDocument10 pagesChapter 1:Physics:An IntroductionKatrina Anne Layson YeenNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 7-Lesson 1Document56 pagesScience Grade 7-Lesson 1clyde domingoNo ratings yet
- Physics - Force and MotionDocument10 pagesPhysics - Force and MotionÅBanDonNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 - Fundamental Physics (Forces)Document6 pagesPhysics 1 - Fundamental Physics (Forces)Claire FabellarNo ratings yet
- General PhysicsDocument5 pagesGeneral PhysicsMariam BabarNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion by JoyDocument49 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion by JoyMjoyTibayNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes 2011Document4 pagesPhysics Notes 2011YY_LNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 8.1 8.2 Forces and MotionDocument38 pagesChapter 8 8.1 8.2 Forces and MotionChuahSiewHoon100% (1)
- Lesson 1-Different Types of ForcesDocument56 pagesLesson 1-Different Types of Forcesclyde domingoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 ForceDocument33 pagesChapter 8 Forcemr.anassahariNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law of MotionDocument44 pagesNewtons Law of MotionAgustin L. IdausosNo ratings yet
- Science8 q1 Slk1 Force-And-motion v1Document17 pagesScience8 q1 Slk1 Force-And-motion v1Cassandra Gia CarbonillaNo ratings yet
- Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsDocument1 pageRotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicskaeppjangedNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Yr 7 PhyDocument1 pageStudy Guide For Yr 7 PhyJOY BOYNo ratings yet
- Topic: ForcesDocument19 pagesTopic: ForcestuvvacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Newton's Laws of Motion - OkDocument14 pagesChapter 4 Newton's Laws of Motion - Okzzz munaNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument3 pagesDefinitionsJohnLIm1962No ratings yet
- Force, Motion & EnergyDocument10 pagesForce, Motion & EnergyShelin GaziNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 (Summary Notes)Document7 pagesUnit-1 (Summary Notes)chellykuukiNo ratings yet
- Class-8 Force and PressureDocument6 pagesClass-8 Force and PressureMamta JoshiNo ratings yet
- GS104 - Exam I - ReviewDocument1 pageGS104 - Exam I - ReviewlonglistNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Force and Motion: Learning OutcomesDocument11 pagesChapter 8 Force and Motion: Learning OutcomesannabellNo ratings yet
- Pod HandlerDocument90 pagesPod HandlerJanaina ProençaNo ratings yet
- Newton S Laws of MotionDocument55 pagesNewton S Laws of MotionNiña Ricci MtflcoNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Amani A. YusefNo ratings yet
- 3Document1 page3Amani A. YusefNo ratings yet
- Balanced ForcesDocument1 pageBalanced ForcesAmani A. YusefNo ratings yet
- Forces Motion WorksheetDocument1 pageForces Motion WorksheetAmani A. YusefNo ratings yet
- FORCES and Their Effects (7K)Document8 pagesFORCES and Their Effects (7K)Amani A. YusefNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument21 pagesBiologyAmani A. YusefNo ratings yet
- Simple Circuit SheetsDocument5 pagesSimple Circuit SheetsAmani A. YusefNo ratings yet
- Science Final Term 2Document41 pagesScience Final Term 2Amani A. YusefNo ratings yet
- Radius Type2 Easy 1Document2 pagesRadius Type2 Easy 1Amani A. YusefNo ratings yet
- Internationalspacestation 2Document4 pagesInternationalspacestation 2Amani A. YusefNo ratings yet
- Physics Manual Notes For CSEC and CAPEDocument114 pagesPhysics Manual Notes For CSEC and CAPEConnor England100% (1)
- 11 Holiday HomeworkDocument199 pages11 Holiday Homeworksupriyarama413No ratings yet
- Dynamics: What Is A Force?Document13 pagesDynamics: What Is A Force?TorettoNo ratings yet
- STUDY MATERIAL For IIT/NEET/AIIMS/JIPMER/UPTU (Of Newton's Laws of Motion)Document19 pagesSTUDY MATERIAL For IIT/NEET/AIIMS/JIPMER/UPTU (Of Newton's Laws of Motion)Anonymous cI0VgvTNo ratings yet
- The Laws of Motion ¿ ¿ Cengage LearningDocument57 pagesThe Laws of Motion ¿ ¿ Cengage LearningNguyễn Khắc HuyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Forces and MotionDocument8 pagesChapter 12 Forces and Motionapi-30718309No ratings yet
- Newton's First Law of Motion Is Often Stated AsDocument5 pagesNewton's First Law of Motion Is Often Stated AsRowena Abdula BaronaNo ratings yet
- Notes-Laws of MotionDocument3 pagesNotes-Laws of MotionJocel BaquilarNo ratings yet
- Loads On Furniture Pdm3scanDocument28 pagesLoads On Furniture Pdm3scanDianna LambertNo ratings yet
- Gr.9 Physics - Extra QuestionsDocument5 pagesGr.9 Physics - Extra QuestionsANIKA PRASHANTKUMAR JAISWALNo ratings yet
- COOK Natalia ThesisDocument74 pagesCOOK Natalia ThesisIIEC pulchowkNo ratings yet
- Y9 Physics Revision BookletDocument20 pagesY9 Physics Revision BookletMaoga2013No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 DynamicsDocument17 pagesChapter 3 DynamicsTutor_KLNo ratings yet
- Cinema Fiction Vs Physics Reality Ghosts, Vampires and Zombies PDFDocument13 pagesCinema Fiction Vs Physics Reality Ghosts, Vampires and Zombies PDFnknknklNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1Document15 pagesGeneral Physics 1Dainielle Marie PascualNo ratings yet
- Weld CostingDocument62 pagesWeld Costingvitet412759100% (2)
- Phy 11 CH 5Document48 pagesPhy 11 CH 5samyakNo ratings yet
- Scicent AB TE U11 eDocument26 pagesScicent AB TE U11 eYuenHei KwokNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics - Part 3Document14 pagesBiomechanics - Part 3Kýñg ButlerNo ratings yet
- Newton's 3rd Law of MotionDocument33 pagesNewton's 3rd Law of MotionRamona EstevesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Force and Laws of Motion PDFDocument20 pagesChapter 2 - Force and Laws of Motion PDFSumit BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion - Force and AccelerationDocument20 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion - Force and AccelerationJohn AldemarNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Module 2 Science 8Document14 pagesQuarter 1 Module 2 Science 8ryzhen80% (5)
- Reto 8 - ForcesDocument2 pagesReto 8 - ForcesJuliana cabrera corellaNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics: Dr. Jewelson M. SantosDocument29 pagesBiomechanics: Dr. Jewelson M. SantosJewelson SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Newton's LawsDocument8 pagesChapter-3 Newton's LawsMd Najmul HudaNo ratings yet
- Phys12 C02 Dynamics PrintDocument28 pagesPhys12 C02 Dynamics PrintSarah WangNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument13 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionAisyah Telah pergiNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Biomechanics and SportsDocument22 pagesUnit 8 Biomechanics and SportsDivyanshu YadavNo ratings yet
- SCI8 Q1 M2 Newtons Laws of MotionDocument28 pagesSCI8 Q1 M2 Newtons Laws of MotionScribd User83% (6)