Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Role and Status 01042021 111357am
Uploaded by
Muhammad Sarmad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views13 pagesOriginal Title
Role-and-Status-01042021-111357am
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views13 pagesRole and Status 01042021 111357am
Uploaded by
Muhammad SarmadCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
Role and Status
Outline
• Status and Role
• Role Set
• Role Conflict
• Role Strain
• Achieved and Ascribed status and role
• Socialization through role and status
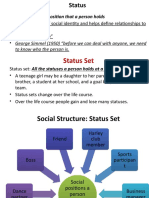
Status
• Ralph Linton (1936) defined status simply as a position in a
social system, such as child or parent.
• Status refers to what a person is, whereas the closely linked
notion of role refers to the behaviour expected of people in
a status.
According to sociologists, status describes the position a
person occupies in a particular setting.
We all occupy several statuses and play the roles that may be
associated with them.
Role
• A status carries with it a set of culturally defined rights and
duties, which sociologists call a role.
• The rights, obligations, and expected behavior
patterns associated with a particular social status.
• Duties and rights are complementary.
• A role is the set of norms, values, behaviors, and personality
characteristics attached to a status. An individual may
occupy the statuses of student, employee, and club
president and play one or more roles with each one.
Role Set
• The different roles attached to
a single status.
• Role set is the term used to
describe the variety of roles
and relationships you have as a
result of your status in society.
Role Conflict
• Occurs between two statuses when trying to fulfill expectations.
• Role conflict can take several different forms.
• Conflict may also occur when people disagree about what the expectations
are for a particular role or when someone simply has difficulty satisfying
expectations because their duties are unclear, too difficult, or disagreeable.
• Example: A working father is expected at work on time but is late because one
of his children is sick. His roles as father and employee are then in conflict. A role
for his father status dictates that he care for his sick child, while a role for his
employee status demands that he arrive at work on time.
Role Strain
• Occurs when a person has difficulty meeting the
role expectations of a single status.
Ascribed status and role
• Statuses and roles are of two sorts:
– Those ascribed to us by our society, irrespective of individual qualities or
efforts, and
– Those we achieve through our own efforts.
• Ascribed status -- assigned according to qualities beyond a person’s control.
– Ascription by Sex
– Ascription by Age
• Status of the Aged
Ascribed status and role
Baby
Aged
Prince
White & Female &
Black Race Male
Achieved status and role
• Acquired through individuals own
direct efforts.
• A social position which is secured
through individual choice and
competition is known as an achieved
status.
Achieved status and role
Socialization through role and status
• Each person must learn to fill roles as child, student, probably
husband or wife, parent, employee, organization member or officer,
member of a particular race and social class, citizen, resident of a
community, and many others.
• Role learning involves at least two aspects:
– We must learn to perform the duties and claim the privileges of
the role, and
– We must acquire the attitudes, feelings, and expectations
appropriate to the role.
• Role training for most of the important roles begins early in
childhood as one starts to from attitudes toward those roles and
statuses.
• Most of the training is painless and unconscious...
!
You might also like
- Status & RoleDocument8 pagesStatus & Role295Sangita PradhanNo ratings yet
- l2 Becoming Member of Society (Autosaved)Document34 pagesl2 Becoming Member of Society (Autosaved)Melody Grace DacubaNo ratings yet
- Enculturation and SocializationDocument52 pagesEnculturation and SocializationSunshine Garson100% (1)
- Performance AnxietyDocument30 pagesPerformance Anxietyhunghl9726No ratings yet
- UCSPDocument67 pagesUCSPFred MartNo ratings yet
- Authentic Happiness Martin SeligmanDocument6 pagesAuthentic Happiness Martin Seligmankanav gupta0% (1)
- Chapter 4 Lesson 1 Enculturation and SocializationDocument54 pagesChapter 4 Lesson 1 Enculturation and SocializationPrincess May Castillo RamosNo ratings yet
- Mark - Parkinson.phd How - To.master - Personality.questionnairesDocument109 pagesMark - Parkinson.phd How - To.master - Personality.questionnairesDagoDump100% (3)
- Research Proposal SampleDocument35 pagesResearch Proposal SampleKhalilahanum Zainal AbidinNo ratings yet
- Understanding Self-Concept: Dimensions, Components and DevelopmentDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Self-Concept: Dimensions, Components and DevelopmentBhuvanaNo ratings yet
- Enculturation/Socialization:: Statuses and RolesDocument64 pagesEnculturation/Socialization:: Statuses and RolesJai Cataluña100% (1)
- Spiritual Struggle Healing Spirit Fall 2008 PDFDocument4 pagesSpiritual Struggle Healing Spirit Fall 2008 PDFphone growthNo ratings yet
- Strain Theory: How Social Values Produce Deviance: Learning ObjectivesDocument3 pagesStrain Theory: How Social Values Produce Deviance: Learning ObjectivesEugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- HC Letter Templates 26jun13Document2 pagesHC Letter Templates 26jun13Jasdeep0% (1)
- Esmeralda Arana - The Path A Practical Approach To SorceryDocument180 pagesEsmeralda Arana - The Path A Practical Approach To Sorcerydimmo100% (1)
- Janet H. Carr, Roberta B. Shepherd - Stroke Rehabilitation - Guidelines For Exercise and Training To Optimize Motor Skill 2002Document314 pagesJanet H. Carr, Roberta B. Shepherd - Stroke Rehabilitation - Guidelines For Exercise and Training To Optimize Motor Skill 2002Patrícia Bragança100% (13)
- Role and Status SOCIOLOGYDocument23 pagesRole and Status SOCIOLOGYRouquia Manzoor71% (14)
- Role and StatusDocument24 pagesRole and StatusKiran VeerNo ratings yet
- Role and Status: Dr. Amita SharmaDocument10 pagesRole and Status: Dr. Amita SharmaCommunity ReminderNo ratings yet
- Social Status and Roles: Ascribed, Achieved, and Role ConflictDocument12 pagesSocial Status and Roles: Ascribed, Achieved, and Role ConflictAbhishek AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Social InteractionDocument30 pagesChapter 4 Social Interactiondewani mastaniNo ratings yet
- Social Structure-2Document16 pagesSocial Structure-2Saman Fatima100% (1)
- Each Person Has Several StatusesDocument9 pagesEach Person Has Several StatusestaeyeonunnieNo ratings yet
- Filipino Values and Status and Roles PDFDocument38 pagesFilipino Values and Status and Roles PDFCANo ratings yet
- Social Status & Social Role. Topic 3Document4 pagesSocial Status & Social Role. Topic 3Ahmed MujtabaNo ratings yet
- CHAP. 2. SOCIAL INTERACTION AND EVERYDAY LIFE. Macionis 15. C06 (Part2)Document14 pagesCHAP. 2. SOCIAL INTERACTION AND EVERYDAY LIFE. Macionis 15. C06 (Part2)Fyna BobNo ratings yet
- Roles and Status Full NotesDocument4 pagesRoles and Status Full NotesArchana Patwal100% (1)
- Enculturation o Socialization Statuses and RolesDocument4 pagesEnculturation o Socialization Statuses and RolesLui HorceradaNo ratings yet
- SociologyDocument10 pagesSociologyMohd Arham100% (1)
- Various Aspects of Role Imposed Upon An Individual in A GroupDocument8 pagesVarious Aspects of Role Imposed Upon An Individual in A GroupfenildgNo ratings yet
- Concept, Characteristics and Components of Social StructureDocument25 pagesConcept, Characteristics and Components of Social StructureAhmad AliNo ratings yet
- Social Status The Meaning Types Essential Elements and Characteristics of Social StatusDocument4 pagesSocial Status The Meaning Types Essential Elements and Characteristics of Social StatusPeter LostNo ratings yet
- Roles in our societyDocument7 pagesRoles in our societyAhmad YounisNo ratings yet
- Behavior - Status and RolesDocument16 pagesBehavior - Status and RolesDoreen MasikaNo ratings yet
- Roles and Statuses in SocietyDocument4 pagesRoles and Statuses in SocietyMarilyn Dizon100% (1)
- Status and RolesDocument2 pagesStatus and RolesTimothy EJERCITONo ratings yet
- chapter 5-1Document35 pageschapter 5-1hak202188No ratings yet
- Status and RoleDocument2 pagesStatus and RoleRiya TewatiaNo ratings yet
- 10. Unit (c) Status and Role (Part III)Document4 pages10. Unit (c) Status and Role (Part III)Vibha YadavNo ratings yet
- Mod 2Document27 pagesMod 2SREYANSH DEVNATH 2123544No ratings yet
- Central University of Kashmir: Role Is The Performance of Status. (Essay)Document16 pagesCentral University of Kashmir: Role Is The Performance of Status. (Essay)saqlainNo ratings yet
- Becoming A Member of SocietyDocument40 pagesBecoming A Member of SocietyPrince LancelotNo ratings yet
- Role (1) ChangeDocument8 pagesRole (1) ChangeAftab KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Social Structure - Section 1 - Building Blocks of Social StructureDocument10 pagesChapter 3 - Social Structure - Section 1 - Building Blocks of Social StructureBassem AdelNo ratings yet
- Definition and Determination of StatusDocument3 pagesDefinition and Determination of StatusBobby S. MathewNo ratings yet
- Meaning of RoleDocument9 pagesMeaning of Roleaman uppal100% (1)
- UcspDocument3 pagesUcspAudrei Zynth MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Concept of Social Group and Social OrganizationDocument15 pagesConcept of Social Group and Social OrganizationVhalyn Grace MissionNo ratings yet
- Social StructureDocument4 pagesSocial StructureechesavirginiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document32 pagesChapter 5Sifat ullah shah pakhtoonNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Philosophy of the Human PersonDocument13 pagesIntroduction to the Philosophy of the Human PersonMaria Angel RuizNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6: Socialization Structure and SocietyDocument25 pagesLesson 6: Socialization Structure and SocietyInsatiable CleeNo ratings yet
- Learn How Enculturation and Socialization Form IdentityDocument24 pagesLearn How Enculturation and Socialization Form IdentityAnne MoralesNo ratings yet
- Society and SocialisationDocument31 pagesSociety and SocialisationMarie Flore KikiNo ratings yet
- Status and RoleDocument4 pagesStatus and Rolearman.tiwari1804No ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document19 pagesLesson 5Dela Cruz, MariahNo ratings yet
- Social Structure Is The Framework ofDocument25 pagesSocial Structure Is The Framework ofAnam DaymaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Social InteractionDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Social Interactionarslan shahNo ratings yet
- Social StructureDocument11 pagesSocial StructureabbiecdefgNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Status and Role : 11.0 ObjectivesDocument13 pagesUnit 11 Status and Role : 11.0 ObjectivesSwayam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Status and RolesDocument3 pagesStatus and Rolestaeyeonunnie100% (1)
- Lecture 5 Social Status and RoleDocument19 pagesLecture 5 Social Status and Roleمہر علی رضاNo ratings yet
- Motivation NSUDocument14 pagesMotivation NSUmirza khan abantiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document18 pagesLecture 2Shakeel SheikhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document18 pagesLecture 2Shakeel SheikhNo ratings yet
- CH 4 SOC210 Powerpoint FA2020Document17 pagesCH 4 SOC210 Powerpoint FA2020janNo ratings yet
- Status Vs RoleDocument2 pagesStatus Vs RoleSama KunNo ratings yet
- Top Benefits Of Having An Impeccable Character With Fast Results To SuccessFrom EverandTop Benefits Of Having An Impeccable Character With Fast Results To SuccessNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Communication Theories 25042022 123242pmDocument5 pagesInterpersonal Communication Theories 25042022 123242pmMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Intercultural Communication 25042022 123426pmDocument9 pagesIntercultural Communication 25042022 123426pmMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Analyzing Business Markets 28102021 033530pmDocument27 pagesChapter 7 Analyzing Business Markets 28102021 033530pmMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Effective Presentation 31032022 011048pmDocument24 pagesEffective Presentation 31032022 011048pmMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Non Verbal FunctionsDocument6 pagesNon Verbal FunctionsMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04 22032021 110327amDocument44 pagesLecture 04 22032021 110327amMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 BUSINESS STATISTICS DANISH 10032021 102617amDocument29 pagesLec 2 BUSINESS STATISTICS DANISH 10032021 102617amMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 BUSINESS STATISTICS DANISH 24032021 103937amDocument20 pagesLec 4 BUSINESS STATISTICS DANISH 24032021 103937amMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Mankiw10e Lecture Slides Ch04Document43 pagesMankiw10e Lecture Slides Ch04Anggi YudhaNo ratings yet
- Personality and Development Part 2 28112020 092755pm 01062021 092133amDocument28 pagesPersonality and Development Part 2 28112020 092755pm 01062021 092133amMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Lec 7 BUSINESS STATISTICS DANISH 14042021 101646amDocument14 pagesLec 7 BUSINESS STATISTICS DANISH 14042021 101646amMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 BUSINESS STATISTICS DANISH 12042021 112105amDocument15 pagesLec 6 BUSINESS STATISTICS DANISH 12042021 112105amMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing Environment AnalysisDocument46 pagesPrinciples of Marketing Environment AnalysisWajahat AliNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 BUSINESS STATISTICS DANISH 17032021 094649amDocument31 pagesLec 3 BUSINESS STATISTICS DANISH 17032021 094649amMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Social Groups 01042021 111655amDocument15 pagesSocial Groups 01042021 111655amMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Social Stratification Edited 11022021 063946pm 10052021 113050pmDocument27 pagesSocial Stratification Edited 11022021 063946pm 10052021 113050pmMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 BUSINESS STATISTICS DANISH 03032021 042024pmDocument15 pagesLec 1 BUSINESS STATISTICS DANISH 03032021 042024pmMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - 3 CH 2 MGT History 22092020 031254pmDocument30 pagesWeek 2 - 3 CH 2 MGT History 22092020 031254pmMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Principles: of Marketing Global EditionDocument33 pagesPrinciples: of Marketing Global EditionWajahat AliNo ratings yet
- Week 8 CH 8 Strategic MGT 22092020 031704pmDocument33 pagesWeek 8 CH 8 Strategic MGT 22092020 031704pmMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Personality and Socializaton 28112020 092433pm 1 01062021 093016amDocument25 pagesPersonality and Socializaton 28112020 092433pm 1 01062021 093016amMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Member Function Same Name Void Return TypeDocument14 pagesMember Function Same Name Void Return TypeMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Culture A 01032023 094759am 03102023 023025pmDocument17 pagesCulture A 01032023 094759am 03102023 023025pmhuzaifaNo ratings yet
- 6Document15 pages6Muhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- CF 7 Operating SystemDocument22 pagesCF 7 Operating SystemMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- IT in Business Instructor: Kashif AbrarDocument67 pagesIT in Business Instructor: Kashif AbrarFarishtey ZahraNo ratings yet
- Lec-1 Intro To ThermodynamicsDocument37 pagesLec-1 Intro To ThermodynamicsMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Default ArgumentsDocument13 pagesDefault ArgumentsMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Symbol Means When Applied To Instances of A Class. This Gives TheDocument22 pagesSymbol Means When Applied To Instances of A Class. This Gives TheMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- AnthropologyDocument2 pagesAnthropologyErwil AgbonNo ratings yet
- Career Portfolio - Bacus Merianne Yvon NicoleiDocument9 pagesCareer Portfolio - Bacus Merianne Yvon Nicoleirose ynqueNo ratings yet
- FS 2Document49 pagesFS 2Theenz AnanayoNo ratings yet
- A Professional Growth Plan Incorporating The STP ProcessDocument3 pagesA Professional Growth Plan Incorporating The STP Processapi-538028309No ratings yet
- TC EC MIDTERM ReviewrDocument15 pagesTC EC MIDTERM ReviewrVictor S. Suratos Jr.No ratings yet
- Nasb Conference - Sup EvaluationDocument34 pagesNasb Conference - Sup Evaluationapi-32275271No ratings yet
- What Is Edtech June 13Document13 pagesWhat Is Edtech June 13api-258099577No ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional Purposes: Dizon, Dominador Jr. NDocument50 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional Purposes: Dizon, Dominador Jr. NMERIDIAN SEESNo ratings yet
- Workplace ethics and disputes guideDocument73 pagesWorkplace ethics and disputes guideKervie Jay Lachaona100% (1)
- The Reading Matrix Vol. 6, No. 1, April 2006Document16 pagesThe Reading Matrix Vol. 6, No. 1, April 2006Alicia GonzalezNo ratings yet
- AdeyemoDocument7 pagesAdeyemoPatricia Zavala GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- CPL Portfolio Components enDocument9 pagesCPL Portfolio Components enapi-343161223No ratings yet
- 1 Classroom Learning ProfileDocument2 pages1 Classroom Learning Profileapi-425043985No ratings yet
- Impact of Stress on Academic PerformanceDocument6 pagesImpact of Stress on Academic Performanceadrianpaul villenaNo ratings yet
- College of Teacher EducationDocument15 pagesCollege of Teacher EducationKesna Jhay EtcobanezNo ratings yet
- Elective 3 Training Design 2019 For StudentsDocument5 pagesElective 3 Training Design 2019 For StudentsNordielyn Bregoli Napoles BringuelaNo ratings yet
- Sense PerceptionDocument18 pagesSense PerceptionUrska AnumanchiNo ratings yet
- Mixed Anxiety and Depressive Disorder (MADDDocument14 pagesMixed Anxiety and Depressive Disorder (MADDMatthew MckenzieNo ratings yet
- Ibstpi-Idsurvey2015 WilliamsDocument7 pagesIbstpi-Idsurvey2015 Williamsapi-333100125No ratings yet
- Journal Club: Psychological Treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder: A Meta-AnalysisDocument19 pagesJournal Club: Psychological Treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder: A Meta-AnalysisRiley Jellal EllenNo ratings yet
- Abraham Maslow Popularized The Concept of SelfDocument4 pagesAbraham Maslow Popularized The Concept of SelfLamm ThongniNo ratings yet