Professional Documents
Culture Documents
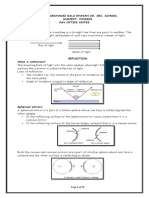
Total Internal Reflection
Uploaded by
abdallah2006ahmed690 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views12 pagesOriginal Title
ph 3.06
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views12 pagesTotal Internal Reflection
Uploaded by
abdallah2006ahmed69Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
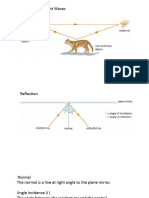
Total Internal Reflection
• Diagram 1 – light is refracted.
• Diagram 2 – Light is refracted at 900, the angle of
incidence in this case is called the critical angle, Θc
• Diagram 3 – Any angle bigger than the critical angle
will show Total Internal Reflection
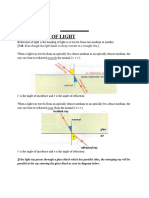
The Critical Angle
• The critical angle,Θc is the angle of
incidence when the angle of refraction is
900.
• It is the smallest angle of incidence above
which Total Internal Reflection occurs. It
is often given the symbol, Θc
Total Internal Reflection
• Takes place when all of a light ray is completely
reflected and none of it is refracted.
• This takes place at angles above the critical angle,
Θc
Uses of Total Internal Reflection
• Total internal reflection is used to send
light signals along optical fibres.
• This can be used to send
telecommunications such as internet, TV
and phone.
• This is how Virgin Media provide their
services.
2008 Qu: 16
2002 Qu: 27
Reflector Telescope
• Parabolic mirror:
• We used parabolic mirror instead of concave mirror is due
to Correction of Spherical Aberration. Spherical aberration
occurs when parallel rays of light incident on a spherical
mirror do not converge to a single focal point. Instead,
different rays focus at different points, resulting in a blurred
image. Parabolic mirrors, with their specific curvature, are
designed to minimize spherical aberration, ensuring that all
parallel rays converge at the same focal point
•
• Reflector telescopes are often used instead of
refractor telescope for several reasons:
• Chromatic aberration: Reflectors typically exhibit less
chromatic aberration compared to refractors. Chromatic
aberration is a phenomenon where different colors of light
come to focus at different points, causing color fringing in the
observed image. Reflectors do not suffer from chromatic
aberration because mirrors reflect all colors of light in the
same way.
You might also like
- 5.applications of TIRDocument4 pages5.applications of TIRnwvzdpmms6No ratings yet
- LightDocument17 pagesLightHunterNo ratings yet
- LightDocument23 pagesLightAmmar AdnanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 - Light & OpticsDocument39 pagesLecture 13 - Light & OpticsPhilip Cedric DolorNo ratings yet
- Basic Optics For Photogrammetry: Janak Raj JoshiDocument32 pagesBasic Optics For Photogrammetry: Janak Raj JoshiAshish ChaliseNo ratings yet
- Lesson 02-MSE 363 - 2023 - 01 - 31 - OMDocument68 pagesLesson 02-MSE 363 - 2023 - 01 - 31 - OMRONALDNo ratings yet
- Reflection & RefractionDocument50 pagesReflection & Refractionannette.geesiawan1No ratings yet
- LIGHT FinalDocument32 pagesLIGHT Finalehan.ilrnestersNo ratings yet
- Class 2 PPT 3 Unit 1Document53 pagesClass 2 PPT 3 Unit 1ece Ms.G.BhargaviNo ratings yet
- Uee - 51Document13 pagesUee - 51Nandini PerlaNo ratings yet
- Lec 25Document31 pagesLec 25Tika NuraeniNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics: Refraction of LightDocument51 pagesRay Optics: Refraction of LightAbishek ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Optical InstrumentsDocument30 pagesOptical InstrumentsSAWATI KUMARINo ratings yet
- Optical InstrumentsDocument30 pagesOptical InstrumentsSAWATI KUMARI100% (1)
- Ray Optics NotesDocument35 pagesRay Optics NotesNarenNo ratings yet
- HPH103 - Waves and Optics 1 - Lecture # 10-1Document45 pagesHPH103 - Waves and Optics 1 - Lecture # 10-1Praise NehumambiNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Moradabad: Science ProjectDocument103 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Moradabad: Science ProjectRishi Bhatia100% (1)
- Light and Mirror GRADE 10Document44 pagesLight and Mirror GRADE 10kimarie kinmon100% (1)
- Optical TelescopeDocument30 pagesOptical TelescopeAbdul Rasyid ZakariaNo ratings yet
- WP2 Light Waves (SDA) 2Document11 pagesWP2 Light Waves (SDA) 2matsweamogelang89No ratings yet
- WP4 Light WavesDocument16 pagesWP4 Light Waveswarona letangNo ratings yet
- Physics Light Waves SanowarDocument11 pagesPhysics Light Waves SanowarMin HanbyeolNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument5 pagesSciencephilipNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Denzel G. Armelon Gen. ScienceDocument50 pagesPrepared By: Denzel G. Armelon Gen. ScienceJohn andre MarianoNo ratings yet
- Light - 3 G8 23-24Document57 pagesLight - 3 G8 23-24hassanaayan03No ratings yet
- LIGHT FinalDocument31 pagesLIGHT FinalyourmoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 1 PDFNama Desalew100% (1)
- L 30 Light and Optics - 2: - Measurements of The Speed of Light (C) - Index of Refraction V C/NDocument22 pagesL 30 Light and Optics - 2: - Measurements of The Speed of Light (C) - Index of Refraction V C/NMohamed AliNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1581407485099Document15 pagesOrca Share Media1581407485099EmmanNo ratings yet
- Calculations and Designs of Lighting Scheme PDFDocument12 pagesCalculations and Designs of Lighting Scheme PDFAzmeraw Zedebre WorkNo ratings yet
- 10 SC Phy LightDocument7 pages10 SC Phy LightAjay AnandNo ratings yet
- Total Internal ReflectionDocument24 pagesTotal Internal ReflectionasyiqqinNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument27 pagesRay Optics and Optical InstrumentsChikchikchat ChatNo ratings yet
- B S - 2 Unit - 2Document49 pagesB S - 2 Unit - 2Minhaj KNo ratings yet
- NS 6145 Laser and LightDocument69 pagesNS 6145 Laser and LightMeesixNo ratings yet
- Refraction and Snell's LawDocument41 pagesRefraction and Snell's LawTJPlayzNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Geometrical Optics UpdatedDocument40 pagesCHAPTER 7 Geometrical Optics UpdatedPriyaa JayasankarNo ratings yet
- Study of Light 2Document13 pagesStudy of Light 2Shrihari DholeNo ratings yet
- Illumination FinalDocument26 pagesIllumination FinalAysha Akter UrmiNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction 2Document63 pagesReflection and Refraction 2Alaa Asim OsmanNo ratings yet
- Illumination 2k17Document88 pagesIllumination 2k17M. kashif karimNo ratings yet
- Light PUREDocument9 pagesLight PUREtalithaonkabetse723No ratings yet
- Light &small Telescopes - StudentDocument42 pagesLight &small Telescopes - StudentadammendozaNo ratings yet
- Physics - Light: Notes and StuffsDocument42 pagesPhysics - Light: Notes and StuffsSijabuliso SibandaNo ratings yet
- CH12 PPT 1Document49 pagesCH12 PPT 1kaungforgameNo ratings yet
- Lightingarchitecturelecture 3 150526062406 Lva1 App6892 PDFDocument11 pagesLightingarchitecturelecture 3 150526062406 Lva1 App6892 PDFGreenNo ratings yet
- Lightingarchitecturelecture 3 150526062406 Lva1 App6892 PDFDocument11 pagesLightingarchitecturelecture 3 150526062406 Lva1 App6892 PDFGreenNo ratings yet
- Microscopes - Rapid Review ProgrammeDocument62 pagesMicroscopes - Rapid Review Programmesharada thiagarajanNo ratings yet
- PropogationoflightDocument33 pagesPropogationoflightShorya SharmaNo ratings yet
- IlluminationDocument45 pagesIlluminationFemi PrinceNo ratings yet
- LIGHT Power Point PresentationDocument34 pagesLIGHT Power Point Presentationmuhammad umair100% (1)
- LIGHT - Light i-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesLIGHT - Light i-WPS OfficeUtsav BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Pengenalan Teleskop Kursus Ilmu Falak OIFDocument42 pagesPengenalan Teleskop Kursus Ilmu Falak OIFHariyadi D. PutragaNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of Light: By: Fajri Mohammed Ophthalmology Resident (R1) JUDO Oct.2021Document61 pagesReflection and Refraction of Light: By: Fajri Mohammed Ophthalmology Resident (R1) JUDO Oct.2021abo kooNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Fundamentals - Machine VisionDocument62 pagesDigital Image Fundamentals - Machine VisionDr. Ajay M PatelNo ratings yet
- Light - Free Exam AcademyDocument20 pagesLight - Free Exam AcademysinojiayogNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument56 pagesOpticsahsan shahNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument36 pagesReflection and Refraction of LightJowee Andrei ClemenoNo ratings yet
- Nota Light - Total Internal ReflectionDocument26 pagesNota Light - Total Internal ReflectionmaiyaaNo ratings yet