Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Popular Methods or Modes of Payment in International Trade
Uploaded by
bineshtya50 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views29 pagesPresented By: Binesh Tyata
Quest International College, Gwarko,Nepal
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPresented By: Binesh Tyata
Quest International College, Gwarko,Nepal
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views29 pagesPopular Methods or Modes of Payment in International Trade
Uploaded by
bineshtya5Presented By: Binesh Tyata
Quest International College, Gwarko,Nepal
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 29
Popular Methods/Modes of
Payment in International Trade
• Significance of methods of payment in
lnternational Trade
• Limitations of method of payment in
international trade
Types of Modes of Payment in
International Trade
To be competitive in business today,
business owners need to think globally.
To sell internationally, it’s critical to offer
appropriate payment methods that are safe
and have favorable terms for both the buyer
(importer) and the seller (exporter).
Contd.
There are risks involved in international trade.
Importers want to receive their goods before
making payment, and exporters want to be
paid before they release the goods.
This is why reliable payment methods are
important.
Contd.
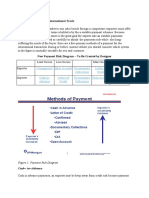
There are 4 main types of payment methods:
Cash in advance
Letter of Credit (L/C)
Open Account
Counter Trade
1.Cash in Advance
Also called ‘advance payment’ or ‘cash with order’,
cash in advance means exactly what it sounds like.
It is a mostly straightforward payment method
where the importer (usually the buyer) pays for the
goods upfront and before shipment.
The payment may be completed by any means
agreed between the exporter and the importer.
Popular options include wire transfer, international
cheque, and payment by debit card.
Benefits of Cash in Advance
This payment term clearly favors the exporter because
they receive payment while still in possession of the
goods.
Cash in advance provides the working capital exporter
need to process the order; there’s no strain on cash flow.
The exporter operates an internet-based business where
the acceptance of credit card payments is a standard
way of conducting business transactions.
Limitations of Cash in Advance
Thisis the least desirable method for importers
because they have the risk of goods not being
shipped.
Cashin advance is usually only used for small
purchases.
Noexporter who requires only this method of
payment can be competitive.
Contd
It also creates an unfavorable cash flow
situation for the importer because they have
to pay all of the price upfronts and in cash
a position most importers/buyers try to
avoid.
2.Letter of Credit
A letter of credit (LC), also known as a documentary
credit or bankers commercial credit, or letter of
undertaking, is a payment mechanism used in
international trade to provide an economic guarantee
from a creditworthy bank to an exporter of goods.
The issuing bank will typically use intermediary
banks to facilitate the transaction and make payment
to the exporter.
Contd.
Letters of credit are used extensively in the
financing of international trade, when the
reliability of contracting parties cannot be readily
and easily determined.
LCs can be arranged easily for one-time
transactions between the exporter and importer,
or used for an ongoing series of transactions.
Benefits of Letter of Credit
LCs are one of the most versatile and secure
instruments available to international traders. Since
LCs are credit instruments, the importer's credit
with their bank is used to obtain an LC.
Ittransfers the credit-worthiness from the exporter
or buyer to the issuing bank. The importer can do
any number of transactions at the same time when
he is backed by an established and larger institution.
Contd.
A letter of credit is safer for the exporter in
case the importer goes bankrupt. Since the
creditworthiness of the seller is transferred
to the issuing bank, it is the bank’s
obligation to pay the amount as agreed in
the letter of credit.
LC promotes instant liquidity.
Limitations of Letter of Credit
It is generally considered to be very
expensive, as the banks involved will
typically charge significant fees.
A letter of credit follows complex governing
rules and has chances that it can be misused
to take advantage of the applicant.
Contd.
A letter of credit fears of a material fraud risk to
the importer. The bank will pay the exporter
upon looking at the shipping documents
thoroughly and not the actual quality of goods
displayed.
A letterof credit has an expiration date and must
be used before it .
Contd.
LCs are often treated by issuers like loans.
LCs must be changed each time there is an
amendment in amount or terms or clauses.
LCs are often tough to terminate or cancel.
3.Open Account
An open account transaction in international trade
is a sale where the goods are shipped and
delivered before payment is due, which is for pre-
specified time typically in 30, 60 or 90 days
Under an open account, the goods, along with all
the necessary export documents, are shipped
directly to the importer who has agreed to pay the
exporter’s invoice at a specified date.
Contd.
Though open account terms will definitely
enhance export competitiveness, exporters
should thoroughly examine the political,
economic and commercial risks as well as
cultural influences to ensure that payment will be
received in full and on time.
Benefits of Open Account
It facilitates to mitigate the risk of non-payment
associated with open account trade by using trade
finance techniques such as export credit insurance and
factoring.
Open account terms may help win customers in
competitive markets.
Itcan make an exporter’s products more competitive
and may even allow them to charge more for their
goods.
Limitations of Open Account
Open account is riskey and the firm should
structure such payment methods with care.
This method is appropriate only with
customers of longstanding or excellent
credit,or with a subsidiary owned by the
exporter.
4.Counter Trade
Countertrade means exchanging goods or
services which are paid for, in whole or part,
with other goods or services, rather than with
money.
A Monetary valuation can however be used in
countertrade for accounting purposes. In dealings
between sovereign states, the term bilateral trade
is used.
Benefits of Counter Trade
Allows for entry into difficult markets.
Increases company sales where person might
not otherwise have business.
Overcomes credit difficulties.
Allows for disposal of declining or surplus
products.
Contd.
Gains competitive advantage over the
competition. (Business men don’t want to
lose a market share as a result of
competitors.)
Limitations of Counter Trade
The time-consuming nature. As in any
unconventional tactic, there will be haggling over
the good trades, so expect a long, drawn-out
negotiation until all parties are satisfied.
Higher transaction costs (including brokerage, for
instance). Costs can quickly add up, especially
while looking for a buyer for the goods,
commissions to middlemen, and more.
Contd.
Logistical issues, especially if commodities
are involved.
Greater uncertainty on the value of the
goods being traded and uncertainty on the
quality of the goods.
Negotiation complexity
Presented By : Binesh Tyata
G-mail: bineshtyata10@gmail.com
Quest International College, Gwarko, Nepal
You might also like
- Payment Collection for Small Business: QuickStudy Laminated Reference Guide to Customer Payment OptionsFrom EverandPayment Collection for Small Business: QuickStudy Laminated Reference Guide to Customer Payment OptionsNo ratings yet
- Guide to International Finance ConceptsDocument11 pagesGuide to International Finance ConceptsShruti ReddyNo ratings yet
- SVB - Trade Finance Guide PDFDocument35 pagesSVB - Trade Finance Guide PDFboggy68No ratings yet
- Letters of Credit and Documentary Collections: An Export and Import GuideFrom EverandLetters of Credit and Documentary Collections: An Export and Import GuideRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Methods of Payment in International TradeDocument2 pagesMethods of Payment in International TrademehandiskNo ratings yet
- You’Re a Business Owner, Not a Dummy!: Understand Your Merchant AccountFrom EverandYou’Re a Business Owner, Not a Dummy!: Understand Your Merchant AccountRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- International Payments MethodsDocument13 pagesInternational Payments MethodsMuhammad Dilshad Ahmed AnsariNo ratings yet
- Methods of Payment: Key PointsDocument3 pagesMethods of Payment: Key PointsZefRy D'e DSNo ratings yet
- Payment MethodsDocument12 pagesPayment Methodsrahul_khanna4321No ratings yet
- Methods of International Payments (Group 2)Document7 pagesMethods of International Payments (Group 2)APEHMIKENo ratings yet
- International Trade Payment MethodsDocument2 pagesInternational Trade Payment MethodsSCRIBD1868100% (1)
- What Is A Letter of Credit?Document29 pagesWhat Is A Letter of Credit?Varun DagaNo ratings yet
- Export Unit 1Document17 pagesExport Unit 1khushwantNo ratings yet
- International Payment MethodsDocument4 pagesInternational Payment MethodsPrabhujot SinghNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Receivables Management: Standards, Length of Credit Period, Cash Discount, Discount Period EtcDocument8 pagesObjectives of Receivables Management: Standards, Length of Credit Period, Cash Discount, Discount Period EtcRekha SoniNo ratings yet
- Assignment of International Trade LawDocument15 pagesAssignment of International Trade LawTanya Tandon0% (1)
- UNIT 5. PAYMENT. L1Document3 pagesUNIT 5. PAYMENT. L1halam29051997No ratings yet
- Export Credit and Financing in International TradeDocument22 pagesExport Credit and Financing in International Tradepromptpaper1No ratings yet
- International Trade Payment MethodDocument7 pagesInternational Trade Payment MethodTazreenNo ratings yet
- C3 Management of Foreign Accounts ReceivableDocument3 pagesC3 Management of Foreign Accounts ReceivableTENGKU ANIS TENGKU YUSMANo ratings yet
- Payment Methods, EmmDocument26 pagesPayment Methods, EmmAmone BenedictNo ratings yet
- Assingnment of International Trade Law ON Payment of International SalesDocument15 pagesAssingnment of International Trade Law ON Payment of International SalesManik Singh KapoorNo ratings yet
- International Payment Methods and RisksDocument20 pagesInternational Payment Methods and Risksmatthew kobulnickNo ratings yet
- Export FinanceDocument8 pagesExport FinanceMushiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Project On International Payment System: J. Watumull Sadhubella Girls CollegeDocument22 pagesProject On International Payment System: J. Watumull Sadhubella Girls CollegeAngel JhamnaniNo ratings yet
- Explaining the 3 Main Financing Options of an Export OrderDocument8 pagesExplaining the 3 Main Financing Options of an Export OrderDiana SumailiNo ratings yet
- METHODS OF INTERNATIONAL PAYMENTDocument6 pagesMETHODS OF INTERNATIONAL PAYMENTnailazmat_91No ratings yet
- Methods of Payment in International TradeDocument13 pagesMethods of Payment in International Tradelovepreet singhNo ratings yet
- Payment MethodsDocument6 pagesPayment MethodsAbhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- Vigas Gerber - Ezquerro, Ana (1045530)Document6 pagesVigas Gerber - Ezquerro, Ana (1045530)Delfino Bernardo ViegasNo ratings yet
- International Trade Payment MethodsDocument15 pagesInternational Trade Payment MethodsAzharNo ratings yet
- Itl Payment of International SalesDocument15 pagesItl Payment of International Salesharsh sahuNo ratings yet
- International Trade Finance Risks and MethodsDocument35 pagesInternational Trade Finance Risks and MethodsAstha NautiyalNo ratings yet
- Pge69 72Document6 pagesPge69 72Xuân Nhi LêNo ratings yet
- Module III - Methods & Instruments of PaymentDocument32 pagesModule III - Methods & Instruments of PaymentManushree PatankarNo ratings yet
- Itab RevieweerDocument13 pagesItab RevieweerAra PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Regulatory Framework & Taxation: Cross Border TransactionsDocument34 pagesUnit Iv Regulatory Framework & Taxation: Cross Border TransactionsRavi PrabuNo ratings yet
- Module 4: Trade Finance Meaning of International Bank: Foreign ExchangeDocument4 pagesModule 4: Trade Finance Meaning of International Bank: Foreign ExchangeAnita VarmaNo ratings yet
- Trade Payment MethodsDocument12 pagesTrade Payment MethodsDhruveet RaiyaniNo ratings yet
- Main international payment methodsDocument3 pagesMain international payment methodsMohammed ShaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Payments in Import International TradeDocument2 pagesMethods of Payments in Import International TradeSujan AnnaiahNo ratings yet
- Roles of BanksDocument2 pagesRoles of BanksĐồng ÁnhNo ratings yet
- Unit 4. Lesson 2 (Cont)Document2 pagesUnit 4. Lesson 2 (Cont)K59 Phan Ai ThuyenNo ratings yet
- Methods of Payment in International TradeDocument5 pagesMethods of Payment in International TradefhinojosacNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5. PAYMENT. L3Document2 pagesUNIT 5. PAYMENT. L3halam29051997No ratings yet
- Letter of Credit AssignmentDocument6 pagesLetter of Credit AssignmentAnjali Angel ThakurNo ratings yet
- Global Finance 1Document6 pagesGlobal Finance 1JASMINE FAITH MEBATONo ratings yet
- International Trade Terms: Unit 4Document49 pagesInternational Trade Terms: Unit 4Raj KumarNo ratings yet
- Trade Finance ProductsDocument35 pagesTrade Finance ProductsAnkit Malde100% (1)
- UMB Seven Financial Tools Every Exporter Should KnowDocument3 pagesUMB Seven Financial Tools Every Exporter Should KnowKashif JavedNo ratings yet
- Prudent Credit Practices and Payment Methods for Export SalesDocument13 pagesPrudent Credit Practices and Payment Methods for Export SalesCharanjeet Singh AroraNo ratings yet
- Modes of Payment in International TradeDocument13 pagesModes of Payment in International TradeHimani BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Final Explanation For The Report in International Trade and AgreementDocument5 pagesFinal Explanation For The Report in International Trade and AgreementChristian DaytoNo ratings yet
- Basic Trade Finance Tools: Payment Methods in International TradeDocument14 pagesBasic Trade Finance Tools: Payment Methods in International Traderamakrishnan84No ratings yet
- FF Issues Payment Terms Export Financing ResourcesDocument6 pagesFF Issues Payment Terms Export Financing Resourcesaiou687No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 LC, CAD and Documentation.Document12 pagesAssignment 2 LC, CAD and Documentation.TaddesseNo ratings yet
- Trade - Advance LevelDocument175 pagesTrade - Advance LevelNusrat JahanNo ratings yet
- Revocable Letter of Credit Can Be Revoked Without The Consent of TheDocument3 pagesRevocable Letter of Credit Can Be Revoked Without The Consent of ThePankaj ThapaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Payment in International TradeDocument18 pagesMethods of Payment in International TradePanav MohindraNo ratings yet
- Daniel Bell's Concept of Post-Industrial Society: Theory, Myth, and IdeologyDocument42 pagesDaniel Bell's Concept of Post-Industrial Society: Theory, Myth, and IdeologyTeni ChitananaNo ratings yet
- Ch1. Considering Materiality and RiskDocument47 pagesCh1. Considering Materiality and RiskAli AlbaqshiNo ratings yet
- The Influence of The English Language On The Russian Youth SlangDocument10 pagesThe Influence of The English Language On The Russian Youth SlangВасилий БоровцовNo ratings yet
- Loan Agreement DetailsDocument21 pagesLoan Agreement DetailssherrieNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 MCQDocument7 pagesUnit 1 MCQHan Nwe OoNo ratings yet
- Confidentiality Agreement GuideDocument11 pagesConfidentiality Agreement GuideSeema WadkarNo ratings yet
- Trump University Asset Protection 101 Trump University PDFDocument4 pagesTrump University Asset Protection 101 Trump University PDFThumper Kates0% (2)
- On Insider TradingDocument17 pagesOn Insider TradingPranjal BagrechaNo ratings yet
- Micro and Macro Environment of NestleDocument2 pagesMicro and Macro Environment of Nestlewaheedahmedarain56% (18)
- Dealey Field Day 10 FlyerDocument1 pageDealey Field Day 10 FlyercooperrebeccaNo ratings yet
- Arabic in UrduDocument5 pagesArabic in UrduNanang Nurcholis0% (1)
- Enhancing Role of SMEs in Indian Defence Industry1 PDFDocument84 pagesEnhancing Role of SMEs in Indian Defence Industry1 PDFINDIRA PALNINo ratings yet
- Gokuldham Marathi Prelim 2023Document8 pagesGokuldham Marathi Prelim 2023Aarushi GuptaNo ratings yet
- DuniaDocument64 pagesDuniaAmith PanickerNo ratings yet
- Báo cáo cuối kì môn thực hành an ninh mạngDocument5 pagesBáo cáo cuối kì môn thực hành an ninh mạngDương Thành ĐạtNo ratings yet
- IDC Infrastructure ProjectsDocument100 pagesIDC Infrastructure Projectsshashi_nspNo ratings yet
- Achievement Gaps Mindset Belonging FeedbackDocument4 pagesAchievement Gaps Mindset Belonging FeedbackResearchteam2014No ratings yet
- History and Political Science: Solution: Practice Activity Sheet 3Document9 pagesHistory and Political Science: Solution: Practice Activity Sheet 3Faiz KhanNo ratings yet
- (UPDATED) BCC Semifinalist GuidebookDocument4 pages(UPDATED) BCC Semifinalist GuidebookYohanes StefanusNo ratings yet
- Bai Tâp Anh 9 - 3-2-2021 Re - CLDocument16 pagesBai Tâp Anh 9 - 3-2-2021 Re - CLDuyen NguyenNo ratings yet
- Minutes Feb 28 2022Document5 pagesMinutes Feb 28 2022Raquel dg.BulaongNo ratings yet
- Case Digests On TrademarksDocument10 pagesCase Digests On Trademarkssei1davidNo ratings yet
- UN Supplier Code of Conduct. United Nations.Document4 pagesUN Supplier Code of Conduct. United Nations.Daniel BorrEka MalteseNo ratings yet
- Reading Report G9Document50 pagesReading Report G9Grade9 2023No ratings yet
- Prisoner of ZendaDocument27 pagesPrisoner of ZendaSauban AhmedNo ratings yet
- Nodalo - Medicard vs. CirDocument3 pagesNodalo - Medicard vs. CirGenebva Mica NodaloNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Journal Article Breaks Down Strategizing vs EconomizingDocument20 pagesStrategic Management Journal Article Breaks Down Strategizing vs EconomizingVinícius RodriguesNo ratings yet
- MG Pete Chiarelli Director of Operations, Readiness and Mobilization NEIT-532Document42 pagesMG Pete Chiarelli Director of Operations, Readiness and Mobilization NEIT-5329/11 Document ArchiveNo ratings yet
- Material For Upper Advanced and TOEFLDocument132 pagesMaterial For Upper Advanced and TOEFLNadia ChavezNo ratings yet
- Entering and Developing A Service Network: Sheena Leek and Louise CanningDocument10 pagesEntering and Developing A Service Network: Sheena Leek and Louise CanningTanisha KrunalNo ratings yet