Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Glandular Epithelium
Glandular Epithelium
Uploaded by
Naveed Akhter0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
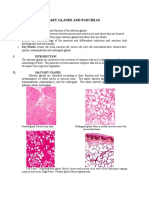
1 views10 pagesGlandular epithelium consists of specialized secretory cells that produce and store secretions in membrane-bound vesicles. Secretions can include proteins, lipids, or carbohydrate-protein complexes and are released via merocrine, apocrine, or holocrine secretion. Glands develop during fetal life from surface epithelium and can be unicellular like goblet cells or multicellular like salivary glands. Glands are either exocrine if they release secretions through ducts or endocrine if the connection to the surface is lost and secretions enter the bloodstream directly. Exocrine glands have simple or compound structures and produce mucous, serous, or mixed secretions.
Original Description:
GLANDULAR EPITHELIUM HISTOLOGY
Original Title
GLANDULAR EPITHELIUM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGlandular epithelium consists of specialized secretory cells that produce and store secretions in membrane-bound vesicles. Secretions can include proteins, lipids, or carbohydrate-protein complexes and are released via merocrine, apocrine, or holocrine secretion. Glands develop during fetal life from surface epithelium and can be unicellular like goblet cells or multicellular like salivary glands. Glands are either exocrine if they release secretions through ducts or endocrine if the connection to the surface is lost and secretions enter the bloodstream directly. Exocrine glands have simple or compound structures and produce mucous, serous, or mixed secretions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views10 pagesGlandular Epithelium
Glandular Epithelium
Uploaded by
Naveed AkhterGlandular epithelium consists of specialized secretory cells that produce and store secretions in membrane-bound vesicles. Secretions can include proteins, lipids, or carbohydrate-protein complexes and are released via merocrine, apocrine, or holocrine secretion. Glands develop during fetal life from surface epithelium and can be unicellular like goblet cells or multicellular like salivary glands. Glands are either exocrine if they release secretions through ducts or endocrine if the connection to the surface is lost and secretions enter the bloodstream directly. Exocrine glands have simple or compound structures and produce mucous, serous, or mixed secretions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
GLANDULAR EPITHELIUM
Specialized cells to produce secretions
Membrane bound vesicles- secretary
granules
Secretary material could be
Protein
Lipids
Complexes of carbohydrates & proteins
Glands with less secretary activity, secrete
substances transported from blood. e.g Sweat
glands
SECRETARY PORTION
DUCT
DEVELOPMENT
During fetal life from surface epithelium, by
proliferation & invasion into subjacent
connective tissue
TYPES
UNICELLULAR:
Single secretary cell e.g. GOBLET CELL
MULTICELLULAR:
Clusters of cells e.g. salivary
glands
PRESENCE OF DUCT
EXOCRINE: exo- outside, krinein-to separate
Retain their contact with surface epithelium
ENDOCRINE: endo- within
Connection is lost, ductless, pour secretions in
blood
SUBTYPES
Anastamosing cords interspersed between
dilated blood capillaries
Vesicles/ follicles surrounding noncellular
material
MODE OF SECRETION
Eccrine
Merocrine
Apocrine
HOLOCRINE
SECRETARY PORTION & DUCT
Simple
compound
TYPE OF SECRETION
MUCOUS: viscid, carbohydrate rich secretion
Mucin- mucous
E.g pyloric glands of stomach
SEROUS: watery, protein rich secretion
E.g. parotid
MIXED: sublingual gland
You might also like
- Acad Sem2 Tej Epit 2022 I CamiloDocument36 pagesAcad Sem2 Tej Epit 2022 I CamiloDenis Gregorio Diaz ZavaletaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Glands: Dr. GM Lochi Lecturer Department of Anatomy and HistologyDocument44 pagesHistology of Glands: Dr. GM Lochi Lecturer Department of Anatomy and Histologylochi gmNo ratings yet
- Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, LucknowDocument44 pagesDr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, LucknowlailaNo ratings yet
- Histology GlandsDocument44 pagesHistology GlandsLakshmikanth PurushothamanNo ratings yet
- Epithelium: Prepared By: Michael John R. Aguilar, RMTDocument124 pagesEpithelium: Prepared By: Michael John R. Aguilar, RMTFrankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- Histology Ch6Document10 pagesHistology Ch6رشا سعيد شبيطةNo ratings yet
- Epithelium: Dr. Kalpajyoti BhattacharjeeDocument125 pagesEpithelium: Dr. Kalpajyoti Bhattacharjeelochi gmNo ratings yet
- Glandular Epithelium: Descriptive HistologyDocument23 pagesGlandular Epithelium: Descriptive HistologyIan LubangaNo ratings yet
- Glandular EpitheliumDocument34 pagesGlandular EpitheliumAnonymous WBMLOgPNo ratings yet
- Lab 04 Glandular EpitheliumDocument2 pagesLab 04 Glandular EpitheliumSarwar JafarNo ratings yet
- Glandular EpitheliumDocument7 pagesGlandular EpitheliumrebeccaboukenjNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Basic HistologyDocument27 pagesLecture 5 - Basic HistologyezebelluciNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 Week 1Document35 pagesGenbio2 Week 1Noel Vincent Agonoy100% (1)
- Epithelium GlandsDocument24 pagesEpithelium GlandsGiane MadrigalNo ratings yet
- 05 Glandular EpitheliumDocument39 pages05 Glandular EpitheliumKhaoula MznNo ratings yet
- Glandular EpitheliumDocument10 pagesGlandular EpitheliumAkar SlemanyNo ratings yet
- Dilek Akakin Glandular TissueDocument32 pagesDilek Akakin Glandular TissueErdem AltunNo ratings yet
- Nimal TissueDocument35 pagesNimal TissueJesika GurungNo ratings yet
- Report Glandular EpitheliumDocument11 pagesReport Glandular EpitheliumKang MonNo ratings yet
- Body TissuesDocument10 pagesBody TissuesAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- Histology Prelim NotesDocument7 pagesHistology Prelim NotesKathleen Cobrador EribalNo ratings yet
- Body TissuesDocument10 pagesBody TissuesAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- Dr. Veny Larasati, M.Biomed: Bagian Histologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sriwijaya 2016Document52 pagesDr. Veny Larasati, M.Biomed: Bagian Histologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sriwijaya 2016NabilahnurqonitahNo ratings yet
- Glands - Types According To Their Function: Structure 28Document26 pagesGlands - Types According To Their Function: Structure 28Manimaran TNo ratings yet
- Single Squamous EpitheliumDocument28 pagesSingle Squamous EpitheliumLyndonn Santos100% (1)
- Tob 4.1Document29 pagesTob 4.1LT DRAGONXNo ratings yet
- Simple Squamous: Epithelial Tissue A. Simple /unstratified SINGLE LAYER OF CELLS IDocument5 pagesSimple Squamous: Epithelial Tissue A. Simple /unstratified SINGLE LAYER OF CELLS IMedical HardikNo ratings yet
- GlandsDocument21 pagesGlandsapi-3769252No ratings yet
- Ductal SystemDocument20 pagesDuctal SystemSounak BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Histology: BY Alawia Abdalla Mohammed 7 Nov 2021Document23 pagesHistology: BY Alawia Abdalla Mohammed 7 Nov 2021التنين الاحمر العظيمNo ratings yet
- EPITHELIAL TISSUE 11th Oct.2012Document25 pagesEPITHELIAL TISSUE 11th Oct.2012Patrick NyakwambaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Lecture 1Document52 pagesEpithelial Tissue Lecture 1Saphira PramuditaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Teaching DemoDocument40 pagesEpithelial Tissue Teaching DemoFrancis Salcedo100% (1)
- EpitheliumDocument46 pagesEpitheliumFady FadyNo ratings yet
- Jaringan Dasar 1 BDocument20 pagesJaringan Dasar 1 BJIHAN ISMAILNo ratings yet
- General Histology: DR Samina ShaheenDocument104 pagesGeneral Histology: DR Samina ShaheenJemarey de RamaNo ratings yet
- 4 TissuesDocument124 pages4 TissuesJanette Monica Barrios100% (1)
- Tissues (Anatomy 1)Document83 pagesTissues (Anatomy 1)nanakwame5769No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 General HistologyDocument14 pagesLesson 2 General HistologyDanaNo ratings yet
- Salivary GlandDocument118 pagesSalivary GlandtdxdvnddmfNo ratings yet
- SSC Polity Civics Capsule 2016Document34 pagesSSC Polity Civics Capsule 2016Panku 7No ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument40 pagesEpithelial TissueTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Epithelium and Glands: 1.classification of Epithelial TissueDocument7 pagesLecture 1: Epithelium and Glands: 1.classification of Epithelial TissueMuizz RasaniNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument32 pagesUntitledStephanie DatoNo ratings yet
- Secretory Epithelia and Specialized Epithelial Cells OriginDocument8 pagesSecretory Epithelia and Specialized Epithelial Cells OriginMajdoleen AlawwadNo ratings yet
- Case 2: Group 2 MD 1-CDocument55 pagesCase 2: Group 2 MD 1-CTyrone Clyde SaludezNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesEpithelial TissueSofia LiNo ratings yet
- BMS - AL 2 - Microscope, Epithelial Connective TissuesDocument41 pagesBMS - AL 2 - Microscope, Epithelial Connective TissuesFoong Zhen HinNo ratings yet
- Organs Associated With The Digestive TractDocument55 pagesOrgans Associated With The Digestive Tractapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Squamous Cuboidal Columnar CiliatedDocument5 pagesSquamous Cuboidal Columnar CiliatedVaishalee 17No ratings yet
- EPITHELIAL TISSUE (Defn, Classification & Functions - PDFDocument29 pagesEPITHELIAL TISSUE (Defn, Classification & Functions - PDFnikitachaudhary1220No ratings yet
- EPITHELIAL TISSUE (Epithelium / Epithelia) : Basement MembraneDocument7 pagesEPITHELIAL TISSUE (Epithelium / Epithelia) : Basement MembraneNanaNo ratings yet
- Exocrine GlandsDocument24 pagesExocrine GlandsKrishma ShakyaNo ratings yet
- BIO2OO - Introduction Tissues, Classification of Living Things & Ecology 1.1.0 Animal TissueDocument19 pagesBIO2OO - Introduction Tissues, Classification of Living Things & Ecology 1.1.0 Animal TissueMark SullivanNo ratings yet
- 13.histology LectureDocument64 pages13.histology LecturepashaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial HighlightedDocument33 pagesEpithelial HighlightedharizgaleonNo ratings yet
- Embryology of Salivary GlandsDocument21 pagesEmbryology of Salivary GlandsAssist Professor Dr-Bayad Jaza Mahmud100% (3)
- Pancreas+salivary GlandsDocument4 pagesPancreas+salivary GlandsAllen BurdowskiNo ratings yet
- 20 July 2Document12 pages20 July 2Subhash YadavNo ratings yet
- Bone HistologyDocument56 pagesBone HistologyNaveed AkhterNo ratings yet
- The Cell MembraneDocument23 pagesThe Cell MembraneNaveed AkhterNo ratings yet
- Respiratoy System HistologyDocument32 pagesRespiratoy System HistologyNaveed AkhterNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System HistologyDocument21 pagesCirculatory System HistologyNaveed AkhterNo ratings yet
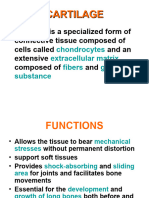
- Cartilage HistologyDocument27 pagesCartilage HistologyNaveed AkhterNo ratings yet
- ArtifactsDocument4 pagesArtifactsNaveed AkhterNo ratings yet
- Required Books For Pharm-DDocument18 pagesRequired Books For Pharm-DNaveed AkhterNo ratings yet
- Prince Price Alide Price Printer Sr. No Books Author Edition QT Y KinesiologyDocument9 pagesPrince Price Alide Price Printer Sr. No Books Author Edition QT Y KinesiologyNaveed AkhterNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2nd Year - NEUROANATOMYDocument3 pagesAssignment 2nd Year - NEUROANATOMYNaveed AkhterNo ratings yet
- Required Books For Pharm-D Edited (AutoRecovered)Document19 pagesRequired Books For Pharm-D Edited (AutoRecovered)Naveed AkhterNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Medical Commission Ord 2019Document32 pagesPakistan Medical Commission Ord 2019Naveed AkhterNo ratings yet
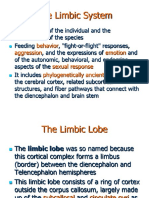
- The Limbic System: Behavior Aggression Emotion Sexual Response Phylogenetically AncientDocument22 pagesThe Limbic System: Behavior Aggression Emotion Sexual Response Phylogenetically AncientNaveed AkhterNo ratings yet