Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plate Girder Design Example of Rev
Uploaded by
lyhalim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageThis document provides a worked example of plate girder design. It summarizes checking the resistance of an intermediate transverse stiffener's cross section and buckling resistance. It then designs intermediate transverse stiffeners at locations B and C to have sufficient stiffness and buckling resistance to withstand compressive axial force from tension in the field. It selects a double-sided stiffening design and checks the outstands meet criteria to avoid torsional and local buckling.
Original Description:
Original Title
34
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a worked example of plate girder design. It summarizes checking the resistance of an intermediate transverse stiffener's cross section and buckling resistance. It then designs intermediate transverse stiffeners at locations B and C to have sufficient stiffness and buckling resistance to withstand compressive axial force from tension in the field. It selects a double-sided stiffening design and checks the outstands meet criteria to avoid torsional and local buckling.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pagePlate Girder Design Example of Rev
Uploaded by
lyhalimThis document provides a worked example of plate girder design. It summarizes checking the resistance of an intermediate transverse stiffener's cross section and buckling resistance. It then designs intermediate transverse stiffeners at locations B and C to have sufficient stiffness and buckling resistance to withstand compressive axial force from tension in the field. It selects a double-sided stiffening design and checks the outstands meet criteria to avoid torsional and local buckling.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Worked example
Plate girder design example
559
Sheet 7 of 10
Rev
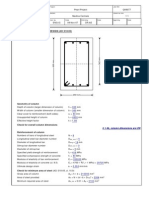
Stiffener cross-section resistance:
N,R,i
= -= 16920
Yuo
1.0
265 x
= 4484
kN > 2293 kN
= Nro
OK
Stiffener buckling resistance:
a,
rfi J F
= = 88.4
L,, =0.75h,+=0.75 x2000 = 1500mm
BS EN 1993-1-5 C19.4(2)
Since
1c 0.2, buckling effects may be ignored and only cross-section checks apply.
BS EN 1993-1-1 C16.3.1.2(4)
Design qf intermediate transverse stijfeners at B and C
The stiffeners at B and C should be designed to have a minimum stiffness and sufficient buckling resistance to withstand a compressive axial force, Pro, arising from the tension field. For panels BC and CD, a = 3900mm. Try double-sided stiffening consisting o,f two flats 80 x 15mm (i.e. h, 80mm; t, = 1 5 m m ) Check outstands: Fort, = 1 5 m m , f , =275N/mm2
BS EN 10025-2
E=
6
235
= 0.92
h, = 80113&t,= 13 x 0.92 x 15 = 180mm
Since h , l t , l l 3 . 0 s torsional buckling is avoided, as is local buckling since h , i t , l l 4 . 0 ~which is the Class 3 limit for a compressed outstand. The effective stiffener section comprises the area of the stiffeners themselves plus an effective web width equal to 1 5 ~ t = , 15 x 0.92 x 15 = 208mm (where E relates to the web material) either side of the stiffeners, where such material is available. The effective stiffener section ,for locations B and C is shown below:
BS EN 199.3-1 -5 Cl 9.2.1 (8)
You might also like
- Masonry Design ExamplesDocument13 pagesMasonry Design ExamplesRoger FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Lifting Lug CalculationDocument5 pagesLifting Lug CalculationEm Mar100% (2)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Single Footing Design - Telecomm, Transmission & Guyed Tower & Pole - TIA 222F & ACIDocument12 pagesSingle Footing Design - Telecomm, Transmission & Guyed Tower & Pole - TIA 222F & ACIasad_naqvi100% (2)
- A1 - Composite Beam PDFDocument6 pagesA1 - Composite Beam PDFNaim YaqeenNo ratings yet
- Steel5 ( 39pages)Document45 pagesSteel5 ( 39pages)Kristin Brienne Leander-Renomeron100% (3)
- Mathcad - Column C-1Document7 pagesMathcad - Column C-1lnt4No ratings yet
- 8 - Design For TorsionDocument34 pages8 - Design For TorsionACTION plusNo ratings yet
- Beam Deflection If Minimum Thickness Is Not Satisfied, Check Beam DeflectionDocument7 pagesBeam Deflection If Minimum Thickness Is Not Satisfied, Check Beam DeflectionLester John PrecillasNo ratings yet
- 2 Way Slab Design - 31 Jul 13Document111 pages2 Way Slab Design - 31 Jul 13Vance Kang100% (1)
- ACI Pad Foundation ExampleDocument7 pagesACI Pad Foundation ExampleEm MarNo ratings yet
- Kda - Factory Ii (Gen - Trias, Cavite) Design of MicropilesDocument4 pagesKda - Factory Ii (Gen - Trias, Cavite) Design of MicropilesRoda Cadiz100% (4)
- Axial Load Capacity of Columns: (Short) : N ST G ST G ST STDocument9 pagesAxial Load Capacity of Columns: (Short) : N ST G ST G ST STAurora VillalunaNo ratings yet
- 3-Pile Cap DesignDocument9 pages3-Pile Cap DesignMitra RampersadNo ratings yet
- Structu4l ST33L De3sign ProblemDocument6 pagesStructu4l ST33L De3sign ProblemLimuel Milo Lebios0% (1)
- Design For RC Flat SlabsDocument70 pagesDesign For RC Flat SlabsAil Aafaaq100% (3)
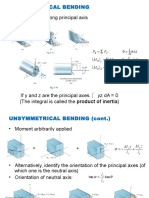
- Unsymmetrical Bending Shear Stress DistributionDocument29 pagesUnsymmetrical Bending Shear Stress DistributionMuhammad RedzuanNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Pile FootingDocument27 pagesTopic 6 - Pile FootingDhanmer Lopez0% (2)
- Ship Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesFrom EverandShip Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- May 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 4: Eview NnovationsDocument3 pagesMay 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 4: Eview NnovationsKian Inductivo100% (1)
- RC Column Design (ACI318-05)Document5 pagesRC Column Design (ACI318-05)Rizwan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Joist SlabDocument13 pagesJoist SlabAhmed Nabil80% (5)
- Lecture7 TrueDocument30 pagesLecture7 TrueSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- Nov2022 Coaching JGBDocument51 pagesNov2022 Coaching JGBNadzNo ratings yet
- May 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 5: Eview NnovationsDocument4 pagesMay 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 5: Eview NnovationsKian Inductivo100% (1)
- Breeder House FoundationDocument16 pagesBreeder House FoundationRobbyTeresaNo ratings yet
- Steel Module 4Document5 pagesSteel Module 4dash1991No ratings yet
- Isolated Footing Design ProblemDocument5 pagesIsolated Footing Design ProblemthabisNo ratings yet
- Cold Formed BendingDocument8 pagesCold Formed BendinggeorgeispasoiuNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Worked Example: Beam Example 4 Sheet4of4 RevDocument1 pageWorked Example: Beam Example 4 Sheet4of4 RevlyhalimNo ratings yet
- Indrumator Metal - EGDocument37 pagesIndrumator Metal - EGhooky1100% (1)
- 603 CompreDocument15 pages603 CompreCj SuarezNo ratings yet
- Corbel DesignDocument31 pagesCorbel DesignAshraf ZayedNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 3Document64 pagesChapter # 3Pharo TotNo ratings yet
- Worked Example: Design QF Bearing Stijfener at ADocument1 pageWorked Example: Design QF Bearing Stijfener at AlyhalimNo ratings yet
- Moment of ResistanceDocument10 pagesMoment of ResistanceBabaYakeNo ratings yet
- Eigen Modes - PDF Timesaving-Torsiondesign-Ia PDFDocument32 pagesEigen Modes - PDF Timesaving-Torsiondesign-Ia PDFGeorge GeorgianNo ratings yet
- Compression MembersDocument172 pagesCompression Membersbsitler100% (1)
- армирование колонаDocument25 pagesармирование колонаtangerineNo ratings yet
- Link Look UpDocument7 pagesLink Look UpValerioZucchelliNo ratings yet
- Shear Design Continuous BeamDocument18 pagesShear Design Continuous Beamsaleh34534rf34No ratings yet
- Beam Example 2 Sheet2of3 Rev: XLBMM'Document1 pageBeam Example 2 Sheet2of3 Rev: XLBMM'lyhalimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document12 pagesLesson 6Zayyan RomjonNo ratings yet
- Beams Reinforced For Tension OnlyDocument47 pagesBeams Reinforced For Tension OnlyArkie TectureNo ratings yet
- Chapt 10Document22 pagesChapt 10yaori700% (1)
- Compression MembersDocument11 pagesCompression Membersayush kumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document60 pagesLecture 5Cecille Grace ReyesNo ratings yet
- Structures For Architects II: ARC 460 ARC 460Document18 pagesStructures For Architects II: ARC 460 ARC 460Omar NajmNo ratings yet
- The Fatigue Strength of Transverse Fillet Welded Joints: A Study of the Influence of Joint GeometryFrom EverandThe Fatigue Strength of Transverse Fillet Welded Joints: A Study of the Influence of Joint GeometryNo ratings yet