Professional Documents
Culture Documents
36884244-IV-fluidsb BN
36884244-IV-fluidsb BN
Uploaded by
Asemed AsemedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
36884244-IV-fluidsb BN
36884244-IV-fluidsb BN
Uploaded by
Asemed AsemedCopyright:
Available Formats
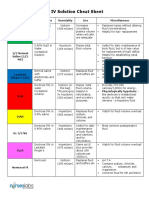
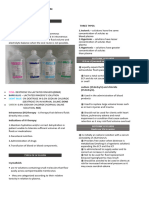
IV FLUIDS
NAME of IV color Type
PNSS Plain LRS D5LRS D5Water D10Water D5 0.3 NaCl
Green Blue Pink Red Blue green Sky blue
Isotonic Isotonic Hypertonic Isotonic Hypertonic Hypertonic
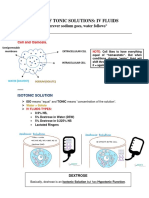
TYPES of FLUID 1. ISOTONIC Fluid no movement of fluid. 2. HYPOTONIC Fluid fluid will enter the cell, the cell will shrink. 3. HYPERTONIC Fluid fluid will go out from the cell, the cell will shrink.
Tonicity of IV Fluids Definition: The tonicity of an IV solution relates to how the red blood cells respond when the solution is added.
Isotonic Fluid moves equally between compartments
Cell volume remains the same
Fluid is moving equally into and out of the compartments
IV FLUIDS
Hypotonic Fluid moves into the cells Fluid moves into RBC causing cell rupture (hemolysis)
Fluid moves from the vascular space into the cells. The major problems with administering hypotonic IV solutions is the hemolyis and swelling of the cells in the brain that occurs
Hypertonic Fluid is pulled out of the cells Fluid moves out of the cell causing crenation (shrinking) of the RBC
Fluid is pulled out of the cells and into the vascular system, so increases intravascular volume.
IV FLUIDS
You might also like
- IV Fluids ChartDocument1 pageIV Fluids Chartzahidtaniv71% (7)
- IV Solution Cheat SheetDocument13 pagesIV Solution Cheat Sheetisapatrick8126100% (4)
- 125.6 (Medicine) DISCHARGE PLANDocument1 page125.6 (Medicine) DISCHARGE PLANNadja Jamilah100% (1)
- Modeling, Change, and SimulationDocument68 pagesModeling, Change, and SimulationArturo Moisés Chávez RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Diagnostics & Laboratory Procedures & Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDiagnostics & Laboratory Procedures & Nursing ResponsibilitiesCamille T. SanchezNo ratings yet
- IV Solution Cheat Sheet: Type Description Osmolality Use MiscellaneousDocument1 pageIV Solution Cheat Sheet: Type Description Osmolality Use MiscellaneousKristine Castillo100% (2)
- Ivf ColorcodingDocument1 pageIvf ColorcodingMariel Coronado100% (1)
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology DiagramDocument4 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology DiagramGuia Rose Sibayan0% (1)
- IV Flow Rate QuizDocument6 pagesIV Flow Rate QuizKannan KalingamNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology HypokalemiaDocument1 pagePathophysiology HypokalemiaRnspeakcomNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NewDocument4 pagesDrug Study NewJehannah Dayanara Berdan HayudiniNo ratings yet
- TesterDocument84 pagesTesterEssantio DeniraNo ratings yet
- 2 Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsDocument6 pages2 Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsHikaru TakishimaNo ratings yet
- 15 Macrodrops Per Minute or 15 Gtss/min 20 Macrodrops Per Minute or 20 Gtts/minDocument4 pages15 Macrodrops Per Minute or 15 Gtss/min 20 Macrodrops Per Minute or 20 Gtts/minShane Pangilinan100% (1)
- IVF Color CodingDocument2 pagesIVF Color CodingLabs Mendoza100% (2)
- IV FluidsDocument1 pageIV FluidsJhensczy Hazel Maye AlbaNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid ComputationDocument2 pagesIV Fluid ComputationRam AugustNo ratings yet
- Emergency CartDocument8 pagesEmergency Cart092109100% (1)
- Different Iv FluidsDocument2 pagesDifferent Iv FluidsBeverly DatuNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 - Fluid and Electrolytes (Unit 1)Document2 pagesNCM 112 - Fluid and Electrolytes (Unit 1)Pauline Mae RobertoNo ratings yet
- Nursing ManagementDocument19 pagesNursing ManagementAjie ZamNo ratings yet
- BSNURSE: NCP - HypertensionDocument3 pagesBSNURSE: NCP - Hypertensionmickey_beeNo ratings yet
- NCP GbsDocument2 pagesNCP GbsJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)Document9 pagesNursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)Gayu Patel100% (2)
- D 5 IMBDocument2 pagesD 5 IMBAloyan Rose JoyNo ratings yet
- Instruments in The Delivery RoomDocument6 pagesInstruments in The Delivery RoomRenea Joy Arruejo0% (1)
- Types of IV FluidsDocument2 pagesTypes of IV FluidsDale DeocaresNo ratings yet
- 13 Areas of AssessmentDocument2 pages13 Areas of Assessmentapi-3718174100% (3)
- IVF Drug StudyDocument5 pagesIVF Drug StudyHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Age Case PresentationDocument21 pagesAge Case PresentationDev AakashNo ratings yet
- RA 7164 Vs RA 9173 - ComparisonDocument15 pagesRA 7164 Vs RA 9173 - ComparisonArlie MarmolejoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities in Blood TransfusionDocument5 pagesNursing Responsibilities in Blood TransfusionPatrick Jayson Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Module 13 - Cystoclysis (Student)Document4 pagesModule 13 - Cystoclysis (Student)Raymond Edge100% (2)
- D5 0.3%Document1 pageD5 0.3%Aloyan Rose Joy0% (1)
- Pcap Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesPcap Pathophysiology PDFMikaela RamosNo ratings yet
- Course in The WardDocument2 pagesCourse in The Wardapi-19762967100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan Pedia TB MeningitisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Pedia TB Meningitisderic100% (10)
- V. The Patient and His CareDocument28 pagesV. The Patient and His CareIanne MerhNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Transes 2Document13 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Transes 2Louise Torres100% (1)
- Senna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeDocument2 pagesSenna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeTempoNo ratings yet
- Intake and OutputDocument2 pagesIntake and OutputNina CervantesNo ratings yet
- IVF Computation Part 1Document6 pagesIVF Computation Part 1JohnNo ratings yet
- Iv FluidsDocument2 pagesIv FluidsKevin Vincent AquinoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 5 Nursing Care PlanMiguelito Galagar GultianoNo ratings yet
- D5LRDocument2 pagesD5LRLouiseville Ann Arcilla PilNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyDimple SumarcaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TramadolDocument2 pagesDrug Study TramadolJemina Rafanan Racadio100% (1)
- D5LRDocument2 pagesD5LRjonoelc100% (5)
- IV FluidsDocument3 pagesIV FluidsAsemed AsemedNo ratings yet
- Am Am - IVDocument7 pagesAm Am - IVamietootNo ratings yet
- Types of IV FluidsDocument15 pagesTypes of IV Fluidskirti thakurNo ratings yet
- Administration of Iv FluidsDocument3 pagesAdministration of Iv FluidsLiza SoberanoNo ratings yet
- What Are IntravenousDocument11 pagesWhat Are IntravenousLynx Angeles RNNo ratings yet
- 5 Lim - Types of IV FluidsDocument16 pages5 Lim - Types of IV FluidsSamantha Ishi LimNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid SelectionDocument12 pagesIntravenous Fluid SelectionTracy100% (4)
- Waterandelectrolyte 170425132238Document50 pagesWaterandelectrolyte 170425132238Sahil SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Iv TherapyDocument3 pagesIv TherapyNashleyah AnayatinNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology 2022-2023 Exercise 13 MaterialsDocument157 pagesPathophysiology 2022-2023 Exercise 13 MaterialsLuis RomanosNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport Unit Passive TransportDocument23 pagesCellular Transport Unit Passive TransportNicolas JayNo ratings yet
- Types of Tonic SolutionsDocument3 pagesTypes of Tonic SolutionsKolimlim, Marienne SD.No ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Selection: Learning ObjectivesDocument11 pagesIntravenous Fluid Selection: Learning ObjectivesKristine AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Maternal Skills ReviewerDocument4 pagesMaternal Skills ReviewerLorel Faith ToradaNo ratings yet
- Maribel M. Galapon: Teacher Iii Caballero Elementary School Sdo Guimba East AnnexDocument13 pagesMaribel M. Galapon: Teacher Iii Caballero Elementary School Sdo Guimba East AnnexEvangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- Mock Test (NQESH) : RequiredDocument12 pagesMock Test (NQESH) : RequiredEvangeline San Jose100% (1)
- Cover LogbookDocument1 pageCover LogbookEvangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- Sinulatan Elementary School Alternative Work Arrangement: 1 2 9 TH F FDocument3 pagesSinulatan Elementary School Alternative Work Arrangement: 1 2 9 TH F FEvangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- Front Covers SBM NewDocument34 pagesFront Covers SBM NewEvangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Grade & Section Advanced StrugllingDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Grade & Section Advanced StrugllingEvangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- We LL Begin With A Box and The Plural Is Boxes But The Plural of Ox Should Be Oxen and Not Oxes Then One Fowl Is GooseDocument14 pagesWe LL Begin With A Box and The Plural Is Boxes But The Plural of Ox Should Be Oxen and Not Oxes Then One Fowl Is GooseEvangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- Office Performance Commitment and Review Form (Opcrf) - Rpms Performance Targets For Sy 2018-2019Document75 pagesOffice Performance Commitment and Review Form (Opcrf) - Rpms Performance Targets For Sy 2018-2019Evangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- A Speaker's Tone Is Revealed Via Diaogues: "Think of Happy Things. It's The Same As Having Wings."Document18 pagesA Speaker's Tone Is Revealed Via Diaogues: "Think of Happy Things. It's The Same As Having Wings."Evangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- Enrolment DataDocument1 pageEnrolment DataEvangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- Idiomatic Expression (Idiom)Document24 pagesIdiomatic Expression (Idiom)Evangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- PoemsDocument33 pagesPoemsEvangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- We LL Begin With A Box and The Plural Is Boxes But The Plural of Ox Should Be Oxen and Not OxesDocument5 pagesWe LL Begin With A Box and The Plural Is Boxes But The Plural of Ox Should Be Oxen and Not OxesEvangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- Singular: Foot Tooth MouseDocument4 pagesSingular: Foot Tooth MouseEvangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- DCP Orientation Handbook As of 18 June 2014Document43 pagesDCP Orientation Handbook As of 18 June 2014Jeffrey MacalinoNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 English Speaking Using Used To VerbDocument8 pagesGrade 4 English Speaking Using Used To VerbEvangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- Our Lady of The Sacred Heart College of Guimba, IncDocument5 pagesOur Lady of The Sacred Heart College of Guimba, IncEvangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- Edtech1 PortfolioDocument2 pagesEdtech1 PortfolioEvangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- IV FluidsDocument3 pagesIV FluidsEvangeline San Jose83% (6)
- IV FluidsDocument3 pagesIV FluidsEvangeline San Jose83% (6)
- How Does This Theory Differ From Traditional Ideas About Teaching and LearningDocument2 pagesHow Does This Theory Differ From Traditional Ideas About Teaching and LearningEvangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- BibliotherapyDocument4 pagesBibliotherapyMonirul Islam100% (2)
- Controlab Catalogue 7th Edition-3Document271 pagesControlab Catalogue 7th Edition-3suboesetsoafiaNo ratings yet
- An Adaptive Communication Architecture For Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument27 pagesAn Adaptive Communication Architecture For Wireless Sensor NetworksmouliomNo ratings yet
- MTU 14 V4000 Gas Engine SpesificationDocument6 pagesMTU 14 V4000 Gas Engine Spesificationengineering asrNo ratings yet
- Ups 10 Kva Eaton ManualDocument116 pagesUps 10 Kva Eaton ManualEnrique BarradasNo ratings yet
- Ch11 - Excel For StudentsDocument90 pagesCh11 - Excel For StudentsSimran Kaur100% (1)
- Vagdevi Vilas School - CBSE, Munnekolalu: Chairman's MessageDocument2 pagesVagdevi Vilas School - CBSE, Munnekolalu: Chairman's MessageKamapantula SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Global Technology Asset Partners Media Comment LetterDocument3 pagesGlobal Technology Asset Partners Media Comment LetterJan VermeulenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Data CompressionDocument18 pagesChapter 5 Data CompressionrpNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Tier-2 8th August 2022 Maths by CrackuDocument29 pagesSSC CGL Tier-2 8th August 2022 Maths by CrackuSHAHEEN AKBARNo ratings yet
- Harmonographs. II. Circular DesignDocument10 pagesHarmonographs. II. Circular DesignAditama MKNo ratings yet
- Experiment #4 Discharge Through An Orifice MeterDocument6 pagesExperiment #4 Discharge Through An Orifice MeterEddy KimathiNo ratings yet
- Discipleship Manual PDFDocument233 pagesDiscipleship Manual PDFBen LombardNo ratings yet
- Aarushi Patidar Geography PPT On Weather Conditions in Different Parts of IndiaDocument14 pagesAarushi Patidar Geography PPT On Weather Conditions in Different Parts of IndiaAarushi PatidarNo ratings yet
- E-Store Project Software Requirements SpecificationDocument14 pagesE-Store Project Software Requirements SpecificationShwetha KulloliNo ratings yet
- Elecricity Multiple Choice Questions Set 1Document2 pagesElecricity Multiple Choice Questions Set 1Joel OkohNo ratings yet
- Philips VisicuDocument8 pagesPhilips Visicupreeti jhaNo ratings yet
- Geometry of Projective Algebraic CurvesDocument429 pagesGeometry of Projective Algebraic CurvesluisufspaiandreNo ratings yet
- ExtimityDocument12 pagesExtimityDamián DámianNo ratings yet
- General Instruction Manual: Organization Consulting DepartmentDocument14 pagesGeneral Instruction Manual: Organization Consulting DepartmentmmmNo ratings yet
- Copia de Caso Healthy Bear 2022Document4 pagesCopia de Caso Healthy Bear 2022rataNo ratings yet
- User Perception and Satisfaction Towardssmart Watch in Coimbatore and TirupurdistrictsDocument7 pagesUser Perception and Satisfaction Towardssmart Watch in Coimbatore and TirupurdistrictsESWARAN SANTHOSHNo ratings yet
- NE40E M2KBV800R022SPH120PatchReleaseNotesDocument20 pagesNE40E M2KBV800R022SPH120PatchReleaseNotesLuan BenatoNo ratings yet
- Vsphere Esxi Vcenter Server 602 Host Management GuideDocument200 pagesVsphere Esxi Vcenter Server 602 Host Management GuideMunib AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Reading Comprehension Grade 3Document6 pagesCritical Thinking Reading Comprehension Grade 3nino tielidzeNo ratings yet
- Use of Media in Language Teaching - Brinton - 2001Document18 pagesUse of Media in Language Teaching - Brinton - 2001Sumayyah Ahmad100% (1)
- (123doc) - Dap-An-Mon-Viet-Tieng-Anh-1-En21-041-ChuanDocument23 pages(123doc) - Dap-An-Mon-Viet-Tieng-Anh-1-En21-041-Chuanttbngoc0805No ratings yet
- TDS Nitoflor Hardtop IDDocument5 pagesTDS Nitoflor Hardtop IDDimas SaputraNo ratings yet