Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem 4.8: Solution: (A)
Problem 4.8: Solution: (A)
Uploaded by
nosferatu123456Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem 4.8: Solution: (A)
Problem 4.8: Solution: (A)
Uploaded by
nosferatu123456Copyright:
Available Formats
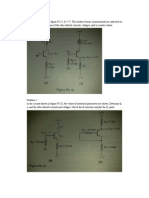
Problem 4.8 The op-amp circuit shown in Fig. P4.
8 has a constant dc voltage of
6 V at the noninverting input. The inverting input is the sum of two voltage sources,
a 6-V dc source and a small time-varying signal
s
.
(a) Use the op-amp equivalent-circuit model given in Fig. 4-5 to develop an
expression for
o
.
(b) Simplify the expression by applying the ideal op-amp model, which lets A
, R
i
and R
o
0.
R
L
s
6 V
6 V
+
_
+
_
+
_
+
_
Figure P4.8: Circuit for Problem 4.8.
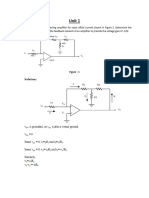
Solution: (a) Replacing the op amp with its equivalent circuit:
R
L
R
o
R
i
s
+
_
+
_
6 V
+
_
6 V
+
_
+
_
+
_
+
_
A(
p
n
)
For node
o
,
o
R
L
+
o
A(
p
n
)
R
o
= 0.
Also,
p
= 6 V,
n
= 6 V+
s
.
Solving for
o
, we have:
o
=
A
s
R
L
R
L
+R
o
.
(b) For R
L
R
o
,
o
=A
s
.
All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. c 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Hence, the output will be amplied by A, but inverted. If |A
s
| V
cc
, then the op
amp will saturate. Hence,
o
=
A
s
, for |
s
|
V
cc
A
V
cc
, if |
s
| >
V
cc
A
and
s
is positive
+V
cc
, if |
s
| >
V
cc
A
and
s
is negative.
Assume all op amps to be ideal from here on forward.
All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. c 2013 National Technology and Science Press
You might also like
- Engr260 Lec5 Op Amps (Ink)Document30 pagesEngr260 Lec5 Op Amps (Ink)Nick RentschNo ratings yet
- Op Amp NotesDocument34 pagesOp Amp NotesUma ShankarNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 6 Basic Op Amp CircuitsDocument10 pagesLaboratory 6 Basic Op Amp CircuitsKamran AliNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Operational AmplifiersDocument12 pagesLab 1 Operational AmplifiersChris BrownNo ratings yet
- QB-OpAmps ApplicationsDocument3 pagesQB-OpAmps ApplicationsRamyaNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Problems DC Equivalent Circuits, Network Theorems, and Bridge CircuitsDocument3 pagesSupplementary Problems DC Equivalent Circuits, Network Theorems, and Bridge CircuitsJomer JuanNo ratings yet
- Basic Op-Amp CircuitsDocument12 pagesBasic Op-Amp CircuitsRoxana100% (1)
- Lab 6Document10 pagesLab 6willstamp2003No ratings yet
- Circuits Exp4Document4 pagesCircuits Exp4ilker.ozcelikkanNo ratings yet
- BEE Tutorial 5Document2 pagesBEE Tutorial 5alysonmicheaalaNo ratings yet
- Lic AssignmentDocument2 pagesLic Assignmentspock773No ratings yet
- Lec5 OpAmp PDFDocument63 pagesLec5 OpAmp PDFPhan Phuong NgocNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 01 (17012019)Document6 pagesTutorial 01 (17012019)Devansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document16 pagesAssignment 3Bảo Đỗ QuốcNo ratings yet
- Lect26 OMP AMPDocument14 pagesLect26 OMP AMPJason LeeNo ratings yet
- Sheet (2) BJTDocument5 pagesSheet (2) BJTdrhammoudaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Problems: Bipolar Junction Transistor (Basic BJT Amplifiers)Document23 pagesTutorial Problems: Bipolar Junction Transistor (Basic BJT Amplifiers)vineetha nagahageNo ratings yet
- OpampDocument37 pagesOpampArief PurwantoNo ratings yet
- Shigley S Mechanical Engineering Design 9th Edition Solutions ManualDocument29 pagesShigley S Mechanical Engineering Design 9th Edition Solutions ManualZaim AkmalNo ratings yet
- Op AmpDocument40 pagesOp AmpSami KasawatNo ratings yet
- EE315 Exp4 BJTssAmpDocument3 pagesEE315 Exp4 BJTssAmpserhatNo ratings yet
- Answer: - 4 V: ProblemsDocument15 pagesAnswer: - 4 V: ProblemsCamilo OtaloraNo ratings yet
- Opamps Are Very Useful Electronic Components 2. We Have Already The Tools To Analyze Practical Circuits Using Op-Amps (Ohm'Skcl and KVL) 3. The Linear Models For Opamps Include Dependent SourcesDocument13 pagesOpamps Are Very Useful Electronic Components 2. We Have Already The Tools To Analyze Practical Circuits Using Op-Amps (Ohm'Skcl and KVL) 3. The Linear Models For Opamps Include Dependent SourcesMuhammad OsamaNo ratings yet
- Files-3-Lesson Notes Lecture 11Document9 pagesFiles-3-Lesson Notes Lecture 11RekhyttolemyNo ratings yet
- Problems-Chapter-5 - ContentsDocument9 pagesProblems-Chapter-5 - ContentsThiện NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronic Circuit (ECE - 201)Document3 pagesAnalog Electronic Circuit (ECE - 201)Manoj Kumar RNo ratings yet
- QB Op AmpDocument3 pagesQB Op AmpBhonandh Sai Kandru100% (1)
- Bogotá, D.C., 20 de Noviembre de 2019 Problemas Ela1 Problemas Propuestos: 1. in The Circuit of Figure A, The Diode Is IdealDocument6 pagesBogotá, D.C., 20 de Noviembre de 2019 Problemas Ela1 Problemas Propuestos: 1. in The Circuit of Figure A, The Diode Is IdealFelipe GuzmánNo ratings yet
- HW 2Document10 pagesHW 2Kyto_oNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Ve BJT3Document23 pagesBai Tap Ve BJT3nguyenphuonghuy1979No ratings yet
- Analysis, Design and Characteristics of Op-Amp & Second Order FilterDocument9 pagesAnalysis, Design and Characteristics of Op-Amp & Second Order FilterManraj GujralNo ratings yet
- Lic 100 Marks QPDocument2 pagesLic 100 Marks QPprofharishjoshiNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits and DesignDocument4 pagesAnalog Circuits and Designlalitkumar bannagareNo ratings yet
- GATE 2018 - Previous Solutions & Video Lectures For FREE - Previous GATE Questions On Operational Amplifiers & Differential Amplifiers - II (2001 - Till Date)Document51 pagesGATE 2018 - Previous Solutions & Video Lectures For FREE - Previous GATE Questions On Operational Amplifiers & Differential Amplifiers - II (2001 - Till Date)Nitin MauryaNo ratings yet
- Circuits Experiment 5Document4 pagesCircuits Experiment 5ilker.ozcelikkanNo ratings yet
- Selected Answers: One Possible SolutionDocument2 pagesSelected Answers: One Possible SolutionAlisha BradleyNo ratings yet
- EE 101 - Assignment - 4Document3 pagesEE 101 - Assignment - 4Harsh ChandakNo ratings yet
- Amplifier Circuit Lab WorkDocument24 pagesAmplifier Circuit Lab WorkSandeep PatwaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Elements of DC CircuitsDocument8 pagesCircuit Elements of DC CircuitsLighto LastoNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Tutorial 3 2024Document21 pagesAnalog Electronics Tutorial 3 2024Mayank SharmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electric Circuits: Introduction To Operational AmplifiersDocument37 pagesBasic Electric Circuits: Introduction To Operational AmplifiersBilal Hafeez0% (1)
- BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: June 2016 Semester End Make Up ExaminationsDocument4 pagesBMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: June 2016 Semester End Make Up Examinationskoushik bhatNo ratings yet
- Lec6 PDFDocument40 pagesLec6 PDFAlain MoratallaNo ratings yet
- Study of R-C Phase Shift OscillatorDocument6 pagesStudy of R-C Phase Shift OscillatorTawsiful AlamNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 1 ECE Lacieras Recon 2 PDFDocument22 pagesLaboratory 1 ECE Lacieras Recon 2 PDFRafael AclanNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1-Op AmpDocument2 pagesSheet 1-Op AmpHossam AhmedNo ratings yet
- Op Amp Using PspiceDocument18 pagesOp Amp Using PspiceSathish BalaNo ratings yet
- EE101A Practice+Final+with+SolutionsDocument14 pagesEE101A Practice+Final+with+SolutionsrandomDayNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions Unit 1,2 and 3Document22 pagesPractice Questions Unit 1,2 and 3gowshik ramNo ratings yet
- Final Project: Operational Amplifier: Martin Lizarde Jr. Susanna Guerrero Dung HuynhDocument29 pagesFinal Project: Operational Amplifier: Martin Lizarde Jr. Susanna Guerrero Dung HuynhChethan Ram NarayanNo ratings yet
- Problems-Chapter-4 - ContentsDocument7 pagesProblems-Chapter-4 - ContentsThiện NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Unit Opamp+Oscillator+Filter RevDocument23 pagesUnit Opamp+Oscillator+Filter Revstudent oldNo ratings yet
- Practice Assignment1-Electronic Circuit DesignDocument4 pagesPractice Assignment1-Electronic Circuit DesignSamreen ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Solid-State Diodes and Diode CircuitsDocument17 pagesChapter 3: Solid-State Diodes and Diode CircuitsLê Hoàng ChínhNo ratings yet
- 09 RLDocument25 pages09 RL1A R. Moch Rizky Sunandar SaputraNo ratings yet
- School of Electrical Engineering and Informatics Institut Teknologi BandungDocument4 pagesSchool of Electrical Engineering and Informatics Institut Teknologi BandungRezzal AndryanNo ratings yet
- Lab No. 2 Title: Simulating Opamp Circuit Transient Response in Pspice To Verify The Gain of The CircuitDocument10 pagesLab No. 2 Title: Simulating Opamp Circuit Transient Response in Pspice To Verify The Gain of The Circuitlearner guyNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet