Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IEC Electrical Motor Duty Cycle Classifications
Uploaded by
bamankarmahesh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views1 pageThe document describes 8 duty cycle designations used by the International Electrotechnical Commission to classify the operating conditions of electrical motors: S1 refers to continuous duty where the motor reaches temperature equilibrium under constant load; S2 refers to short-time duty where temperature equilibrium is not reached under constant load due to short run times and long rest periods; S3-S8 refer to various types of intermittent periodic duty involving starting, running under constant or changing loads, with or without rest periods or electric braking.
Original Description:
iec ip prot
Original Title
IEC IP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes 8 duty cycle designations used by the International Electrotechnical Commission to classify the operating conditions of electrical motors: S1 refers to continuous duty where the motor reaches temperature equilibrium under constant load; S2 refers to short-time duty where temperature equilibrium is not reached under constant load due to short run times and long rest periods; S3-S8 refer to various types of intermittent periodic duty involving starting, running under constant or changing loads, with or without rest periods or electric braking.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views1 pageIEC Electrical Motor Duty Cycle Classifications
Uploaded by
bamankarmaheshThe document describes 8 duty cycle designations used by the International Electrotechnical Commission to classify the operating conditions of electrical motors: S1 refers to continuous duty where the motor reaches temperature equilibrium under constant load; S2 refers to short-time duty where temperature equilibrium is not reached under constant load due to short run times and long rest periods; S3-S8 refer to various types of intermittent periodic duty involving starting, running under constant or changing loads, with or without rest periods or electric braking.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
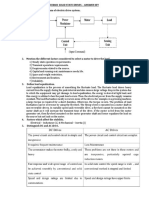
IEC (the International Electrotechnical Commission) uses eight duty cycle designations to
describe an electrical motors operating conditions:
S1 Continuous duty
The motor works at a constant load for enough time to
reach temperature equilibrium.
S2 Short-time duty
The motor works at a constant load, but not long
enough to reach temperature equilibrium. The rest
periods are long enough for the motor to reach ambient
temperature.
S3 Intermittent periodic duty
Sequential, identical run and rest cycles with constant
load. Temperature equilibrium is never reached.
Starting current has little effect on temperature rise.
S4
Intermittent periodic duty
with starting
Sequential, identical start, run and rest cycles with
constant load. Temperature equilibrium is not reached,
but starting current affects temperature rise.
S5
Intermittent periodic duty
with electric braking
Sequential, identical cycles of starting, running at
constant load and running with no load. No rest periods.
S6
Continuous operation
with intermittent load
Sequential, identical cycles of running with constant
load and running with no load. No rest periods.
S7
Continuous operation
with electric braking
Sequential identical cycles of starting, running at
constant load and electric braking. No rest periods.
S8
Continuous operation
with periodic changes in
load and speed
Sequential, identical duty cycles run at constant load
and given speed, then run at other constant loads and
speeds. No rest periods.
You might also like
- Detail Project Report (DPR) : 1MW Utility Scale Solar PV Power PlantDocument28 pagesDetail Project Report (DPR) : 1MW Utility Scale Solar PV Power Plantamritmandal019188% (51)
- Electrical Steering Gear System ExplainedDocument16 pagesElectrical Steering Gear System ExplainedAdwaith Krishnan100% (1)
- Duty Cycle PDFDocument1 pageDuty Cycle PDFBedabyas DehuryNo ratings yet
- Motor Duty Cycles-IEC - S1... EtcDocument1 pageMotor Duty Cycles-IEC - S1... Etccirius_coolNo ratings yet
- IEC Duty Cycles PDFDocument1 pageIEC Duty Cycles PDFdhruvNo ratings yet
- Rewiring & Special Duty Capabalities, SiteDocument18 pagesRewiring & Special Duty Capabalities, SiteMAHESH VNo ratings yet
- Práctica 1 (Presentacion Del Profe)Document11 pagesPráctica 1 (Presentacion Del Profe)daniel LazoNo ratings yet
- AC Motor Duty Cycle Types As Per IEC StandardsDocument2 pagesAC Motor Duty Cycle Types As Per IEC Standardsavandetq15100% (2)
- IEC Duty CyclesDocument1 pageIEC Duty CyclesVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Sensitivity: LNT Construction Internal UseDocument2 pagesSensitivity: LNT Construction Internal Usesowndarya balambikaNo ratings yet
- Motor Duty Cycle Types As Per IEC StandardsDocument1 pageMotor Duty Cycle Types As Per IEC Standardsjasmindpatel100% (1)
- IEC standard for motor duty cycleDocument2 pagesIEC standard for motor duty cycleriyasjob20No ratings yet
- Motor Efficiency: Definitions of Technical TermsDocument5 pagesMotor Efficiency: Definitions of Technical TermsWesly Ruben ManroeNo ratings yet
- IEC Duty CyclesDocument3 pagesIEC Duty CyclesbrijeshBNo ratings yet
- Pen Stock DegghgjhvhvjDocument16 pagesPen Stock DegghgjhvhvjSirish ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Drive & LampDocument21 pagesDrive & LampAditya SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Selection - of - Crane - Duty - Motors - Part - 1Document4 pages4.4 Selection - of - Crane - Duty - Motors - Part - 1Edison EstrellaNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Characteristics under Different VoltagesDocument4 pagesDC Motor Characteristics under Different Voltagesbilalkhan3567No ratings yet
- R5410202 Power Semiconductor DrivesDocument1 pageR5410202 Power Semiconductor DrivessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Study of Single-Phase Directional Overcurrent RelayDocument5 pagesStudy of Single-Phase Directional Overcurrent RelayJoshtyler 21No ratings yet
- AC Machines UEE 401 Lab ManualDocument107 pagesAC Machines UEE 401 Lab ManualVivek TiwariNo ratings yet
- Ee2304 Set3Document4 pagesEe2304 Set3naveenaNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument5 pagesResearch PaperHoney AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Ac Drive (Simple Theory To Understand) By: Nitish DhawanDocument10 pagesAc Drive (Simple Theory To Understand) By: Nitish DhawanNitish DhawanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank SSD EaswariEnggDocument46 pagesQuestion Bank SSD EaswariEnggmenakaNo ratings yet
- Power EletronicDocument1 pagePower EletronicRanaSurjeetNo ratings yet
- 3 4 Point StarterDocument3 pages3 4 Point StarterXingfang91No ratings yet
- A.C Single Phase 4-Pole Squirrel Cage Induction Motor TheoryDocument5 pagesA.C Single Phase 4-Pole Squirrel Cage Induction Motor TheoryCønstäh Van Der WüppertälärîanskíhNo ratings yet
- Blocked Rotor TestDocument11 pagesBlocked Rotor TestIjabi100% (1)
- WYE Delta / Soft Starter Comparison Guide: DefinitionDocument7 pagesWYE Delta / Soft Starter Comparison Guide: DefinitionFudhail MumtazNo ratings yet
- EMD Important Questions Unit-III Starting MethodsDocument9 pagesEMD Important Questions Unit-III Starting MethodsJoseph HarindranathNo ratings yet
- Motor Sincrono SYNCGUIDEDocument48 pagesMotor Sincrono SYNCGUIDEluisfilipeminenervaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Drives QuestionsDocument2 pagesElectrical Drives QuestionsUmang MewaraNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor Modelling and Analysis with Inverter Dead-Time EffectDocument21 pagesInduction Motor Modelling and Analysis with Inverter Dead-Time Effectcontrol 4uonlyNo ratings yet
- Machine 2 Lab Exp 6Document11 pagesMachine 2 Lab Exp 6Ahmed Bin MustafaNo ratings yet
- Draw The Block Diagram of Electric Drive SystemDocument9 pagesDraw The Block Diagram of Electric Drive SystemcoolkannaNo ratings yet
- Ee8353 QP2 PDFDocument7 pagesEe8353 QP2 PDFBhavani MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 04 - EEE210 - Sadikul Hasan Mridha Atul - 181016024Document9 pagesLab Report 04 - EEE210 - Sadikul Hasan Mridha Atul - 181016024অদেখা ভুবনNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Basics - of - Motor - DrivesDocument38 pagesChapter 1 Basics - of - Motor - DrivesMarco SamehNo ratings yet
- Ee2304 Set3Document4 pagesEe2304 Set3kaliappan45490No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: IntroductionDocument118 pagesChapter 1: Introductionrizwan_adilNo ratings yet
- Brushless Motor and ArduinoDocument8 pagesBrushless Motor and ArduinostellaNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Induction MotorDocument10 pagesThree-Phase Induction MotorMadarwi SarwaNo ratings yet
- AC Motors PCIDocument30 pagesAC Motors PCIThomas DuNo ratings yet
- Static Characteristics of SCRDocument62 pagesStatic Characteristics of SCRtechimranNo ratings yet
- EE2301 Power Electronics Question BankDocument11 pagesEE2301 Power Electronics Question Bankvenkatesh_paboluNo ratings yet
- AC Machines - III ASSIGNMENT QUESTIONSDocument4 pagesAC Machines - III ASSIGNMENT QUESTIONSVarun SandeshNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Characteristics ExperimentDocument7 pagesDC Motor Characteristics Experimentbilalkhan3567No ratings yet
- My Procedure - FinalDocument8 pagesMy Procedure - FinalSe FunsNo ratings yet
- Problems Bank 2Document7 pagesProblems Bank 2rida.hamza.muhammadNo ratings yet
- Understanding Complete Test Performed To Induction MotorDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Complete Test Performed To Induction MotorFirmanJohannesNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Induction Motor PerformanceDocument10 pagesThree-Phase Induction Motor PerformanceMohamed Meeran100% (1)
- Dcservo NewkitDocument11 pagesDcservo NewkitNikita MalikNo ratings yet
- 293 Kumar PDFDocument6 pages293 Kumar PDFMaulana JayalaksanaNo ratings yet
- Start TestDocument2 pagesStart Testhelp3rNo ratings yet
- GTU Last-3 Paper Questions Power Electronics-IIDocument2 pagesGTU Last-3 Paper Questions Power Electronics-IIAkshit PatelNo ratings yet
- Shridhar, Bhim Singh and Jha Dept of Engg, Delhi, Hauz DelhiDocument7 pagesShridhar, Bhim Singh and Jha Dept of Engg, Delhi, Hauz DelhiDulal MannaNo ratings yet
- EE1301 Electrical Machines II PDFDocument7 pagesEE1301 Electrical Machines II PDFsivaeinfoNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseFrom EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseNo ratings yet
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Make Your Settings Only Into White Boxes Corresponding To Desired Standard Curve!Document4 pagesMake Your Settings Only Into White Boxes Corresponding To Desired Standard Curve!bamankarmaheshNo ratings yet
- Current Transformers How To Specify Them PDFDocument36 pagesCurrent Transformers How To Specify Them PDFargari19No ratings yet
- CTVA BurdenDocument4 pagesCTVA BurdenbamankarmaheshNo ratings yet
- Solar PV Policy (For MNRE Schemes) 31-10-2011Document2 pagesSolar PV Policy (For MNRE Schemes) 31-10-2011bamankarmaheshNo ratings yet
- Battery and Charger SizingDocument47 pagesBattery and Charger SizingUsman034No ratings yet
- ClearancesDocument6 pagesClearancesbamankarmaheshNo ratings yet
- Inverter Duty Vector Performance AC Motors Product GuideDocument14 pagesInverter Duty Vector Performance AC Motors Product GuidebamankarmaheshNo ratings yet
- Inverter Duty Vector Performance AC Motors Product GuideDocument14 pagesInverter Duty Vector Performance AC Motors Product GuidebamankarmaheshNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit - ETAPDocument4 pagesShort Circuit - ETAPvaithy1990No ratings yet
- International StandardsDocument2 pagesInternational Standardsrocknroll0078No ratings yet
- APFC Panel DesigningDocument16 pagesAPFC Panel Designingyrmn200% (1)
- Beskyttelse KanalskinnerDocument32 pagesBeskyttelse Kanalskinnerandrescardona1No ratings yet
- Kezunovic PSERC Public Webinar Slides Feb2011Document39 pagesKezunovic PSERC Public Webinar Slides Feb2011Cao Ortega GNo ratings yet