Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tolerance of Position MMC
Uploaded by
Vineeth MvkaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tolerance of Position MMC
Uploaded by
Vineeth MvkaCopyright:
Available Formats
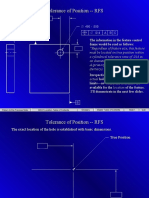
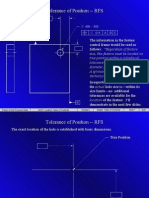
Tolerance of Position -- RFS
.490 - .500 A C .014 A B C
The information in the feature control frame would be read as follows: Regardless of feature size, this feature must be located on true position within a cylindrical tolerance zone of .014 in. on diameter, with reference to datums A (primary), B(secondary), and C (tertiary).
Irrespective of how large or small the actual hole size iswithin its size limitsno additional tolerances are available for the location of the feature. Ill demonstrate in the next few slides.
Glossary Master Table of Contents Slide 1 Quit
B
Return to the Previous Slide GD&T Location Table of Contents
Tolerance of Position -- RFS
The exact location of the hole is established with basic dimensions. True Position
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 2
Quit
Tolerance of Position -- RFS
The cylindrical tolerance zone is established in the feature control frame ( .014). True Position
.014 A B C
Location Tolerance Zone RFS
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 3
Quit
Tolerance of Position -- RFS
For the worst possible condition, the hole axis is located at the extreme limit of the cylindrical tolerance zone. True Position
.014 A B C
Location Tolerance Zone RFS
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 4
Quit
Tolerance of Position -- RFS
When the axis is located at the extreme limit of the tolerance zone, the MMC hole axis would be offset from the true position by a distance equal to one-half of the position tolerance (.007). True Position
.014 A B C
MMC Diameter
Location Tolerance Zone RFS
(Always the Same)
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 5
Quit
Tolerance of Position -- RFS
The actual hole size may vary between MMC (smallest diameter) and LMC (largest diameter), but the axis location cannot violate the boundaries of its location tolerance. True Position
.014 A B C
MMC Diameter LMC Diameter
Location Tolerance Zone RFS (Always the Same)
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 6
Quit
Tolerance of Position -- RFS
The white circle represents the MMC boundary. Its center is located at true position. No element of the hole surface can be inside this boundary. True Position
.014 A B C
MMC Boundary (VC Functional Gauge MMC Diameter LMC Diameter Location Tolerance Zone RFS
(Always the Same)
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 7
Quit
The outer white circle represents the LMC boundary centered on true position. No elements on the surface of the hole can be outside of this boundary. The following series of slides will sequence the progressive position of the center of the hole as it moves around the tolerance zone.
Tolerance of Position -- RFS
LMC Boundary True Position
.014 A B C
MMC Boundary (VC Functional Gauge)
MMC Diameter LMC Diameter
Location Tolerance Zone RFS
(Always the Same)
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 8
Quit
The outer white circle represents the LMC boundary. No elements on the surface of the hole can be outside of this boundary. The following series of slides will sequence the progressive position of the center of the hole as it moves around the tolerance zone.
Tolerance of Position -- RFS
LMC Boundary True Position
.014 A B C
MMC Boundary (VC Functional Gauge)
MMC Diameter LMC Diameter
Location Tolerance Zone RFS
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 9
Quit
The outer white circle represents the LMC boundary. No elements on the surface of the hole can be outside of this boundary. The following series of slides will sequence the progressive position of the center of the hole as it moves around the tolerance zone.
Tolerance of Position -- RFS
LMC Boundary True Position
.014 A B C
MMC Boundary (VC Functional Gauge)
MMC Diameter LMC Diameter
Location Tolerance Zone RFS
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 10
Quit
The outer white circle represents the LMC boundary. No elements on the surface of the hole can be outside of this boundary. The following series of slides will sequence the progressive position of the center of the hole as it moves around the tolerance zone.
Tolerance of Position -- RFS
LMC Boundary True Position
.014 A B C
MMC Boundary (VC Functional Gauge)
MMC Diameter LMC Diameter
Location Tolerance Zone RFS
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 11
Quit
The outer white circle represents the LMC boundary. No elements on the surface of the hole can be outside of this boundary. The following series of slides will sequence the progressive position of the center of the hole as it moves around the tolerance zone.
Tolerance of Position -- RFS
LMC Boundary True Position
.014 A B C
MMC Boundary (VC Functional Gauge)
MMC Diameter LMC Diameter
Location Tolerance Zone RFS
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 12
Quit
The outer white circle represents the LMC boundary. No elements on the surface of the hole can be outside of this boundary. The following series of slides will sequence the progressive position of the center of the hole as it moves around the tolerance zone.
Tolerance of Position -- RFS
LMC Boundary True Position
.014 A B C
MMC Boundary (VC Functional Gauge)
MMC Diameter LMC Diameter
Location Tolerance Zone RFS
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 13
Quit
The outer white circle represents the LMC boundary. No elements on the surface of the hole can be outside of this boundary. The following series of slides will sequence the progressive position of the center of the hole as it moves around the tolerance zone.
Tolerance of Position -- RFS
LMC Boundary True Position
.014 A B C
MMC Boundary (VC Functional Gauge)
MMC Diameter LMC Diameter
Location Tolerance Zone RFS
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 14
Quit
The outer white circle represents the LMC boundary. No elements on the surface of the hole can be outside of this boundary. The following series of slides will sequence the progressive position of the center of the hole as it moves around the tolerance zone.
Tolerance of Position -- RFS
LMC Boundary True Position
.014 A B C
MMC Boundary (VC Functional Gauge)
MMC Diameter LMC Diameter
Location Tolerance Zone RFS
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 15
Quit
The outer white circle represents the LMC boundary. No elements on the surface of the hole can be outside of this boundary. The following series of slides will sequence the progressive position of the center of the hole as it moves around the tolerance zone.
Tolerance of Position -- RFS
LMC Boundary True Position
.014 A B C
MMC Boundary (VC Functional Gauge)
MMC Diameter LMC Diameter
Location Tolerance Zone RFS
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 16
Quit
TOLERANCE OF POSITION AT MAXIMUM MATERIAL CONDITION
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 17
Quit
Tolerance of Position -- MMC
The next example will illustrate the concept of bonus tolerance, in connection with position tolerances. We will use the same drawing example that was used to discuss tolerances of position, when applied regardless of feature size (RFS). One of the significant differences you will see is the advantages of defining the tolerance zone for the axis of a hole as we did beforebut this time, we will add the modifier for maximum material condition (MMC) to the tolerance specification in the feature control frame. Notice the changes that occur in location tolerances when modifiers are used, and as departure from MMC occurs.
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 18
Quit
Tolerance of Position -- MMC
.490 - .500 A C .014 M A B C
The information in the feature control frame would be read as follows: This feature must be located on true position within a cylindrical tolerance zone of .014 on diameter with reference to datums A (primary), B (secondary), and C (tertiary), when the hole is at its smallest size, or MMC.
As the actual hole size increases in size from MMC, additional tolerance (equal to the amount of departure) may be added to the location tolerance for the feature.
Glossary Master Table of Contents Slide 19 Quit
B
Return to the Previous Slide GD&T Location Table of Contents
Tolerance of Position -- MMC
The exact location of the hole is established by basic dimensions. True Position
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 20
Quit
Tolerance of Position -- MMC
The maximum material condition diameter of .490 is shown at its maximum offset from true positionone-half the specified location tolerance.
MMC Diameter (Axis at Maximum Offset) True Position
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 21
Quit
Tolerance of Position -- MMC
As the size of the hole changes within its tolerance range from MMCsmallest hole size limit, and increases in size towards the LMC, or upper size limit, an equal amount of tolerance can be added to the axis location tolerance.
MMC Diameter True Position
Location Tolerance Zone at LMC
Return to the Previous Slide GD&T Location Table of Contents Glossary Master Table of Contents Slide 22 Quit
Tolerance of Position -- MMC
The additional tolerance for the hole axis location (which is equal to the amount of departure from MMC), is called bonus tolerance.
MMC Diameter True Position
LMC Diameter
Bonus Tolerance
Location Tolerance Zone at LMC
Return to the Previous Slide GD&T Location Table of Contents Glossary Master Table of Contents Slide 23 Quit
Tolerance of Position -- MMC
When the hole size is at its lower limit (MMC), and positioned at the extreme limit of the MMC location tolerance, the MMC boundary is established. When the feature of size is at this limit, no elements of the hole surface may be inside this theoretical boundary. This is the virtual condition of the hole, which also simulates the mating part at its maximum material condition.
MMC Diameter True Position
LMC Diameter
MMC Boundary
Location Tolerance Zone at LMC
Return to the Previous Slide GD&T Location Table of Contents Glossary Master Table of Contents Slide 24 Quit
Tolerance of Position -- MMC
When the hole size is at its upper limit (LMC), and positioned at the extreme limit of the location tolerance, the LMC boundary is established. No elements of the hole surface can be out-side this boundary.
MMC Diameter True Position
LMC Diameter
MMC Boundary
LMC Boundary Location Tolerance Zone at LMC
Return to the Previous Slide GD&T Location Table of Contents Glossary Master Table of Contents Slide 25 Quit
Tolerance of Position -- MMC
In this next series of slides, note that while the size and location of the actual hole may vary, the elements on the surface of the holes never violate their boundaries. This series will help you to understand how the hole size changes can affect the location of the center axisand its orientation.
MMC Diameter True Position
LMC Diameter
MMC Boundary (VC=MMC-Tol)
LMC Boundary Location Tolerance Zone at LMC
Return to the Previous Slide GD&T Location Table of Contents Glossary Master Table of Contents Slide 26 Quit
Tolerance of Position -- MMC
Axis location variance possibilities when position tolerance is modified to MMC.
MMC Diameter True Position
LMC Diameter
MMC Boundary (VC=MMC-Tol)
LMC Boundary
Location Tolerance at MMC Location Tolerance at LMC
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 27
Quit
Tolerance of Position -- MMC
Axis location variance possibilities when position tolerance is modified to MMC.
MMC Diameter True Position
LMC Diameter
MMC Boundary (VC=MMC-Tol)
LMC Boundary
Location Tolerance at MMC Location Tolerance at LMC
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 28
Quit
Tolerance of Position -- MMC
Axis location variance possibilities when position tolerance is modified to MMC.
MMC Diameter True Position
LMC Diameter
MMC Boundary (VC=MMC-Tol)
LMC Boundary
Location Tolerance at MMC Location Tolerance at LMC
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 29
Quit
Tolerance of Position -- MMC
Axis location variance possibilities when position tolerance is modified to MMC.
MMC Diameter True Position
LMC Diameter
MMC Boundary (VC=MMC-Tol)
LMC Boundary
Location Tolerance at MMC Location Tolerance at LMC
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 30
Quit
Tolerance of Position -- MMC
Axis location variance possibilities when position tolerance is modified to MMC.
MMC Diameter True Position
LMC Diameter
MMC Boundary (VC=MMC-Tol)
LMC Boundary
Location Tolerance at MMC Location Tolerance at LMC
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 31
Quit
Tolerance of Position -- MMC
Axis location variance possibilities when position tolerance is modified to MMC.
MMC Diameter True Position
LMC Diameter
MMC Boundary (VC=MMC-Tol)
LMC Boundary
Location Tolerance at MMC Location Tolerance at LMC
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 32
Quit
Tolerance of Position -- MMC
Axis location variance possibilities when position tolerance is modified to MMC.
MMC Diameter True Position
LMC Diameter
MMC Boundary (VC=MMC-Tol)
LMC Boundary
Location Tolerance at MMC Location Tolerance at LMC
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 33
Quit
Tolerance of Position -- MMC
Axis location variance possibilities when position tolerance is modified to MMC.
MMC Diameter True Position
LMC Diameter
MMC Boundary (VC=MMC-Tol)
LMC Boundary
Location Tolerance at MMC Location Tolerance at LMC
Return to the Previous Slide
GD&T Location Table of Contents
Glossary
Master Table of Contents
Slide 34
Quit
You might also like
- Tolerance of Position - RFSDocument34 pagesTolerance of Position - RFSAd Man GeTigNo ratings yet
- Positional Tolerancing: Typical Product RequirementDocument4 pagesPositional Tolerancing: Typical Product RequirementNairobiNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Engineering Part3Document10 pagesDimensional Engineering Part3Avneet MaanNo ratings yet
- PositionDocument5 pagesPositionberemiz009No ratings yet
- GD&T WIZ Tutor Covers The Vast Breadth of Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Without Compromising On The Depth. The Topics Covered AreDocument1 pageGD&T WIZ Tutor Covers The Vast Breadth of Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Without Compromising On The Depth. The Topics Covered AreVinay ManjuNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T)Document43 pagesGeometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T)Victor Manuel Estrada0% (1)
- Study - Deck End Rotation ReportDocument2 pagesStudy - Deck End Rotation ReportLinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Dimensioning and TolerancingDocument51 pagesGeometrical Dimensioning and TolerancingMahender Kumar100% (3)
- Form Location Tolerances enDocument2 pagesForm Location Tolerances enSanjay Mehrishi100% (3)
- GDT TutorialDocument76 pagesGDT Tutorialscience ki DuniyaNo ratings yet
- Flow MR Kecamatan & TA OvershootDocument2 pagesFlow MR Kecamatan & TA OvershootAsep MakmurNo ratings yet
- VoLTE One Pager MoS DriveBasedDocument1 pageVoLTE One Pager MoS DriveBasedJITU_VISHNo ratings yet
- Gaining Confidence With GD T - Part 3Document20 pagesGaining Confidence With GD T - Part 3Abraham ThomasNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning & TolerancingDocument47 pagesGeometric Dimensioning & TolerancingVinoth BalasubramaniyanNo ratings yet
- Long Side Failure: Ultimate Bearing Capacity, Q Net Bearing Capacity, Q Computed Factor of Safety, FS N Value N ValuesDocument24 pagesLong Side Failure: Ultimate Bearing Capacity, Q Net Bearing Capacity, Q Computed Factor of Safety, FS N Value N ValuesPervy SageNo ratings yet
- Size and Mobility ModifiersDocument8 pagesSize and Mobility ModifiersMelvin B EkboteNo ratings yet
- Min Max Steel Reinforcement For SlabDocument1 pageMin Max Steel Reinforcement For SlabRodel, Jr. NatividadNo ratings yet
- Pages From Smith & Hendy 2009 8Document1 pagePages From Smith & Hendy 2009 8Napong SubanpongNo ratings yet
- TolerancingDocument19 pagesTolerancingKRKSANNo ratings yet
- Tolerance of Position - RFSDocument34 pagesTolerance of Position - RFSsandipusNo ratings yet
- Technical Column: Fretting (Inner Ply) PotentialDocument1 pageTechnical Column: Fretting (Inner Ply) PotentialRose Mary ChackoNo ratings yet
- Forces From Junction - Concrete and Channel Column C1A: Design PhilosopyDocument1 pageForces From Junction - Concrete and Channel Column C1A: Design PhilosopyNitish TakalkarNo ratings yet
- Ductile SteelDocument41 pagesDuctile SteelRaquib AhsanNo ratings yet
- True Position: Special NoteDocument15 pagesTrue Position: Special NoteanishNo ratings yet
- Admittance of A Cavity-Backed Annular Slot Antenna : J. Ga4Lejsj', T. Thompson,$Document8 pagesAdmittance of A Cavity-Backed Annular Slot Antenna : J. Ga4Lejsj', T. Thompson,$julio perezNo ratings yet
- Single Sections in BendingDocument1 pageSingle Sections in BendingmrmerajNo ratings yet
- CE 581 Reinforced Concrete Structures: Lecture 11: Performance Based Assessment and StrengtheningDocument131 pagesCE 581 Reinforced Concrete Structures: Lecture 11: Performance Based Assessment and StrengtheningCelil OrakNo ratings yet
- Precast - Wall - Connection Wire Loop Design ForcesDocument7 pagesPrecast - Wall - Connection Wire Loop Design ForcesrahuljainNo ratings yet
- The Tolerance of Position: 856 Salt Lake Court San Jose, Ca 95133 (408) 251-5329Document4 pagesThe Tolerance of Position: 856 Salt Lake Court San Jose, Ca 95133 (408) 251-5329Ba BuNo ratings yet
- Basics of GD&TDocument50 pagesBasics of GD&T2023ht30006No ratings yet
- Computing The Strength of Indexing Plungers: Shear LoadsDocument2 pagesComputing The Strength of Indexing Plungers: Shear LoadsAsh KetchumNo ratings yet
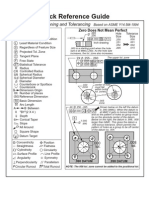
- Quick Reference GuideDocument1 pageQuick Reference Guidekranthi142434No ratings yet
- Understanding Seismic Interpretation Methodology - Onajite2014 - Tarea - 21-28Document8 pagesUnderstanding Seismic Interpretation Methodology - Onajite2014 - Tarea - 21-28Fabian ruiz sanchezNo ratings yet
- 15 Design Constr Rigid Inclu Ground Improv Proj 540387 7Document45 pages15 Design Constr Rigid Inclu Ground Improv Proj 540387 7Stefan GuranNo ratings yet
- Pwls 2d 0206Document6 pagesPwls 2d 0206emilia597No ratings yet
- Moment Redeistribution and YLADocument132 pagesMoment Redeistribution and YLAArjun Raj100% (1)
- ReviewModule24 Steel2Document3 pagesReviewModule24 Steel2JM De Guzman TuzonNo ratings yet
- Is.456.2000 24Document1 pageIs.456.2000 24ShafeenNo ratings yet
- Directional Element Design For ProtectingDocument11 pagesDirectional Element Design For ProtectingAngeles Ataupillco MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Terms: The Definitions of 16 Critical Terms Defined by The 2009 StandardDocument6 pagesTerms: The Definitions of 16 Critical Terms Defined by The 2009 StandardLikith LikiNo ratings yet
- Rock Type Course - Rev2Document225 pagesRock Type Course - Rev2Mario Mallaviabarrena100% (4)
- 10 - Esfuerzos PermisiblesDocument5 pages10 - Esfuerzos PermisiblesDaniloNo ratings yet
- Iimits & FitsDocument27 pagesIimits & FitsDr.P.Arivalagan ASST. PROFNo ratings yet
- Fit, Limit & Tolerance: Diplom A Te KN Ologi Me Kan Ikal (Luk Isan & R E Kabe N Tu K)Document7 pagesFit, Limit & Tolerance: Diplom A Te KN Ologi Me Kan Ikal (Luk Isan & R E Kabe N Tu K)Anupam AlokNo ratings yet
- J TSF 2014 02 044Document8 pagesJ TSF 2014 02 044Adelin CorodescuNo ratings yet
- End Zone Design: Essam AbdouDocument61 pagesEnd Zone Design: Essam AbdouShijo AntonyNo ratings yet
- Coplanar It yDocument4 pagesCoplanar It yBubba RocketNo ratings yet
- Craig's Soil Mechanics - (Principal Symbols)Document10 pagesCraig's Soil Mechanics - (Principal Symbols)Asfin HaqueNo ratings yet
- Concrete Structures: Chapter II Mechanical Properties of Steel and Concrete MaterialsDocument45 pagesConcrete Structures: Chapter II Mechanical Properties of Steel and Concrete MaterialsdavidNo ratings yet
- C19 Soil Structure Interaction For Seismic DesignDocument2 pagesC19 Soil Structure Interaction For Seismic DesignMohamed ElshafaiNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning and Tolerancing: (C) Where Positional Tolerances Are Used To Locate Holes andDocument56 pagesDimensioning and Tolerancing: (C) Where Positional Tolerances Are Used To Locate Holes andavr8784100% (1)
- Babu 2016Document22 pagesBabu 2016Monitering EyeNo ratings yet
- Prec Eng Linear Tol Part1Document11 pagesPrec Eng Linear Tol Part1Mohamad PoortoosiNo ratings yet
- Schlumberger PrivateDocument13 pagesSchlumberger PrivateDiana BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Load CellDocument3 pagesLoad Celllmriose94No ratings yet
- Vibrating Wire Settlement Systems: 4600 SeriesDocument4 pagesVibrating Wire Settlement Systems: 4600 SeriesKael CabezasNo ratings yet
- Weak Convergence of Measures: Probability and Mathematical Statistics: A Series of Monographs and TextbooksFrom EverandWeak Convergence of Measures: Probability and Mathematical Statistics: A Series of Monographs and TextbooksNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 NX IntroDocument7 pagesLecture 2 NX IntroKishore BhatNo ratings yet
- Siemens NX 8 - Gettin Started PDFDocument14 pagesSiemens NX 8 - Gettin Started PDFSalvador Lagé Cànovas50% (2)
- NX Drafting Commands II: How To Show Hidden LinesDocument17 pagesNX Drafting Commands II: How To Show Hidden LinesKishore BhatNo ratings yet
- Ug Drafting Basic OperationsDocument3 pagesUg Drafting Basic Operationsdinesh_apkNo ratings yet
- Siemens NX 8 - Gettin Started PDFDocument14 pagesSiemens NX 8 - Gettin Started PDFSalvador Lagé Cànovas50% (2)
- Man 013Document4 pagesMan 013Kishore BhatNo ratings yet
- UG-NX TutorialDocument235 pagesUG-NX Tutorialesrayansenkeliat50% (2)
- Ug NXDocument12 pagesUg NXerjaichauhanNo ratings yet
- Compression-Spring Design ExampleDocument5 pagesCompression-Spring Design Examplestphn_maturinNo ratings yet
- Multiphysics SimulationDocument32 pagesMultiphysics Simulationminutiae100% (1)
- NV ToleranceDocument42 pagesNV ToleranceaqibazizkhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 NX IntroDocument7 pagesLecture 2 NX IntroKishore BhatNo ratings yet
- Heat Sink Selection: Thermal Management of Electronics San José State University Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument19 pagesHeat Sink Selection: Thermal Management of Electronics San José State University Mechanical Engineering DepartmentKishore BhatNo ratings yet
- Thermal Management Considerations For PCBS: Measurement Techniques and Heat ConductionDocument37 pagesThermal Management Considerations For PCBS: Measurement Techniques and Heat ConductionKishore BhatNo ratings yet
- Metal Fatigue SpreadsheetsDocument73 pagesMetal Fatigue SpreadsheetsKishore BhatNo ratings yet
- Tolerance AnalysisDocument0 pagesTolerance AnalysisKishore BhatNo ratings yet
- Conversion CalculatorDocument5 pagesConversion CalculatorKishore BhatNo ratings yet
- 12 Injection MoldingDocument56 pages12 Injection MoldingFranzMigNo ratings yet
- 3 PlasticsDocument33 pages3 PlasticsRamakrishnan RangaNo ratings yet
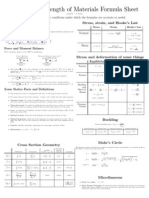
- Statics and Strength of Materials Formula SheetDocument1 pageStatics and Strength of Materials Formula SheetRichard TsengNo ratings yet
- Structures and Mechanisms BookletDocument77 pagesStructures and Mechanisms BookletKishore BhatNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Tolerance Stackup and Analysis - Muya PDFDocument230 pagesMechanical Tolerance Stackup and Analysis - Muya PDFcalidad_bogota100% (3)
- Dimension Stack-Up SheetDocument8 pagesDimension Stack-Up SheetKishore BhatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Threads and FastenersDocument128 pagesChapter 5 - Threads and FastenersPradeep Kumar MehtaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Lifts and ManipulatorsDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Lifts and ManipulatorsKishore BhatNo ratings yet
- BEng (Hons) Mechanical Engineering (Extended)Document27 pagesBEng (Hons) Mechanical Engineering (Extended)Kishore BhatNo ratings yet
- MS 01 180 SwagelokDocument88 pagesMS 01 180 SwagelokKishore Bhat100% (1)
- Analyzing Structural MembersDocument35 pagesAnalyzing Structural MembersKishore BhatNo ratings yet
- Good)Document62 pagesGood)shrinidheeNo ratings yet
- Scissor Lift CalculatorDocument2 pagesScissor Lift CalculatorKishore Bhat50% (4)