Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4th Grade Sound
Uploaded by
maryjean.sacay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views12 pagesSound is a form of energy that travels through air or other mediums in the form of vibrations. The pitch of a sound depends on its frequency or vibrations per second, while the loudness depends on its intensity or amount of energy. For sound to be heard, it must travel through a medium like air or water by causing the particles in the medium to vibrate as the sound wave passes through. The speed of sound depends on properties of the medium like its elasticity and temperature. Humans use sound for communication through speech and listening.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSound is a form of energy that travels through air or other mediums in the form of vibrations. The pitch of a sound depends on its frequency or vibrations per second, while the loudness depends on its intensity or amount of energy. For sound to be heard, it must travel through a medium like air or water by causing the particles in the medium to vibrate as the sound wave passes through. The speed of sound depends on properties of the medium like its elasticity and temperature. Humans use sound for communication through speech and listening.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views12 pages4th Grade Sound
Uploaded by
maryjean.sacaySound is a form of energy that travels through air or other mediums in the form of vibrations. The pitch of a sound depends on its frequency or vibrations per second, while the loudness depends on its intensity or amount of energy. For sound to be heard, it must travel through a medium like air or water by causing the particles in the medium to vibrate as the sound wave passes through. The speed of sound depends on properties of the medium like its elasticity and temperature. Humans use sound for communication through speech and listening.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
WHAT IS SOUND?
A form of energy that travels
through the air.
WHAT IS SOUND?
• Sound is made when something
vibrates.
• Sound needs a medium to travel.
• The loudness of a sound is called
volume.
Intensity:The amount of energy that flows through
a certain area in a specific amount of time
• Louder sound waves carry more
energy
• Intensity decreases as distance
increases.
WHAT IS PITCH?
• The pitch of a sound is how high or
low it is.
• A sound with a high frequency has a
high pitch.
• Frequency is the number
of vibrations per second.
HOW IS SOUND TRANSMITTED?
Transmission of sound requires
matter (air, liquids, solids) as
transmitting medium, unlike light
which can travel through matter
and space.
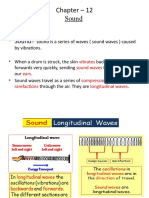
HOW SOUND TRAVELS
• Sound waves carry energy through
a medium without moving particles
of the medium along
• Each particle of the medium
vibrates as the disturbance passes.
• When the disturbance passes your
ear you hear the sound
• A common medium for sound is air,
but sound can travel through many
other mediums
Speed of Sound: Elasticity
• The more elastic the medium, the faster sound
travels
– Sound travels well in solids because they are usually
more elastic
• Particles of solids do not move very far , so they bounce
back and forth very quickly as the compressions and
rarefaction of the sound waves pass
– Most liquids are not very elastic and sound does not
travel well
– Sound travels very slowly in gases because gases are
not very elastic
Speed of Sound: Temperature
• Sound travels more slowly at lower
temperatures than at higher temperatures
– This is because at low temperatures, the
particles of the medium move more slowly
– At low temperatures the particles are
harder to move and return to their original
positions more slowly.
• Example: @ 20ᵒC 343 m/s
@ 0ᵒC 330 m/s
HOW DO WE USE SOUND?
• For human beings, sound is one of the most
important ways to communicate by:
• expressing himself through speech
• obtaining information through listening
• obtaining stimulation (music)
WHAT IS SOUND?
The tools of information exchange through
sound are:
Throat: vocal cords for producing and
modulating speech sounds
Ear: for listening and analyzing sounds
HOW DO YOU MAKE SOUND?
• You force air up through your voice box,
or larynx
• Your larynx consists of two folds of tissue
called vocal chords (like guitar strings)
You might also like
- Mechanical Waves and Sound Powerpoint NotesDocument54 pagesMechanical Waves and Sound Powerpoint NotesRGDayanan100% (2)
- 4 - 5 - 03 Sounds and Pitches PowerPointDocument8 pages4 - 5 - 03 Sounds and Pitches PowerPointKalpana Saravana Kumar100% (1)
- SoundDocument28 pagesSoundKunal100% (1)
- Grade 8Document5 pagesGrade 8edwin dumopoyNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Notes Grade 8Document22 pagesModule 4 Notes Grade 8Jenny JuanitezNo ratings yet
- Acoustics - Module 1Document40 pagesAcoustics - Module 1Ashna AshrafNo ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument17 pagesSound WavesArebeeJayBelloNo ratings yet
- Investigating The Properties of SoundDocument15 pagesInvestigating The Properties of SoundMaria Rosalia B. ApostolNo ratings yet
- Sound Notes With Q&A VIIIDocument12 pagesSound Notes With Q&A VIIISatwikNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument6 pagesSoundJijo P SebastianNo ratings yet
- SoundsDocument15 pagesSoundsISMAILA UMARNo ratings yet
- PWSUNP193420220927111318062sound Waves-2Document20 pagesPWSUNP193420220927111318062sound Waves-2rishit.yadav1102No ratings yet
- Science Grade 5-Lessons 5 & 6 Light & Sound EnergyDocument48 pagesScience Grade 5-Lessons 5 & 6 Light & Sound Energyclyde domingoNo ratings yet
- SoundsDocument19 pagesSoundsmonasteriomatthew7No ratings yet
- Sound Waves:: A Mechanical WaveDocument37 pagesSound Waves:: A Mechanical WaveL.A. Ly GualbertoNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument23 pagesSoundSahat Rein Jeremay PardedeNo ratings yet
- Light Sound Compression and RarefactionDocument10 pagesLight Sound Compression and RarefactionShadyNo ratings yet
- Sound 2nd JanDocument43 pagesSound 2nd JanKashish TilokaniNo ratings yet
- Light PresentationDocument63 pagesLight PresentationJylle Vernie HembraNo ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument15 pagesSound WavesKate BarneyNo ratings yet
- Sound: Third Year ScienceDocument23 pagesSound: Third Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Types of Waves, Production and Propagation of Sound WavesDocument7 pagesTypes of Waves, Production and Propagation of Sound WavesDorego TaofeeqNo ratings yet
- 4 - 5 - 03 Sounds and Pitches PowerPointDocument10 pages4 - 5 - 03 Sounds and Pitches PowerPointlinaNo ratings yet
- High Pitch Low PitchDocument2 pagesHigh Pitch Low PitchLovieAlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Informazione Multimediale - Audio - : Lecture 1: Sound & Digital AudioDocument52 pagesInformazione Multimediale - Audio - : Lecture 1: Sound & Digital AudioMichele FioriNo ratings yet
- Ound NotesDocument5 pagesOund Notesmokshithakapoor657No ratings yet
- Properties of SoundDocument14 pagesProperties of SoundJhon Michael Cadajas RinoNo ratings yet
- Sound: PPT Prepared By: Richa SethDocument50 pagesSound: PPT Prepared By: Richa SethPranati Sharma100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Sound WavesDocument30 pagesChapter 10 Sound Wavesg-32347797No ratings yet
- Science 8 - SoundDocument30 pagesScience 8 - SoundClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- Science of Sound-Unit1Document45 pagesScience of Sound-Unit1Nivedita Teja GadamsettyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Sound WaveDocument27 pagesLesson 4 - Sound WaveElijah AlcorezaNo ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument36 pagesSound Wavesmistymint.crewneticNo ratings yet
- Sound PPT - 1Document14 pagesSound PPT - 1prabhavkalsiNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Sound Energy Through VibrationDocument1 pageTransfer of Sound Energy Through VibrationWEI SHANGLI STANLEY NGAINo ratings yet
- Acoustic Sound and Human EarDocument26 pagesAcoustic Sound and Human EarEmmanuel EhuronNo ratings yet
- What Is Sound and How Does It Travel?: Difference Between Music and NoiseDocument2 pagesWhat Is Sound and How Does It Travel?: Difference Between Music and NoiseMushtaq MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Hearing Sound: by Denise CarrollDocument41 pagesHearing Sound: by Denise CarrollarlikaNo ratings yet
- Science 2Document37 pagesScience 2Hannah Leigh CoronelNo ratings yet
- S9 - SoundDocument7 pagesS9 - SoundKhushwant NagpalNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Theory of SoundDocument20 pagesIntroduction and Theory of SoundAditha Varma RajaNo ratings yet
- Something About Sound Wave: Hui LeiDocument19 pagesSomething About Sound Wave: Hui Leimohan raoNo ratings yet
- EsII - Lec-Sound (I)Document25 pagesEsII - Lec-Sound (I)Hadiqa ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- Acoustics 1 (Sound Theory)Document21 pagesAcoustics 1 (Sound Theory)bishal dasNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument7 pagesSoundShanto NiceschoolNo ratings yet
- SOUND PROPjxjDocument15 pagesSOUND PROPjxjFlorenda OpdiNo ratings yet
- ch16 Sec1 RCDocument25 pagesch16 Sec1 RCXavier Santos RamosNo ratings yet
- SOUNDDocument22 pagesSOUNDJhazrie GuzmanNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument4 pagesSoundmahammalik20142023No ratings yet
- Art Integration ProjectDocument14 pagesArt Integration Projectkislay kathuriaNo ratings yet
- SOUND - Reporting (Science 5)Document8 pagesSOUND - Reporting (Science 5)Alexa Kyle R. CabunocNo ratings yet
- Sound 8Document10 pagesSound 8Shanto NiceschoolNo ratings yet
- Hearing 1Document42 pagesHearing 1Gillian CoreyNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 15 SoundDocument25 pagesChapter - 15 SounddigamberNo ratings yet
- Propagation-of-Sound-Waves 2Document4 pagesPropagation-of-Sound-Waves 2Piyush RoyNo ratings yet
- Properties of SoundDocument25 pagesProperties of SoundManongdo AllanNo ratings yet
- Vibrations & Waves & Sound: - "A Periodic Motion of The Particles of AnDocument20 pagesVibrations & Waves & Sound: - "A Periodic Motion of The Particles of Anapi-19920724No ratings yet
- Laws of Reflection OfsoundDocument17 pagesLaws of Reflection OfsoundCharukesh SNo ratings yet
- Unit 16, SoundDocument29 pagesUnit 16, Soundaaronharper112No ratings yet
- CH 12Document21 pagesCH 12Nancy GiriNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer OperationsDocument10 pagesHeat Transfer OperationsShafique AhmedNo ratings yet
- Melting Boiling Condensation SolidificationDocument12 pagesMelting Boiling Condensation Solidificationsalmanismart123No ratings yet
- Chap 10Document31 pagesChap 10bettieboomNo ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument6 pagesRankine Cyclesbmmla100% (1)
- Thermodynamic Cycle, Gas Turbine, Turbo-Super ChargerDocument30 pagesThermodynamic Cycle, Gas Turbine, Turbo-Super ChargerTamim Islam JoyNo ratings yet
- (08.03.2021) - OBJ - XII - INT - REV - P - Modern pHYDocument17 pages(08.03.2021) - OBJ - XII - INT - REV - P - Modern pHYAbhinav SMNo ratings yet
- Hanoi University of Science and Technology - Advanced Programs - Physics Homework 1. 4 PDocument8 pagesHanoi University of Science and Technology - Advanced Programs - Physics Homework 1. 4 PDương Nguyễn MạnhNo ratings yet
- Ch.1-4, Thermal Resistance NetworkDocument15 pagesCh.1-4, Thermal Resistance NetworkBilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- PHY 121 9 - Standing WavesDocument26 pagesPHY 121 9 - Standing WavesChristopher NdamboNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument54 pagesElectromagnetic WavesjosephrandalldeiparineNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer From A Hot Moving CylinderDocument13 pagesHeat Transfer From A Hot Moving CylinderfabioNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics All DerivationsDocument8 pagesThermodynamics All Derivationsanuragrabha99No ratings yet
- (PHYSICS) Chapterwise Question BankDocument7 pages(PHYSICS) Chapterwise Question BankHariharan NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Es Final Exam Set A AnswerDocument20 pagesEs Final Exam Set A AnswerjohnjabarajNo ratings yet
- PHY103 Course Outline and ScheduleDocument1 pagePHY103 Course Outline and ScheduleVAILA OBYNo ratings yet
- Natural ConvectionDocument7 pagesNatural ConvectionLuthfy AditiarNo ratings yet
- Problem 12-26Document2 pagesProblem 12-26Amelia SantosNo ratings yet
- Cir PDFDocument9 pagesCir PDFahoaseoNo ratings yet
- 05 Thermal Energy Transfer NotesDocument48 pages05 Thermal Energy Transfer Notesapi-262878413No ratings yet
- Brayton Cycle: Submitted byDocument8 pagesBrayton Cycle: Submitted byاحمد الريسNo ratings yet
- Seatwork No. 1Document4 pagesSeatwork No. 1YouNo ratings yet
- Sound Is A Mechanical Wave VF 123Document2 pagesSound Is A Mechanical Wave VF 123Hamza AalloucheNo ratings yet
- Transport Phenomena: CHE411ADocument2 pagesTransport Phenomena: CHE411AonyxNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Rajput PDFDocument919 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Rajput PDFSugat DhoneNo ratings yet
- Icse Std. X: Karnataka Icse Schools Association Preparatory Examination 2024Document15 pagesIcse Std. X: Karnataka Icse Schools Association Preparatory Examination 2024Shardul GhuleNo ratings yet
- Mechanical work: Δw=F Δx=P A Δx=Pδv (P=F/A)Document35 pagesMechanical work: Δw=F Δx=P A Δx=Pδv (P=F/A)Hemida Hamed Hemida MohammedNo ratings yet
- Microplan Sound LessonDocument3 pagesMicroplan Sound LessonMani RohitNo ratings yet
- AQA Trilogy Unit 6.6: Waves and Electromagnetic Waves - Foundation A 1 F I CDocument8 pagesAQA Trilogy Unit 6.6: Waves and Electromagnetic Waves - Foundation A 1 F I CStudent TrialNo ratings yet
- Sam Prince Franklin - 20MIS1115 - Physics Lab 9Document7 pagesSam Prince Franklin - 20MIS1115 - Physics Lab 9Sam100% (1)