Professional Documents
Culture Documents
กรณ - ศ - กษาท - - 1
Uploaded by
KiddyRx LoukkadeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
กรณ - ศ - กษาท - - 1
Uploaded by
KiddyRx LoukkadeCopyright:
Available Formats
1
1 15
30 2553
Quatiapine
risperidone
ascites
Amlodipine 10 mg
2.5
mg
3
ascites
Metoclopamide 10
mg
Clcr 10-40 ml/min
50 %
normal dose
4.
mg/
Amlodipine 20
10 mg/
5
Aspirin Aspirin
CVD event
AF
Ischemic stroke
Warfarin
hs 3 mg
3 mg
INR 0.9
5 mg * 1
*1 hs 2
1*1 hs 5
INR
7
HIV/TB
..
48010710130
: (General Medicine I)
: 15 30 2553
: 1 2553
56 55 170
(.2)
20 2553
CC: 3 day PTA
HPI:
Known case TVD S/P PCI 5 , CABG 6
MRI CABG , EF 30 %, CABG
3 Day PTA
1 Day PTA
PMH: TVD, Diabetes mellitus, Hypertension ~ 5 yr PTA
FH:
SH:
~ 30 ,
~ 5
ALL: Sulfonamide ,
Med PTA :
Furosemide (40) 2*1 pc
Aspirin (81) 1*1 O pc
Isosorbide mononitrate (20) 1*2 O ac
Spironolactone (25) 1*1 O pc
Carvedilol (6.25) *2 O pc
Enalapril (5) 1 *2 O pc
Amlodipine (10) *2 O pc
Gemfibrozil (300) 2*2 O pc
Air-X (80) 1*3 O pc
FBC 1*3 O pc
Simvastatin (20) 1*1 O pc
Lorazepam (0.5) 1*1 O hs
Esomeprazole (20) 1*1 O ac
Warfarin (3) 1
Physical Examination
V/S:
T 37.2 c
BP 94/61 mmHg
PR 86 bpm RR 20 bpm
Gen : A man, good conscious.
HEENT: not pale, no jaundice
Heart: Regular, no murmur
EKG: No AF
Lung: Fine crepitation both lung
Extremities: Pitting edema 2+
Abdomen: Soft not tender
CXR: Cardiomegaly, Pulmonaly edema.
Data/Lab
Normal
20
21
22
23
24
25
135-148
121
129
128
4.31
3.91
3.57
92
97
97.5
21
24
26
37
26
Electrolyte
Na
mEq/L
3.5-5.5
mEq/L
95-106
Cl
mEq/L
22-30
CO2
mEq/L
1.8-2.6
Mg
mg/dL
8.6-
Ca
Phos
1.9
8
10.3mEq/d
L
2.84.9
mEq/dL
Renal Relate
BUN
SCr
FBG
HbA1c
7-18 mg/dL
40
0.6-1.2
2.27
70110
208
mg/dL
mg/dL
9.6
233
1.7
1.5
139
143 346
1.47
9.6
Hematology
4.4-
11.310 /
WBC
3.37
8.7
8.4
27
26.3
g/dL
36.0-45.0
Hct
MCV
80-96 fL
80.2
27.5-33.2
25.9
33.4-35.5
32.3
11.6-16.5
24
150-400
138
Neu
40-65 %
69
Lym
20-40 %
24
Data/Lab
Normal
20
Mono
210 %
Eos
0-9 %
Baso
0-1 %
MCH
MCHC
RDW
3.2
10 /L
12.3-15.3
Hb
10.3
L
4.5-5.9
RBC
9.1
pg
%
MPV
Plt
10 /L
21
22
23
24
25
Poikilocyto
sis
Ovalocyte
Hypochrom
asia
Anisocytosi
s
Macrocytos
is
Microcytosi
s
Target cell
Reticulocyt
0.5-2.5%
ec
Feritin
10-300
ng/ml
Serum iron
61-165
ugm%
UIBC
170-230
ugm%
TIBC
228-428
ugm%
% iron sat.
30-50 ugm
%
Coagulation
PT
10.2-14.1
68.1
>120
5.4
2.6
PT ratio
INR
1.1
23.1-32.3
58.3
103.
PTT
33.8
Protein
3.4-4.8
2.8
1.5
2.8
2.7-3.5
3.9
2.8
3.8
SGOT
10-37
40
54
SGPT
10-37
14
20
ALK
34-104
511
T.bil
0-1
3.5
2.8
D.bi
0-0.3
2.1
1.5
0-171
244
Alb
g/dL
Glo
g/dL
LFT
Other
CPK
CKMB
2.99
3.1
0.14
0.1
Tro-p
Patient Data Record Form
Date
Day
Admissi
after
on
Systolic
BP
Diastolic
Respirations
20
21
22
23
24
25
90-
90-
80-
100-
110-
100-
94
107
110
119
119
120
56-
51-
46-
60-
60-
62-
61
62
64
84
80
82
20
20
20
20
20
10
20
Temperature(max)
Pulse
37.2
37.2
37.1
37.4
37.3
37.0
86
80-
76-
82-
84-
84-89
86
86
84
88
600
Intake
560
555
1,385
Output
320
100
1,700 1,900
Medications
Order for One Day
Drug/Dosage regimen
Administrati
on
20 21 22 23 24
Furosemide 40 mg
Iv stat
Dobutamine (2:1)
5 ud/min
3 LPM
SC
O2 canular
HR
25
IF 201-250 = 4 U
251-300= 6 U
301-350= 8 U
Vitamin K 2 mg
FFP 2 unit
Furosemide 20 mg
IV
Drip in 1 hr
IV
Order for Continue
Drug/Dosage regimen
Pantoprazole 40 mg
administratio
20
21
22
23
IV OD
Of
24
25
10
11
Warfarin 3 mg
* 1 O hs
of
1*1 O hs
Air-x
1*3 O pc
Simvastatin 20 mg
1*1 O pc
Lorazepam 0.5 mg
1*1 O hs
prn
ASA 81 mg
1*1 O pc
Spironolactone 25 mg
1*1 O pc
of
administratio
20
21
22
23
24
25
Drug/Dosage regimen
n
Ferrous fumarate
1*3 O pc
Isodil 5 mg
1 tab SL prn
Rupect
1*3 O pc
Of
Clarithromicin 500 mg
1*2 O pc
of
Furosemide 40 mg
1*2 O pc
Enalapril 5 mg
of
*1 O pc
Pantoprazole 40 mg
1*1 O ac
NAC 600 mg
1*2 O pc
of
Vitamin C 500 mg
6*2 O pc
of
Furosemide 40 mg
1*1 O pc
Problem lists
1. CHF with TVD s/p PCI and CABG
2. Bleeding per- gum
11
12
3. R/O Cardiac cirrhosis
4. Acute renal injury
5. Anemia
6. Diabetes mellitus
7. Hypertension
Hospital course
21/3/2553
Case 56
CC : 3
PI :
Known case TVD s/p PCI 5
CABG : 6
12
13
MRI CABG EF= 30 %
CABG
3 PTA
GA : Good conscious ,not pale
Lung : Fine crepitation both lung
Ext : pitting edema 2+
Tro-p : 0.18
EKG : No AF
CXR: Cardiomegaly, pulmonary edema
Plan :
of enalapril/aldactone Cr rising
enoxaparin OD
V/S
Liver : Liver sign
Cr
Plan start ARB ( pt. ACEI )
23/3/2553
LVEF = 26 %
MR +/_ (19/2/53)
1) CHF : pitting edema 1+
No Crepitation
Heart normal s1s2 , No murmur,No gallop , I/O = 1,385/1,700
Plan : continue diuretic
2) PT > 120 ,PTT 91.2
Vit K 2 mg IV , FFP 2 unit PT =31.2 ,INR 2.6 ,
PTT =48.8
13
14
F/U
PT = 12.3 , INR = 1.1 , PTT =
30.3
23/3/2553
Echo W/U poor LVEF poor LVEF
Consult Plan medication
Revascularization by PCI
set CAG
Medication
Re-challeng warfarin D/C
24/ 3/ /2553
TVD S/P CABG 5 MO . LVEF 26 % on warfarin & ASA
Admit CHF Precipitate ????
1) CHF with TVD S/P CABG
precipitate neg I/O
Plan : balance I/U , Challenge ACEI - Aldactone
2) Bleeding per-gum & Hemolysis (non massive with coagulopathy)
INR prolong on warfarin & Clarithromicin
Bleeding correct with vit K & FFP INR 1.1
Plan : If clinical : no bleeding plan start warfarin
3) R/O Cardiac Cirrhosis
No Hx Alcohol/Herb
IF no stigmata , Ascite +
LFT : reverse A/G ratio & billirubin ^
Plan : V/S upper abdomen
14
15
4) AKI
Cr ^ -> prerenal azotemia CHF -> low CO CHF
improve BUN/Cr (1.5)
Problem 1: CHF with TVD s/p PCI and CABG : DRP warfarin
drug interaction with simvastatin aspirin enalapril furosemide
S : Subjective data
3 day PTA
O: Objective data
PMH: TVD, Diabetes mellitus, Hypertension ~ 5 yr PTA
Med PTA :
Furosemide (40) 2*1 pc
Aspirin (81) 1*1 O pc
Isosorbide mononitrate (20) 1*2 O ac
15
16
Spironolactone (25) 1*1 O pc
Carvediol (6.25) *2 O p
Enalapril (5) 1 *2 O pc
Amlodipine (10) *2 O pc
Gemfibrozil (300) 2*2 O pc
Simvastatin (20) 1*1 O pc
Esomeprasole (20) 1*1 O ac
Warfarin (3) s1
Physical Examination
V/S: BP 94/61 mmHg
Lung: Fine crepitation both lung
Extremities: Pitting edema 2+
CXR: Cardiomegaly, Pulmonaly edema.
Na
121
Alb
2.8
Cl
92
Glo
3.9
BUN
40
Cr
2.27
CPK
244
CKMB
2.99
Tro-p
0.14
Intake
56
0
Medications
Output
32
0
16
17
Order for One Day
Drug/Dosage regimen
Administrati
on
20 21 22 23 24
Furosemide 40 mg
iv stat
Dobutamine (2:1)
5 ud/min
3 LPM
SC
O2 canular
HR
25
IF 201-250 = 4 U
251-300= 6 U
301-350= 8 U
Furosemide 20 mg
IV
Order for Continue
Drug/Dosage regimen
Administratio 20
21
22
23
of
24
25
n
Pantoprazole 40 mg
IV OD
Warfarin 3 mg
* 1 O hs
of
1*1 O hs
Simvastatin 20 mg
1*1 O pc
ASA 81 mg
1*1 O pc
Spironolactone 25 mg
1*1 O pc
of
Isodil 5 mg
1 tab SL prn
Furosemide 40 mg
1*2 O pc
of
Enalapril 5 mg
*1 O pc
Pantoprazole 40 mg
1*1 O ac
Furosemide 40 mg
1*1 O pc
17
18
A: Assessment
Etiology : Congestive heart failure (CHF)
edema
fluid overload pulmonary congestion peripheral
peripheral
edema
(TVD) (MR)
CHF Tripple vessel disease (TVD)
coronary artery
Indication for therapy :
TVD
18
19
Assessment
of
therapy : stage
CHF ACC/AHA Practice Guidelines
stage
B-C Structural heart disease
cardiomegaly X-ray
peripheral edema HTN TVD
New York Heart Associated (NYHA)
classification Class III
ACC/AHA Practice Guidelines
Stage C Diuretics, ACEI, ARBs,
Aldosterone antagonist, Beta-blockers, Hydralazine/nitrates
Catecholamine Dopamine dobutamine
Medications
Order for One Day
Drug/Dosage regimen
Administrati
on
20 21 22 23 24
Furosemide 40 mg
Iv stat
Dobutamine (2:1)
5 ud/min
3 LPM
O2 canular
Furosemide 20 mg
IV
25
19
20
Order for Continue
Drug/Dosage regimen
Administratio 20
21
Spironolactone 25 mg
1*1 O pc
of
Furosemide 40 mg
1*2 O pc
Enalapril 5 mg
*1 O pc
Furosemide 40 mg
1*1 O pc
22
23
24
25
Of
1) Lasix 20-80
mg/dose 20-40 mg 6-8
20-40 mg
1-2
2) Dobutamine beta-receptor
cardiac output
2-3
IV drip 2-5 mcg/kg/min
3 mcg/kg/min (7)
3) Enalapril 2.5 mg 1-2 target dose
10-20 mg 2
Cr
Raising
4) Spironolactone 12.5-25 mg/day maximum dose 50
mg/day
20
21
TVD
ACC/AHA
- 130/80 mmHg
- 130 mg/dL HbA1C
7 %
- LDL-C 100 mg/dL
- HDL-C 60 mg/dL
- BMI = 18.5-24.9 kg/m
- 30-60 3-4
Antiplatelet agent ,Antiischemic agent , Statin secondary prophylaxis
Order for Continue
Drug/Dosage regimen
Administratio 20
21
22
23
Of
24
25
n
Pantoprazole 40 mg
IV OD
Warfarin 3 mg
* 1 O hs
of
1*1 O hs
Simvastatin 20 mg
1*1 O pc
ASA 81 mg
1*1 O pc
21
22
Isodil 5 mg
1 tab SL prn
1) ASA (81) 1*1 O pc Antiplatelet agent
Aspirin 75325 mg
2) Isosorbide dinitrate (5)
3) Simvastatin (20) 1 *hs secondary prevention
plaque rupture 20-40 mg/day
(max dose 80 mg/day)
4) Pantoprazole 40 mg IV
Aspirin
peripheral edema serum creatinine
acute renal failure SCr Bblocker ACEI
MR warfarin
INR prolong,
warfarin 1-2 dose
bleeding INR
warfarin
P :
Therapeutic plan :
22
23
Drug/Dosage regimen
administratio
n
Furosemide 40 mg
iv stat
Dobutamine (2:1)
5 ud/min
O2 canular
Drug/Dosage regimen
3 LPM
administratio
n
Pantoprazole 40 mg
IV OD
Simvastatin 20 mg
1*1 O pc
ASA 81 mg
1*1 O pc
Spironolactone 25 mg
1*1 O pc
Isordil 5 mg
1 tab SL prn
Enalapril 5 mg
*1 O pc
Pantoprazole 40 mg
1*1 O ac
Furosemide 40 mg
1*1 O pc
AKI
Goal :
23
24
Therapeutic monitoring :
-
-
- Balance Intake / output
- BP
ADRs
monitoring :
Furosemide
Electrolyte
Simvastatin
BUN Cr
Isosorbide dinitrate
Enalapril
BP
BP ,
ASA
CBC ,Bleeding
Dobutamine
HR , BP ,PR
Patient education :
-
HTN, DM CAD
- < 130/80 mmHg
- < 130 mg%
Future plan :
24
25
- Beta-blockers
carvidilol, metoprolol
Problem 2 : Bleeding per-gum & Hemolysis (non massive with
coagulopathy) : DRP : Over dose of warfarin , Subtherapeutic
S : Subjective data
-
O: Objective data
RBC
3.37
Hb
8.7
Hct
27
MCH
25.9
MCHC
32.3
RDW
Plt
24
138
25
26
Neu
69
PT
68.1
INR
5.4
PTT
58.3
A: Assessment
Etiology: Bleeding INR prolong
warfarin 5 Tipple vessel
disease (TVD) +/- Mitral valve regurgitation (MR)
Myocardial infarction
22
INR prolong Bleeding
warfarin 1. 2.
warfarin 3.
metabolite 4. factor
7. 8.
simvastatin aspirin enalapril
furosemide clahrithromycin
Warfarin acute kidney
injury , cardiac cirrhosis , congestive heart failure, Hypertension,
Diabetes mellitus
Bleeding
Indication for therapy :Bleeding
26
27
Assessment of therapy : Bleeding
ACCP guideline 2008
Dose alteration for goal INR
2.0-3.0
INR < 2
INR 3-3.5
INT 3.6-4
INR > 4
Increase weekly
Decrease weekly
Withhold no
Withhold no
dose by
dose by 5-15
dose to one dose
dose to one dose
27
28
Decrease weekly
dose by 10-15
Decrease weekly
dose by 10-20
15 mg/wk INR admit =
5.4 1- 2 dose 10-20 %
12- 13.5 mg/wk
13.5 mg/wk
INR prolong
22 (
non massive) ACCP guideline 2008
vitamin K 10 mg Fresh fasting plasma 150 300 ml
(1 unit = 300 ml) 2 unit
P :
Goal :
1. bleeding
2. INR
3.
4.
Therapeutic plan :
1. vitamin k 10 mg slow IV infusion
2. FFP 1 unit drip in 1 hr.
28
29
3. bleeding INR warfarin
* 1 O pc
Therapeutic monitoring :
1. INR 2-3 (monitor bleeding )
2. HF (SOB, DOE, nocturia, edema)
3. CBC
4. PT, PTT
ADRs monitoring :
1. warfarin : bleeding (INR PT PTT)
2. vitamin k : INR PT PTT
3. FFP : Hypersensitivity ( CBC)
Education plan
1.
warfarin
2.
Future plan : F/U 7 PT, INR
Problem 3: Cardiac cirrhosis without DRP
29
30
S: Subjective data
-
O: Objective data
SGOT
40
ALK
511
T.bil
3.5
D.bi
2.1
A: Assessment
Etiology: Cardiac cirrhosis fibrosis
portal fibrosis
AST, ALT, LDH Total billirubin
Indication for therapy :
Assessment of therapy :
P :
Therapeutic plan :
Goal :
1.
2. BUN = 7-18 mg/dL
3. SCr = 0.6 1.2 mg/dl
4. BUN/SCr = 10-15 : 1
Therapeutic monitoring :
30
31
1. BUN/Cr
ADRs
monitoring :
Patient education :
1.
2.
Future plan :
Problem 4 : Acute renal injury without DRP
S: Subjective data
-
O: Objective data
Extremities: Pitting edema 2+
Na
121
Cl
92
BUN
40
SCr
2.27
Alb
2.8
Glo
3.9
Intake
56
Output
32
0
0
31
32
Medications
Order for One Day
Drug/Dosage regimen
Administrati
20 21 22 23 24
25
on
Furosemide 40 mg
iv stat
Furosemide 20 mg
IV
/
/
Order for Continue
Drug/Dosage regimen
administratio
20
21
22
23
24
of
25
n
Furosemide 40 mg
1*2 O pc
NAC 600 mg
1*2 O pc
of
Vitamin C 500 mg
6*2 O pc
of
Furosemide 40 mg
1*1 O pc
A: Assessment
Etiology: Acute kidney injury (AKI)
( ) Glomerular filtration rate
BUN/Cr
400
ml/day stage 1 SCr 1.5-2
Baseline Oliguria
400 ml 24
32
33
Prerenal pre-renal
hypovolemia efective circulatory hypovolemia
efective circulatory
hypotension, heart failure
renal blood
flow Enalapril ACEI
Indication for therapy:
Assessment of therapy :
Dialysis
BUN/Cr
Enalapril
mannital 20% 12.5-25
g IV mannital AKI
33
34
Loop diuretic furosemide initial IV loading dose 40-80 mg
continuous infusion 10- 20 mg/hr.
1-3 g/day
Furosemide IV stat 40 mg
Furisemide (40) 1*2 O pc
N-acytylcystein (NAC) Vitamin c
1 600 mg q 12 hr 1
antioxidant
Nitric oxide
P :
Therapeutic plan :
Goal :
Furosemide IV stat 40 mg then
Furisemide (40) 1 * 2 O pc
1. s
2. BUN = 7-18 mg/dL
3. SCr = 0.6 1.2 mg/dl
4. BUN/SCr = 10-15 : 1
Therapeutic monitoring :
2. body weightss
3. input/output
4. Potassium
5. BUN/Cr
ADRs
monitoring :
Furisemide : Orthostatic hypotension (BP),
hyperglycemia (FBS), hypokalemia,
34
35
hyponatremia(electrolyte)
Patient education :
1.
2.
Phosphate
Future plan :
Problem 5 : Anemia without DRP
S: Subjective data
3 day PTA
O: Objective data
Med PTA :
FBC 1*3 O pc
RBC
3.37
Hb
8.7
Hct
27
MCH
25.9
MCHC
32.3
RDW
Plt
24
138
35
36
Medications
ferrous fumarate 1* 3 o pc
A: Assessment
Etiology : anemia Hemoglobin
12
bleeding
Indication for therapy :
Assessment of therapy :
200 mg/day 2-3 ferrous fumarate 1* 3
o pc
P :
Therapeutic plan :
Goal :
ferrous fumarate 1* 3 o pc
1. Hb > 13
2. HCT > 33
ADRs
Therapeutic monitoring :
monitoring :
CBC
ferrous fumarate :
Patient education :
36
37
Future plan :-
1. Wells BG, DiPiro JT, Schinghmmer TL and Hamilton CW.
th
Pharmacotherapy Handbook. 6 ed. Mc Graw Hill ; 2006.
2. . . 7.
. ; 2548.
3. Tatro DS. Drug interaction facts 2007. Wolters Kluwer; 2007.
4. David NG, Robert CM, George ME, et al. The Sanford
th
guideline to antimicrobial therapy 2009. 39 ed. Sperryville:
antimicrobial therapy; 2006.
5. Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Longo DL, Braunwald E, Hauser SL, and
th
Jameson JL. Harisons Principles of Internal Medicine. 16 ed.
Mc Graw Hill; 2005
6. Lacy CF, Armstrong LL, Goldman MP, Lance LL. Drug
th
Information Handbook. 17 ed. Lexi-Comp; 2009.
7. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on
Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood
Pressure. JAMA 2003;289:256071.
2
:
..
48010710130
37
38
: (General Medicine I)
: 15 30 2553
: 29 2553
46 106 160
(.3) 19
2553
CC: 1 day PTA
HPI:
6 Day PTA
2 Day PTA
1 Day PTA
PMH: Diabetes mellitus, Hypertension , Chronic kidney disease R/O
ACD
FH:
SH:
ALL: NKDA
Med PTA :
Mixtard insulin 10-0-6
Clindamycin (300) 2*3 O pc
Cefspan (100) 1*3 O pc
Ferrous fumarate 1*3 O pc
Folic acid 1*1 O pc
38
39
Senokot 2* 1O hs
Prenolol (50) 1*1 O pc
CaCO3 (1.25 g) 1*1 O pc
Hydralazine (25) 1 Q 6 hr
Sodamint 2*3 O pc
Zimmex (20) 1* 1O hs
Physical Examination
V/S:
T 39.5 c
BP 180/90 mmHg
PR 86 bpm RR
40 bpm
Gen : A woman, good conscious.
HEENT: not pale, no jaundice, Marked obesity, Pharynx inject
Heart: Regular, no murmur
Lung: Clear
Extremities: pitting edema 1+, no cellulitis
Old scar (Hyperpigment) Lt leg
Dry wound at both foot
Abdomen: Soft not tender
Data/Lab
Normal
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
135-148
125
134
132
135
136
139
3.5-5.5
3.17 3.06 3.30
3.5
3.12
3.4
102
106
107.2
Electrolyte
Na
K
Cl
mEq/L
mEq/L
95-106
mEq/L
90
99.7
97.5
39
40
22-30
CO2
20
25
23
20
22
37
32
34
0.6-1.2
5.71 5.46 5.32 5.1
4.36
4.75
70110
444
mEq/L
1.8-2.6
Mg
2.1
mg/dL
8.6-
Ca
Phos
24
9.1
10.3mEq/d
L
2.84.9
5.2
mEq/dL
Renal Relate
BUN
SCr
FBG
7-18 mg/dL
mg/dL
44
40
393
mg/dL
40
402
294 240 219 216
199
HbA1c
Hematology
4.4-
18.4 10.8
3
WBC
RBC
Hb
Hct
11.310 /
L
4.5-5.9
3.69 3.41
12.3-15.3
9.8
36.0-45.0
29.5 27.6
10 /L
g/dL
%
9.2
40
41
150-400
227
234
Plt
10 /L
40-65 %
Neu
89.6 78.1
Lym
20-40 %
5.1
13.2
Mono
210 %
4.7
7.7
Eos
0-9 %
0.3
0.7
3.4-4.8
3.4
Protein
Alb
g/dL
Data/Lab
Normal
19
2.7-3.5
4.6
SGOT
10-37
17
SGPT
10-37
17
ALK
34-104
84
T.bil
0-1
0.5
D.bi
0-0.3
0.1
Glo
g/dL
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
LFT
Patient Data Record Form
Date
Day
Admiss
after
ion
BP
Systoli
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
180
170
160
160
160
90
90
90
90
90
170 180
170
c
Diastol
80
90
90
41
42
ic
20
20
20
39.5
37.5
37.1
Pulse
98
84
94
Intake
1500
3800
Output
2900
2200
Respirations
Temperature(m
ax)
20
20
20
20
37.4
36.8
37.5
36.8
37.2
90
88
88
84
92
20
Medications
Order for One Day
Drug/Dosage regimen
Administratio 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 2
n
0.9% NSS 1000 ml
Iv 100 ml/hr /
RI At ER 10 Unit
SC
KCL elixer 50 ml
Q 4 hr ,2
dose
KCL elixer 50 ml
1 dose
0.9% NSS 1000 ml
Iv 80 ml/hr
0.9% NSS 1000 ml
Iv 60 ml/hr
Hs
Milk of magnesia 30 ml
Drug/Dosage regimen
Administratio 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 2
n
HN 6 unit
Stat
HR 8 unit
Stat
HN 4-0-10
SC
HN 6-0-12
SC
/
/
42
43
HN 10-0-14
SC
HN 14-0-14
SC
HN 14-0-12
SC
Mixtard 18 U
SC
/
/
/
/
Order for Continue
Drug/Dosage regimen
Ceftriazone 2 g
Administratio 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
n
Iv
of
1*hs
CaCO3 1.25 g
1*1 O pc
Folic acid
1*1 O pc
Apresoline 25 mg
1*3 Opc
of
Amlodipine 10 mg
1*1 O pc
of
Eprex 4000 UNIT
SC q 1 wk
of
Bromhexine
1*3Opc
Amlodipine 10 mg
1*2 Opc
Eprex 4000 UNIT
SC 2
Simvastatin 20 mg
/WK
Ommicef 100 mg
2*2Opc 2day
Apresoline 25 mg
2*3 Opc
43
44
Insulin
Sliding scale
201-250 HR 4 U
251-300 HR 6 U
301-350 HR 8 U
351-400 HR 10 U
//
Regular
Humulin
19/4/53
ER
444
20.00
241
06.00
141
11.00
393
10
15.00
358
20.00
350
06.00
290
20.00
402
10
06.00
249
11.00
257
15.00
236
20.00
294
20/4/53
21/4/53
22/4/53
insulin(u)
N(u)
4
4-0-10
6-0-12
44
45
23/4/53
24/453
25/4/53
26/4/53
06.00
208
11.00
240
15.00
223
20.00
192
06.00
152
11.00
147
15.00
219
20.00
204
06.00
140
11.00
216
15.00
212
20.00
214
06.00
199
10-0-14
14-0-14
14-0-12
Home medication
Mixtard insulin 20-0-12
Folic acid 1*1 O pcs
Senokot 2* 1O hs
CaCO3 (1.25 g) 1*1 O pc
Hydralazine (25) 1 Q 6 hr
Zimmex (20) 1* 1O hs
Amlodipine(10) 1*2O pc
Eprex 4000 U 2/week
Bromhexine 1*3 O pc
Problem lists
45
46
1. Acute febrile illness R/O Urinary tract infection
2. Diabetes mellitus with Dyslipidemia
3. Hypertension
4. Chronic kidney disease
5. Anemia of chronic kidney disease
Problem 1: Acute febrile illness R/O Urinary tract infection
Without DRP
S: CC:
HPI:
1 day PTA
6 Day PTA
2 Day PTA
O:
V/S:
1 Day PTA
T 39.5 c
Data/Lab
Normal
19
4.4-
20
18.4
3
WBC
11.310 /
L
46
47
Neu
40-65 %
89.6 78.1
Medications
Order for Continue
Drug/Dosage regimen
Administratio 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
n
Ceftriazone 2 g
Ommicef 100 mg
Iv
2*2Opc 2day
of
/
A:
Acute febrile illness (AFI)
6 Viral infection: Dengue fever Influenza ,
Rickettsiosis Leptospirosis , Malaria ,Typhoid fever ,Bacteremia
WBC ,neutrophil
Empiric Cefriaxone 2 g IV
5
Ceftriaxone
1-2 g /day
2 g / day
P :
Therapeutic plan : {Pharmacist plan}
47
48
- Ceftriaxone 2 g IV
- Cefdinir 300 mg 1*1 pc
Goal :
- WBC 4.4-11.310 /L
- Netrophile 40-65 %
Therapeutic monitoring :
- WBC
- Neutrophile
ADR
monitoring : -
- Ceftriaxone : Hemoglobin, Hematocrit , Transminase, Alkaline
phosphatase
- Cefdinir : rash
Patient education :
-
-
Problem 2 : Diabetes malletus DRP : Need to add drug
(Aspirin)
S:
O:
Old scar (Hyperpigment) Lt leg
Dry wound at both foot
48
49
Med PTA :
Mixtard insulin 10-0-6
Zimmex (20) 1* 1O hs
Data/Lab
FBG
Normal
19
70110
444
< 6.5
7.6
mg/dL
HbA1c
20
21
393 402
22
23
24
25
26
294
240
219
216
199
Medications
Order for One Day
Drug/Dosage regimen
Administratio 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 2
n
RI At ER 10 Unit
SC
HN 6 unit
Stat
HR 8 unit
Stat
HN 4-0-10
SC
HN 6-0-12
SC
HN 10-014
SC
HN 14-0-14
SC
HN 14-0-12
SC
Mixtard 18 U
SC
/
/
/
/
/
/
Insulin
//
19/4/53
ER
444
Regular
Humulin
insulin(u)
N(u)
49
50
20/4/53
21/4/53
22/4/53
23/4/53
24/453
25/4/53
26/4/53
20.00
241
06.00
141
11.00
393
10
15.00
358
20.00
350
06.00
290
20.00
402
10
06.00
249
11.00
257
15.00
236
20.00
294
06.00
208
11.00
240
15.00
223
20.00
192
06.00
152
11.00
147
15.00
219
20.00
204
06.00
140
11.00
216
15.00
212
20.00
214
06.00
199
4-0-10
6-0-12
10-0-14
14-0-14
14-0-12
Order for Continue
50
51
Drug/Dosage regimen
Administratio 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 2
n
Simvastatin 20 mg
1*hs
6
/
A:
Etiology
Insulin
metabolism
Insulin
ADA
200 mg/dl ,
Fast plasma glucose 126 mg/dl Oral glucose
tolerance test 200 mg/dl
Indication for therapy
Assessment of therapy
ADA
metfomin 2 3
51
52
HbA1C
6.5
Sulfonylurea, Thiazolidinedione Insulin
Insulin
Insulin Slinding scale
Dyslipidemia
TG < 150 , HDL> 40 , HDL> 50
LDL < 100 ,
DM CVD
52
53
1. LDL<100
2. >40 y statin LDL 30-40%
3. <40 y CVD risk factor
LDL goal
DM CVD
1. statin LDL 30-40%
2. LDL goal<70 high dose statin
3. TG<150, HDL>40/50 (M/F)
1. ASA (75-162 mg/day) secondary prevention
DM+CVD
2. ASA (75-162 mg/day) primary prevention
Type2 or Type1DM > 40
CVD, HTN, smoking, dyslipidemia, or
albuminuria
40
Simvastatin 20 mg
Coronary event
20-40 mg 20 mg
Aspirin
75-162 mg/day
Aspirin(81mg) 1*1 O pc
P :
Therapeutic plan : {Pharmacist plan}
Mixtard insulin 20-0-12
Goal :
Simvastatin 20 mg 1*hs
Aspirin 81 mg 1*1 O pc
53
54
- FBS <126 mg%
- HbA1C < 6.5%
Therapeutic monitoring :
- FBS
- HbA1C
ADR
monitoring : -
Mixtard insulin : FBS
Simvastatin : Transminase , CPK 3
Aspirin : Bleegind
Patient education :
-
Future plan :
FBS, HbA1C
Lipid profile
Problem 3: Hypertention DRP: Over dosage of Amlodipine
S:
54
55
O:
Med PTA :
Prenolol (50) 1*1 O pc
Hydralazine (25) 1 Q 6 hr
Patient Data Record Form
Date
Day
after
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
Admiss
Systoli
180
170
160
160
160
Diastol
90
90
90
90
90
ion
c
BP
ic
170 180
80
170
90
90
Medications
Order for Continue
Drug/Dosage regimen
Administratio 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 2
n
Apresoline 25 mg
1*3 Opc
Amlodipine 10 mg
1*1 O pc
of
f
Amlodipine 10 mg
1*2 Opc
Apresoline 25 mg
2*3 Opc
A:
Etiology
55
56
Hypertension ()
140/90 .
JNC 7
2 Essential
hypertension
secondary hypertension
primary renal disease, oral contraceptive,
pheochromocytoma, primary hyperaldosteronism
Premature cardiovascular disease
, Left ventricular hypertrophy, stroke
End stage renal failure
Indication for therapy
56
57
Assessment of therapy
130/80 mmhg ACEI,ARB
Glucose metabolism Diabetic
nephropathy Renal vascular resistance perfusion
pressure Proteinuria Diuretic
beta blocker
Hypoglycemia
CCB
57
58
130/80 ACEI
Creatinine
loop diuretic Volume overload
dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker
10
> 160 /90 mmHg JNC 7 Hypertension
stage 2
Clcr 20.6 ml/min
ARB
CCB Amlodipine(10) 1*2
Opc Hydralazine (25) 1*3 O pc
1. Amlodipine(10) 1*1 O pc CCB
proteinuria 2.52
10 mg/day (max 10 mg/day) 20 mg
2. Hydralazine (25) 2*3 O pc Direct
smooth muscle
vasodilator
Artery Vein severe hypertension
25-100 mg (Max 300 mg) 2
P :
150 mg /day
Therapeutic plan :
{Pharmacist plan}
Hydralazine (25) 2*3 O pc
58
59
Amlodipine (10) 1*1 O pc
Goal :
- BP<130/80 mmHg
Therapeutic monitoring :
- BP
ADRs
titer
monitoring :
Hydralazine
Heart rate , blood pressure, ANA
Amlodipine
Heart rate , blood pressure ,
Peripheral edema
Patient education :
- 130/80 mmHg
- 30
3
-
Future plan :
- 130/80 mmHg
59
60
Problem 4 : Chronic renal failure DRP : Low dose of Sodium
bicarbonate
S:
-
O:
Med PTA :
CaCO3 (1.25 g) 1*1 O pc
Sodamint 2*3 O pc
Extremities: pitting edema 1+
Data/Lab
Normal
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
135-148
125
134
132
135
136
139
3.17 3.06 3.30
3.5
3.12
3.42
Electrolyte
Na
mEq/L
3.5-5.5
mEq/L
95-106
Cl
99.7
97.5
102
106
107.2
20
25
24
23
20
22
mEq/L
2.84.9
Phos
90
mEq/L
22-30
CO2
5.2
mEq/dL
Renal Relate
60
61
BUN
7-18 mg/dL
SCr
37
32
34
0.6-1.2
5.71 5.46 5.32 5.1
4.36
4.75
4.5-5.9
3.69 3.41
mg/dL
44
40
40
Hematology
6
RBC
10 /L
12.3-15.3
Hb
9.8
9.2
g/dL
36.0-45.0
Hct
29.5 27.6
Patient Data Record Form
Date
19
20
21
22
23
180
170
160
160
160
90
90
90
90
90
Intake
1500
3800
Output
2900
2200
Systoli
24
25
26
170 180
170
BP
Diastol
80
90
90
ic
Order for Continue
Drug/Dosage regimen
CaCO3 1.25 g
Administratio 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 2
n
1*1 O pc
A:
61
62
Chronic renal failure
,
BUN Cr proteinuria
Creatinin clearance CockcrofGault equation ClCr = 20.6 ml/min Stage 4
hyperphosphatemia
hyperphosphatemia
Ca correct = (4-Alb)*0.8+Ca= (4-3.4)*0.8+ 9.1
Ca*Phos
= 9.58*5.2
= 9.58 mEq/L
= 49.81
KDOQI guideline CaCO3
phosphate binder
0.5-1.5 g (Max 3 g ) tid with meal
phosphate
1.25 g/day
Metabolic acidosis Anion gap =
125 -( 90+20)= 10 mmol/L NaHCO3 HCO3
-
deficit = 0.5 x BW(kg) x ((HCO3 desired) - ( HCO3 measured))
= 0.5(106)(22-20)=106 mEq
-
CO2 22 mEq/L HCO3 106 mEq
-
53 mEq HCO3
300 mg HCO3 3.6 mEq
Sodamint 4x3 O pc bicarbonate
HCO2
62
63
P :
Therapeutic plan :
Sodamint 4x3 O pc
Caco3 1*1 Opc
Goal :
PO4 2.84.9 mEq/dL
CO2 22-30 mEq/L
Therapeutic monitoring :
- CO2
- PO4
-
2
ADRs
monitoring :
CaCO3
PO4, Calcium, Constipation, stomach cramps, nausea,
NaHCO3
vomiting,
HCO3 , metabolic alkalosis, pulmonary edema
Patient education :
-
-
1 g/day
- 8 /
63
64
30 3 /
Future plan :
- electrolyte (HCO3 )
1. Wells BG, DiPiro JT, Schinghmmer TL and Hamilton
th
CW. Pharmacotherapy Handbook. 6 ed. Mc Graw Hill ;
2006.
2. . . 7.
. ; 2548.
3. Tatro DS. Drug interaction facts 2007. Wolters Kluwer;
2007.
4. David NG, Robert CM, George ME, et al. The Sanford
th
guideline to antimicrobial therapy 2009. 39 ed.
Sperryville: antimicrobial therapy; 2006.
5. Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Longo DL, Braunwald E, Hauser
SL, and Jameson JL. Harisons Principles of Internal
th
Medicine. 16 ed. Mc Graw Hill; 2005
6. Lacy CF, Armstrong LL, Goldman MP, Lance LL. Drug
th
Information Handbook. 17 ed. Lexi-Comp; 2009.
7. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on
Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High
Blood Pressure. JAMA 2003;289:256071.
64
65
65
66
Cost effectiveness of COX 2 selective inhibitors and
traditional NSAIDs alone or in combination with a
proton pump inhibitor for people with osteoarthritis.
Objective: cyclooxygenase-2 (COX 2)
selective inhibitors traditional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory
drugs (NSAIDs) proton pump inhibitor
osteoarthritis
Design : Markov model
Systematic review.
RCT 3
Observational
Western Ontario and McMaster
Universities (WOMAC) osteoarthritis index score ( meta- analysis)
osteoarthritis Subgroup analyses
Comparator : COX 2 selective inhibitors (celecoxib etoricoxib)
traditional NSAIDs (diclofenac, ibuprofen, and naproxen)
Paracetamol proton pump inhibitor (omeprazole)
66
67
Main outcome measures : cost - efectiveness quality adjusted
life years gained Quality adjusted life year scores
efficacy
major adverse events (dyspepsia; symptomatic ulcer;
complicated gastrointestinal perforation, ulcer, bleed; myocardial
infarction; stroke; and heart failure)
Results : proton pump inhibitor COX 2 selective
inhibitors traditional NSAIDs cost efective (incremental
cost efectiveness ratio 1000 (1175, $1650).
PPI
(incremental cost efectiveness ratio 10 000)
COX 2 selective inhibitor traditional NSAID
Conclusion: proton pump inhibitor Osteoartitis
traditional NSAID COX 2 selective inhibitor
Cost-efective
traditional NSAID COX 2 selective inhibitor
67
68
Introduction
osteoarthritis Traditional
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
cyclo-
oxygenase-2 (COX 2) selective inhibitors.
osteoarthritis United kingdom NSAID
COX 2 selective inhibitor.
2007 COX 2
selective agents traditional NSAIDs COX2 selective
Inhibitors celecoxib and etoricoxib
5.8% NSAIDs 20%
traditional
NSAIDs
COX 2 selective inhibitors
traditional NSAIDs
gastrointestinal side efects COX 2 selective Inhibitors
gastrointestinal side efects
cardiovascular safety
National Institute for Health and Clinical
Excellence clinical guidance for the management of osteoarthritis
cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX 2) selective inhibitors
osteoarthritis rheumatoid arthritis
serious
NSAIDs
gastrointestinal adverse events traditional
guildeline
gastroprotactive cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX 2) selective
inhibitors
National Institute for Health and
Clinical Excellence guidance
adverse events
gastroprotection
68
69
proton pump inhibitor
National Institute for Health
and Clinical Excellence clinical guidance
Traditional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
(NSAIDs)
cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX 2) selective inhibitors
Gastroprotactive Osteoartitis
Methods
- National Institute for
Health and Clinical Excellence clinical guidance
quality adjusted life years
healthcare
payer NHS England Wales.
Comparator
NSAIDs
RCT
RCT
the celecoxib long-term arthritis safety study (CLASS), the
therapeutic arthritis research andgastrointestinal event trial (TARGET)
multinational etoricoxib and diclofenac arthritis longterm
(MEDAL) study CLASS MEDAL rheumatoid
arthtitis
guideline
69
70
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Osteoarthritis
Guideline
osteoarthritis rheumatoid arthritis
arthritis 1
CLASS, TARGET, MEDAL COX
2 selective inhibitors (celecoxib and etoricoxib)
traditional NSAIDs (diclofenac, ibuprofen, and naproxen)
80% ,
, paracetamol proton
pumpinhibitor (omeprazole) NSAIDs
NSAIDs
Model Design
70
71
economic model
Model Design parametors 2, 3, 4
model
gastrointestinal cardiovascular adverse
events Osteoarthritis
71
72
Clinical
dyspepsia; symptomatic ulcer; complicated
gastrointestinal perforation, ulcer, or bleed; myocardial infarction;
stroke; and heart failure
age specific
cardiovascular
gastrointestinal adverse events
Dyspepsia
COX 2 selective inhibitors traditional NSAIDs
PPI
paracetamol
cardiovascular gastrointestinal adverse events
Patient population
55 baseline risks of 21 and 42 per 10 000
person years serious gastrointestinal cardiovascular
72
73
events 65 (relative risks 2.96 and
1.94 for gastrointestinal and cardiovascular events, )
Adverse event
CLASS, TARGET
MEDAL study
traditional
NSAIDs ( )
COX 2 selective inhibitors
dose relate
OA
ADV RCT
ADV RCT
55 2
probabilistic sensitivity analysis
PPI Traditional NSaids Cox 2
Meta analysis trail
Traditional NSaids
Cox 2 ( 2)
73
74
Costs
NHS
( 2) ( 4) GI ADV
Healthcare Resource Group codes and average length
of stay Department of Health reference costs
Unit
cost CVD-ADV GI AVD
the Healthcare Resource Group and average length of
stay reference cost data, National Institute for Health and Clinical
Excellence clinical guideline for hypertension.
British National Formulary
3.5 %
the National Institute for Health and Clinical
Excellence
Quality of life weights
The Western
Ontario and McMaster Universities (WOMAC) osteoarthritis index
Meta-analysis total WOMAC scores
quality of life utility weights
Meta-analysis
traditional Nsaids Coxc2 inhibitor
traditional
Nsaids Coxc2 inhibitor
ADV ( 4 ) traditional Nsaids Coxc2
inhibitor Paracetamol
74
75
short-term (3 ) MI HF
Stroke
traditional Nsaids Coxc2 inhibitor
HF utility score
Health Survey for England
Sensitivity analysis
observational data sensitivity analyses
model. sensitivity analyses 5.
Results
75
76
76
77
1 quality adjusted life years costs
11 3
PPI traditional Nsaids Coxc2 inhibitor
quality adjusted life years cost
(
) PPI Cost 1000 (1175 ,
$1650 ) quality adjusted life years low
risk GI ADV
PPI
Incremental cost 20000 quality adjusted life years
Cost-efective
Cost-efectiveness 6
Celecoxib 200
77
78
mg PPI Incremental cost 1000 quality adjusted
life years low risk high risk
78
79
2 Celecoxib 200 mg PPI
Cost-efectiveness 50 % threshold of
30 000 per quality adjusted life year
Celecoxib 200 mg PPI ibuprofen 1200 mg plus a
proton pump inhibitor incremental cost efectiveness 30
400 21 000 quality adjusted life year gained
55 65
CVD-ADV
CLASS casts celecoxib
etoricoxib
stroke
celecoxib 200 mg 10/10000 MEDAL
study
etoricoxib 30 mg stroke
24/10000
MEDAL study stroke risk cox 2
etoricoxib PPI Cost-efectiveness
Traditional Nsaids
ADV ( 1 2 )
CVD , GI ADV (
65 ) Traditional Nsaids Cost- efective
paracetamol PPI
quality
79
80
adjusted life year
gained OA
Tradional Nsaids ADV ( 1)
Discussion
PPI traditional Nsaids Cox -2 inhibitor low
risk GI- ADV
PPI
Nsaids
cost- efective
PPI RR GI-ADV 0.98
threshold 20000 quality adjusted life year
PPI COX -2 Cost
efective Traditional Nsaids
GI ADV
COX 2
GI ADV
ADR
traditional Nsaid
cox 2 Cost efective
Cox 2
( 65 ) paracetamol
traditional nsaids PPI COX2
low risk traditional nsaids cox2
PPI paracetamol
traditional nsaids cox2
80
81
Cox2
traditional nsaids
GI,
CVD-ADV PPI
traditional nsaids cox2
PPI traditional nsaids
cox2 Cost efective
OA Low risk
CVD COX 2 PPI
OA
CVD COX 2
Cox 2 cox- 2
NSaids
traditional nsaids cost-efective COX 2
OA CVD
RCT
CVD, GI
ADV traditional nsaid cox 2 PPI
81
82
ADV
RCT
PPI hip
fracture
Conclusion
NSAIDs COX 2 OA PPI
Cost efective Cox 2 PPI
AVD
Founding : The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
commissioned and funded this analysis
Competing interests: All authors were members of the National
Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Osteoarthritis Guideline
Development Group
82
83
Ethical approval: Ethical approval was not required for this research
1.
Cost effectiveness of COX 2 selective
inhibitors and traditional NSAIDs alone o
in combination with a proton pump
inhibitor for people with osteoarthritis
2.
Nicholas Latimerg
health economics
Joanne Lord, health economics
Robert
Grant,
senior
technic
adviser,medical statistician
Rachel OMahony, research fellow
John Dickson, community physician
rheumatology
Philip
Conaghan,professor
musculoskeletal medicine
83
84
The National Institu
for
Health
and
Clinical
Excellenc
Osteoarthritis Guideline Development Grou
3.
British
Medical Journal
Impac
factor (2008) : 12.827
4.
cyclooxygenase-2 (COX 2) selective
inhibitors traditional non-steroidal anti
inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
proton pump inhibitor
osteoarthritis
Objectiv
5.
6.
1.
Review
65
55
84
85
2.
3.
4.
RCT
Systematic review
RCT
Review
5.
Cox 2 selective inhibito
Cox 2 selective
inhibitor PPI Cost-
85
86
efective
6. (
)
7.
8.
OA
RCT
CVD, GI ADV
traditional nsaid co
2 selective inhibitor PPI
RCT
86
87
7.
PPI Hip
fracture
8.
ve
9.
NSAIDs
subjecti
10.
PPI NSAIDs
Osteoartritis
11.
( 1- 10
)
87
88
1. Patient care round
08.00-12.00 .
88
89
2. Medication conciliation
3.
4.
5.
6. Warfarin
7.
8. Academic in service
9. Journal club
10.
89
90
1.
2.
3.
90
91
91
You might also like
- เอกสารประกอบการนำเสนอกรณีศึกษา-H pyloriDocument12 pagesเอกสารประกอบการนำเสนอกรณีศึกษา-H pyloriหมวย' คำปู้จู้No ratings yet
- คู่มือการให้ยา warfarin และ IE prophylaxis ในผู้ป่วย CVT 2013 นพ.ธีรพงศ์ โตเจริญโชค และ อ.ธีรวิทย์ พันธุ์ชัยเพชรDocument22 pagesคู่มือการให้ยา warfarin และ IE prophylaxis ในผู้ป่วย CVT 2013 นพ.ธีรพงศ์ โตเจริญโชค และ อ.ธีรวิทย์ พันธุ์ชัยเพชรMantras KomolNo ratings yet
- e Rdu-รพ.โนนสูง ภญ.สุทธินีDocument75 pagese Rdu-รพ.โนนสูง ภญ.สุทธินีSurasit SukseeluangNo ratings yet
- สำเนา ปฏิบัติการ การบำบัดทดแทนไตDocument14 pagesสำเนา ปฏิบัติการ การบำบัดทดแทนไตInThe ZNo ratings yet
- Drug Consideration Information 2554Document41 pagesDrug Consideration Information 2554zedozedoNo ratings yet
- Soap TBDocument12 pagesSoap TBวิภาวนันท์ จรลีNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document6 pagesModule 3nattayadaNo ratings yet
- เคสคอน Gen3 แก้อยู่จ้าDocument41 pagesเคสคอน Gen3 แก้อยู่จ้านางสาวพิชชาพร แก่นเมืองNo ratings yet
- บทบาทของรังสีรักษาและเคมีบ าบัดใน RhabdomyosarcomaDocument12 pagesบทบาทของรังสีรักษาและเคมีบ าบัดใน RhabdomyosarcomakarnjNo ratings yet
- MCQ 1-2555 Day 2Document26 pagesMCQ 1-2555 Day 2Covermark Thailand60% (5)
- Soap DisDocument13 pagesSoap Dissukrita26No ratings yet
- รายงานตอบคำถาม 2Document15 pagesรายงานตอบคำถาม 2Nathakorn RodklongtanNo ratings yet
- แนวทางการให้ long acting antiboby (LAAB) ปรับปรุงครั้งที่ 2Document17 pagesแนวทางการให้ long acting antiboby (LAAB) ปรับปรุงครั้งที่ 2ArkaNay PraPanNo ratings yet
- MCQ 2557 PsuDocument28 pagesMCQ 2557 PsuNitiwut Meenun100% (2)
- คู่มือแพทย์เวร PDFDocument24 pagesคู่มือแพทย์เวร PDFTanawat Singboon67% (3)
- CPG PedDocument53 pagesCPG PedMc Chayapon100% (1)
- 006-07-2566 บทความ TDF TriggerDocument11 pages006-07-2566 บทความ TDF TriggerNattapat SuksriNo ratings yet
- Guideline TB 2018Document38 pagesGuideline TB 2018Dhanu GaysonsiriNo ratings yet
- Soap 2Document11 pagesSoap 2fine198775% (4)
- แนวปฏิบัติการใช้ยา EnoxaparinDocument7 pagesแนวปฏิบัติการใช้ยา Enoxaparinsupanee kittitanyaponNo ratings yet
- Complicated Cystitis EditDocument13 pagesComplicated Cystitis EditBeau PhatruetaiNo ratings yet
- UGIBDocument7 pagesUGIBBambi NatchaNo ratings yet
- tci admin,+ ($userGroup) ,+5+คุณจันทนา+ม่วงทอง+รพ.สิงห์บุรีDocument8 pagestci admin,+ ($userGroup) ,+5+คุณจันทนา+ม่วงทอง+รพ.สิงห์บุรีWann JinjerNo ratings yet
- การบริหารจัดการยาฉุกเฉินและยาที่ให้ทันทDocument7 pagesการบริหารจัดการยาฉุกเฉินและยาที่ให้ทันทkandawasri.chaNo ratings yet
- Mon9May2011103358PM - SOAP - OPD - Warfarin OverdoseDocument6 pagesMon9May2011103358PM - SOAP - OPD - Warfarin OverdoseBeau PhatruetaiNo ratings yet
- ไอโซโทปรังสีทางการแพทย์Document17 pagesไอโซโทปรังสีทางการแพทย์Darin BrownNo ratings yet
- แนวทางการดูแลรักษาผู้ป่วย ภาวะเลือดออกในทางเดินอาหารส่วนต้นในประเทศไทย 2557Document13 pagesแนวทางการดูแลรักษาผู้ป่วย ภาวะเลือดออกในทางเดินอาหารส่วนต้นในประเทศไทย 2557เด็กชายสมันตภัทร แฟนคลับอาจารย์กวง100% (1)
- Holistic Approach For Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument20 pagesHolistic Approach For Acute Coronary SyndromeMim Yoo-UmNo ratings yet
- DengeDocument33 pagesDengeStafarneNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Examination Osce SI PDFDocument26 pagesComprehensive Examination Osce SI PDFAbdullahKhan100% (3)
- kdj, Journal manager, 10 ยาต้านเกล็ดเลือดฯDocument16 pageskdj, Journal manager, 10 ยาต้านเกล็ดเลือดฯSetta LeeNo ratings yet
- MCQ1-56 Psu PDFDocument16 pagesMCQ1-56 Psu PDFMimasenke Pyokon100% (1)
- รายงานตอบคำถาม 1Document14 pagesรายงานตอบคำถาม 1Nathakorn RodklongtanNo ratings yet
- TB Case Conference 12-3-64 FinishDocument31 pagesTB Case Conference 12-3-64 FinishMilky Milky WayNo ratings yet
- 260563Document48 pages260563Sari SiriNo ratings yet
- รวมข้อสอบ MCQ ใบประกอบวิชาชีพเภสัชกรรมDocument29 pagesรวมข้อสอบ MCQ ใบประกอบวิชาชีพเภสัชกรรมCheNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2567-03-21 at 14.33.57Document168 pagesScreenshot 2567-03-21 at 14.33.57TeeradetNo ratings yet
- แนวทางการใช้ยาในผู้ป่วยโรค NCD สำหรับโรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบล-2561Document37 pagesแนวทางการใช้ยาในผู้ป่วยโรค NCD สำหรับโรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบล-2561ArkaNay PraPanNo ratings yet
- แนวทางเวชปฏิบัติกรณีสมองบาดเจ็บ 2556Document46 pagesแนวทางเวชปฏิบัติกรณีสมองบาดเจ็บ 2556เด็กชายสมันตภัทร แฟนคลับอาจารย์กวง100% (1)
- กระบวนการคัดกรอง - Ttiage - MOPHEDTRIAGEDocument24 pagesกระบวนการคัดกรอง - Ttiage - MOPHEDTRIAGEiwongpiaNo ratings yet
- การใช้ยาVancomycinDocument11 pagesการใช้ยาVancomycinPépé TechopathamNo ratings yet
- Exam 2005Document35 pagesExam 2005priscillaNo ratings yet
- แนวทางการรักษาโรคหืดหรับผู้ใหญ่ในประเทศไทย 2565Document30 pagesแนวทางการรักษาโรคหืดหรับผู้ใหญ่ในประเทศไทย 2565เด็กชายสมันตภัทร แฟนคลับอาจารย์กวงNo ratings yet
- 1.J2 User 22092565Document41 pages1.J2 User 22092565papergirl.ptjNo ratings yet
- MCQ-2558 Part 2Document14 pagesMCQ-2558 Part 2Nitiwut Meenun100% (3)
- Covid VaccineDocument5 pagesCovid VaccineEkkapap UnityNo ratings yet
- Antidote Book3-15 Example7Document5 pagesAntidote Book3-15 Example7박열린parkyeolrinNo ratings yet
- ยาเคมีบำบัดสูตร r ChopDocument1 pageยาเคมีบำบัดสูตร r Chop1-สรชัช พรมดวงNo ratings yet
- weerayutmskh, ($userGroup), 13ปรมาภรณ์ คลังพระศรีDocument12 pagesweerayutmskh, ($userGroup), 13ปรมาภรณ์ คลังพระศรีThitipong NonnoiNo ratings yet
- คู่มือเวชปฏิบัติ บำบัดบุหรี่Document154 pagesคู่มือเวชปฏิบัติ บำบัดบุหรี่bangbon drugstoreNo ratings yet
- Fluid OverloadDocument9 pagesFluid OverloadMai PorungNo ratings yet
- ฝังเข็มโรคหลอดเลือดสมองDocument66 pagesฝังเข็มโรคหลอดเลือดสมองพิริยะพฤนท์ นาคพันธุ์โยนกNo ratings yet
- 20 - จุฑารัตน์ คำกาศ patient profileDocument4 pages20 - จุฑารัตน์ คำกาศ patient profileTiNTiNNo ratings yet
- CE2015 NU Ans PDFDocument303 pagesCE2015 NU Ans PDFIcekung KasamepongtongdeeNo ratings yet
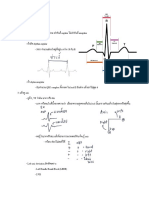
- Ekg PDFDocument5 pagesEkg PDFKiddyRx LoukkadeNo ratings yet
- 31 Practical Point PDFDocument18 pages31 Practical Point PDFKiddyRx LoukkadeNo ratings yet
- Adult Vaccine Recommendation RCPT Final Version PDFDocument9 pagesAdult Vaccine Recommendation RCPT Final Version PDFKiddyRx LoukkadeNo ratings yet
- Melli Oidos IsDocument9 pagesMelli Oidos IsKiddyRx LoukkadeNo ratings yet
- Lesson10 Acid Base1 2c68Document37 pagesLesson10 Acid Base1 2c68KiddyRx LoukkadeNo ratings yet
- 01Ch210 Volumetry2554 STDocument15 pages01Ch210 Volumetry2554 STKiddyRx LoukkadeNo ratings yet
- Acids BasesDocument82 pagesAcids BasesKiddyRx Loukkade100% (1)