Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 5 Light (Student)
Chapter 5 Light (Student)
Uploaded by
Asmida Abdul HalimOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 5 Light (Student)
Chapter 5 Light (Student)
Uploaded by
Asmida Abdul HalimCopyright:
Available Formats
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
CHAPTER 5: LIGHT
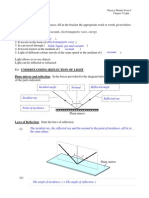
In each of the following sentences, fill in the rac!et the appropriate word or words gi"en elow# solid, liquid, gas, vacuum, electromagnetic wave, energy $# Light is a form of % &# '# It tra"els in the form of % & (# In can tra"el through % & 4# It tra"els fastest in the medium of % & 5# Light of different colours tra"els at the same speed in the medium of % Light allows us to see o )ects# Light can e reflected or refracted# 5.1 UNDERSTANDING REFLECTION OF LIGHT Plane mirror and refle !ion* In the o+es pro"ided for the diagram elow, write the name of each of the parts shown#
&
Plane mirror La"# of Refle !ion* ,tate the laws of reflection# %i& -----------------------------------# ---------------------------------## --#
r Plane mirror
%ii&
-----------------------------------# #
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
-----------------------------------# # E$er i#e 1. .he diagram elow shows how the relationship etween incident angle and reflected angle can e in"estigated# Fill in the "alues of the angles of reflection, r in the ta le elow
mirror i r
/N /FF /N /FF
i r
mirror
Laser pen
Laser pen
ir$0'0(04050
E$er i#e %:
/riginal direction Mirror
1ased on the diagram on the left, calculate the angle, # 2ence determine the angle of de"iation, d#
50
o o
normal
E$er i#e &*
'
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
Mirror efore rotation
Mirror rotated o
Incident ray
norm
al
7eflected ray efore rotation 7eflected ray after rotation
1ased on the diagram a o"e, when the mirror is rotated an angle , without changing the incident ray, what is the angle rotated ,, for the reflected ray in terms of 5
Ima'e formed () a *lane mirror* 3sing the law of reflection, complete the ray diagram to determine the position of the image#
6 1
o )ect
i$ r$
8ye
4hat can you say a out the line )oining o )ect and image5 --------------4hat can you say a out the distances 61 and 1C5 ------------------## Differen e# (e!"een real and +ir!,al ima'e*
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
7eal image9irtual imageCan e caught on a screenCannot e caught on a screenFormed y the meeting of real rays#Form at a position where rays appear to e originating#
C-ara !eri#!i # of ima'e formed () *lane mirror* / ser"e the pictures elow as well as using pre"ious !nowledge, list the characteristics# i& ii& iii& i"&
o )ect
mir ror
image
E$er i#e 1* Complete the ray diagram elow consisting of ' rays originating from the o )ect, reflected and entering the eye such that the eye sees the image#
Mirror
8ye
o )ect
E$er i#e %*
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
6hmad is mo"ing with speed ' m s:$ towards a plane mirror# 6hmad and his image will approach each other at $ m s:$ ' m s:$ ( m s:$ 4 m s:$ E$er i#e &* Four point o )ects 6, 1, C and ; are placed in front of a plane mirror MN as shown# 1etween their images, which can e seen y the eye5
8ye
6 1 C ;
ACTI.IT/*
Find out some of the uses of plane mirrors %application of reflection&#
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
C,r+ed 0irror#* Concave mirror Convex mirror
C r
C r
Terminolo')* 7efer to the diagrams a o"e and gi"e the names for the following*
C = r = P = PC =
Effe ! of ,r+ed mirror# on in iden! ra)#* a& In iden! ra)# *arallel !o !-e *rin i*al a$i#*
Concave mirror
Convex mirror P P F C
f r
,tudy the diagrams a o"e and fill in the lan!s for the following sentences# Rays parallel to the principal axis converge at the , F F is positioned at the .. between C and P FP is named the which is denoted by f. Hence write an equation giving the relationship between r and f.
f r
<
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
& In iden! ra)# *arallel !o ea - o!-er (,! no! *arallel !o !-e *rin i*al a$i#*
Con a+e mirror
Con+e$ mirror
Focal plane
Focal plane F f r P P F f r C
,tudy the diagrams a o"e and fill in the lan!s in the following sentences# Parallel rays con"erge at a point called ----------.he focal plane )oins F, the principal focus and all ----------##and is ---------# to the principal a+is .he ray passing through C is reflected ac! along the line of the--------#ray# .he distance etween the focal plane and the mirror is the ----------#,f#
Ima'e formed () ,r+ed mirror %ray diagram method& Prin i*le of dra"in' ra) dia'ram#* a. Ra)# *arallel !o !-e *rin i*al a$i# are refle !ed !-ro,'- !-e *rin i*al fo ,#1 F. E$am*le:
Concave mirror
Convex mirror
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
E$er i#e 1* Complete the ray diagrams elow*
Concave mirror
Convex mirror
(2 Ra)# *a##in' !-ro,'- !-e *rin i*al fo ,# are refle !ed *arallel !o !-e *rin i*al a$i#. E$am*le:
Concave mirror E$er i#e %* Complete the ray diagrams elow*
Convex mirror
Concave mirror
Convex mirror
2 Ra)# *a##in' !-ro,'- !-e en!er of ,r+a!,re are refle !ed dire !l) (a 3.
Concave mirror
Convex mirror
>
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
E$er i#e &* Complete the ray diagrams elow*
Concave mirror
Convex mirror
Ima'e formed () on a+e mirror: 3sing the principles of construction of ray diagram, complete the ray diagrams for each of the cases shown elow* u ? o )ect distance@ v ? image distance @ f ? focal length @ r ? radius of cur"ature Ca#e 1: u 4 %f Conca"e mirror o )ect C F F
2ence state the characteristics of image formed* i& Ca#e %: u 5 %f or u = r Conca"e mirror o )ect C F F ii& iii&
Characteristics of image formed* i& ii& iii&
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
Ca#e &: f 6 u 6 %f Conca"e mirror o )ect C F F
Characteristics of image formed* i& Ca#e 7: u5f Conca"e mirror o )ect C F F ii& iii&
Characteristics of image formed* i& Ca#e 5: u6f
Conca"e mirror o )ect F F
Characteristics of image formed* i& ii& iii&
$0
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
Ima'e formed () on+e$ mirror: %using construction of ray diagram&# u ? o )ect distance @ v ? image distance @ f ? focal length @ r ? radius of cur"ature o )ect C F Conca"e mirror F
Characteristics of image formed* i& U#e# of ,r+ed mirror#* Ne"!on8# Tele# o*e* Fill in the o+es the type of mirror used ii& iii&
Lens Eye
Car -ead lam*
Cur"ed mirror
lamp
OFF
4here should the lamp e placed to achie"e the a o"e result5
$$
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
A !i+i!)* Find more uses of cur"ed mirrors#
$'
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
5.% UNDERSTANDING REFRACTION OF LIGHT
air
water
4hat is the phenomenon which causes the ending of light in the picture a o"e5 --------------------------------------4hy did this ending of light occur5 %thin! in terms of "elocity of light& ---------------------------------------
Refra !ion of li'-!* Fill in each of the o+es the name of the part shown
i
Air
Blass r r
Air
$(
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
Dire !ion of refra !ion* normal Less dense medium ;enser medium normal
denser medium Less dense medium
;raw on the diagrams a o"e the appro+imate directions the refracted rays# 4hen light tra"els from a less dense medium to a denser medium, the ray is refracted 9!o"ard:a"a) from2 the normal at point of incidence# 4hen light tra"els from a more dense medium to a less dense medium, the ray is refracted 9!o"ard:a"a) from2 the normal at point of incidence# Snell8# la"* ,nellCs law states that --------------------
4hat is the name and sym ol of the constant5 ----------## E$er i#e 1* 7eferring to the diagram on the right, Calculate the refracti"e inde+ of liDuid:E# 6ir LiDuid:E (0o <0o
$4
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
E$er i#e %* 7eferring to the diagram on the right, Calculate the refracti"e inde+ of liDuid:F# 6ir LiDuid:F (0o 45o
E$er i#e &* 8ye 6ir /n the diagram to the right, draw two rays which originate from the fish to show how a person o ser"ing from a o"e the surface of the water is a le to see the image of the fish at an apparent depth less than the actual depth of the fish# water
o )ect
E$er i#e 7* 6n eDuation that gi"es the relationship etween apparent depth, real depth and the refracti"e inde+ of water for the diagram a o"e is
n= real depth apparent depth
If the fish is at an actual depth of 4 m and the refracti"e inde+ of water is $#((, what is the apparent depth of the image5
$5
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
5.& UNDERSTANDING TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION OF LIGHT Cri!i al an'le and !o!al in!ernal refle !ion* Figures a, and c show rays eing directed from liDuid:F which is denser than air towards the air at different angles of incident,# 6ir 6ir A0o LiDuid:F GC Figure a LiDuid:F C Figure
6mong the figures a, and c, only Figure a has a complete ray diagram# %i& %ii& %iii& Complete the ray diagrams for Figure and Figure c# .he angle, C is called --------# .he phenomenon which occurs in Figure c yang is called --------------# %i"& ,tate ' conditions which must e satisfied in order for the phenomenon you mentioned in %iii& to occur# ----------------------------------------------------------------E$er i#e 1* 7eferring to figure d and using ,nellCs law, write an eDuation that gi"es the relationship etween the critical angle, C, the refracted angle and the refracti"e inde+ of liDuid:F 6ir LiDuid:F C A0o 6ir LiDuid:F HC Figure c
Figure d
$<
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
E$er i#e %* 7eferring to Figure e, determine the refracti"e inde+ of liDuid:I 6ir LiDuid:I (0o E$er i#e &* Figure e A0o
8+plain why a pencil partially immersed in water loo!s ent#%3se a ray diagram&# 8ye
E$er i#e 7* Complete the path of the ray in the diagram elow and e+plain how a mirage is formed# o )ect Layer of cool air 8ye
Layer of hot air ground
$=
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
E$er i#e 5* Completing the ray diagram elow, to show how a periscope wor!s* %critical angle of glass ? 4'o&
/ )ect
Blass prism
8ye
$>
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
5.7 UNDERSTANDING LENSES T-in Len#e# * T)*e# of len#e# * Name the types of lenses shown elow# %i&
a#
c#
%ii&
a#
c#
Forma!ion of a on+e$ len# and !erminolo'): name the parts shown
Forma!ion of a on a+e len# and !erminolo'): name the parts shown
$A
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
Refra !ion of ra)# *arallel !o !-e *rin i*al a$i# of a on+e$ len#* ;raw in the following diagrams the paths of the rays after passing through the lens# 4rite in the o+ed pro"ided, the name of the point or line shown# i&
ii&
iii& F
i"&
'0
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
Prin i*le# of on#!r, !in' ra) dia'ram#* Complete the path of each ray after passing through the lens i& ii& iii&
F F i"& F F F F
F F
"& F
"i& F F
"ii&
"iii&
F F F
E$er i#e 1* ,tate the meaning of each of the following terms* i& Focal length , f *
ii& / )ect distance, u * iii& Image distance, v * E$er i#e %* ;escri e how you would estimate the focal length of a con"e+ lens in the school la #
'$
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
C-ara !eri#!i # of ima'e formed () a on+e$ len# * %Construction of ray diagram method& Construct ray diagrams for each of the following cases and state the characteristics of the image formed# i2 Ca#e 1 * u 4 %f where u ? o )ect distance @ and f ? focal length of lens# Lens o )ect 'F Characteristics of image* F F
ii2 Ca#e % * u 5 %f Lens o )ect 'F F F
Characteristics of image*
iii2 Ca#e & * %f 4 u 4 f Lens o )ect 'F F F
Characteristics of image* i+2 Ca#e 7 * u = f
''
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
Lens o )ect 'F F F
Characteristics of image*
+2 Ca#e 5 * u < f
Lens o )ect 'F F F
Characteristics of image*
E$er i#e* In each of the following statements elow, fill in the space pro"ide one of the following conditions# % u > 2f / 2f = u / 2f > u > f / u > f / u < f & i& .o o tain a real image, the o )ect must e placed at a distance u such that - --ii& .o o tain a "irtual image, the o )ect must e placed at a distance u such that ---
'(
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
C-ara !eri#!i # of ima'e formed () on a+e len# * % y construction of ray diagrams & Construct a ray diagram for each of the following and state the characteristics of the image formed i& Lens o )ect 'F F F
Characteristics of image* ii& Lens o )ect 'F F F
Characteristics of image * No!e* Image formed y a conca"e lens is always diminished, "irtual and on the same side of the lens as the o )ect# Po"er of a len# 9p2 .he power of the lens is gi"en y* Power of lens ? focal length Si'n on+en!ion %for focal length& and the ,#I# unit for power of a lens# .he focal length of a con"e+ lens is %positi"eJnegati"e& .he focal length of a conca"e lens is %positi"eJnegati"e& .he ,#I# unit for the power of a lens is-####-and its sym ol is- 4hen calculating the power of a lens, the unit of the focal length must e in %mJcm& E$er i#e 1 * 6 conca"e lens has a focal length of $0 cm# 4hat is its power5
$
'4
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
E$er i#e % * .he power of a lens is K 5 ;# ,tate whether it is a con"e+ lens or a conca"e lens and calculate its focal length#
Linear 0a'nifi a!ion 9m2 * ;efinition* Linear ma'nifi a!ion ? height of o )ect
m= hi h0
height of image
1ased of the definition a o"e and the ray diagram elow, deri"e an e+pression for the relationship etween linear magnification, m, the o )ect distance, u and the image distance, v#
1 ho 6 u
Lens /
v C ; hi
Len# form,la * .he relationship etween the o )ect distance, u, image distance, v, and the focal length, f, of a lens is gi"en y
$ $ $ + = u v f
.his lens formula is "alid for oth con"e+ and conca"e lenses#
4hen using the len# form,la, the Lreal i# *o#i!i+e #i'n on+en!ionC must e followed# .he rules stated in this sign con"ention are*
'5
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
$& '& (&
A**li a!ion of !-e len# form,la* E$er i#e 1# 6n o )ect is placed $0 cm in front of a con"erging lens of focal length $5 cm# Calculate the image distance and state the characteristics of the image formed#
E$er i#e % *
6n o )ect is placed (0 cm in front of a con"erging lens of focal length '5 cm# a& Find the position of the image, and state whether the image is real or "irtual# & Calculate the linear magnification of the image#
La!i-an & * 6n o )ect is placed (0 cm in front of a di"erging lens of focal length '0 cm# Calculate the image distance and state whether the image is real or "irtual#
Len#e# and o*!i al in#!r,men!# *
'<
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
1. 0a'nif)in' 'la## 9#im*le mi ro# o*e 2* 6 lens acts as a magnifying glass when the o )ect is placed as in case 5 on page '(# i& 6 magnifying glass consists of a % on+er'in' : di+er'in'& lens# ii& .he o )ect must e placed at a distance %more !-an f : #ame a# f : le## !-an f : (e!"een f and %f : more !-an %f& in order for the lens to act as a magnifying glass# iii& .he characteristics of the image formed y a magnifying glass are yang %real : +ir!,al& @ %in+er!ed : ,*ri'-!& @ %ma'nified :dimini#-ed& @ %on !-e #ame #ide a# !-e o(;e ! : on !-e o**o#i!e #ide of !-e o(;e !&# i"& Breater magnification can e o tained y using a lens which has %lon' : #-or!& focal length# Complete the ray diagram elow to show how a magnifying glass produces an image of the o )ect#
Lens o )ect 'F F F
E$er i#e 1 * 6 magnifying glass produces an image with linear magnification ? 4# If the power of the lens is K$0 ;, find the o )ect distance and image distance#
'=
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
E$er i#e %:
4hich of the following lenses with their powers gi"en elow ma!es the magnifying glass with the highest power of magnification5 6# M 5 ; 1# M'5 ; C# K5 ; ;# K'5 ;#
%. Sim*le amera * .he diagram elow shows the structure of a simple camera# In the o+es pro"ided, write the names of the parts shown# Focusing screw Film drum
;iaphragm ad)ustment ring For each of the parts you ha"e named, state its function#
&. Slide *ro;e !or * .he diagram elow shows the structure of a simple camera# In the o+es pro"ided, write the names of the parts shown ,creen
Light source
Complete the ray diagram a o"e to e+plain how the slide pro)ector wor!s#
'>
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
7. A#!ronomi al !ele# o*e * 0a3in' of !-e a#!ronomi al !ele# o*e. .he astronomical telescope consists of ' % on+er'in' : di+er'in'& lenses# .he o )ecti"e lens has focal length, fo and the eye lens has focal length, fe where % fo 6 fe J fo 4 fe &# .he lenses are arranged such that the distance etween the o )ecti"e lens and the eye lens is %fo < fe J fo = fe J fo $ fe J fo:fe&#
Parallel rays from distant / )ecti"e lens o )ect Fo Fe
8ye lens
Complete the ray diagram a o"e to show how the astronomical telescope wor!s# C-ara !eri#!i # of ima'e formed () an a#!ronomi al !ele# o*e* .he first image formed y the o )ecti"e lens is %"irtualJreal @ uprightJin"erted @ diminishedJmagnified&# .he final image is %"irtualJreal @ uprightJin"erted @ diminishedJmagnified&# .he final image is located at % Fo : Fe : infini!)&#
0a'nif)in' Po"er 902 * M?
f f
0 e
E$er i#e* 6n astronomical telescope with high power of magnification can e uilt using eye lens of %long J short& focal length and o )ecti"e lens of %long J short& focal length#
'A
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
5. T-e om*o,nd mi ro# o*e * S!r, !,re of !-e om*o,nd mi ro# o*e* 6 compound microscope consists of ' %con"erging J di"erging& lenses .he focal length of the eye lens is %long J short& and the focal length of the o )ecti"e lens is %long J short&# .he o )ecti"e lens is arranged such that the o )ect distance, u is %u = fo / fo < u < 2 fo / u =2fo&# .he eye lens is used as a %magnifying J di"erging J pro)ector& lens# .he total length, s, etween oth lenses is % s = fo + fe @ s > fo+fe &
L0 / )ect Fo Fe
Le
8ye
Complete the ray diagram a o"e to show how the compound microscope wor!s# C-ara !eri#!i # of ima'e formed () om*o,nd mi ro# o*e* .he first image formed y the o )ecti"e lens is %realJ"irtual @ diminishedJmagnified @ uprightJin"erted &# .he final image is %realJ"irtual @ diminishedJmagnified @ uprightJin"erted &#
E$er i#e 1 9a2 * 6 compound microscope consists of two lenses of focal lengths ' cm and $0 cm# 1etween them, which is more suita le as the eye lens5 8+plain your answer#
9(2* 2ow would you arrange the lenses in %a& to ma!e an astronomical telescope5
(0
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
Reinfor emen!* Par! A* $# 1etween the following statements a out reflection of light, which is no! true5 6# 6ll light energy incident on a plane mirror is reflected# 1# .he angle of incidence is always the same as the angle of reflection# C# .he incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the point of incidence, all lie on the same plane# ;# .he speed of the reflected ray is the same as the speed of the incident ray# '# 6 oy stands in front of a plane mirror# 2e o ser"es the image of some letterings printed on his shirt# .he letterings on his shirt is as shown in Figure $#
Figure $ 1etween the following images, which is the image o ser"ed y the oy5 6 1 C ;
(# Figure ' shows an o )ect, / placed in front of a plane mirror# 1etween the positions 6, 1, C and ;, which is the position of the image5 6 Plane mirror / Figure ' 4# 6 student is mo"ing with a "elocity of ' m s:$ towards a plane mirror# .he distance etween the student and his image will mo"e towards each other at the rate 6# ' m s:$ 1# ( m s:$ C# 4 m s:$ ;# 5 m s:$ 8# < m s:$ 1 C ;
5# .he ta le elow shows the characteristics of the images formed y a conca"e mirror for "arious positions of the o )ect# 6ll sym ols used ha"e the usual meanings# 4hich of them is no! !r,e5
($
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
6 1 C ;
Po#i!ion of o(;e ! u > 2f f < u < 2f u=f u<f
C-ara !eri#!i # of ima'e ;iminished, in"erted, real Magnified, in"erted, real ,ame siNe, in"erted, real Maginfied, upright, "irtual
<# 4hich of the following ray diagram is correct5 6 50o 50o C F C F 1 C
Plane mirror
Con"e+ mirror
Conca"e mirror
=# .he depth of a swimming pool appears to e less than its actual depth# .he light phenomenon which causes this is 6# 1# C# ;# 7eflection 7efraction ;iffraction Interference
># .he critical angle in glass is 4'o# 4hat is the refracti"e inde+ of glass5 6# $#' 1# $#( C# $#4 ;# $#5 8# $#<
A# 4hich of the following are the characteristics of an image formed y a magnifying glass5 6# 1# C# ;# Magnified, "irtual, in"erted ;iminished, real, upright Magnified, "irtual, upright ;iminished, "irtual, in"erted
('
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
$0# 6 student is gi"en three con"e+ lenses of focal lengths ' cm, $0 cm and 50 cm# 2e wishes to construct a powerful astronomical telescope# 4hich of the following arrangements should he choose5 6 1 C ; Par! > $# 8ye Focal length of o )ecti"e lens J cm 50 $0 ' 50 Focal length of eye lens J cm ' $0 50 $0
air water
Figure ( Figure ( shows the eye of a person loo!ing at a fish# a& ,!etch a ray diagram consisting of ' rays originating from the eye of the fish to show why the image of the fish is seen closer to the surface# & .he fish is at a depth of ' m# If the refracti"e inde+ of water is $#((, calculate the apparent depth of the fish#
((
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
'# a& ,tarting with the lens formula, u + v = f , deri"e an eDuation that gi"es the relationship etween liner magnification, m and the image distance, v# 2ence s!etch the graph of m against v on the a+es pro"ided elow#
$ $ $
% & ,tate the "alue of m at the point of intersection of the graph with the "ertical a+is#
%c& ;escri e how you would determine the focal length of the lens using the graph#
(4
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
Par! C $# 6 student used a slide pro)ector to pro)ect a picture onto the screen# Figure $a and $ show the relati"e positions of the slide, pro)ector lens and the screen# It is o ser"ed that when the screen is mo"ed further away %Figure $ &, the lens of the pro)ector has to e mo"ed nearer to the slide to o tain a sharp image# Pro)ector lens ,creen ,lide image
Figure $a
Pro)ector lens ,creen ,lide image Figure $ 1ased on your o ser"ations and !nowledge of lenses@ a& ma!e one suita le inference#
& state an appropriate hypothesis that could e in"estigated#
c& descri e how you would design an e+periment to test your hypothesis using a con"e+ lens, filament ul and other apparatus# In your description, state clearly the following* %i& aim of the e+periment
(5
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
%ii&
"aria les in the e+periment
%iii& List of apparatus and materials
%i"& 6rrangement of the apparatus
%"& .he procedure of the e+periment, which includes the method of controlling the manipulated "aria le and the method of measuring the responding "aria le
%"i& .he way you ta ulate the data
%"ii& .he way you would analyse the data
(<
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
'# 6 student carried out an e+periment to in"estigate the relationship etween o )ect distance, u, and image distance, v, for a con"e+ lens# .he student used "arious "alues of u and recorded the corresponding "alues of v# .he student then plotted the graph of uv against u + v as shown in Figure '#
uvJ cm'
500 450 400 (5055 (000 '50
'000 $50 $00 50
$0
'0 Fig!re "
(0
40
50 u + v J cm
(=
JPN Pahang
Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light
a&
1ased on the graph in Figure ', %i& state the relationship etween uv and u + v ---------------------------------O1 markP ' %ii& determine the "alue of u + v when the "alue of uv ? 400 cm # ,how on the graph how you o tained the "alue of u K "# From the "alue of u + v o tained, calculate the image distance, v when u ? '0 cm#
O marksP %iii& calculate the gradient of the graph# ,how clearly on the graph how you o tained the "alues needed for the calculation#
O marksP & Bi"en that the relationship etween u, v and focal length, f of the con"e+ lens used, is represented y the eDuation $ K $ ? $ u v f ;eri"e an eDuation which gi"es the relationship etween uv and %u + v &#
O2 marksP c& 3sing the eDuation deri"ed in % &, and the "alue of gradient calculated in %a&%iii&, determine the focal length of the lens used in the e+periment#
O2 marksP d& ,tate one precaution ta!en to ensure the accuracy of the e+periment# -------------------------------O1 markP
(>
You might also like
- Tantra - Sex For The Soul - Somananda Moses MaimonDocument498 pagesTantra - Sex For The Soul - Somananda Moses MaimonRafael Rodrigues94% (18)
- Sec 3 Indices & Surds (Assignment Questions)Document2 pagesSec 3 Indices & Surds (Assignment Questions)Andy ChengNo ratings yet
- SPM Tips PhysicDocument2 pagesSPM Tips PhysicIzzuddin AzizanNo ratings yet
- Physic Chapter 5 - LightDocument37 pagesPhysic Chapter 5 - LighteffahaziraNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 5Document48 pagesForm 4 Physics Chapter 5Misratul A'la Mahyuddin100% (4)
- Chapter 10 Radioactivity Teacher Guide1Document29 pagesChapter 10 Radioactivity Teacher Guide1Hazrol Fazly Husin100% (1)
- Difference Between Theory and LawDocument17 pagesDifference Between Theory and Lawmira01No ratings yet
- 8th Grade Science ReviewDocument2 pages8th Grade Science Reviewapi-327567606No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Light Teachers GuideDocument38 pagesChapter 5 Light Teachers GuideSyahrulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Forces & Pressure Teachers GuideDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Forces & Pressure Teachers GuideAhmad Zaidi100% (3)
- Chapter 7 - Electricity (Teacher's Guide)Document60 pagesChapter 7 - Electricity (Teacher's Guide)kamalharmoza90% (21)
- Chapter 4 Heat StudentsDocument33 pagesChapter 4 Heat StudentsSyazwan AkidNo ratings yet
- Anglican High School Sec 2 Science Worksheet: Mass, Weight, DensityDocument4 pagesAnglican High School Sec 2 Science Worksheet: Mass, Weight, DensityFrancis Ho HoNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Physics RevisionDocument5 pagesForm 4 Physics RevisionannmarieNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers WorksheetDocument3 pagesComplex Numbers WorksheetArsalan RaisaniNo ratings yet
- 8 MYP Physics Sem 2 29 Apr 2015 v01Document18 pages8 MYP Physics Sem 2 29 Apr 2015 v01kailaNo ratings yet
- SPM Trial 2013 Physics Qa SBPDocument92 pagesSPM Trial 2013 Physics Qa SBPkamalharmozaNo ratings yet
- Function: Edexcel IAL A Level Pure Mathematics 3 Revision NotesDocument28 pagesFunction: Edexcel IAL A Level Pure Mathematics 3 Revision NotesPrince YugNo ratings yet
- Algebra - Maths ExerciseDocument15 pagesAlgebra - Maths ExerciseJannifer Love UNo ratings yet
- SPM Questions (Differentiation) - Paper 2Document4 pagesSPM Questions (Differentiation) - Paper 2Sanjey RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Radioactivity Student'sDocument29 pagesChapter 10 Radioactivity Student'sMohd Khairul Anuar100% (3)
- Chapter 9-Electronics (Teacher's Guide)Document37 pagesChapter 9-Electronics (Teacher's Guide)Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (6)
- MPHG2009-Chapter 7 ElectricityDocument60 pagesMPHG2009-Chapter 7 ElectricityMohd Khairul Anuar100% (6)
- Chapter 9: Electronics: 9. 1: Uses of The Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (C.R.O) 9.1.1: Thermionic EmissionDocument35 pagesChapter 9: Electronics: 9. 1: Uses of The Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (C.R.O) 9.1.1: Thermionic EmissionMohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- P3 JAN 21 Revision Worksheet All ChaptersDocument3 pagesP3 JAN 21 Revision Worksheet All ChaptersSheikh HassanNo ratings yet
- Exercise For HKDSE (Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences)Document4 pagesExercise For HKDSE (Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences)Henry Leung100% (2)
- Modul 2 Quadratic EquationsDocument13 pagesModul 2 Quadratic Equationshasnitajb33% (3)
- Sec 2 MathDocument30 pagesSec 2 MathSpike BearingNo ratings yet
- Revision For Form 1 Maths Exams 2017 Term 1Document2 pagesRevision For Form 1 Maths Exams 2017 Term 1naseebNo ratings yet
- Structur Questions SPM Physics Chapter 9 Radioactive Detector 1Document6 pagesStructur Questions SPM Physics Chapter 9 Radioactive Detector 1Niceman Natiqi100% (1)
- E Maths Sec 42011Document267 pagesE Maths Sec 42011Timothy Handoko100% (1)
- Chapter 5 - Factorisation and Alegrabraic Fractions PDFDocument31 pagesChapter 5 - Factorisation and Alegrabraic Fractions PDFaurora100% (3)
- Chapter 2: Inequalities and Absolute ValuesDocument4 pagesChapter 2: Inequalities and Absolute Valueszan2812No ratings yet
- Chemistry Note Form 4 Chapter 7Document32 pagesChemistry Note Form 4 Chapter 7Rashidah Utama100% (2)
- IGCSE 33 LightWavesDocument36 pagesIGCSE 33 LightWavesAhmed MawahibNo ratings yet
- Revision - Additional Mathematics F4.1 - FunctionsDocument4 pagesRevision - Additional Mathematics F4.1 - FunctionsJiaRenTeohNo ratings yet
- Science - Energy Notes TeacherDocument2 pagesScience - Energy Notes Teacherapi-232744621No ratings yet
- Vector Worksheet 10 AnsDocument13 pagesVector Worksheet 10 AnsMegan GohNo ratings yet
- Regent Physics by Abhishek JaguessarDocument343 pagesRegent Physics by Abhishek Jaguessarreedoye21No ratings yet
- Modul Perfect Score SBP 2009Document124 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP 2009Jia HuiNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE PMR Notes and ExperimentsDocument221 pagesSCIENCE PMR Notes and ExperimentsAzlina Ahmad100% (1)
- Light StudentDocument40 pagesLight StudentzakiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Light Teacher's GuideDocument38 pagesChapter 5 Light Teacher's Guidekamalharmoza80% (5)
- Chapter 5: Light: Solid, Liquid, Gas, Vacuum, Electromagnetic Wave, EnergyDocument35 pagesChapter 5: Light: Solid, Liquid, Gas, Vacuum, Electromagnetic Wave, EnergySharuNo ratings yet
- Answer Scheme-Physics LightDocument38 pagesAnswer Scheme-Physics LightSelva RajNo ratings yet
- Documents - MX Chapter 5 Light Teachers Guide 558445afb6f9eDocument38 pagesDocuments - MX Chapter 5 Light Teachers Guide 558445afb6f9eMK Joey ThamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Light Teacher's GuideDocument38 pagesChapter 5 Light Teacher's GuideFahmi AmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Light - Teacher'sDocument36 pagesChapter 5 Light - Teacher'sSuadrifRunDamahumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34B - Reflection and Mirrors II (Analytical)Document28 pagesChapter 34B - Reflection and Mirrors II (Analytical)Heindrich Lloyd Mendoza BasiNo ratings yet
- 5 Light TDocument44 pages5 Light TRuddyMartini0% (1)
- Chapter 5: Light: Normal Reflected Angle Incident AngleDocument13 pagesChapter 5: Light: Normal Reflected Angle Incident AngleChristopher AuNo ratings yet
- Light PuntlandDocument131 pagesLight PuntlandSaid Mohamed Mahad100% (1)
- Ari 12 CH 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument54 pagesAri 12 CH 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsCommandoNo ratings yet
- 34b Reflection and Mirrors II AnalyticalDocument27 pages34b Reflection and Mirrors II AnalyticalseijikellsNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Lecture UnacademyDocument57 pagesRay Optics Lecture UnacademyAbhishek Shukla100% (1)
- Physics MIRRORS ProjectDocument39 pagesPhysics MIRRORS Projectaneesh.ubanNo ratings yet
- Optics Review AnswersDocument5 pagesOptics Review Answersben0706No ratings yet
- Light ModuleDocument38 pagesLight ModuleZulhisyam NordinNo ratings yet
- Chapter VII OpticHTAMDocument67 pagesChapter VII OpticHTAMIhza Fikry Aryaditama ArroziNo ratings yet
- Light-Re Ection and Refraction: SyllabusDocument7 pagesLight-Re Ection and Refraction: SyllabusKumar AbhishantNo ratings yet
- C7 LightDocument40 pagesC7 LightKyle Miguel YcasianoNo ratings yet
- Ac Q BankDocument52 pagesAc Q BankASHISH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Photoelasticity for Designers: International Series of Monographs in Mechanical EngineeringFrom EverandPhotoelasticity for Designers: International Series of Monographs in Mechanical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Epipolar Geometry: Unlocking Depth Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandEpipolar Geometry: Unlocking Depth Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Bahan Fizik SPM Paper 3B 2010Document11 pagesBahan Fizik SPM Paper 3B 2010Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (2)
- Physics Form 4 Yearly Lesson Plan 2010Document26 pagesPhysics Form 4 Yearly Lesson Plan 2010Mohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Ms Addm Paper2 Trial SPM 09Document13 pagesMs Addm Paper2 Trial SPM 09idawatieNo ratings yet
- Eksperimen Wajib Fizik 2010Document14 pagesEksperimen Wajib Fizik 2010Mohd Khairul Anuar71% (7)
- Q&A Bi k1 Trial SPM PHG 09Document3 pagesQ&A Bi k1 Trial SPM PHG 09Mohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Answer P109sbpDocument6 pagesAnswer P109sbpidawatieNo ratings yet
- Sample - Physics Form 5yearly Lesson Plan 2010Document20 pagesSample - Physics Form 5yearly Lesson Plan 2010Mohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- 11.SBP (P2) OkDocument20 pages11.SBP (P2) OkSrp KaMie LooNo ratings yet
- Ans Phy P2 Terengganu SPM 2009Document8 pagesAns Phy P2 Terengganu SPM 2009Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (1)
- Marking Scheme Physics P1P2P3 SPM Kelantan 2009Document9 pagesMarking Scheme Physics P1P2P3 SPM Kelantan 2009Mohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- SBP-answer PHYSICS P1 P2 P3-TRIAL SPM 2009Document15 pagesSBP-answer PHYSICS P1 P2 P3-TRIAL SPM 2009kamalharmoza100% (3)
- Marking Scheme Paper 1 2 3 SBP Trial SPM 2009Document21 pagesMarking Scheme Paper 1 2 3 SBP Trial SPM 2009Mohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-Electronics (Teacher's Guide)Document37 pagesChapter 9-Electronics (Teacher's Guide)Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (6)
- SPM 2009 Physics Paper1 PerlisDocument27 pagesSPM 2009 Physics Paper1 PerlisMohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Electromagnet Teacher's Guide 2009Document48 pagesChapter 8 Electromagnet Teacher's Guide 2009Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (18)
- Chapter 7 - Electricity (Teacher's Guide) 2009Document60 pagesChapter 7 - Electricity (Teacher's Guide) 2009Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (13)
- SPM Physics Form 5Document46 pagesSPM Physics Form 5Woody CysNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Teachers Guide 2009Document34 pagesChapter 4 Teachers Guide 2009Devan KanesanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Waves Teacher's Guide 2009Document42 pagesChapter 6 Waves Teacher's Guide 2009Mohd Khairul Anuar86% (7)
- Chapter 3 Force & Teacher) 2009Document22 pagesChapter 3 Force & Teacher) 2009Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (9)
- Teacher's Guide: Force and MotionDocument45 pagesTeacher's Guide: Force and MotionMohd Khairul Anuar100% (16)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Physics Teacher' Guide 2009Document19 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Physics Teacher' Guide 2009Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (12)
- Fizik Tingkatan 5Document56 pagesFizik Tingkatan 5Sakinah Ridzuan0% (1)
- Huraian Sukatan Pelajaran Fizik Tingkatan 4Document57 pagesHuraian Sukatan Pelajaran Fizik Tingkatan 4Nadiah RaffiqueNo ratings yet
- MPHG2009-Chapter 9 ElectronicsDocument34 pagesMPHG2009-Chapter 9 ElectronicsMohd Khairul Anuar100% (6)
- MPHG2009-Chapter 6 WavesDocument40 pagesMPHG2009-Chapter 6 WavesMohd Khairul Anuar100% (9)
- MPHG2009-Chapter 3 Forces and PressureDocument21 pagesMPHG2009-Chapter 3 Forces and Pressuresainsmathspa5550No ratings yet
- MPHG2009-Chapter 5 LightDocument36 pagesMPHG2009-Chapter 5 Lightsainsmathspa5550100% (1)
- MPHG2009-Chapter 7 ElectricityDocument60 pagesMPHG2009-Chapter 7 ElectricityMohd Khairul Anuar100% (6)
- Are We Really Made of StarsDocument7 pagesAre We Really Made of StarsMerlita TuralbaNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Energy - Bernoulli's EquationDocument11 pagesConservation of Energy - Bernoulli's Equationtaha zafarNo ratings yet
- Bundelkhand University, Jhansi B. Tech. (Food Tech.) I SemesterDocument51 pagesBundelkhand University, Jhansi B. Tech. (Food Tech.) I SemesterAnupNo ratings yet
- Lec 04Document6 pagesLec 04MesipNo ratings yet
- A Critical History of Greek PhilosophyDocument279 pagesA Critical History of Greek PhilosophyNo Timeline PamaiNo ratings yet
- Lect 2 cvg4150 PDFDocument9 pagesLect 2 cvg4150 PDFMewnEProwtNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab ReportDocument8 pagesPhysics Lab ReportNurul Hasanah75% (4)
- II0 00I 0I: United States PatentDocument12 pagesII0 00I 0I: United States PatentDaniel BurwellNo ratings yet
- Exp 1Document5 pagesExp 1Vikas SharmaNo ratings yet
- Uses of EM WavesDocument3 pagesUses of EM WavesPallika DhingraNo ratings yet
- Anna University - Electromagnetic Theory (EMT) - Question Bank - All UnitsDocument7 pagesAnna University - Electromagnetic Theory (EMT) - Question Bank - All UnitsMunish KalimuthuNo ratings yet
- Jee Mains 2009 Question PaperDocument28 pagesJee Mains 2009 Question PaperYASHNo ratings yet
- Unsymmetrical Fault Analysis 1Document27 pagesUnsymmetrical Fault Analysis 1thavaselvanNo ratings yet
- Phy - 122 DAE (1st Year)Document5 pagesPhy - 122 DAE (1st Year)Abdul Qayyum100% (4)
- Force and Motion: Sections 3.1-3.6Document52 pagesForce and Motion: Sections 3.1-3.6Ahmad Shex MhamadNo ratings yet
- UF MAE Schedule Fall 2016Document2 pagesUF MAE Schedule Fall 2016salil91No ratings yet
- 11 STEM Physics FIRST QUARTER LMsDocument22 pages11 STEM Physics FIRST QUARTER LMsNeil Trezley Sunico BalajadiaNo ratings yet
- Dip 2 MCQsDocument16 pagesDip 2 MCQsKarthikeyan SNo ratings yet
- Physics Intro & KinematicsDocument41 pagesPhysics Intro & KinematicsRyan Clerigo ColinaresNo ratings yet
- A Two Wheel Self-Balancing VehicleDocument16 pagesA Two Wheel Self-Balancing VehicleMuzz HarryNo ratings yet
- MCHT 213 - Section 1 and 2 Strength of MaterialsDocument42 pagesMCHT 213 - Section 1 and 2 Strength of MaterialsWael Fawzy MohamedNo ratings yet
- GRADE 9 Ws 2Document3 pagesGRADE 9 Ws 2Abdullah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 282Document19 pages282Prashant Trivedi100% (1)
- Night Vision Using Digital Image Processing: Department of EceDocument9 pagesNight Vision Using Digital Image Processing: Department of Ecemurali KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Single-Tuned Filter Design For Harmonic Mitigation and Optimization With Capacitor BanksDocument7 pagesSingle-Tuned Filter Design For Harmonic Mitigation and Optimization With Capacitor BanksNelson ParijósNo ratings yet
- CH 5 - Sensors & Their ApplicationsDocument20 pagesCH 5 - Sensors & Their ApplicationsmahmoudNo ratings yet
- CFD BasicsDocument63 pagesCFD BasicssivivargheseNo ratings yet