Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ra 10121
Uploaded by
Ericka Beros Canales0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views31 pagesOriginal Title
RA-10121
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views31 pagesRa 10121
Uploaded by
Ericka Beros CanalesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 31
RA 10121
Philippine Disaster Risk
Reduction and Management Act
(DRRM Act)
MA. ELOISA E. RIVERA MAED - TEM
AN ACT STRENGTHENING THE PHILIPPINE
DISASTER RISK REDUCTION AND
MANAGEMENT SYSTEM, PROVIDING FOR THE
NATIONAL DISASTER RISK REDUCTION AND
MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK AND
INSTITUTIONALIZING THE NATIONAL
DISASTER RISK REDUCTION AND
MANAGEMENT PLAN, APPROPRIATING FUNDS
THEREFOR AND FOR OTHER PURPOSES.
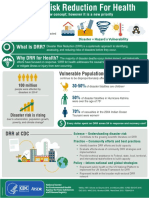
Why do we need to
have a new law?
Republic Act No. 10121 or the Philippine
Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Act
of 2010 (DRRM Act) is a law which transforms
the Philippines’ disaster management system
from disaster relief and response towards
disaster risk reduction (DRR).
We need a more proactive approach to managing disaster
risks. The DRRM Act transforms and reforms the way we
deal with disasters. We now recognize that impacts of
disasters can be reduced by addressing the root cause
of disaster risks. The government shifts its focus from
disaster response to disaster risk reduction (DRR). This
puts more emphasis on strengthening people’s capacity
to absorb stress, maintain basic functions during a
disaster and bounce back better from disasters. The
DRRM Act institutionalizes the best practices of local
communities which have been implementing effective
DRMM in their respective areas.
Not only was the role of local governments
as the first line of defense in facing
disasters was finally recognized but it also
marks the paradigm shift from focus on
“rescue and recovery” to “preparedness
and risk reduction.”
The Disaster Risk Reduction Bill, which was
actively pushed by the Philippine Consortium on
Good Local Governance (PCGLG), the Disaster
Risk Reduction Network among others, has been
signed into law by President Gloria Macapagal-
Arroyo last 27 May 2010 by virtue of Republic Act
10121.
DEFINITION OF TERMS
○ Disaster – Disasters are often described as a result of the
combination of: the exposure to a hazard; the conditions of
vulnerability that are present; and insufficient capacity or
measures to reduce or cope with the potential negative
consequences, Disaster impacts may include loss of life, injury,
disease and other negative effects on human, physical, mental
and social well-being, together with damage to property,
destruction of assets, loss of services, Social and economic
○ disruption and environmental
Disaster Mitigation– degradation
the lessening or limitation of the adverse
impacts of hazards and related disasters. Mitigation measures
encompass engineering techniques and hazard-resistant
construction as well as improved environmental policies and
public awareness.
DEFINITION OF TERMS
○ Disaster Prevention – the outright avoidance of adverse impacts of
hazards and related disasters. It expresses the concept and intention
to completely avoid potential adverse impacts through action taken in
advance such as construction of dams or embankments that eliminate
flood risks, land-use regulations that do not permit any settlement in
high-risk zones, and seismic engineering designs that ensure the
survival and function of a critical building in any likely earthquake.
○ Disaster Response – the provision of emergency services and public
assistance during or immediately after a disaster in order to save lives,
reduce health impacts, ensure public safety and meet the basic
subsistence needs of the people affected. Disaster response is
predominantly focused on immediate and short-term needs and is
sometimes called “disaster relief”.
DEFINITION OF TERMS
○ Disaster Risk – the potential disaster losses in lives, health status,
livelihood, assets and services, which could occur to a particular
community or a Society over some specified future time period.
○ Disaster Risk Reduction and Management - the systematic process of
using administrative directives, organizations, and operational skills
and capacities to implement strategies, policies and improved coping
capacities in order to lessen the adverse impacts of hazards and the
possibility of disaster. Prospective disaster risk reduction and
management refers to risk reduction and management activities that
address and seek to avoid the development of new or increased
disaster risks, especially if risk reduction policies are not put in place.
DEFINITION OF TERMS
○ Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Information System – a
specialized database which contains, among others, information on
disasters and their human material, economic and environmental
impact, risk assessment and mapping and vulnerable groups.
○ Early Warning System – the set of capacities needed to generate and
disseminate timely and meaningful warning information to enable
individuals, communities and organizations threatened by a hazard to
prepare and to act appropriately and in sufficient time to reduce the
possibility of harm or loss.
○ Emergency – unforeseen or sudden occurrence, especially danger,
demanding immediate action.
DEFINITION OF TERMS
○ Emergency Management – the organization and management of
resources and responsibilities for addressing all aspects of
emergencies, in particular preparedness, response and initial
recovery steps.
○ National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Framework” or
“NDRRMF” – provides for comprehensive, all hazards, multi-sectoral,
inter-agency and community - based approach to disaster risk
reduction and management.
○ National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Plan” or “NDRRMP” –
the document to be formulated and implemented by the Office of Civil
Defense (OCD) that sets out goals and specific objectives for reducing
disaster risks together with related actions to accomplish these
objectives.
DEFINITION OF TERMS
○ Response – any concerted effort by two (2) or more agencies, public
or private, to provide assistance or intervention during or
immediately after a disaster to meet the life preservation and basic
subsistence needs of those people affected and in the restoration of
essential public activities and facilities.
○ Risk– the combination of the probability of an event and its negative
consequences.
○ Risk Assessment – a methodology to determine the nature and extent of
risk by analyzing potential hazards and evaluating existing conditions
of vulnerability that together could potentially harm exposed people,
property, services, livelihood and the environment on which they
depend.
DEFINITION OF TERMS
○ Risk Management – the systematic approach and practice of
managing uncertainty to minimize potential harm and loss.
○ State of Calamity – a condition involving mass casualty and/or major
damages to property, disruption of means of livelihoods, roads and
normal way of life of people in the affected areas as a result of the
occurrence of natural or human-induced hazard.
○ National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Plan” or “NDRRMP” –
the document to be formulated and implemented by the Office of Civil
Defense (OCD) that sets out goals and specific objectives for reducing
disaster risks together with related actions to accomplish these
objectives.
SCOPE
This Act provides for the development of policies and
plans and the implementation of actions and measures
pertaining to all aspects of disaster risk reduction and
management, including good governance, risk
assessment and early warning, knowledge building and
awareness raising, reducing underlying risk factors, and
preparedness for effective response and early recovery.
The DRRM Act provides a responsive and proactive
manner of addressing disasters through a framework
that:
● Prioritizes on community level DRRM focusing on the
most vulnerable sectors (i.e., the poor, the sick,
people with disabilities, the elderly, women and
children)
● Recognizes the important role and strengthens
capacities of local communities
● Ensures broad‐based and greater participation from
Civil Society
● Addresses root causes of disaster risks
What is
NDrRMC
?
National Disaster Risk Reduction & Management Council
Secretary of the Department of Science and Technology (DOST)
VC for Disaster Prevention and Mitigation
Secretary of the Department of the Interior and
Local Government (DILG)
Secretary of the Department of
VC for Disaster Preparedness
National Defense (DND)
Chairperson
Secretary of the Department of Social Welfare and
Development (DSWD)
VC for Disaster Response
Director-General of the National Economic
and Development Authority (NEDA)
VC for Disaster Rehabilitation & Recovery
MEMBERS OF NDRRMC
(a) Secretary of the Department of Health (DOH);
(b) Secretary of the Department of Environment and Natural
Resources (DENR);
(c) Secretary of the Department of Agriculture (DA);
(d) Secretary of the Department of Education (DepED);
(e) Secretary of the Department of Energy (DOE);
(f) Secretary of the Department of Finance (DOF);
(g) Secretary of the Department of Trade and Industry (DT!);
(h) Secretary of the Department of Transportation and
Communications (DOTC);
MEMBERS OF NDRRMC
(i) Secretary of the Department of Budget and Management (DBM);
(j) Secretary of the Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH);
(k) Secretary of the Department of Foreign Affairs (DFA);
(l) Secretary of the Department of Justice (DOJ);
(m) Secretary of the Department of Labor and Employment (DOLE);
(n) Secretary of the Department of Tourism (DOT);
(o) The Executive Secretary;
(p)Secretary of the Office of the Presidential Adviser on the Peace Process
(OPAPP);
MEMBERS OF NDRRMC
(q) Chairman, Commission on Higher Education (CHED);
(r) Chief of Staff, Armed Forces of the Philippines (AFP);
(s) Chief, Philippine National Police (PNP);
(t) The Press Secretary;
(u) Secretary General of the Philippine National Red Cross (PNRC);
(v) Commissioner of the National Anti-Poverty Commission-Victims of Disasters and
Calamities Sector (NAPCVDC);
(w) Chairperson, National Commission on the Role of Filipino Women;
(x) Chairperson, Housing and Urban Development Coordinating Council (HUDCC);
(y) Executive Director of the Climate Change Office of the Climate Change
Commission;
(z) President, Government Service Insurance System (GSIS);
MEMBERS OF NDRRMC
(aa) President, Social Security System (SSS);
(bb) President, Philippine Health Insurance Corporation (PhilHealth);
(cc) President of the Union of Local Authorities of the Philippines (ULAP);
(dd) President of the League of Provinces of the Philippines (LPP);
(ee) President of the League of Cities of the Philippines (LCP);
(ff) President of the League of Municipalities of the Philippines (LMP);
(gg) President of the Liga ng Mga Barangay (LMB);
(hh) Four (4) representatives from the CSOs;
(ii) One (1) representative from the private sector; and
(jj) Administrator of the OCD.
What is the basis of
the DRRM Act?
The DRRM Act adopts and adheres to principles &
strategies consistent with the international standards set
by the Hyogo Framework for Action (HFA). The HFA is a
comprehensive, action‐oriented response to international
concern about the growing impacts of disasters on
individuals, communities & national development.
The HFA was developed following the tsunami in 2004
which claimed more than 200,000 lives and massively
damaged properties and the environment. This
emphasized the need for a paradigm shift from disaster
response to disaster risk reduction (DRR).
The HFA was formulated and adopted by 168 governments at the
World Conference on Disaster Reduction held in Kobe, Hyogo
Prefecture, Japan in 2005. It is aimed at building the resilience of
nations and communities to disasters, and reducing
vulnerabilities and risks to hazards. On September 14, 2009, the
Philippine Senate ratified the ASEAN Agreement on Disaster
Management and Emergency Response (AADMER) which is
ASEAN’s affirmation of its commitment to the HFA.
WHAT ARE
THE
SALIENT
FEATURES
OF DRRM
ACT?
• Coherence with international framework
• Adherence to universal norms, principles, and standards of
humanitarian assistance
• Good governance through transparency and accountability
• Strengthened institutional mechanism for DRRM
• Integrated, coordinated, multi‐sectoral, inter ‐agency, and
community‐based approach to disaster risk reduction
• Empowerment of local government units (LGUs) and civil
society organizations (CSOs) as key partners in disaster risk
reduction
• Integration of the DRRM into the educational system
• Establishment of the DRRM Fund
• (DRRMF) at the national and local levels
• Providing for provisions on the declaration of a state of
calamity, remedial measures, prohibited acts and penalties
Thank you!
You might also like
- National Disaster Response Plan NDRP Earthquake and Tsunami 2018Document109 pagesNational Disaster Response Plan NDRP Earthquake and Tsunami 2018QPDRRMO RAP 3No ratings yet
- DRRM - Final ReportDocument52 pagesDRRM - Final Reportirishkate matugasNo ratings yet
- VulnerabilityDocument19 pagesVulnerabilitymaddoxNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk Reduction and ManagementDocument6 pagesDisaster Risk Reduction and ManagementSteven Sison100% (1)
- DRRR q1 Mod1 Basicconceptofdisasteranddisasterrisk v2Document26 pagesDRRR q1 Mod1 Basicconceptofdisasteranddisasterrisk v2Kymbherleigh100% (1)
- DLL-Performance TaskDocument3 pagesDLL-Performance TaskProfED TVNo ratings yet
- CP For Covid&EREIDDocument118 pagesCP For Covid&EREIDAriane joy Rodrigueza100% (1)
- DRRR G11Document10 pagesDRRR G11Mark John GuardamanoNo ratings yet
- CP Earthquake April 2023Document29 pagesCP Earthquake April 2023Marlon Villena100% (1)
- Week 6 DRR Key Concepts, Elements, Principles and ImportanceDocument32 pagesWeek 6 DRR Key Concepts, Elements, Principles and ImportanceHashitomo75% (4)
- DO 37 S 2022 Guidelines On The Cancellation or Suspension of Classes EditedDocument15 pagesDO 37 S 2022 Guidelines On The Cancellation or Suspension of Classes EditedEmma RuthNo ratings yet
- G6 - Disaster Management ContinuumDocument92 pagesG6 - Disaster Management ContinuumCLARISSE CLOIE LAMBERTENo ratings yet
- NDRRMC MakadiyosDocument14 pagesNDRRMC Makadiyosfrancheska ruizNo ratings yet
- Dr. Teresita B. Bayaron ProfessorDocument29 pagesDr. Teresita B. Bayaron ProfessorKhim BalcitaNo ratings yet
- Conversation TopicsDocument3 pagesConversation TopicsAlexandra NistiriucNo ratings yet
- Crisis Management: Strategies for Mitigating and Recovering from DisastersFrom EverandCrisis Management: Strategies for Mitigating and Recovering from DisastersNo ratings yet
- Ra 10121Document6 pagesRa 10121Nowell SimNo ratings yet
- DRR Lesson 6.1Document56 pagesDRR Lesson 6.1Leo EspinoNo ratings yet
- Philippine Disaster Risk Reducation and ManagementDocument10 pagesPhilippine Disaster Risk Reducation and ManagementDareNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk Management IrrDocument5 pagesDisaster Risk Management IrrMaeGadiazaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For DRR Provincial Quiz BeeDocument8 pagesReviewer For DRR Provincial Quiz BeeShalzie Wezza Dico100% (3)
- What Is DRRMDocument21 pagesWhat Is DRRMKhim Murillo78% (9)
- RRL April13Document11 pagesRRL April13Noralden AminolahNo ratings yet
- 4 Infromation and Resources From Government (DRRM Projects and Programs)Document7 pages4 Infromation and Resources From Government (DRRM Projects and Programs)valerie venturaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk Reduction ManagemntDocument26 pagesDisaster Risk Reduction ManagemntGamer's GroundNo ratings yet
- Notre Dame of Dadiangas University Notre Dame of Kidapawan CollegeDocument16 pagesNotre Dame of Dadiangas University Notre Dame of Kidapawan CollegeJames Domini Lopez LabianoNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk Reduction ManagementDocument104 pagesDisaster Risk Reduction ManagementDray GarciaNo ratings yet
- Projected Population - 158,590 (As of 2011)Document19 pagesProjected Population - 158,590 (As of 2011)Cdrrmc DigosNo ratings yet
- Disaster Awareness, Preparedness and ManagementDocument18 pagesDisaster Awareness, Preparedness and Managementabby panesNo ratings yet
- DRRRDocument4 pagesDRRRسانو روديلNo ratings yet
- DRRR 1Document3 pagesDRRR 1Gwen Bess N. CacanindinNo ratings yet
- Big PictureDocument6 pagesBig PictureleviNo ratings yet
- Adapted From: HTTPS://WWW - Noaa.govDocument40 pagesAdapted From: HTTPS://WWW - Noaa.govKenken GenotivaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in NSTPDocument17 pagesReviewer in NSTPNicole Roshelle BumatayNo ratings yet
- Ew, Not Another Cfed ''Quiz''Document4 pagesEw, Not Another Cfed ''Quiz''Elektra WintourNo ratings yet
- The National MandateDocument27 pagesThe National MandateJairah AngueNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk Reduction and ManagementDocument13 pagesDisaster Risk Reduction and ManagementKin LeeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 DRRM Principles Trends TermsDocument28 pagesLesson 3 DRRM Principles Trends TermsLanz Sedrick PascuaNo ratings yet
- PDRRM Act of 2010Document14 pagesPDRRM Act of 2010JulianaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk Reduction - Learning MaterialDocument4 pagesDisaster Risk Reduction - Learning MaterialRaven BerzabalNo ratings yet
- NSTP Module For FinalDocument53 pagesNSTP Module For FinalAlliah BulanonNo ratings yet
- NSTP - Disaster Risk Reduction and Management ConceptsDocument23 pagesNSTP - Disaster Risk Reduction and Management ConceptsSilver Kobe PerezNo ratings yet
- Law & Disaster Management: Naved MustafaDocument12 pagesLaw & Disaster Management: Naved MustafaAzharNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For DRR Quiz BeeDocument2 pagesReviewer For DRR Quiz Bee「 」100% (1)
- Module 4 Emergency Preparedness and Response ManagementDocument18 pagesModule 4 Emergency Preparedness and Response ManagementMa. AlbinaNo ratings yet
- Key Players in Disaster Risk Reduction and Management: DR & RR 11Document3 pagesKey Players in Disaster Risk Reduction and Management: DR & RR 11jessafesalazarNo ratings yet
- Victorio - BSHM 2-4D - ExamDocument3 pagesVictorio - BSHM 2-4D - ExamMa. Veroncia VictorioNo ratings yet
- NSTP Common Module 3 - Disaster Awareness, Preparedness, and MangementDocument45 pagesNSTP Common Module 3 - Disaster Awareness, Preparedness, and MangementClarisse BenedictoNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Why Disaster Risk Reduction Is Important During and After EmergenciesDocument6 pages1.4 Why Disaster Risk Reduction Is Important During and After EmergenciesSK Tim RichardNo ratings yet
- Hazard and MitigationDocument14 pagesHazard and MitigationShiela SaangNo ratings yet
- DRRR CourseModule 3 4Document15 pagesDRRR CourseModule 3 4Mori OugaiNo ratings yet
- Idisaster Management: An OverviewDocument15 pagesIdisaster Management: An Overviewashish shahNo ratings yet
- DRRR Module 8 Concept of Disaster Risk Reduction and ManagementDocument22 pagesDRRR Module 8 Concept of Disaster Risk Reduction and ManagementJodie CabreraNo ratings yet
- Contingency Planning CP Guidebook 2016Document85 pagesContingency Planning CP Guidebook 2016Richell Grace Jamito PerezNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument36 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentPrijeesh Naduvalath100% (1)
- Republic Act 10121Document23 pagesRepublic Act 10121Zo ThelfNo ratings yet
- Philippines NDRRM Plan 2011-2028Document83 pagesPhilippines NDRRM Plan 2011-2028Therese Mae MadroneroNo ratings yet
- Governance - Info Kit 4 DRR - Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) and PreparednessDocument3 pagesGovernance - Info Kit 4 DRR - Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) and Preparednessjohn frits gerard mombayNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk ReductionDocument16 pagesDisaster Risk Reductionfashion20trendsNo ratings yet
- Policies of Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (DRRM) : Tammy Salome Berango-MolatoDocument65 pagesPolicies of Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (DRRM) : Tammy Salome Berango-MolatoEmmam LucanasNo ratings yet
- 05 DRRM Awareness Preparation and Management (Answer)Document40 pages05 DRRM Awareness Preparation and Management (Answer)Stanley George AlvaroNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk Reduction Managementgruop2Document20 pagesDisaster Risk Reduction Managementgruop2Erwin de JesusNo ratings yet
- Disaster ManagementDocument53 pagesDisaster ManagementVivek RanganathanNo ratings yet
- Policy Note - Understanding Risk in an Evolving WorldFrom EverandPolicy Note - Understanding Risk in an Evolving WorldNo ratings yet
- Module 1. E-BookDocument17 pagesModule 1. E-BookGold KnightNo ratings yet
- Sub Theme 6 AbstractDocument69 pagesSub Theme 6 AbstractDedi ApriadiNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk InfographicDocument1 pageDisaster Risk InfographicMa. Noeben L TorresNo ratings yet
- Ics Facility: PSJLC Class 2021-03 AlphaDocument2 pagesIcs Facility: PSJLC Class 2021-03 AlphaEvan SongahidNo ratings yet
- Kalalo Kian RDocument5 pagesKalalo Kian RYuri CaperareNo ratings yet
- Natural Disasters and Hazards Caused by Climate Change and Mitagation MeasuresDocument1 pageNatural Disasters and Hazards Caused by Climate Change and Mitagation MeasuresCiara BermejoNo ratings yet
- TV Brod Script Ihma Events July and AugustDocument7 pagesTV Brod Script Ihma Events July and AugustPatricia Angelyn DavidNo ratings yet
- Narrative On Fire Drill SY 2018-2019Document8 pagesNarrative On Fire Drill SY 2018-2019arlene rabanoNo ratings yet
- Vstep Reading Practice Test 9Document9 pagesVstep Reading Practice Test 9vananhhgmtNo ratings yet
- 7CE6-60.2 U3 L15-L20 BY Ranveer Singh GurjarDocument25 pages7CE6-60.2 U3 L15-L20 BY Ranveer Singh Gurjarapoorvasainimitrc2020No ratings yet
- ICS Form 203 TemplateDocument3 pagesICS Form 203 TemplateArlon Ryan ChavezNo ratings yet
- Recovery of LoveDocument1 pageRecovery of LoveClitz Myle Ochea YmbongNo ratings yet
- FLORES-Activities For Module 1Document4 pagesFLORES-Activities For Module 1Maureen FloresNo ratings yet
- Research Assignement Presentation1Document15 pagesResearch Assignement Presentation1habtamu fenta100% (1)
- 19 Disaster SurgeryDocument45 pages19 Disaster SurgeryAhmed noor Ahmed noorNo ratings yet
- Legend: Significant Earthquakes 2150 B.C. To 2010 Seismic Hazard (PGA, M/S)Document1 pageLegend: Significant Earthquakes 2150 B.C. To 2010 Seismic Hazard (PGA, M/S)peshoaNo ratings yet
- Geog Tectonic LormsDocument5 pagesGeog Tectonic LormscharNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 1: I. Phonetics Choose The Option Whose Stress Pattern Is Different From The Others'Document11 pagesPractice Test 1: I. Phonetics Choose The Option Whose Stress Pattern Is Different From The Others'11CV2-03- Lai Xuân BìnhNo ratings yet
- 8 Scientists From The Philippines: (Photo: Silliman University)Document3 pages8 Scientists From The Philippines: (Photo: Silliman University)Francoise PestanioNo ratings yet
- Bidang Keahlian Nautika (Ant-Iv) Tingkat OperasionalDocument7 pagesBidang Keahlian Nautika (Ant-Iv) Tingkat OperasionalJacky RikoNo ratings yet
- Contextualized Lesson Plan MIKEE CABANLIGDocument3 pagesContextualized Lesson Plan MIKEE CABANLIGJohn JumigNo ratings yet
- CDCS French Forein MinistryDocument36 pagesCDCS French Forein MinistryZakaria ABBIOUINo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Is Everyone's ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesCyber Security Is Everyone's ResponsibilityAtthulaiNo ratings yet
- The Physical Characteristics of Tropical Cyclones: Case Study: The 1970 Bhola CycloneDocument24 pagesThe Physical Characteristics of Tropical Cyclones: Case Study: The 1970 Bhola CycloneJovi AbabanNo ratings yet
- Office of The Municipal Mayor: Republic of The Philippines Province of Siquijor Municipality of Enrique VillanuevaDocument1 pageOffice of The Municipal Mayor: Republic of The Philippines Province of Siquijor Municipality of Enrique VillanuevaLuchiMel Dim PorscheNo ratings yet