Professional Documents
Culture Documents
N L B N: The Logarithmic Function
N L B N: The Logarithmic Function
Uploaded by
jaydeepgoswami5180Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
N L B N: The Logarithmic Function
N L B N: The Logarithmic Function
Uploaded by
jaydeepgoswami5180Copyright:
Available Formats
The Logarithmic Function: L = log b N The inverse function is: N = b L For example: log 2 8 = 3 since 8 = 2 3 log10 0.
01 = 2 since 0.01 = 10 2
log 5 5 = 1 since 5 = 51 log b 1 = 0 since 1 = b 0
Selected Algebra Topics Basic Laws of Exponents Law Example m n m+ n a a =a x 5 x 2 = x 3 x5 am mn = x2 = a , a 0 an x3
(ab )m
m
(a )
m n
= a mn
= a mb m
(xy )2 = x 2 y 2
x x2 = y y2 1 x 3 = 3 x 0 2(3x ) = 2(1) = 2
2
(x )
2 3
= x 6
am a = m ,b 0 b b 1 a m = m , a 0 a 0 a = 1, a 0
a1 = a
(3x )
2 1
= 3x 2
Laws for fractional exponents Law Example
a
n n m n
= n am =n a ,b 0 b
x
3 3
= 3 x2 =3 8=2
a b
1 2
16
= 2 a1 = a , a 0
2 25 = 5, (not 5)
Trigonometric Identities
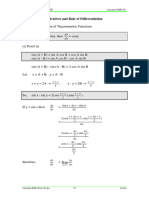
sin ( ) =
a c b cos( ) = c sin ( ) a tan ( ) = = cos( ) b
1 c = sin ( ) a 1 c sec( ) = = cos( ) b cos( ) b cot ( ) = = sin ( ) a
csc( ) =
sin ( x ) = sin ( x ) csc( x ) = csc( x ) cos( x ) = cos( x ) sec( x ) = sec( x ) tan ( x ) = tan ( x ) cot ( x ) = cot ( x )
sin 2 ( x ) + cos 2 ( x ) = 1 tan 2 ( x ) + 1 = sec 2 ( x ) cot 2 ( x ) + 1 = csc 2 ( x ) sin ( x y ) = sin ( x ) cos( y ) cos( x )sin ( y ) cos( x y ) = cos( x ) cos( y ) sin ( x )sin ( y ) tan ( x ) tan ( y ) tan ( x y ) = 1 tan ( x ) tan ( y ) sin (2 x ) = 2 sin (x ) cos(x ) cos(2 x ) = cos 2 ( x ) sin 2 (x ) = 2 cos 2 ( x) 1 = 1 2 sin 2 ( x ) 2 tan ( x ) tan (2 x ) = 1 tan 2 ( x ) 1 1 sin 2 ( x ) = cos(2 x ) 2 2
1 1 + cos(2 x ) 2 2 (x y ) (x + y ) sin ( x ) sin ( y ) = 2 sin cos 2 2 (x y ) (x + y ) cos( x ) cos( y ) = 2 sin sin 2 2 Given Triangle abc, with angles A,B,C; a is opposite to A, b is opposite to B, and c is opposite to C: Law of Sines: a b c = = sin ( A) sin (B ) sin (C )
cos 2 ( x ) =
Law of Cosines: c 2 = a 2 + b 2 2ab cos(C ) b 2 = a 2 + c 2 2ac cos(B ) a 2 = b 2 + c 2 2bc cos( A)
Law of Tangents:
(a b ) = tan (12 ( A B )) (a + b ) tan (1 ( A + B ))
2
Important Statistics Formulas: Parameters:
Population mean: =
(X i ) N
( X i ) 2 N
Population Standard Deviation: = Population Variance: 2 = Standardized Score: Z =
( X i ) 2 N (X )
( X x ) (Yi y ) 1 Population Correlation Coefficient: = * i * N y x Statistics: Sample mean: x =
( x i ) n
Sample standard deviation: s =
( xi x ) 2 (n 1)
Sample variance: s 2 =
( xi x ) 2 (n 1)
1 ( x x) ( y i y ) * i Sample Correlation coefficient: r = * (n 1) sy s x Normal Distribution Formula: Or
(x )2 exp 2 2 2 z2 1 exp 2 2 1
Simple Linear Regression: Simple linear regression line: y = b0 + b1 x Regression coefficient: b1 =
^
xi x y i y xi x
[(
)(
)]
2
Regression slope intercept: b0 = y b1 * x
^ y i y i (n 2)
Standard error of regression slope: s b1 =
xi x
Random Variables: Expected value of X: E ( X ) = x = [xi * P( xi )]
2
Variance of X: Var ( X ) = 2 = [xi E ( x) )] * P( xi ) = [xi x ] * P( xi ) (x ) Normal Random Variable: z score = z =
2
Expected value of sum of random variables: E ( X + Y ) = E ( X ) + E (Y ) Expected value of difference between random variables: E ( X Y ) = E ( X ) E (Y ) Variance of the sum of independent random variables: Var ( X + Y ) = Var ( X ) + Var (Y ) Variance of the difference between independent random variables: Var ( X Y ) = Var ( X ) Var (Y ) Sampling Distributions: Standard deviation of the mean: x = Standard Error: Standard error of the mean: SE x = s x =
s n
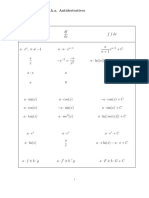
Taylor series expansion:
f ( x + x ) =
n =0
f ( n ) ( x ) x n f ' ' ( x ) x 2 f ' ' ' ( x ) x 3 = f ( x ) + f ' ( x ) x + + +L n! 2! 3!
Maclaurin series expansion:
f ( x) =
n =0 5
f ( n ) ( 0) x n n!
x x x x + + + +L 2! 3! 4! 5! x3 x5 x7 x9 sin x = x + + +L 3! 5! 7! 9! x 2 x 4 x6 x8 cos x = 1 + + +L 2! 4! 6! 8! ex = 1 + x +
You might also like
- Libro Dyadic Data Analysis PDFDocument480 pagesLibro Dyadic Data Analysis PDFLu100% (1)
- Mat3320 Ass3 SolDocument2 pagesMat3320 Ass3 SolRichard BeardNo ratings yet
- Variance Value Flow To COPADocument28 pagesVariance Value Flow To COPAAnonymous JyOLzC9LNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesTrigonometry Cheat SheetVaishnav VIPANCHIKANo ratings yet
- FRM 2023Document4 pagesFRM 2023olemas1984No ratings yet
- NCEA L3 Calculus FormulaeResource 2018Document4 pagesNCEA L3 Calculus FormulaeResource 2018Saksham SahaNo ratings yet
- MAT 121 Lecture NotesDocument46 pagesMAT 121 Lecture Noteshollabang8No ratings yet
- Math 249and265FormulaSheetDocument1 pageMath 249and265FormulaSheetjosephbutler477No ratings yet
- Analyse FormulebladDocument1 pageAnalyse FormulebladBassieNo ratings yet
- Formula List MF15Document8 pagesFormula List MF15niveumaNo ratings yet
- AMA1110 Tutorial - 2sDocument3 pagesAMA1110 Tutorial - 2sBrian LiNo ratings yet
- Calculus 2 Exam PDFDocument13 pagesCalculus 2 Exam PDFrobert daltonNo ratings yet
- Some Useful Formulae For Mman 2400 Basic Formulas: R E I M yDocument5 pagesSome Useful Formulae For Mman 2400 Basic Formulas: R E I M ySaurabh SapreNo ratings yet
- Phythagorean IdentitiesDocument2 pagesPhythagorean IdentitiesDarko PovolniNo ratings yet
- Formula CompilationDocument6 pagesFormula CompilationKirstie Alley San JoseNo ratings yet
- Math Tutorial SheetDocument3 pagesMath Tutorial SheetKondwani BandaNo ratings yet
- Combined TutorialDocument8 pagesCombined TutorialVongNo ratings yet
- 1462535320E textofChapter7Mod1Document8 pages1462535320E textofChapter7Mod1JejsNo ratings yet
- MF15Document8 pagesMF15Lim Zi Ai100% (1)
- Ma1505 FormulasDocument7 pagesMa1505 FormulasSherman LiamNo ratings yet
- Solution 4Document3 pagesSolution 4Chen ShyanNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Physics Useful Formulae PDFDocument29 pagesMathematical Physics Useful Formulae PDFKunal RanaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics FormulasDocument5 pagesEngineering Mathematics Formulasvenkata sridhar DhulipalaNo ratings yet
- NaturemathfDocument3 pagesNaturemathfzdfbdfb12No ratings yet
- Trig ReviewDocument3 pagesTrig ReviewSayee SaranNo ratings yet
- Science Data BookletDocument581 pagesScience Data BookletManjunath.RNo ratings yet
- Formule Pt/UvDocument6 pagesFormule Pt/UvИваРужићNo ratings yet
- Test2 - 20182019 SchemeDocument11 pagesTest2 - 20182019 SchemenorsyahirahafiqahNo ratings yet
- MATH 259 - Review Sheet (Prerequisite Topics) : (This Is NOT A Comprehensive List!)Document4 pagesMATH 259 - Review Sheet (Prerequisite Topics) : (This Is NOT A Comprehensive List!)Celal KermangilNo ratings yet
- AppendixDocument1 pageAppendixLee Zhiyi (Angelene)No ratings yet
- MAST10006 Calculus 2 Exercise Sheets 2023s1Document34 pagesMAST10006 Calculus 2 Exercise Sheets 2023s1Shyam MahendraNo ratings yet
- Test1 SSCM1023 20192020 1Document2 pagesTest1 SSCM1023 20192020 1Aisyah NadhirahNo ratings yet
- Legendre FunctionsDocument10 pagesLegendre Functionssohannur3No ratings yet
- Fourier Series:: Periodic FunctionsDocument8 pagesFourier Series:: Periodic FunctionswisamNo ratings yet
- Algebra: TopicsDocument26 pagesAlgebra: Topicsgundu1234No ratings yet
- End of Stage 1/AS Mathematics:: Mathematics A (H230, H240) Paper 2: Pure Mathematics and MechanicsDocument21 pagesEnd of Stage 1/AS Mathematics:: Mathematics A (H230, H240) Paper 2: Pure Mathematics and MechanicsrebeccaNo ratings yet
- Calculus For Engineers FormulaeDocument4 pagesCalculus For Engineers FormulaeKHÁNH VÂN DIỆPNo ratings yet
- Principles of Semiconductor Devices-L5Document21 pagesPrinciples of Semiconductor Devices-L5LIAKMANNo ratings yet
- Cal1 TD2 (2023 24)Document2 pagesCal1 TD2 (2023 24)Da VyNo ratings yet
- Precalc Identities TriglawsDocument2 pagesPrecalc Identities TriglawsJulio Alejo Ruiz0% (1)
- Mathematics 30-1 Formula Sheet: Ax BXCDocument1 pageMathematics 30-1 Formula Sheet: Ax BXCyeetmylifedotcomNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1 FormulaDocument2 pagesCalculus 1 FormulaAuto CadNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet OOODocument27 pagesFormula Sheet OOOchahd assoufiNo ratings yet
- Math Formulas Ans Statistical Tables-ALevelsDocument16 pagesMath Formulas Ans Statistical Tables-ALevelsSheryl CoronelNo ratings yet
- Ssce 1793 Test 1 201420152Document4 pagesSsce 1793 Test 1 201420152Gantan Etika MurtyNo ratings yet
- Dynamics 2Document55 pagesDynamics 2Ahmed MandorNo ratings yet
- MiscelaniasDocument5 pagesMiscelaniasxoliday639No ratings yet
- FMSQ Revision NotesDocument5 pagesFMSQ Revision NotesJay AmbadkarNo ratings yet
- Edexcel - As Levels MathsDocument4 pagesEdexcel - As Levels MathsAhmad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Calculus (Diff) Note 02Document11 pagesCalculus (Diff) Note 02amy.like.cooking.77No ratings yet
- Handout IntegrationDocument10 pagesHandout IntegrationSubhajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Resumen FísicaDocument2 pagesResumen FísicaJosefa BelmarNo ratings yet
- Formulas DerivativeDocument1 pageFormulas DerivativeGaurav GedamNo ratings yet
- Step Formula Booklet PDFDocument24 pagesStep Formula Booklet PDFA FryNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Question Bank For Probabilty Queueing Theory Regulation 2013Document19 pagesQuestion Bank For Probabilty Queueing Theory Regulation 2013PRIYA RAJI100% (1)
- Effects of Using Tagalog As Medium of Instruction in Teaching Grade 6 ScienceDocument16 pagesEffects of Using Tagalog As Medium of Instruction in Teaching Grade 6 ScienceJasmin GalanoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 For EngDocument2 pagesWorksheet 3 For EngAdmasuNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 11 Maths May22 Chapter 15 StatisticsDocument52 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 11 Maths May22 Chapter 15 StatisticsPriyanshuNo ratings yet
- (Open Agriculture) Genotype X Environment Interaction For Yield of Pickling Cucumber in 24 U.S. EnvironmentsDocument16 pages(Open Agriculture) Genotype X Environment Interaction For Yield of Pickling Cucumber in 24 U.S. EnvironmentsAlfredo Muñoz PardoNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Oral Motor Exercises On Diadochokinetic RatesDocument23 pagesThe Effects of Oral Motor Exercises On Diadochokinetic RatesNicole GrayNo ratings yet
- CH03 - 2021 2022 Sem 1Document83 pagesCH03 - 2021 2022 Sem 1Mathew Chong Vui KitNo ratings yet
- ACET TopicsDocument4 pagesACET TopicsAshutosh AherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 of Dar Al Handasah Manual Concrete QC 1668530999Document13 pagesChapter 15 of Dar Al Handasah Manual Concrete QC 1668530999Eslam EmamNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Science & Technology University Department of Electrical & Computer EngineeringDocument63 pagesAddis Ababa Science & Technology University Department of Electrical & Computer EngineeringObsi EliasNo ratings yet
- 12.ptsp Question BankDocument4 pages12.ptsp Question BankShaik WazeedNo ratings yet
- Abstract in School Absenteesim Research PDFDocument128 pagesAbstract in School Absenteesim Research PDFMarvin M PulaoNo ratings yet
- Mini Tab 16 Help Data SetsDocument21 pagesMini Tab 16 Help Data Setsronsrony0% (1)
- Random VariablesDocument23 pagesRandom VariablesashviniNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods For EconomistsDocument7 pagesQuantitative Methods For EconomistsyulaNo ratings yet
- ch07 v1Document22 pagesch07 v1Nguyen An Ninh K15 HCMNo ratings yet
- Two-Variable Regression Model, The Problem of EstimationDocument67 pagesTwo-Variable Regression Model, The Problem of Estimationwhoosh2008No ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Employee Performance of PT - Kiyokuni IndonesiaDocument15 pagesFactors Affecting Employee Performance of PT - Kiyokuni IndonesiaRenaNo ratings yet
- ClassWork 04 Experiments With Blocking Factors - SolDocument21 pagesClassWork 04 Experiments With Blocking Factors - SolMohamad HarazeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Econometrics Practice MCDocument38 pagesChapter 4 Econometrics Practice MCYiğit KocamanNo ratings yet
- QUANTITATIVE METHODS - Common Probability Distribution Test QuestionsDocument28 pagesQUANTITATIVE METHODS - Common Probability Distribution Test QuestionsEdlyn KooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Variance AnalysisDocument15 pagesChapter 10 - Variance AnalysisNurryn QistinaNo ratings yet
- FRM LOBs 111320-FinalDocument65 pagesFRM LOBs 111320-Finalgenius_2No ratings yet
- SaaaDocument3 pagesSaaazeyin mohammed aumerNo ratings yet
- AC ResistivityDocument6 pagesAC ResistivityJulio TedescoNo ratings yet
- Risk and ReturnDocument28 pagesRisk and ReturnrichaparasharNo ratings yet
- Authentic Leadership and Creativity - The Mediating Role of HappinessDocument18 pagesAuthentic Leadership and Creativity - The Mediating Role of HappinesspsicandreiaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis PDFDocument23 pagesHypothesis PDFkamalkant05No ratings yet