Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heat Exchange
Heat Exchange
Uploaded by
praveenCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Heat Exchange
Heat Exchange
Uploaded by
praveenCopyright:
Available Formats
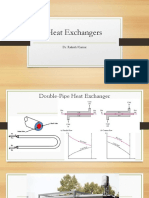
Heat Exchangers
Chapter 18
ChEN 4253
Terry A. Ring
Flo !atterns
"
!arallel Flo
"
Co#nter C#rrent Flo
"
$hell an% T#&e ith &a''les
"
Cross Flo
Te(perat#re !ro'iles
)T * Approach Te(perat#re
Heat
Exchanger
Te(perat#re
!ro'iles
Flo $tr#ct#re
+*, A F )T
l(-co#nter
( )
( )
( )
( )
in cold in hot
in cold out cold
in cold out cold
out hot in hot
T T
T T
S
T T
T T
R
R R S
R R S
R
RS
S
R
F
1
1
]
1
+ + +
+ +
1
]
1
1 1 2
1 1 2
ln 1
1
1
ln 1
2
2
2
./erall Heat Trans'er Coe''icient
"
$eries o' Resistances
"
0asis
1
2nsi%e
1
.#tsi%e
( ) ( ) [ ] ( )
1
3 3
1 4 ln5 2 1 4 1 5
1
]
1
+ + + +
o f o i o o w i i o
i
o
i f o
R h D D D k h D D
A
A
R U
2nsi%e
T#&es
R
'
*'o#ling 'actors3 insi%e an% o#tsi%e
$ee ta&le 18.5 'or range o' , /al#es 'or %i''erent cases.
Heat Trans'er insi%e a t#&e
T#r&#lent 666 3 16 Re
766 3 18 !r 7 . 6
e s(ooth t#& 3 86 9
!r Re 627 . 6
14 . 6
3 9 1 8 . 6
>
< <
>
,
_
f
p
w
b
f
k
C
D L
k
hD
Nu
Also other correlations /ali% o/er i%er ranges
Heat Trans'er o#tsi%e o' T#&e
666 3 166 Re 46
366 !r 87 . 6
2 . 5 25 . 6
!r 4 Re 68 . 6 Re 4 . 6 5
25 . 6
4 . 6 3 9 2 5 . 6
< <
< <
< <
,
_
+
f
p
w
b
w
b
f
k
C
k
hD
Nu
Also other correlations /ali% o/er i%er ranges
Ther(al Con%#cti/ity
:hat Te(perat#re Approach
"
He#ristic 28.
1
Near-opti(al (ini(#( te(perat#re approaches
in heat exchangers %epen% on the te(perat#re
le/el as 'ollos;
1
16<F or less 'or te(perat#res &elo a(&ient3
1
26<F 'or te(perat#res at or a&o/e a(&ient #p to 366<F3
1
56<F 'or high te(perat#res3
1
256 to 356<F in a '#rnace 'or 'l#e gas te(perat#re a&o/e
inlet process 'l#i% te(perat#re.
:here are the Heat Exchangers=
:hat is happening in each
.ctane Reaction
2C
2
H
4
> C
4
H
16
C
8
H
18
!* 26 psia3 T*?3C3
@*?8A Con/ersion
T
0!
C
2
H
4
B163.7 <C
C
4
H
16
>6.5 <C
C
8
H
18
>125.52 <C
:here are the Heat Exchangers=
Heat Trans'er :ith !hase Change
"
TricCy !ro&le(s
1
Exa(ples
"
Re&oiler on Distillation ,nit
"
Con%enser on Distillation ,nit
"
Flash ,nits
"
0oilers
A :or% A&o#t $tea(
"
$i(#lator Ass#(ptions
1
2nlet 1 $at#rate% Eapor
1
!ress#re
1
166A Eapor
1
.#tlet 1 $at#rate% FiG#i%
"
FiG#i% .nly Fea/es /ia stea( trap
1 !ress#re * !
in
- )! 51.5 psi3 He#ristic-314
1
166A FiG#i%
:here are the TricCy
Heat Exchangers=
Con%ensation Heat Trans'er
"
Drop :ise Con%ensation
1
$pecial Case
"
Eery High Heat Trans'er
"
5 to 16 x Fil( Con%ensation
"
Fil( Con%ensation
1
Fa(inar
4 9 1
3
4 5 4
4 5
1
1
]
1
x T T
k H g
k
x h
Nu
w v l
l vap v l l
l
x
x
Fa(inar to T#r&#lent Con%ensate
Flo
0oiling Heat Trans'er Coe''icient
Eario#s correlations %epen%ing #pon &oiling (echanis(
Highest Heat
Trans'er Coe'.
0#t har% to
control H@
operating here
He#ristic 28
"
0oil a p#re liG#i% or close-&oiling liG#i%
(ixt#re in a separate heat exchanger3 #sing
a (axi(#( o/erall te(perat#re %ri/ing
'orce o' 45 F to ens#re n#cleate &oiling an%
a/oi% #n%esira&le 5lo h4 'il( &oiling.
E''ecti/e
Flo
Con%itions
ith
0oiling in
Ther(o
siphon
Hettle 5Re40oiler Design
Aspen - Ione Analysis
!roJax 1 Heat Release 2ncre(ents
"
He#ristic 2?.
1
:hen cooling an% con%ensing a strea( in a heat exchanger3 a Kone
analysis3 %escri&e% in $ection 18.13 sho#l% &e (a%e to (aCe s#re
that the te(perat#re %i''erence &eteen the hot strea( an% the
col% strea( is eG#al to or greater than the (ini(#( approach
te(perat#re at all locations in the heat exchanger. The Kone
analysis is per'or(e% &y %i/i%ing the heat exchanger into a
n#(&er o' seg(ents an% applying an energy &alance to each
seg(ent to %eter(ine correspon%ing strea( inlet an% o#tlet
te(perat#res 'or the seg(ent3 taCing into acco#nt any phase
change. A process si(#lation progra( con/eniently acco(plishes
the Kone analysis.
!ress#re Drop
L Flo Rate
"
Fa(inar /s. T#r&#lent
1
He#ristic 31.
"
Esti(ate heat-exchanger press#re %rops as 'ollos;
1
1.5 psi 'or &oiling an% con%ensing3
1
3 psi 'or a gas3
1
5 psi 'or a lo-/iscosity liG#i%3
1
7-? psi 'or a high-/iscosity liG#i%3
1
26 psi 'or a process 'l#i% passing thro#gh a '#rnace.
Controlling )! in $i(#lator
"
$hell si%e
1
NoKKle %ia(eter
"
2nlet an% .#tlet
1
N#(&er o' 0a''les
1
T#&es
"
N#(&er3 %ia(eter3 pitch3 No. passes
"
T#&e si%e
1
NoKKle %ia(eter
"
2nlet an% .#tlet
1
T#&es
"
N#(&er3 %ia(eter3 pitch3 No. passes
Note interactionsM
$hell Hea%s3 $hell Type
"
$ee !roJax Help9in%ex N$hell3 typesO
H@ Cost
"
$iKe Factor H@ Area
" C
0ase58-26664
*expP11.6545-6.?228Qln5A4>6.6?881Qln5A4
2
R
"
!#rchase !rice
1 C
!-'o&
*F
P
5!4QF
Material
5A4QF
L
5F4QC
0ase
Q5C!293?44
1 C
0J
*F
0J
QC
!-'o&
1 C
0J
*3.17QC
!-'o&
"
Cost %epen%s on H@ Area
"
!#(ping Cost
1
:orC * +Q)!
Controlling A in $i(#lator
" A * N
t#&es
S D
t#&es
F
t#&es
"
$hell
1 $hell Dia(eter an% pitch %eter(ines N
t#&es
"
T#&es
1 D
t#&es
1 F
t#&es
1
T#&e pitch-The trans/erse pitch is the shortest %istance 'ro(
the center lines o' to a%Tacent t#&es.
1
T#&e pitch ratio 1.25 to 1.5 typically
Controlling , in a $i(#lator
"
For a gi/en heat %#ty an% geo(etry - , %eter(ines the H@
area
"
$teps
1
2%enti'y the controlling heat trans'er resistance
1 h
o
-Janip#late the shell si%e Reynol%s n#(&er
" $hell %ia(eter
"
T#&e pitch
"
N#(&er o' &a''les
1 h
i
-Janip#late the t#&e si%e Reynol%s n#(&er
" T#&e %ia(eter
" N#(&er o' t#&es 5shell %ia(eter an% t#&e pitch4
" N#(&er o' passes
1
2' o%% things happen checC to see that yo# ha/e the sa(e controlling heat
trans'er resistance
Note interactionsM
.ther 2ss#es
Materials of Construction
Strength at temperature, life time, heat
conduction, fouling
Design layout
Tube pitch, baffles, tube and shell diameters
Heat Exchanger
!ro&le(s
"
Te(perat#res Cross Each
.ther
1
Non-'#nctioning Exchanger
1
To sol/e increase approach )T
"
Con%ensation9E/aporation
1
Heat trans'er ith (#ltiple
heat trans'er coe''icients in a
single apparat#s
"
Eario#s regi(es o' &oiling
"
Eario#s regi(es o' con%ensation
You might also like
- Continuously Variable Transmission India PDFDocument20 pagesContinuously Variable Transmission India PDFswapnil pandeNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Heating, Ventilating and Air ConditioningFrom EverandHandbook of Heating, Ventilating and Air ConditioningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Structure Design of Foundation of Light Pole IS 875Document8 pagesStructure Design of Foundation of Light Pole IS 875YashwantRajVermaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Shell Tube Heat ExchangerDocument138 pagesChapter 7 Shell Tube Heat ExchangerPHƯƠNG ĐẶNG YẾNNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger For StudentsDocument71 pagesHeat Exchanger For StudentsYasaswi NathNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangersDocument36 pagesHeat ExchangersSyukri ShahNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangersDocument71 pagesHeat Exchangersvenkeeku100% (2)
- Heat Exchanger DesignDocument28 pagesHeat Exchanger DesignHussein AyoubNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger DesignDocument27 pagesHeat Exchanger DesignTri Vicca WibisonoNo ratings yet
- Faculty Development Programme On Recent Trends in Thermo-Fluids Engineering (RTTFE 2018)Document42 pagesFaculty Development Programme On Recent Trends in Thermo-Fluids Engineering (RTTFE 2018)Minhaz SixNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger - LD7Document49 pagesHeat Exchanger - LD7Văn Bão TôNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-1 - Heat Exchanger CalculationsDocument50 pagesLecture 3-1 - Heat Exchanger CalculationsBilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Continuously Variable Transmission: LD College of EngeneeringDocument16 pagesContinuously Variable Transmission: LD College of Engeneeringswapnil pandeNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangersDocument77 pagesHeat ExchangersMervin PerezNo ratings yet
- HX Rules of ThumbDocument41 pagesHX Rules of ThumbWeston Light100% (1)
- Iso 14175Document12 pagesIso 14175Juan Carlos100% (3)
- Undergraduate First Year Practicals ManualDocument39 pagesUndergraduate First Year Practicals ManualVytheeshwaran Vedagiri97% (31)
- Section 09 - Heat Transfer & ExchangersDocument54 pagesSection 09 - Heat Transfer & Exchangershwang2No ratings yet
- EOSDocument7 pagesEOShobidjidjiNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Heat TransferDocument31 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Heat TransferarulmuruguNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangersDocument30 pagesHeat Exchangerstakis.papadopoulos6672No ratings yet
- Basics of Heat-Exchangers Design by N. SinagaDocument81 pagesBasics of Heat-Exchangers Design by N. SinagaİBRAHİM HAZAR AYTULUNNo ratings yet
- S Announcement 20872 PDFDocument90 pagesS Announcement 20872 PDFHey YoNo ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Exchanger YuanDocument37 pagesShell and Tube Exchanger YuanVerdianto Indra WNo ratings yet
- Drop Through The Exchanger, Which Can Result in HigherDocument6 pagesDrop Through The Exchanger, Which Can Result in HigherSajid nazir mirNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger: 5.1: Types of Heat ExchangersDocument34 pagesHeat Exchanger: 5.1: Types of Heat Exchangersamirul ashrafNo ratings yet
- Thermosyphons and Heat PipeDocument14 pagesThermosyphons and Heat PipespurwonofjpNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Heat Exchangers: The Basics of Heat Transfer What Are Exchangers For? Main Heat Exchanger TypesDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Heat Exchangers: The Basics of Heat Transfer What Are Exchangers For? Main Heat Exchanger Typesl kishoreNo ratings yet
- 3 Alat Penukar Kalor LMTD Ntu Fouling FDocument31 pages3 Alat Penukar Kalor LMTD Ntu Fouling FrezaafadhilNo ratings yet
- University of Tennessee - ChattanoogaDocument49 pagesUniversity of Tennessee - ChattanoogaMALIK ZARYABBABARNo ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers: Prajitno© 1Document46 pagesShell and Tube Heat Exchangers: Prajitno© 1Aryo Arief Adhitomo SaifudinNo ratings yet
- Inbound 532829914Document64 pagesInbound 532829914angellene.lucky18No ratings yet
- hmt21 - ID - CHP - 11a - Heat Exchangers (LMTD)Document41 pageshmt21 - ID - CHP - 11a - Heat Exchangers (LMTD)KaanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: EctureDocument20 pagesHeat Transfer: EctureaymaNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Design - Part 2Document15 pagesHeat Exchanger Design - Part 2Siddhant SoymonNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchangers PDFDocument44 pagesHeat Exchangers PDFRajeevNo ratings yet
- TMES - Part4 - Heat PipesDocument30 pagesTMES - Part4 - Heat Pipesm sriNo ratings yet
- Lowest Shell Side Thermal Resistance !!!: Design of Condensers/Condensing ZonesDocument42 pagesLowest Shell Side Thermal Resistance !!!: Design of Condensers/Condensing ZonesMargarida PedroNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Chapter 11Document12 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Chapter 11yogesh shindeNo ratings yet
- Air-Preheater For Conservation of Flue Gas EnergyDocument31 pagesAir-Preheater For Conservation of Flue Gas EnergyIntelligence News BureauNo ratings yet
- LECTURE - 15 - CDB 3044 - Equipment Design - Heat ExchangersDocument39 pagesLECTURE - 15 - CDB 3044 - Equipment Design - Heat ExchangersOng Jia YeeNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer and Heat ExchangersDocument39 pagesHeat Transfer and Heat ExchangersPradeepNo ratings yet
- EconomiserDocument15 pagesEconomiserjadgugNo ratings yet
- 15-Chapitre - 10-Heat ExchangersDocument25 pages15-Chapitre - 10-Heat ExchangersTaki Goumri100% (1)
- HEAT ExchangersDocument27 pagesHEAT ExchangersBeatriceNo ratings yet
- HW # 6 /tutorial # 6 WWWR Chapters 21 & 22 ID Chapters 10 & 11Document48 pagesHW # 6 /tutorial # 6 WWWR Chapters 21 & 22 ID Chapters 10 & 11arfpowerNo ratings yet
- Finger Tips For Heat Transfer PDFDocument1 pageFinger Tips For Heat Transfer PDFyogi4yogeshNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document22 pagesLecture 1sivagrnthnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document28 pagesLecture 5Mesbahose SalekeenNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Chapter 11 SummaryDocument8 pagesHeat Transfer Chapter 11 SummaryJeremiah ValeraNo ratings yet
- CB307 - 11 Sep - CondensersDocument18 pagesCB307 - 11 Sep - CondensersKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Heat TransferDocument21 pagesChapter 11 Heat TransferaimanrslnNo ratings yet
- Boiling - CondensationDocument48 pagesBoiling - CondensationAtif AhmedNo ratings yet
- ConvectionDocument26 pagesConvectionDozdiNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Condensation and Boiling-10.04Document42 pagesCH 9 Condensation and Boiling-10.04Deeptank KumarNo ratings yet
- 8 3 Packed Bed ReactorsDocument20 pages8 3 Packed Bed ReactorsridhajamelNo ratings yet
- ME421 Heat Exchanger and Steam Generator Design: Lecture Notes 6 Double-Pipe Heat ExchangersDocument19 pagesME421 Heat Exchanger and Steam Generator Design: Lecture Notes 6 Double-Pipe Heat ExchangersMeravigliorso76No ratings yet
- One Dimensional Steady Heat Conduction Problems: Simple Ideas For Complex ProblemsDocument23 pagesOne Dimensional Steady Heat Conduction Problems: Simple Ideas For Complex ProblemsKai MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Material 2Document82 pagesMaterial 2SS TarunNo ratings yet
- Intercambiadores de CalorDocument42 pagesIntercambiadores de CalorDANIEL MAURICIO VANEGAS ZUNIGANo ratings yet
- Basicdesignmethodsof HE1Document50 pagesBasicdesignmethodsof HE1Manas ChuriNo ratings yet
- 13 L1 L2 Reactor DesignDocument48 pages13 L1 L2 Reactor DesignalfinNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Heat ExchangersDocument37 pagesTopic 4 Heat Exchangersar1001876No ratings yet
- Metal RodDocument65 pagesMetal RodVidhya NairNo ratings yet
- Virtual Interview Guide - Candidates - TE Connectivity India PVT LTDDocument1 pageVirtual Interview Guide - Candidates - TE Connectivity India PVT LTDswapnil pandeNo ratings yet
- Design & Development of C Arm X Ray SystemDocument5 pagesDesign & Development of C Arm X Ray Systemswapnil pandeNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Complex 3D Tolerance Stacks: Francesco Leali, Francesco Gherardini, Cristina Renzi, Davide PanariDocument25 pagesDesign and Analysis of Complex 3D Tolerance Stacks: Francesco Leali, Francesco Gherardini, Cristina Renzi, Davide Panariswapnil pandeNo ratings yet
- Study of Reliability Analysis of CVT SystemDocument11 pagesStudy of Reliability Analysis of CVT Systemswapnil pandeNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis of FMEA: March 2009Document9 pagesFailure Analysis of FMEA: March 2009swapnil pandeNo ratings yet
- (2016) GE Jet Engine Bracket Challenge: A Case Study in Sustainable DesignDocument14 pages(2016) GE Jet Engine Bracket Challenge: A Case Study in Sustainable Designswapnil pandeNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of A Low Cost SCR System For NO Reduction in A Diesel EngineDocument4 pagesDesign and Development of A Low Cost SCR System For NO Reduction in A Diesel Engineswapnil pandeNo ratings yet
- Study of Reliability Analysis of CVT SystemDocument13 pagesStudy of Reliability Analysis of CVT Systemswapnil pandeNo ratings yet
- Schaeffler Kolloquium CVT PDFDocument7 pagesSchaeffler Kolloquium CVT PDFswapnil pandeNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ClutchesDocument54 pagesUnit 3 Clutchesswapnil pandeNo ratings yet
- Separating Springs For Active Separation of The Friction Plates in Wet Clutch SystemsDocument11 pagesSeparating Springs For Active Separation of The Friction Plates in Wet Clutch Systemsswapnil pandeNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Process Parameters For Plasma Arc Welding of Austenitic Stainless Steel (304 L) With Low Carbon Steel (A-36)Document15 pagesOptimization of Process Parameters For Plasma Arc Welding of Austenitic Stainless Steel (304 L) With Low Carbon Steel (A-36)swapnil pandeNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Process Parameters For Plasma Arc Welding of Austenitic Stainless Steel (304 L) With Low Carbon Steel (A-36)Document15 pagesOptimization of Process Parameters For Plasma Arc Welding of Austenitic Stainless Steel (304 L) With Low Carbon Steel (A-36)swapnil pandeNo ratings yet
- Unit2 2 180616044304Document41 pagesUnit2 2 180616044304swapnil pandeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet5Document5 pagesTutorial Sheet5Lê Anh QuangNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Cycle: Jessica Harwood Douglas Wilkin, PH.DDocument6 pagesThe Carbon Cycle: Jessica Harwood Douglas Wilkin, PH.DSalvador Vizcarra RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Waves PDFDocument11 pagesWaves PDFRaj RK0% (1)
- Simulating Environment With Winogradsky Report 2Document3 pagesSimulating Environment With Winogradsky Report 2Kai ChenNo ratings yet
- A93a00782aus Hba1c WB CalDocument2 pagesA93a00782aus Hba1c WB CalRuliandiNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project Query: Compiled by Moosa Naseer & Assisted by TeamDocument2 pagesFinal Year Project Query: Compiled by Moosa Naseer & Assisted by TeamMoosa NaseerNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: I. Chemistry, Mineralogy and Geochemistry of GoldDocument80 pagesGeneral Chemistry: I. Chemistry, Mineralogy and Geochemistry of GoldHAMZA LAMSALAHNo ratings yet
- Tabelul Periodic - Google SearchDocument1 pageTabelul Periodic - Google SearchMariaNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument15 pagesZener DiodeEEE M.AASTHIKANo ratings yet
- D2D SyllabusDocument2 pagesD2D SyllabusokNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project - ConductivityDocument21 pagesChemistry Project - ConductivityVaibhav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document5 pagesCH 1SOHAIB ZAFARNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Test 2Document5 pagesGrade 8 Test 2dowanahamidNo ratings yet
- Experiment 05Document4 pagesExperiment 05Aayan ShahNo ratings yet
- 10+2 Assignment-3 - Electrochemistry - ChemistryDocument8 pages10+2 Assignment-3 - Electrochemistry - ChemistrySarthak KawatraNo ratings yet
- Baryons TableDocument2 pagesBaryons TableGopinathan MNo ratings yet
- Scientific RevolutionDocument60 pagesScientific RevolutionCARLO CORNEJONo ratings yet
- 8.2 Aerodynamics 8.2.1: Airflow Around A BodyDocument6 pages8.2 Aerodynamics 8.2.1: Airflow Around A BodyNayem Hashan NayemNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Breadboard and Ohms LawDocument6 pagesLab 3 Breadboard and Ohms LawRasul Amirov100% (1)
- Combustion Behavior of Lithium Iron Phosphat - 2017 - Journal of Loss PreventionDocument9 pagesCombustion Behavior of Lithium Iron Phosphat - 2017 - Journal of Loss PreventionPysdellNo ratings yet
- Autotrophic NutritionDocument22 pagesAutotrophic NutritionBWAMBALE HARISONNo ratings yet
- Experiment #2 Specific Gravity & Absorption of Fine and Coarse AggregatesDocument4 pagesExperiment #2 Specific Gravity & Absorption of Fine and Coarse AggregatesChristelle Kharrat100% (1)
- Numerical Flow Analysis of An Axial Flow PumpDocument6 pagesNumerical Flow Analysis of An Axial Flow Pumpbinho58No ratings yet
- WWW - PVD Coatings - Co.uk Theory of PVD Coatings MagnetronDocument3 pagesWWW - PVD Coatings - Co.uk Theory of PVD Coatings MagnetronFrank WilliamNo ratings yet
- Measuring Renilla Luciferase Luminescence in Living CellsDocument5 pagesMeasuring Renilla Luciferase Luminescence in Living CellsMoritz ListNo ratings yet
- Alkoholi: OH C C OH OH CDocument53 pagesAlkoholi: OH C C OH OH CElvir MNo ratings yet