0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views26 pagesUrinary System
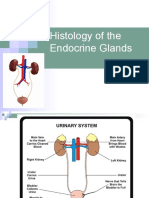
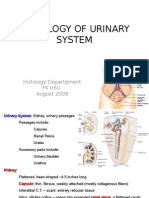
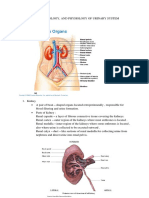
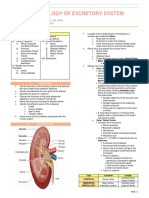
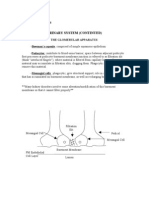
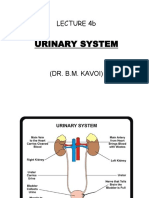
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter the blood and produce urine, removing waste and regulating water balance. The urine travels from the kidneys down the ureters into the urinary bladder, which stores urine until emptying through the urethra.
Uploaded by
nadeen moughrabiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views26 pagesUrinary System
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter the blood and produce urine, removing waste and regulating water balance. The urine travels from the kidneys down the ureters into the urinary bladder, which stores urine until emptying through the urethra.
Uploaded by
nadeen moughrabiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd