Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stepper Motors
Stepper Motors
Uploaded by
crsarin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views9 pagesjj
Original Title
3625
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentjj
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views9 pagesStepper Motors
Stepper Motors
Uploaded by
crsarinjj
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Stepper Motors
A stepper motor is a pulse-driven motor that changes the angular position of the rotor in steps Define
= the step angle (per input pulse) Resolution = the number of steps/revolution = total angle traveled by the rotor
= X # of steps
n = the shaft speed = ( X fp) / 360
fp = # of pulses/second
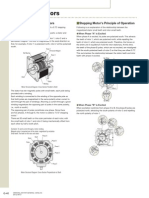
Variable-Reluctance Stepper Motor
Toothed Rotor and Toothed Stator
Principle of Operation:
Reluctance of the magnetic circuit formed by the rotor and stator teeth varies with the angular position of the rotor Here, energize coils A and A (Phase A) Rotor steps to align rotor teeth 1 and 4 with stator teeth 1 and 5
Variable-Reluctance Stepper Motor
Energize coils B and B (Phase B)
Rotor steps forward Rotor teeth 3 and 6 align with Stator teeth 1 and 5 Let Ns = # of teeth on the stator Nr = # of teeth on the rotor = Step Angle in space degrees
Ns Nr Ns Nr
360
Variable-Reluctance Stepper Motor
Energize Phase C
Rotor steps forward another 15
Variable-Reluctance Stepper Motor
Energize Phase D
Rotor steps forward another 15
Variable-Reluctance Stepper Motor
Repeat the sequence
Energize Phase A
Rotor steps forward again
Variable-Reluctance Stepper Motor
Switching Circuit for the stepper motor
Close switches in order 1, 2, 3, and 4 to turn the rotor clockwise Close switches in reverse order 4, 3, 2, and 1 to change rotation to the opposite (counter-clockwise) direction
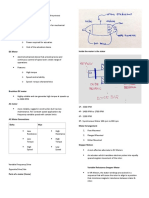
Variable-Reluctance Stepper Motor Typical Driver Circuit
F = filter block C = Up/Down Counter D = Decoder S = Electronic Switch (transistor)
Typical Switching Circuit
Decoder provides logic output to turn QA On/Off Amplifier A conditions the logic pulses When QA turns On, it conducts current in the motor phase A winding When QA turns Off, D and RS conduct current to discharge the phase winding
You might also like
- Stepper MotorsDocument9 pagesStepper MotorsmanojNo ratings yet
- VR SMDocument15 pagesVR SMramprabhakarjNo ratings yet
- Module 4 5Document35 pagesModule 4 5Atharva KhadseNo ratings yet
- SmotorDocument20 pagesSmotorAamer MohammedNo ratings yet
- Stepper MotorsDocument49 pagesStepper MotorsamraemamNo ratings yet
- Special MotorsDocument20 pagesSpecial MotorsRs sniperNo ratings yet
- Stepper MotorDocument14 pagesStepper MotorprobirparuiNo ratings yet
- Stepper MotorDocument27 pagesStepper Motorjena_anshumanNo ratings yet
- Requara. H. Wickens Fundamentals of Rail Vehicle Dynamics Guidance and StabiliteDocument42 pagesRequara. H. Wickens Fundamentals of Rail Vehicle Dynamics Guidance and Stabilitetesfaye awelNo ratings yet
- 9927 CH 9Document25 pages9927 CH 9varaprasad93No ratings yet
- Unit-1 Stepper MotorDocument39 pagesUnit-1 Stepper MotorkoundinyaNo ratings yet
- Stepper MotorDocument12 pagesStepper MotorSomya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Three-Phase Induction MotorsDocument93 pagesUnit 4 - Three-Phase Induction MotorsMaribe TshegoNo ratings yet
- Computer Numerical Control: Engineering Analysis of NC Positioning SystemsDocument30 pagesComputer Numerical Control: Engineering Analysis of NC Positioning SystemsibraheemNo ratings yet
- Module1.Stepper Motor and Its ControlDocument79 pagesModule1.Stepper Motor and Its ControlOmkar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motor Construction and Its FunctionsDocument25 pagesStepper Motor Construction and Its FunctionsIlakiya MaduraiNo ratings yet
- Spacial Mech Unit3Document15 pagesSpacial Mech Unit3Abhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Stepper MotorDocument32 pagesStepper Motorapi-26587237100% (2)
- Stepper MotorsDocument53 pagesStepper MotorsirfancardiagnosticNo ratings yet
- EE 205 Lecture 30Document14 pagesEE 205 Lecture 30Akshat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motors: Stepper Motor vs. Servo MotorDocument13 pagesStepper Motors: Stepper Motor vs. Servo MotorGurwinder Singh100% (1)
- HSI Stepper Motor TheoryDocument14 pagesHSI Stepper Motor TheoryalexmradNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motor: CO2: LO: Understand Construction and Operation Write The Control SequenceDocument25 pagesStepper Motor: CO2: LO: Understand Construction and Operation Write The Control SequenceAzeem .kNo ratings yet
- Cluster 1 - StepperDocument124 pagesCluster 1 - StepperBhargav Ram ThallapudiNo ratings yet
- Stepping Motors Brushless Pag 21Document49 pagesStepping Motors Brushless Pag 21Luis R. Cabrales JimenezNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor - NotesDocument9 pagesInduction Motor - NotesG2zapper gamingNo ratings yet
- Module2 1Document27 pagesModule2 1Arunima SankarNo ratings yet
- Variable Reluctance MotorDocument14 pagesVariable Reluctance MotorgbksnNo ratings yet
- Notes 2Document14 pagesNotes 2Manish PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorsDocument24 pagesInduction MotorsJaniel MalitNo ratings yet
- Stepper MotorDocument6 pagesStepper MotorAsith Savinda100% (1)
- Sem NotesDocument189 pagesSem NotesAish KrishNo ratings yet
- Stepper MotorsDocument25 pagesStepper Motorsapi-3827132100% (8)
- Stepper Motor: B.E.E-IV Section-B2 Roll-001610801123Document27 pagesStepper Motor: B.E.E-IV Section-B2 Roll-001610801123abhrajit ghoshNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics SystemsDocument3 pagesMechatronics SystemsJay Patrick Vincent JameroNo ratings yet
- Rotating Electrical MachinesDocument75 pagesRotating Electrical MachinesRajan SinghNo ratings yet
- Slip and Its Effects or Rotor Frequency and Rotor VoltageDocument35 pagesSlip and Its Effects or Rotor Frequency and Rotor Voltageover allNo ratings yet
- Ch2 Stepper MotorDocument60 pagesCh2 Stepper MotorKinjal ShahNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motor and DrivesDocument8 pagesStepper Motor and DrivesLasantha Abeykoon100% (2)
- AC Induction Motors: Terminal BoxDocument19 pagesAC Induction Motors: Terminal BoxFadlan RoslanNo ratings yet
- Stepper MotorDocument18 pagesStepper MotorLasantha Abeykoon67% (3)
- Stepper MotorDocument8 pagesStepper MotorHassan Muhammad ZahidNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motor Theory of OperationDocument11 pagesStepper Motor Theory of OperationSherif EltoukhiNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction Machines-1pDocument58 pagesThree Phase Induction Machines-1pSaikat SahuNo ratings yet
- Induction MachinesDocument81 pagesInduction Machinessandyarajagopalan321No ratings yet
- Lec1 - Stepper MotorDocument25 pagesLec1 - Stepper Motorabdo lokaNo ratings yet
- See 1307Document181 pagesSee 1307EEEDEPTGECNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motor Handwritten NotesDocument7 pagesStepper Motor Handwritten Notesstudy plus 7No ratings yet
- Jagan Nath Gupta Institute of Technology Presentation On "Stepper Motor"Document22 pagesJagan Nath Gupta Institute of Technology Presentation On "Stepper Motor"Mayank BansalNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor (Part 2) : Speed of RMF, Rotor Slip, Equivalent Circuit of IMDocument23 pagesInduction Motor (Part 2) : Speed of RMF, Rotor Slip, Equivalent Circuit of IMNiha chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument74 pagesInduction Motormera nam chinNo ratings yet
- Single Phase MotorsDocument24 pagesSingle Phase Motorssnh.2k19No ratings yet
- Arbaminch University: Facality of Electrical and Computer Engineering Interface and Micro Computer Progect Steper MotorDocument12 pagesArbaminch University: Facality of Electrical and Computer Engineering Interface and Micro Computer Progect Steper MotorEphrem DanielNo ratings yet
- Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkNo ratings yet
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- II ModuleDocument51 pagesII ModuleJisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Physics, Chapter 38: Mirrors and Lenses: Digitalcommons@University of Nebraska - LincolnDocument25 pagesPhysics, Chapter 38: Mirrors and Lenses: Digitalcommons@University of Nebraska - LincolnJisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Earlier in Lesson 3: Mirror Equation Magnification EquationDocument6 pagesEarlier in Lesson 3: Mirror Equation Magnification EquationJisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Mar Athanasius College of Engineering, KothamangalamDocument1 pageDepartment of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Mar Athanasius College of Engineering, KothamangalamJisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Electric Drives: Drive BasicsDocument5 pagesElectric Drives: Drive BasicsJisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Generation and Formulation of The ProblemDocument55 pagesHypothesis Generation and Formulation of The ProblemJisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam 1Document5 pagesPractice Exam 1Jisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Presented by Ajish V C (Ce) Sudheer Padikkal (Ce) Rajesh Menon B (Me)Document21 pagesPresented by Ajish V C (Ce) Sudheer Padikkal (Ce) Rajesh Menon B (Me)Jisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- 14 ResearchDocument43 pages14 ResearchJisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Scaling: Group No: 16Document35 pagesMeasurement and Scaling: Group No: 16Jisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- 22 RM - Group 22Document44 pages22 RM - Group 22Jisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Group 18Document63 pagesGroup 18Jisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Earlier in Lesson 3: Mirror Equation Magnification EquationDocument6 pagesEarlier in Lesson 3: Mirror Equation Magnification EquationJisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Research: Jayasoorya. J Mayakn Needhu VargheseDocument52 pagesExperimental Research: Jayasoorya. J Mayakn Needhu VargheseJisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Ata Collection Procedures: P V Gopinadhan Parameswaran M Miji CherianDocument19 pagesAta Collection Procedures: P V Gopinadhan Parameswaran M Miji CherianJisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Reluctance MotorDocument10 pagesSynchronous Reluctance MotorJisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Loss OF: Minimization Control An Induction Motor DriveDocument6 pagesLoss OF: Minimization Control An Induction Motor DriveJisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- The Direct Torque Control of Induction Motor To Basis of The Space Vector ModulationDocument6 pagesThe Direct Torque Control of Induction Motor To Basis of The Space Vector ModulationJisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Loss Minimization in Scalar-Controlled Induction Motor Drives With Search ControllersDocument8 pagesLoss Minimization in Scalar-Controlled Induction Motor Drives With Search ControllersJisha Kuruvilla100% (1)
- Modeling, Simulation and Analysis of Matrix Converter Using Matlab&SimulinkDocument5 pagesModeling, Simulation and Analysis of Matrix Converter Using Matlab&SimulinkJisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet