Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Comgas
Uploaded by
Philip Anthony Masilang0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesOriginal Title
comgas
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesComgas
Uploaded by
Philip Anthony MasilangCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
PROXIMATE AND ULTIMATE ANALYSIS – SAMPLE FOR GASEOUS FUELS
Thermodynamic Cycle which uses gaseous fuel is the Brayton Cycle.
Shown below is the schematic diagram for the Brayton Cycle
Source: Gas Turbine Engineering Handbook 2nd Edition - Meherwan P Boyce, 2002
Source: Siemens AG, 2018
Sample properties of natural gas, consider 254% excess air.
Component Chemical % by Volume
Formula
Methane CH4 90.28
Ethane C2H6 2.77
Propane C3H8 2.42
Carbon Dioxide CO2 3.79
Nitrogen N2 0.74
Total 100
Combustion Analysis on the sample properties of
Natural Gas
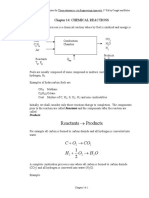
Ultimate Analysis Reactants Product of Combustion
Methane(CH4) = 90.28 % CH4 + 2 02 CO2 + 2 H2O
Ethane (C2H6) = 2.77 % C2H6 + 3.5 O2 2 CO2 + 3 H2O
Propane (C3H8) = 2.42 % C3H8 + 5 O2 3 CO2 + 4 H2O
Air Fuel Ratio
Theoretical Air Fuel Ratio
Actual Air Fuel Ratio
Flue Gas Computation for Natural Gas
• Volume of Nitrogen (N2)
• Volume of Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
• Volume of Water (H2O)
Theoretical Flue gas-fuel ratio
Actual Flue gas-fuel ratio
You might also like
- Synthetic Natural Gas: From Coal, Dry Biomass, and Power-to-Gas ApplicationsFrom EverandSynthetic Natural Gas: From Coal, Dry Biomass, and Power-to-Gas ApplicationsTilman J. SchildhauerNo ratings yet
- CombustionDocument78 pagesCombustionhansley100% (1)
- Combustion Engineering - Topic 1-4Document8 pagesCombustion Engineering - Topic 1-4JosafatNo ratings yet
- Combustion 2222222222222222222Document47 pagesCombustion 2222222222222222222Habtamu Tkubet Ebuy100% (1)
- COMBUSTION2222222222222222222Document47 pagesCOMBUSTION2222222222222222222Habtamu Tkubet EbuyNo ratings yet
- L36 - Combustion ReactionsDocument25 pagesL36 - Combustion ReactionsĐặng Tấn PhátNo ratings yet
- Gasoline: US Gallon 115,000 Btu 121 MJ 32 MJ/liter (LHV) - HHV 125,000 Btu/gallon 132 MJ/gallon 35 MJ/literDocument12 pagesGasoline: US Gallon 115,000 Btu 121 MJ 32 MJ/liter (LHV) - HHV 125,000 Btu/gallon 132 MJ/gallon 35 MJ/literHarryBouterNo ratings yet
- Combustion Engineering-52949589Document23 pagesCombustion Engineering-52949589Justine BoqsNo ratings yet
- Combustion EngineeringDocument23 pagesCombustion EngineeringRoby Anne GaloNo ratings yet
- CH - 3 Fuel and CombustionDocument50 pagesCH - 3 Fuel and Combustionabe9090901No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Fundamental of CombustionDocument34 pagesChapter 1 Fundamental of CombustionNUREEN DAYANA BINTI MOHD IZMANIZAN A21ET0194No ratings yet
- Class Problem-S 2Document15 pagesClass Problem-S 2Khubaib AsadiNo ratings yet
- Chap.13.THERMOchemical Examples IIDocument19 pagesChap.13.THERMOchemical Examples IIKidus Yado GirmaNo ratings yet
- Combustion 2222222222222222222Document52 pagesCombustion 2222222222222222222Habtamu Tkubet EbuyNo ratings yet
- Estimation and Selection of Air For A FuelDocument19 pagesEstimation and Selection of Air For A FuelMichael Vincent MirafuentesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Technology of Organic CompoundsDocument28 pagesChemical Technology of Organic CompoundsPhung Thi Anh ThuNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Composition (Mol%)Document37 pagesNatural Gas Composition (Mol%)tauseefaroseNo ratings yet
- Combustion Engineering 2020Document113 pagesCombustion Engineering 2020Anthropophobe NyctophileNo ratings yet
- Flares CalculationsDocument14 pagesFlares CalculationsAnonymous oVRvsdWzfBNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas: Hrishikesh Wagh (RISHI) Guided By: Dr. Tae Hoon Kim L20419338Document18 pagesNatural Gas: Hrishikesh Wagh (RISHI) Guided By: Dr. Tae Hoon Kim L20419338Hrishi WaghNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Mass BalanceDocument24 pagesAmmonia Mass BalanceNurulFatimahalzahra100% (1)
- Combustion Engineering Lecture NotesDocument40 pagesCombustion Engineering Lecture NotesFake AccountNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Mass BalanceDocument34 pagesAmmonia Mass Balanceaskaridumbo82% (17)
- Adv Thermo 2018 Tutorial 1Document2 pagesAdv Thermo 2018 Tutorial 1Greg PolemanNo ratings yet
- Engine FuelsDocument21 pagesEngine FuelsRohit NewarNo ratings yet
- 1.4 The Determination of Heating Values of Fuels: Department of Fuel and Energy 3 Class 1 Term /lecture 6Document5 pages1.4 The Determination of Heating Values of Fuels: Department of Fuel and Energy 3 Class 1 Term /lecture 6Zayn AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit 42: Heat Transfer and Combustion: Unit Code: K/601/1443 QCF Level: 5 Credit Value: 15Document20 pagesUnit 42: Heat Transfer and Combustion: Unit Code: K/601/1443 QCF Level: 5 Credit Value: 15david19890109No ratings yet
- Reacting Mixtures and CombustionDocument54 pagesReacting Mixtures and CombustionnunuNo ratings yet
- SEE4121 (2023) - Basic Gas Engineering & Energy Market - Lecture 2 - 16 Jan 2023Document85 pagesSEE4121 (2023) - Basic Gas Engineering & Energy Market - Lecture 2 - 16 Jan 2023MelodyNo ratings yet
- Octo1 2Document17 pagesOcto1 2Padam NabhNo ratings yet
- Synthesis Gas 2019 Part 1 - 2 PDFDocument71 pagesSynthesis Gas 2019 Part 1 - 2 PDFcap n3moNo ratings yet
- 07 - Combustion - Optimisation PDFDocument90 pages07 - Combustion - Optimisation PDFLakshmi NarayanNo ratings yet
- Determination of Traces in Natural GasDocument34 pagesDetermination of Traces in Natural GasDr. Wisam Al-Shalchi100% (6)
- TB 03 Calculations Normalisations ConversionsDocument17 pagesTB 03 Calculations Normalisations ConversionsRaul BxinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3: Combustion 1Document41 pagesLecture 3: Combustion 1ChocolatePancakesNo ratings yet
- Combustion Senator. LibyaDocument12 pagesCombustion Senator. Libyasenator.libyaNo ratings yet
- Bab 12 Perhitungan Proses PembakaranDocument32 pagesBab 12 Perhitungan Proses PembakaranRicardo Aries Boy TariganNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument4 pagesQuestionsDean Joyce Alboroto0% (1)
- G2E - Plant Design Presentation1Document21 pagesG2E - Plant Design Presentation1RUANGLADDA LIMPONGSAWATNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Tutorial No.8 Combustion of Fuels: - Let's Start by Revising The BasicsDocument25 pagesThermodynamics Tutorial No.8 Combustion of Fuels: - Let's Start by Revising The BasicsKEVIN JOE PEREZ ASENCIOS100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - 2-Fuel and Combustions Cont.Document47 pagesChapter 3 - 2-Fuel and Combustions Cont.Habtamu Tkubet Ebuy100% (1)
- CHPT 14Document30 pagesCHPT 14Ysabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Wobbe Index - WikipediaDocument3 pagesWobbe Index - Wikipediabala rNo ratings yet
- Ibp1084 - 17 Gross Characterization Method For The Calculation of Thermophysical Properties of Natural Gas Using The Gerg-2008 Equation of StateDocument11 pagesIbp1084 - 17 Gross Characterization Method For The Calculation of Thermophysical Properties of Natural Gas Using The Gerg-2008 Equation of StateJeeEianYannNo ratings yet
- 02 - Combustion - OptimisationDocument88 pages02 - Combustion - OptimisationDSGNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 Basic Combustion Chemistry PDFDocument77 pagesChap 2 Basic Combustion Chemistry PDFMelvin MhdsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engg SeminarDocument23 pagesChemical Engg SeminarAbdus Saboor KhalidNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 Basic Combustion ChemistryDocument71 pagesChap 2 Basic Combustion ChemistryИлия ГеоргиевNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Recovery: JUNIO 2017Document32 pagesHydrocarbon Recovery: JUNIO 2017Soniale Sánchez GómezNo ratings yet
- Overview of Material Balance For Combustion ProcessDocument18 pagesOverview of Material Balance For Combustion ProcessMehbuba SaymaNo ratings yet
- Consonni - de Carbonized HydrogenDocument27 pagesConsonni - de Carbonized HydrogenBangrivNo ratings yet
- Fuel and CombustionDocument21 pagesFuel and CombustionAnil DubeNo ratings yet
- PROCESS DESCRIPTION AND LCA ICA PresentationDocument15 pagesPROCESS DESCRIPTION AND LCA ICA PresentationTehmasipNo ratings yet
- CHE 322 - Gaseous Fuel Problems PDFDocument26 pagesCHE 322 - Gaseous Fuel Problems PDFDanice LunaNo ratings yet
- CHE 322 - Gaseous Fuel ProblemsDocument26 pagesCHE 322 - Gaseous Fuel ProblemsDanice LunaNo ratings yet
- ATE - Fuels and Combustion - DR R DEEPAKKUMARDocument38 pagesATE - Fuels and Combustion - DR R DEEPAKKUMARMAYUR BHOSALENo ratings yet
- Parameters SG-621: Steam Pressure (kg/cm2 - G)Document2 pagesParameters SG-621: Steam Pressure (kg/cm2 - G)Harris IjazNo ratings yet
- Calculations Based On Fuel AnalysisDocument3 pagesCalculations Based On Fuel AnalysisBrille Adrian FernandoNo ratings yet
- 1PPD ShaPhiDocument5 pages1PPD ShaPhiPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- TERMS GeothermalDocument4 pagesTERMS GeothermalPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- Gasloop GuideDocument20 pagesGasloop GuideRome John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Coal UnloaderDocument14 pagesCoal UnloaderPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- 2PPD ShaPhiDocument24 pages2PPD ShaPhiPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric Chart Stoecker and JonesDocument1 pagePsychrometric Chart Stoecker and JonesPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- FINAL COMPILATION-editedDocument147 pagesFINAL COMPILATION-editedPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Learning ActivityDocument5 pagesModule 5 Learning ActivityPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- RHU Hermosa FPDocument8 pagesRHU Hermosa FPPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- RHU Hermosa SpecsDocument9 pagesRHU Hermosa SpecsPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- 1PPD ShaPhiDocument5 pages1PPD ShaPhiPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- Exp 3Document28 pagesExp 3Philip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- 2PPD ShaPhiDocument24 pages2PPD ShaPhiPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- Data - PhilipDocument21 pagesData - PhilipPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- Types of Drainage PipesDocument1 pageTypes of Drainage PipesPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-ME Laws-EquipmentDocument4 pagesChapter 2-ME Laws-EquipmentPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- SentDocument12 pagesSentPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- PPD - 051623 - Chap 3Document23 pagesPPD - 051623 - Chap 3Philip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- Types of WaterDocument1 pageTypes of WaterPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- PPD - 051623 - Chap 3Document23 pagesPPD - 051623 - Chap 3Philip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- Coal Handling Stacking and ReclaimingDocument3 pagesCoal Handling Stacking and ReclaimingPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- SentDocument12 pagesSentPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- Piping Diagram TablesDocument3 pagesPiping Diagram TablesPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- PPD - 051623 - Chap 4Document1 pagePPD - 051623 - Chap 4Philip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- Piping DiagramDocument15 pagesPiping DiagramPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-ME Laws-ComputeDocument10 pagesChapter 3-ME Laws-ComputePhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-ME Laws-EquipmentDocument4 pagesChapter 2-ME Laws-EquipmentPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet