Professional Documents
Culture Documents
E Waste Recycling For Malaysia
Uploaded by
linkin 11 park0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesBy 2020, Malaysia is estimated to generate 1,119,155 metric tons of e-waste annually. In 2014, 232,000 metric tons of e-waste was generated in Malaysia. The amount of global e-waste is projected to reach 690,827,529 metric tons between 2008-2020. Current e-waste recycling practices in Malaysia are limited and more advanced recycling methods are needed. The government aims to fully implement extended producer responsibility for e-waste by 2035 to improve recycling.
Original Description:
Original Title
e Waste Recycling for Malaysia
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBy 2020, Malaysia is estimated to generate 1,119,155 metric tons of e-waste annually. In 2014, 232,000 metric tons of e-waste was generated in Malaysia. The amount of global e-waste is projected to reach 690,827,529 metric tons between 2008-2020. Current e-waste recycling practices in Malaysia are limited and more advanced recycling methods are needed. The government aims to fully implement extended producer responsibility for e-waste by 2035 to improve recycling.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesE Waste Recycling For Malaysia
Uploaded by
linkin 11 parkBy 2020, Malaysia is estimated to generate 1,119,155 metric tons of e-waste annually. In 2014, 232,000 metric tons of e-waste was generated in Malaysia. The amount of global e-waste is projected to reach 690,827,529 metric tons between 2008-2020. Current e-waste recycling practices in Malaysia are limited and more advanced recycling methods are needed. The government aims to fully implement extended producer responsibility for e-waste by 2035 to improve recycling.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
For Malaysia
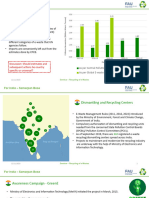
Generation of E-Waste
E-WASTE IN MALAYSIA
By year 2020, Malaysia were estimated to
generate 1,119,155 metric tons of e-waste.
• The StEP (Solving the E-waste Problem)
organization had published a data from 184
countries on e-waste generation.
• The latest amount recorded for generation
of e-waste in Malaysia for 2014 alone was
232,000 metric ton.
• The estimation of projected total with
690,827,529 metric ton of e-waste
generation by year 2008-2020
Discussion: How can we reduce the e-waste from
Personal computers?
17/03/2024 Seminar – Recycling of e-Wastes 1
For India – Samarpan Bose
Dismantling and Recycling Centers
• Based on the storage and production capacity of the
recovery facilities, every e-waste facility will be restricted by
an e-waste receiving quota set by the DOE. The online portal
eSWIS (2018) reported 119 facilities (by October 2018)
dealing with 36 are classified as full recovery facilities and
the remaining 77 are partial recovery facilities.
17/03/2024 Seminar – Recycling of e-Wastes 3
Government Legislation
E-waste management Stakeholders
• Manufacturers of electrical and electronic products
• Importers of electrical and electronic products (new and secondhand)
• Retailers of electrical and electronic products
• Local councils
• Charities and NGOs
• Consumers
• DOE licensed e-waste contractors
• Scrap collectors
• Department of Environment, Ministry of Natural Resources and the Environment
• National Solid Waste Management Department (NSWMD), Ministry of Housing and
Local Government Malaysia (MHLG)
E-waste recycling practices and
challenges
• Most of recovery facilities still limited to wet chemical processes,
electrolysis processes, air separation and thermal. Those all lacking
components need an urgent strategy and vast implementation in order
to tackle the e-waste issue.
• Full implementation of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) by
2035.
• The Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a strategy to promote
the integration of environmental cost in a way of extending the
producer’s responsibility to the post-consumer stage. It is involving the
entire lifecycle especially for take back, recycle and final disposal.
You might also like
- Field Project Bright Chibesa Kasongo 12NDocument16 pagesField Project Bright Chibesa Kasongo 12NCrazybunny2kNo ratings yet
- E WasteDocument25 pagesE Wasteanandpwaindeshkar86% (14)
- E Waste PPT GRP 1Document26 pagesE Waste PPT GRP 1Gurpreet Singh100% (1)
- E-Waste Management PPT V1Document12 pagesE-Waste Management PPT V1Biswajit Ghosh100% (1)
- E Waste ManagementDocument68 pagesE Waste ManagementJc GarciaNo ratings yet
- E-Waste Management in India: Kunal Verma Vasu MittalDocument37 pagesE-Waste Management in India: Kunal Verma Vasu MittalKunal VermaNo ratings yet
- Plastic Road PresentationDocument27 pagesPlastic Road PresentationRaaj ViraajNo ratings yet
- Sample E Waste Recycling BusinessDocument9 pagesSample E Waste Recycling BusinessBaddeti SyamNo ratings yet
- E-Waste Presentation For CollegesDocument20 pagesE-Waste Presentation For CollegesManjunaths GowdaNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument3 pagesProject ProposalJoenard Sadorra Cabael86% (43)
- Solid Waste Management PolicyDocument4 pagesSolid Waste Management PolicyJundell DiazNo ratings yet
- Waste to Energy in the Age of the Circular Economy: Best Practice HandbookFrom EverandWaste to Energy in the Age of the Circular Economy: Best Practice HandbookNo ratings yet
- E Waste Management - IndiaDocument17 pagesE Waste Management - IndiaAkhilesh Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Decarbonising End-use Sectors: Green Hydrogen CertificationFrom EverandDecarbonising End-use Sectors: Green Hydrogen CertificationNo ratings yet
- Why ISO 14001:2015? A Wareness Presentation: Subtitle or PresenterDocument16 pagesWhy ISO 14001:2015? A Wareness Presentation: Subtitle or PresenterTatiana Rilo100% (1)
- Green MarketingDocument25 pagesGreen MarketinggeetukumariNo ratings yet
- Best Practices On Electronic Scrap ManagementDocument28 pagesBest Practices On Electronic Scrap ManagementChinmay RoutNo ratings yet
- E-Waste Managemen in SingaporeDocument34 pagesE-Waste Managemen in SingaporeJanejira SereeyotinNo ratings yet
- EWasteDocument23 pagesEWastesurajsingh85% (20)
- Ready For Disposal in India: Over 2 Million Old PcsDocument25 pagesReady For Disposal in India: Over 2 Million Old Pcsasfdh5850No ratings yet
- Initial DataDocument7 pagesInitial Datalinkin 11 parkNo ratings yet
- Draft E-Waste Policy - Comments - VKS 13.4Document14 pagesDraft E-Waste Policy - Comments - VKS 13.4Paryavaran NamaNo ratings yet
- E-Waste Management Rules, 2015 - A Critical Analysis: January 2016Document5 pagesE-Waste Management Rules, 2015 - A Critical Analysis: January 2016Madhura AbhyankarNo ratings yet
- OverviewDocument40 pagesOverviewAvinash MishraNo ratings yet
- Handbook For Setting Up of An E-Waste Recycling FacilityDocument35 pagesHandbook For Setting Up of An E-Waste Recycling FacilitySachinSharmaNo ratings yet
- Project File: Electronic Waste Management in LpuDocument19 pagesProject File: Electronic Waste Management in Lpuswadhin pattnayakNo ratings yet
- E-Waste Management in India - Waste Management - IndiaDocument6 pagesE-Waste Management in India - Waste Management - IndiaIshitaNo ratings yet
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) K D Bhardwaj K D BhardwajDocument25 pagesExtended Producer Responsibility (EPR) K D Bhardwaj K D BhardwajRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- EwasteDocument9 pagesEwasteMichaelNo ratings yet
- EwasteDocument9 pagesEwasteKartika Bhuvaneswaran NairNo ratings yet
- EwasteDocument9 pagesEwasteRohitNo ratings yet
- E-Waste Notes For UPSC ExamDocument4 pagesE-Waste Notes For UPSC ExamDnyaneshwar ZambareNo ratings yet
- Best Practices and Innovative Approaches For Sustainable Waste ManagementDocument38 pagesBest Practices and Innovative Approaches For Sustainable Waste ManagementAbd RahmanNo ratings yet
- Collection of E-WasteDocument3 pagesCollection of E-WasteamitheserathinasamyNo ratings yet
- E WasteDocument25 pagesE Waste9915622484No ratings yet
- AsmaDocument27 pagesAsmakarthikgowda306090No ratings yet
- E-Waste Management in MalaysiaDocument16 pagesE-Waste Management in MalaysiaYusmadi J Mohamad0% (1)
- Blockchain-Based E-Waste Management in 5G Smart CommunitiesDocument6 pagesBlockchain-Based E-Waste Management in 5G Smart CommunitiesRahulNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id3352600Document32 pagesSSRN Id3352600mohil patelNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Towards E-WasteDocument13 pagesConsumer Behaviour Towards E-WasteAnubhav JainNo ratings yet
- Samsung India Electronics Pvt. LTD., - Approved EPR PlanDocument105 pagesSamsung India Electronics Pvt. LTD., - Approved EPR PlanRakesh JainNo ratings yet
- E-Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 2011Document18 pagesE-Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 2011Roshni Thammaiah0% (1)
- Irjet V6i479 PDFDocument4 pagesIrjet V6i479 PDFfathima melgoNo ratings yet
- E-Waste Management RulesDocument18 pagesE-Waste Management RulesNaveen Anilkumar NairNo ratings yet
- HCMC Waste Collection 2Document26 pagesHCMC Waste Collection 2Chad FreemanNo ratings yet
- E-Waste ManagementDocument6 pagesE-Waste Managementayushi vermaNo ratings yet
- 2018 - VIETNAM WTE - CountryPresentationDocument33 pages2018 - VIETNAM WTE - CountryPresentationLuong Thu HaNo ratings yet
- ArmDocument22 pagesArmHemanth XcienciaNo ratings yet
- E-Waste in India PresentationDocument4 pagesE-Waste in India PresentationAdri ChakraNo ratings yet
- Recycling Trends: Ecycling Leadership InitiativeDocument3 pagesRecycling Trends: Ecycling Leadership InitiativejohnribarNo ratings yet
- Electronic Waste: Presented by:-P.AkhilDocument13 pagesElectronic Waste: Presented by:-P.AkhilPalthi RahulNo ratings yet
- Status of E-Waste Management in India and Impact of Impending LegislationDocument29 pagesStatus of E-Waste Management in India and Impact of Impending LegislationrahulbafnaNo ratings yet
- Ex Sum-Web15Document10 pagesEx Sum-Web15vaashish7602No ratings yet
- E-Waste: An Indian PerspectiveDocument17 pagesE-Waste: An Indian PerspectivePrakash VijayvargiaNo ratings yet
- E-Waste: An Indian PerspectiveDocument17 pagesE-Waste: An Indian PerspectiveBalasubramaniNo ratings yet
- Epra PalnDocument31 pagesEpra PalnManish SadhuNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'EV10003-C9-E-waste-spr2023' With YouDocument17 pagesI Am Sharing 'EV10003-C9-E-waste-spr2023' With YouSaloni ShawNo ratings yet
- A Proposed Sustainable and Digital Collection and Classification Center Model To Manage E-Waste in Emerging EconomiesDocument25 pagesA Proposed Sustainable and Digital Collection and Classification Center Model To Manage E-Waste in Emerging EconomiesSara ArtangNo ratings yet
- EST MicroprojectDocument12 pagesEST MicroprojectRohan ChavanNo ratings yet
- E-Waste ManagementDocument3 pagesE-Waste ManagementAvnip SharmaNo ratings yet
- E WasteDocument27 pagesE WasteDelroy Sebastian AguiarNo ratings yet
- SA E-Waste ProfileDocument11 pagesSA E-Waste ProfileinfoNo ratings yet
- E-Waste LawDocument11 pagesE-Waste LawhaloangleNo ratings yet
- Electronic Waste Management in IndiaDocument3 pagesElectronic Waste Management in Indiamatrixrajiv34No ratings yet
- Offshore Algae CultivationDocument50 pagesOffshore Algae Cultivationlinkin 11 parkNo ratings yet
- GCM Eberswalde AG Policies EuropeDocument32 pagesGCM Eberswalde AG Policies Europelinkin 11 parkNo ratings yet
- 07sussefficientenergyfinal 190617201407Document11 pages07sussefficientenergyfinal 190617201407linkin 11 parkNo ratings yet
- Advanced Liquid Biofuels Synthesis: Adding Value To Biomass GasificationDocument91 pagesAdvanced Liquid Biofuels Synthesis: Adding Value To Biomass Gasificationlinkin 11 parkNo ratings yet
- Setiadi@che - Ui. Hasbila@eng - Ui.ac - Id: Makalah (Code KKR 09)Document33 pagesSetiadi@che - Ui. Hasbila@eng - Ui.ac - Id: Makalah (Code KKR 09)linkin 11 parkNo ratings yet
- Slowing Down The Deactivation of H ZSM 5Document46 pagesSlowing Down The Deactivation of H ZSM 5linkin 11 parkNo ratings yet
- Journal of Energy Chemistry: Youming Ni, Zhaopeng Liu, Peng Tian, Zhiyang Chen, Yi Fu, Wenliang Zhu, Zhongmin LiuDocument5 pagesJournal of Energy Chemistry: Youming Ni, Zhaopeng Liu, Peng Tian, Zhiyang Chen, Yi Fu, Wenliang Zhu, Zhongmin Liulinkin 11 parkNo ratings yet
- Methanol Marine July 2023Document32 pagesMethanol Marine July 2023linkin 11 parkNo ratings yet
- STUW HT 2016 Ward Weishaar Wilkison RuskowskyDocument105 pagesSTUW HT 2016 Ward Weishaar Wilkison Ruskowskylinkin 11 parkNo ratings yet
- Accepted ManuscriptDocument21 pagesAccepted Manuscriptlinkin 11 parkNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Methanol To Hydrocarbons oDocument13 pagesConversion of Methanol To Hydrocarbons olinkin 11 parkNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 11 Trends Biopolymers and Profitability Recycling - 100723Document26 pagesLecture - 11 Trends Biopolymers and Profitability Recycling - 100723linkin 11 parkNo ratings yet
- Initial DataDocument7 pagesInitial Datalinkin 11 parkNo ratings yet
- Cite 201900108Document17 pagesCite 201900108linkin 11 parkNo ratings yet
- Samarpan For IndiaDocument5 pagesSamarpan For Indialinkin 11 parkNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris DialogDocument4 pagesBahasa Inggris Dialogemerald edoNo ratings yet
- Corporate Social Responsibility Project ProposalDocument15 pagesCorporate Social Responsibility Project ProposalAngelika PanilagNo ratings yet
- Presented By:: Rajvardhan Rishi (Setb137) Nikhil (Setb103) Arjun Mandge (Setb138) DIPAK (SETB105) Shivshankar (Setb114)Document22 pagesPresented By:: Rajvardhan Rishi (Setb137) Nikhil (Setb103) Arjun Mandge (Setb138) DIPAK (SETB105) Shivshankar (Setb114)Atul UttamNo ratings yet
- Virtual Lab-Water QualityDocument5 pagesVirtual Lab-Water Qualityapi-267050298No ratings yet
- DANO (Recycling)Document60 pagesDANO (Recycling)John Timothy LapinigNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Forestry Under Changing ClimateDocument2 pagesSustainable Forestry Under Changing ClimateMahendra paudel PaudelNo ratings yet
- Letter To EngrDocument5 pagesLetter To EngrMeycauayan DialysisNo ratings yet
- Presentation With LGUsDocument25 pagesPresentation With LGUsJohn Marc LanzaroteNo ratings yet
- TCW Module 14 The Global Food SecurityDocument5 pagesTCW Module 14 The Global Food SecuritySamantha SmithNo ratings yet
- Ways To Prevent Air PollutionDocument2 pagesWays To Prevent Air PollutionTrinidad, Gwen StefaniNo ratings yet
- Toxic RhetoricDocument1 pageToxic RhetoricAkmalZintZoNo ratings yet
- Elements of Spatial Disorder: Apostol Dillera Esguerra Dolorito MundinDocument10 pagesElements of Spatial Disorder: Apostol Dillera Esguerra Dolorito MundinJC DoloritoNo ratings yet
- Wake Up To Climate Change: Feature WritingDocument2 pagesWake Up To Climate Change: Feature Writingً SEONPREMACYNo ratings yet
- Plastic in The World's Oceans Set To Triple Over Next Decade Quick QuestionsDocument2 pagesPlastic in The World's Oceans Set To Triple Over Next Decade Quick QuestionsPaula AyalaNo ratings yet
- Modular Aftertreatment System BrochureDocument4 pagesModular Aftertreatment System BrochureSalatyelNo ratings yet
- Revise Concept PaperDocument6 pagesRevise Concept PaperJoshua BermoyNo ratings yet
- Implementing Rules and Regulation of The Philippine Clean Air Act of 1999Document4 pagesImplementing Rules and Regulation of The Philippine Clean Air Act of 1999Gian Mhyco GambaNo ratings yet
- Coastal Regulation ZoneDocument8 pagesCoastal Regulation ZoneSaran T SNo ratings yet
- BACKGROUND OF THE STUDYDocument10 pagesBACKGROUND OF THE STUDYJohn Mark AdorzaNo ratings yet
- Android RecyclerviewDocument10 pagesAndroid Recyclerviewhunterdii9879No ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Human-Environment SystemDocument3 pagesLesson 7 - Human-Environment SystemAgatha Guevan PunzalNo ratings yet
- Why Should We Stop DeforestationDocument3 pagesWhy Should We Stop Deforestationbestjungthongdee0% (1)
- Feu Reflection Paper Format1Document5 pagesFeu Reflection Paper Format1Arly Tabarrejo0% (1)
- School of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering, Uitm Shah AlamDocument5 pagesSchool of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering, Uitm Shah AlamaleepphNo ratings yet
- E-Waste ManagementDocument6 pagesE-Waste Managementayushi vermaNo ratings yet