Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Histology, Frog Musculature
Uploaded by
Anna TongcoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Histology, Frog Musculature
Uploaded by
Anna TongcoCopyright:
Available Formats
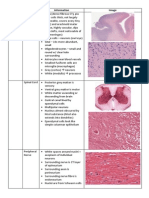
Histology Skin Layer/ Part Stratum (subcutaneous) corneum Stratum (subcutaneous) germinativum Stratum spongiosum/ laxum Stratum compactum
Chromatophore Cutaneous gland Features Outermost layer of epidermis Several rows of columnar cells Loose connective tissue Deepest layer of dermis; tightly packed Cells contain pigment granules Multicellular grand (formed by infolding) Function Non-living; shed off Living; replace stratum corneum cells Contains chromatophores, pigment granules, cutaneous glands, blood vessels, lymph spaces Contains blood vessels and nerves Produce and control skin coloration Secrete mucus; keep skin moist
Liver Layer/ Part Hepatocyte Sinusoid Pigment granule Bile duct Artery Vein Features Liver cell (polygonal, dark spherical nuclei) Endothelial tubes Irregularly scattered Lined with cuboidal epithelium Thick-walled Thin-walled Function Protein synthesis; detoxification Very permeable; absorption Produce coloration Produce and secrete bile (fat emulsifier) Bring oxygenated blood from heart to body Bring deoxygenated blood from body to heart
Kidney Layer/ Part Malpighian body/ renal corpuscle Glomerulus Bowmans capsule Uriniferous tubule Collecting tubule Wolffian duct/ mesonephric duct Features Round masses on ventral part of kidney Capillary network inside Malpighian body Cup-shaped double membrane of glomerulus Long coiled tubule With wide lumen lined with cuboidal cells Near renal portal vein Function Filters blood Filters blood Covers glomerulus Reabsorption of water and other substances Continuation of uriniferous tubules Opening of collecting tubules
Intestine Layer/ Part Valves of Kerkring Lumen Goblet cell Tunica mucosa Tunica submucosa Tunica muscularis Stratum circulare Stratum longitudinale Tunica serosa Mesothelium Features Circular folds of inner wall of intestine Cavity/ interior of intestinal tract Unicellular gland; slender base, dilated apex Innermost layer; mucous coat Outside mucosa; loose connective tissue Outside submucosa; muscular coat Thick inner circular layer Thin outer longitudinal layer Outermost layer; very thin layer of loose connective tissue; covered with mesothelium Pavement epithelial cells Function Slow passage of food; increased absorption N/A Secrete mucin (which becomes mucous) Traps pathogens; facilitates movement Contains blood vessels and lymph space Consists of 2 layers; facilitates gut movement Spindle-shaped smooth muscle cells Cross-sections of muscle cells Serous coat; visceral peritoneum Facilitate intracoelomic movement; Line internal cavity; derived from mesoderm
Stomach Layer/ Part Ruga Lumen Tunica mucosa Columnar cells Lamina propria Gastric gland Zymogenic/ chief cell Parietal cell Muscularis mucosa Tela submucosa Tunica muscularis Subserosa Tunica serosa Features Large wavy folds of inner wall of stomach Cavity/ interior of stomach Innermost layer; mucous coat Innermost layer Outer layer of connective tissue Branched tubular glands with neck and body Base of fundus Wedged between chief cells Outside lamina propria; consists of 2 layers Loose connective tissue Very thick; circular layer of smooth muscle Narrow layer of connective tissue Outermost layer; covered with mesothelium Function Absorption N/A Facilitates movement; composed of 2 layers Secretion and absorption Contain openings for gastric pits Secrete mucus, gastric acid, etc. Secrete pepsinogen, rennin Secrete gastric acid and intrinsic factor Facilitates outflow from gastric glands Contains large blood and lymph vessels Facilitates movement of food particles Contains sections of blood vessels Visceral peritoneum; contains nerves
Spinal Cord Layer/ Part White matter Gray matter Cornua (dorsal and ventral) Fissure (dorsal and ventral) Central canal Ependymal cell Neuroglia/ glia cell Motor cell Motor neuron/ efferent neuron Dura mater Subdural space Arachnoid mater Pia mater Features Outer layer; loosely arranged medullated nerve fibers and supporting neuroglia Inner layer; made up of cell bodies Horn-like projections (ventral is farther apart) Invagination of spinal cord surface Cavity found in center of spinal cord Cells lining central canal Small oval bodies; scattered in spinal cord Concentrated in cornua; star-shaped Concentrated in cornua; 3-7 at each horn Thick loose connective tissue; made up of fatty tissue with many veins Lies beneath dura mater Spiderweb-like layer of connective tissue Thin layer of connective tissue Function Passage of messages Controls muscles, sensory perception, etc Controls axial muscles, touch and sensation Contains spinal artery Contains cerebrospinal fluid Produces cerebrospinal fluid Non-neuronal cells; support and protection Connection with neurons Makes synaptic connection with interneuron Carries blood from brain to heart; supports dural sinuses Artificial space created as a result of trauma Allows cerebrospinal fluid flow beneath Contains blood vessels investing the spinal cord; nourishes brain
You might also like
- BIOLAB FROG Organ HistologyDocument7 pagesBIOLAB FROG Organ HistologyCloie Anne Rabinetas100% (1)
- Tissue TableDocument4 pagesTissue TableMarcie BooneNo ratings yet
- 13.histology LectureDocument64 pages13.histology LecturepashaNo ratings yet
- Lab 7Document25 pagesLab 7202310446No ratings yet
- CH 14 Digestive System and Body MetabolismDocument21 pagesCH 14 Digestive System and Body MetabolismKim Buenaflor GaloyoNo ratings yet
- Digestive Tract: State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu"Document78 pagesDigestive Tract: State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu"Dan SlivinschiiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - TissuesDocument3 pagesChapter 4 - TissuesAngelyka CabaloNo ratings yet
- Biology 112: Chapter 5: TissuesDocument5 pagesBiology 112: Chapter 5: TissuesSwetha GowthamNo ratings yet
- Human Biology v1Document6 pagesHuman Biology v1JNo ratings yet
- Histology UnkownsDocument11 pagesHistology UnkownsBec Jeans100% (2)
- Histology of Digestive SystemDocument100 pagesHistology of Digestive SystemFadhila Putri Palupi100% (3)
- Epithelial TissueDocument22 pagesEpithelial TissueMariam HaroonNo ratings yet
- Maya Tejasari Histology Department Faculty of Medicine Bandung Islamic UniversityDocument65 pagesMaya Tejasari Histology Department Faculty of Medicine Bandung Islamic UniversitydeasyahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Equine Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Equine Anatomy and PhysiologySavannah Simone Petrachenko100% (1)
- Yy Yyy Y Yy Y YYYDocument64 pagesYy Yyy Y Yy Y YYYsreedam100% (1)
- Genbio2 Week 1Document35 pagesGenbio2 Week 1Noel Vincent Agonoy100% (1)
- Germ Cell-Sperm, Egg : Accessory OrgansDocument2 pagesGerm Cell-Sperm, Egg : Accessory OrgansHanahMayBagunuNo ratings yet
- Tissue Level of OrganizationDocument71 pagesTissue Level of OrganizationMuhammad Ammar100% (1)
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument106 pagesMale and Female Reproductive SystemRaissa Grace Acebo Carranza100% (3)
- Lecture 1: Epithelium and Glands: 1.classification of Epithelial TissueDocument7 pagesLecture 1: Epithelium and Glands: 1.classification of Epithelial TissueMuizz RasaniNo ratings yet
- Dr. Veny Larasati, M.Biomed: Bagian Histologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sriwijaya 2016Document52 pagesDr. Veny Larasati, M.Biomed: Bagian Histologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sriwijaya 2016NabilahnurqonitahNo ratings yet
- Histology - Male Reproductive SystemDocument46 pagesHistology - Male Reproductive SystemKim AcostaNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument8 pagesExcretory SystemMaria Charlene OrpillaNo ratings yet
- EPITHELIAL TISSUE (Epithelium / Epithelia) : Basement MembraneDocument7 pagesEPITHELIAL TISSUE (Epithelium / Epithelia) : Basement MembraneNanaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument57 pagesEpithelial TissuePreet Kaur100% (1)
- Histology of The Digestive System: Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.DDocument36 pagesHistology of The Digestive System: Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.Dchocoholic potchiNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument6 pagesHistologyveerdoriNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Lecture 1Document52 pagesEpithelial Tissue Lecture 1Saphira PramuditaNo ratings yet
- Ana Histo MaleDocument4 pagesAna Histo MaleCarlito RiveraNo ratings yet
- In The Name of God THE Compassionate The MercifulDocument75 pagesIn The Name of God THE Compassionate The MercifulGaziza MaaroofNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument1 pageEpithelial Tissuesapi-265736810No ratings yet
- AlimentaryCanal (Author V.fulga)Document55 pagesAlimentaryCanal (Author V.fulga)gokulkrishnayadhavNo ratings yet
- By: Dr. Susianti, M.SCDocument47 pagesBy: Dr. Susianti, M.SCAnityo NugrohoNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System EssayDocument3 pagesThe Digestive System EssayJerilee SoCute Watts0% (1)
- Histology of Git and Circulatory SystemDocument45 pagesHistology of Git and Circulatory SystemRan CelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Digestive SystemDocument46 pagesAnatomy of The Digestive Systemprincess joy sustiguerNo ratings yet
- Hesi ADocument214 pagesHesi Ayisel56100% (6)
- The Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsDocument15 pagesThe Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsYchel P. YapNo ratings yet
- Anatomy IntroDocument4 pagesAnatomy IntroAlex HirschNo ratings yet
- Fish Pathology - Anatomy Histology PDFDocument59 pagesFish Pathology - Anatomy Histology PDFvinimoja100% (1)
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument7 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentBiancaPascuNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System and Body Metabolism 1Document19 pagesThe Digestive System and Body Metabolism 1Bea GualbertoNo ratings yet
- CH 05 TissuesDocument50 pagesCH 05 TissuesAlina Ghe100% (1)
- Bio 11 Lab Exam 3 ReviewerDocument5 pagesBio 11 Lab Exam 3 Revieweririsiri28No ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument4 pagesAnatomyCelestine TanNo ratings yet
- Notes - Second Half (Incomplete)Document8 pagesNotes - Second Half (Incomplete)gnol_ttamNo ratings yet
- Oesophagus, Stomach-Fundus & Pylorus: Dr. Makarchuk IrynaDocument35 pagesOesophagus, Stomach-Fundus & Pylorus: Dr. Makarchuk IrynaSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- Study of Microscopic Anatomy - Only 200 Different Cells Types - Four Primary Tissue ClassesDocument61 pagesStudy of Microscopic Anatomy - Only 200 Different Cells Types - Four Primary Tissue ClassesvanderphysNo ratings yet
- Simple Squamous Epithelium: Structure: Function: LocationDocument3 pagesSimple Squamous Epithelium: Structure: Function: LocationdianesamanthaNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Digestive System-1Document14 pagesOrgans of The Digestive System-1PrintScapeNo ratings yet
- General HistologyDocument29 pagesGeneral HistologyShalini SinghNo ratings yet
- Tissues (Anatomy 1)Document83 pagesTissues (Anatomy 1)nanakwame5769No ratings yet
- What Are The 4 Major Histological Layers of The Digestive System?Document6 pagesWhat Are The 4 Major Histological Layers of The Digestive System?Witty the PoohtanginaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 4 TissuesDocument55 pagesCh. 4 TissuesBora YaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab Quizlet Flashcards Converted For AnkiDocument6 pagesAnaphy Lab Quizlet Flashcards Converted For AnkiAldrin LimcuandoNo ratings yet
- Tissue Level of OrganizationDocument49 pagesTissue Level of Organizationainabayhon7No ratings yet
- Bio 11 UPD Third Lec Exam ReviewerDocument111 pagesBio 11 UPD Third Lec Exam ReviewerMedjugorje Beltran DalanNo ratings yet
- Histology: BY Alawia Abdalla Mohammed 7 Nov 2021Document23 pagesHistology: BY Alawia Abdalla Mohammed 7 Nov 2021التنين الاحمر العظيمNo ratings yet
- Service Standard - City of Paranaque, PhilippinesDocument23 pagesService Standard - City of Paranaque, PhilippinesAnna TongcoNo ratings yet
- Anions TestingDocument1 pageAnions TestingAnna TongcoNo ratings yet
- HACCP (Tagalog) - MPVAzanzaDocument6 pagesHACCP (Tagalog) - MPVAzanzaAnna TongcoNo ratings yet
- Reservation Form For Wedding in The Parish New PDFDocument2 pagesReservation Form For Wedding in The Parish New PDFAnna TongcoNo ratings yet
- Remember Me (Coco OST) - KalimbaDocument2 pagesRemember Me (Coco OST) - KalimbaAnna TongcoNo ratings yet
- Over The Rainbow - KalimbaDocument2 pagesOver The Rainbow - KalimbaAnna Tongco100% (2)
- Happy Birthday - KalimbaDocument1 pageHappy Birthday - KalimbaAnna TongcoNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Electrochemistry and Electrode PotentialDocument12 pagesLab Report: Electrochemistry and Electrode PotentialAnna Tongco100% (2)
- Psalm 73Document4 pagesPsalm 73Anna TongcoNo ratings yet
- Ryan Caybyab - Araw GabiDocument6 pagesRyan Caybyab - Araw GabiAnna Tongco81% (16)
- PNS For Table EggsDocument24 pagesPNS For Table EggsAnna TongcoNo ratings yet
- Birch Wedding Guide EbookDocument52 pagesBirch Wedding Guide EbookAnna Tongco100% (2)
- Qualitative Analysis For AnionsDocument1 pageQualitative Analysis For AnionsAnna TongcoNo ratings yet
- Electron and Molecular GeometryDocument2 pagesElectron and Molecular GeometryAnna TongcoNo ratings yet
- MagnesiumDocument30 pagesMagnesiumAnna TongcoNo ratings yet
- Planning in ManagementDocument22 pagesPlanning in ManagementAnna TongcoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Instrumental Methods For Identification of Components in FoodDocument15 pagesAdvanced Instrumental Methods For Identification of Components in FoodAnna TongcoNo ratings yet
- Organization in ManagementDocument38 pagesOrganization in ManagementAnna TongcoNo ratings yet
- Frog Dissection: Skeletal and Muscular SystemsDocument10 pagesFrog Dissection: Skeletal and Muscular SystemsAnna Tongco87% (15)
- Detection of Vibrio Spp. in Raw Maguro SashimiDocument18 pagesDetection of Vibrio Spp. in Raw Maguro SashimiAnna TongcoNo ratings yet
- Kuhs AntidoteDocument105 pagesKuhs AntidoteAsna FasilNo ratings yet
- Nursing Abbreviations, Prefixes and SuffixesDocument10 pagesNursing Abbreviations, Prefixes and Suffixesjava_biscocho1229100% (4)
- Drug Induced Renal Disease Patofarmol 3.0Document37 pagesDrug Induced Renal Disease Patofarmol 3.0livelyNo ratings yet
- Renal Anatomy & Physiology: NotesDocument5 pagesRenal Anatomy & Physiology: NotesTawhid ZihadNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Ayurvedacharya (BAMS) CourseDocument115 pagesSyllabus of Ayurvedacharya (BAMS) Coursenrp_rahulNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions AnswersDocument785 pagesExam Questions AnswersLetlet Basabe100% (1)
- (Physiology) Endocrine MCQ 1Document21 pages(Physiology) Endocrine MCQ 1Eslam HamadaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 10th Science Solved Question Paper 2018Document18 pagesCbse Class 10th Science Solved Question Paper 2018Parth LadNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Canine Clinical Nutrition PDFDocument514 pagesEncyclopedia of Canine Clinical Nutrition PDFErika Villarreal100% (2)
- 10th BIOLOGY PRACTICALS (1-19)Document31 pages10th BIOLOGY PRACTICALS (1-19)vidisha bhansaliNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis Case StudiesDocument11 pagesUrinalysis Case Studiesdandooshe38% (13)
- Noel A. Villanueva, MD, FPCP, FPSNDocument62 pagesNoel A. Villanueva, MD, FPCP, FPSNagilNo ratings yet
- Isolated Glomerular Diseases Associated With Recurrent Gross HematuriaDocument17 pagesIsolated Glomerular Diseases Associated With Recurrent Gross HematuriaMay PingolNo ratings yet
- Maternal LecDocument23 pagesMaternal LecKate Onniel Rimando100% (1)
- Literature 11Document9 pagesLiterature 11Bayu SuyantoNo ratings yet
- Kidney: Biochemical Tests For Assessing Renal FunctionsDocument56 pagesKidney: Biochemical Tests For Assessing Renal FunctionsPaulina Paskeviciute100% (1)
- Drug Studies (DMII) (Humulin, NACh03, Losartan, Vessel Due F)Document5 pagesDrug Studies (DMII) (Humulin, NACh03, Losartan, Vessel Due F)Alvin OrizaNo ratings yet
- CALC - Fluor. Calcium FluorideElasticity Salt - Contributes To Elasticity WallsDocument22 pagesCALC - Fluor. Calcium FluorideElasticity Salt - Contributes To Elasticity Wallsapi-11375880100% (1)
- Frances Boa Methodology QuestionDocument39 pagesFrances Boa Methodology Questionmonday125No ratings yet
- Tetada Kalimasad1Document16 pagesTetada Kalimasad1Rasaraj Ramon Castaneda100% (2)
- Sodium Bicarbonate in J AftDocument9 pagesSodium Bicarbonate in J AftMohd Faizal SimonNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Kidney Diseases: CKF (Chronic Kidney Failure), Characteristics in ChildrenDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Kidney Diseases: CKF (Chronic Kidney Failure), Characteristics in ChildrenAcademic JournalNo ratings yet
- A Case Study-FinalDocument45 pagesA Case Study-FinalJáylord OsorioNo ratings yet
- Excretion and KidneysDocument39 pagesExcretion and KidneyselizabethNo ratings yet
- The Essential Review Guide For Passing The Mblex Licensing Exam 2017 EditionDocument192 pagesThe Essential Review Guide For Passing The Mblex Licensing Exam 2017 EditionSabrina Marie100% (3)
- Excretory System WorksheetDocument4 pagesExcretory System WorksheetAlexis CastellanosNo ratings yet
- December 2008final FRCA VivaDocument43 pagesDecember 2008final FRCA Vivajahangirealam100% (2)
- Does This Patient Have Acute Kidney Injury? An AKI ChecklistDocument4 pagesDoes This Patient Have Acute Kidney Injury? An AKI ChecklistOlga HMNo ratings yet
- The Digestive and Excretory SystemDocument16 pagesThe Digestive and Excretory SystemMiguel Angel Loor MolinaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Laboratory Tests Handout VersionDocument58 pagesIntroduction To Laboratory Tests Handout VersionFiorellaBeatrizNo ratings yet