Professional Documents
Culture Documents
sm1 19
Uploaded by
awoods12835Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
sm1 19
Uploaded by
awoods12835Copyright:
Available Formats
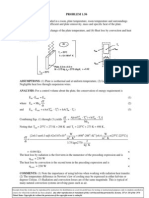
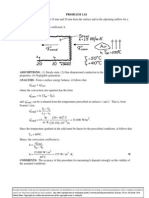
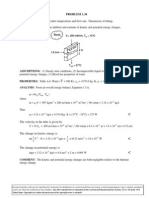
PROBLEM 1.19 KNOWN: Length, diameter and maximum allowable surface temperature of a power transistor.
Temperature and convection coefficient for air cooling. FIND: Maximum allowable power dissipation. SCHEMATIC:
ASSUMPTIONS: (1) Steady-state conditions, (2) Negligible heat transfer through base of transistor, (3) Negligible heat transfer by radiation from surface of transistor. ANALYSIS: Subject to the foregoing assumptions, the power dissipated by the transistor is equivalent to the rate at which heat is transferred by convection to the air. Hence,
Pelec = qconv = hA ( Ts T )
2 where A = DL + D2 / 4 = 0.012m 0.01m + ( 0.012m ) / 4 = 4.90 104 m 2 .
For a maximum allowable surface temperature of 85C, the power is Pelec = 100 W/m 2 K 4.90 104 m 2
) (85 25) C = 2.94 W
<
COMMENTS: (1) For the prescribed surface temperature and convection coefficient, radiation will be negligible relative to convection. However, conduction through the base could be significant, thereby permitting operation at a larger power. (2) The local convection coefficient varies over the surface, and hot spots could exist if there are locations at which the local value of h is substantially smaller than the prescribed average value.
Excerpts from this work may be reproduced by instructors for distribution on a not-for-profit basis for testing or instructional purposes only to students enrolled in courses for which the textbook has been adopted. Any other reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted by Sections 107 or 108 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without the permission of the copyright owner is unlawful.
You might also like
- Insulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsFrom EverandInsulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- sm1 31Document1 pagesm1 31awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 68Document1 pagesm1 68awoods12835No ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Example ProblemsDocument121 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Example ProblemsFauiqe YousafNo ratings yet
- CHE 260 Week 11 Solutions-1Document4 pagesCHE 260 Week 11 Solutions-1erfanyeganehfarNo ratings yet
- ACSR Conductor SelectionDocument12 pagesACSR Conductor SelectionSushant ChauguleNo ratings yet
- CH1Document98 pagesCH1miles_e_newton50% (2)
- Heat TransgerDocument56 pagesHeat TransgerShusha Shomali67% (3)
- sm1 54Document1 pagesm1 54awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 24Document1 pagesm1 24awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 20Document1 pagesm1 20awoods12835No ratings yet
- Park 2001Document7 pagesPark 2001soma AlmasoodyNo ratings yet
- sm1 45Document2 pagessm1 45awoods12835No ratings yet
- Solutions From OnlineDocument36 pagesSolutions From OnlineNiniGooseNo ratings yet
- G3 - Solved ProblemsDocument36 pagesG3 - Solved ProblemsSridhar RaoNo ratings yet
- sm1 30Document1 pagesm1 30awoods12835No ratings yet
- Batch 3 - Roll Nos:52 To 58: March 6, 2015 Heat Transfer LabDocument4 pagesBatch 3 - Roll Nos:52 To 58: March 6, 2015 Heat Transfer LabaruNo ratings yet
- FFHMT 161Document7 pagesFFHMT 161KarimNo ratings yet
- Target and Horn Cooling For The Very Long Baseline Neutrino ExperimentDocument3 pagesTarget and Horn Cooling For The Very Long Baseline Neutrino ExperimentFadhlanFachrozaHasibuanNo ratings yet
- Ps1 SolutionsDocument15 pagesPs1 SolutionsSomrita BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 1st Attempt Final Exam (2022-2023)Document4 pages1st Attempt Final Exam (2022-2023)alhussenyNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 5: AIM: Study and Calculate The Efficiency of Fin in Natural and Forced ConvectionDocument17 pagesExperiment - 5: AIM: Study and Calculate The Efficiency of Fin in Natural and Forced ConvectionRushabh PatelNo ratings yet
- Mech 302 HW 6 SDocument8 pagesMech 302 HW 6 SKeep GreeneryNo ratings yet
- Steady Heat ConductionDocument81 pagesSteady Heat ConductionIsmail MughalNo ratings yet
- sm13 111Document2 pagessm13 111Timothy JonesNo ratings yet
- 4 4 G J S J: Any Other Reproduction or Translation of This Work Beyond That Permitted by Sections 107 or 108 of The 1976Document1 page4 4 G J S J: Any Other Reproduction or Translation of This Work Beyond That Permitted by Sections 107 or 108 of The 1976tommypurdueNo ratings yet
- Dielectric ConstantDocument4 pagesDielectric ConstantSutapa DeyNo ratings yet
- sm1 18Document1 pagesm1 18awoods12835No ratings yet
- AN-1604 Application Note: Thermal Management Calculations For RF Amplifiers in LFCSP and Flange PackagesDocument10 pagesAN-1604 Application Note: Thermal Management Calculations For RF Amplifiers in LFCSP and Flange PackagesAhsan AmeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 (Building Thermal Loads)Document25 pagesChapter 5 (Building Thermal Loads)AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Convection Radiation (EDocFind - Com)Document10 pagesLab Manual Convection Radiation (EDocFind - Com)Hilmi ÖlmezNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer From Pin-Fin Apparatus. Extended Surfaces of Fins Are Used To Increase The Heat Transfer Rate From ADocument22 pagesHeat Transfer From Pin-Fin Apparatus. Extended Surfaces of Fins Are Used To Increase The Heat Transfer Rate From AAlen SajuNo ratings yet
- HW 1 SolDocument9 pagesHW 1 SolNatalia AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 7 Pin Fin ApparatusDocument5 pagesExperiment No 7 Pin Fin Apparatusgaur123450% (2)
- Experimental and Numerical Study of A Mechanically Ventilated Enclosure With Thermal EffectsDocument8 pagesExperimental and Numerical Study of A Mechanically Ventilated Enclosure With Thermal EffectsIbnu SufajarNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 & 2Document10 pagesExercise 1 & 2mohammadNo ratings yet
- 2nd Attempt Final Exam (2022-2023)Document3 pages2nd Attempt Final Exam (2022-2023)alhussenyNo ratings yet
- TEST ON A PIN - FIN APPATATUS BY FORCED CONVECTION - Pin Fin New-2Document5 pagesTEST ON A PIN - FIN APPATATUS BY FORCED CONVECTION - Pin Fin New-2Jady chess24No ratings yet
- AUPHMTmj 07Document4 pagesAUPHMTmj 07Khadeeja NicyNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: CVS 467 Building Physics and ServicesDocument14 pagesHeat Transfer: CVS 467 Building Physics and ServicesharryNo ratings yet
- Ijaiem 2014 03 26 096Document6 pagesIjaiem 2014 03 26 096International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals: Combined Convection and Radiation Heat Transfer (H2)Document17 pagesKing Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals: Combined Convection and Radiation Heat Transfer (H2)hutime44No ratings yet
- Ps7 SolutionsdvdDocument14 pagesPs7 SolutionsdvdBilal ZafarNo ratings yet
- HT T5Document5 pagesHT T5Rohit MehtaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer 1.17Document1 pageHeat Transfer 1.17PurdueMeNo ratings yet
- Thermal ConductivityDocument5 pagesThermal Conductivityopkbvjmn123No ratings yet
- G2 - Problem BankDocument37 pagesG2 - Problem BankSridhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Thermal Analysis of Cables in Unfilled Troughs - Investigation of The IEC Standard (Leon2012)Document9 pagesThermal Analysis of Cables in Unfilled Troughs - Investigation of The IEC Standard (Leon2012)daegerteNo ratings yet
- Calculation of The Fault Level Contribution of Distributed Generation According To Iec Standard 60909Document4 pagesCalculation of The Fault Level Contribution of Distributed Generation According To Iec Standard 60909str69d46No ratings yet
- Chap03 Steady Heat ConductionDocument63 pagesChap03 Steady Heat ConductionDilara ŞimşekNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Wasmohammed mahadi.aNo ratings yet
- Convective Heat Transfer in Impinging-Gas - Jet ArrangementsDocument13 pagesConvective Heat Transfer in Impinging-Gas - Jet ArrangementsArlez HernandezNo ratings yet
- Chap03 HT 3e LectureDocument73 pagesChap03 HT 3e LecturebpulatstudentNo ratings yet
- Physlca ®: Scaling Law For Vortex Dynamics in SuperconductorDocument5 pagesPhyslca ®: Scaling Law For Vortex Dynamics in SuperconductorpietrasekNo ratings yet
- sm1 56Document1 pagesm1 56awoods12835No ratings yet
- Lect. Notes For MEC223 Jun 2021Document144 pagesLect. Notes For MEC223 Jun 2021Dalia MagdyNo ratings yet
- sm1 64Document2 pagessm1 64awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 66Document1 pagesm1 66awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 67Document1 pagesm1 67awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 61Document1 pagesm1 61awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 56Document1 pagesm1 56awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 50Document1 pagesm1 50awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 46Document2 pagessm1 46awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 54Document1 pagesm1 54awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 47Document1 pagesm1 47awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 44Document1 pagesm1 44awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 39Document1 pagesm1 39awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 45Document2 pagessm1 45awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 35Document1 pagesm1 35awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 38Document1 pagesm1 38awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 36Document1 pagesm1 36awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 30Document1 pagesm1 30awoods12835No ratings yet