Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture Notes (Chapter 2.2 (B) Double Integrals As Surface Area)
Uploaded by
shinee_jayasila2080Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture Notes (Chapter 2.2 (B) Double Integrals As Surface Area)
Uploaded by
shinee_jayasila2080Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2: Multiple Integrals
Double Integrals as Surface Area
Let f be a continuous function over R, and f has partial derivatives f x and f y , then the
area of surface S is given by:
Surface Area dS ( f x )2 ( f y ) 2 1dA
R
Where dA can be dxdy , dydx or rdrd .
Similarly, instead of the projection on xy-plane, we can extend the projection to xzplane and yz-plane, where:
xz-plane
Surface Area dS ( f x )2 1 ( f z ) 2 dA
R
where y f ( x, z ) and dA can be dxdz , dzdx or rdrd .
yz-plane
Surface Area dS 1 ( f y )2 ( f z ) 2 dA
R
where x f ( y, z ) and dA can be dydz , dzdy or rdrd .
Chapter 2: Multiple Integrals
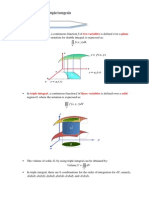
Example 1
Find the surface area of the portion of the curve f ( x, y) x y 6 over the region
R {( x, y) | 0 x 1,0 y 1} .
Solution
The required surface area S is shown in the following figure.
f ( x, y) x y 6
1
1
Given that f ( x, y) x y 6 ; hence, f x 1 and f y 1
Surface Area, S dS
R
( f x ) 2 ( f y ) 2 1dA
R
1 1
(1) 2 (1) 2 1dydx
0 0
1
3 y 0 dx
1
0
1
3dx
0
3x0
1
Chapter 2: Multiple Integrals
Example 2
Find the surface area of the portion of the paraboloid z 4 x 2 y 2 over the xy-plane.
Solution
The required surface area S is shown in the following diagram.
z
4
z 4 x2 y 2
When z = 0 (xy-plane), the region R is a circle x 2 y 2 4 , with inequalities
2 x 2 and 4 x2 y 4 x 2 .
y 4 x2
R
2
y 4 x2
f ( x, y ) 4 x 2 y 2
f x 2 x, f y 2 y
Surface Area, S dS
R
( f x )2 ( f y ) 2 1dA
R
Chapter 2: Multiple Integrals
2
2 y 4 x
(2 x) 2 (2 y ) 2 1dydx
2 y 4 x 2
2
2 y 4 x
4 x 2 4 y 2 1dydx
2 y 4 x 2
2
2 y 4 x
4( x 2 y 2 ) 1dydx
2 y 4 x 2
By polar coordinates, 0 r 2 0 2 , and x 2 y 2 r 2
Hence,
2 2
4r 2 1rdrd
0 0
3
1
(4r 2 1) 2 d
12
o
0
2
2
1
17
1d
12 0
3
1
(17 2 1)
12
3
1
(17 2 1)
6
2
0
Using substitution:
u r2
du 2rdr
du
rdr
2
4r 2 1rdr 4u 1
3
1 2 1
4u 1 2
2 3 4
3
1
4r 2 1 2
12
du
2
You might also like
- Endocrine WorksheetDocument7 pagesEndocrine WorksheetBrenda Zaragoza63% (8)
- Lecture Notes (Chapter 2.1 Double Integral)Document9 pagesLecture Notes (Chapter 2.1 Double Integral)shinee_jayasila2080No ratings yet
- Lecture 35: Surface Area Surface IntegralsDocument2 pagesLecture 35: Surface Area Surface IntegralsshiladityNo ratings yet
- Sol IntegralsDocument18 pagesSol IntegralsEstefi PeñalozaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12.4Document4 pagesLecture 12.4Tran Huong LanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Multiple IntegralDocument56 pagesChapter 3 - Multiple IntegralTuan Jalai100% (1)
- Tutorial Worksheet 5Document3 pagesTutorial Worksheet 5nicomathias74No ratings yet
- MAL120 Tutorial Sheet 1 24 JAN FINAL With AnswersDocument2 pagesMAL120 Tutorial Sheet 1 24 JAN FINAL With AnswersYoteshYadavNo ratings yet
- Double Integrals: A y X F Da y X FDocument31 pagesDouble Integrals: A y X F Da y X FsaperuddinNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 ApplicationsDocument14 pagesChap 3 ApplicationsGrace HeNo ratings yet
- Integrals DoubledDocument16 pagesIntegrals DoubledsabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- Triple SubstitutionDocument4 pagesTriple SubstitutionTinaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Calculus of Multi Variables 2011Document22 pagesLecture 2 Calculus of Multi Variables 2011Yiauw ShenqNo ratings yet
- Handout IIDocument5 pagesHandout IIMarian Galvez-LuisNo ratings yet
- Area of BodedDocument5 pagesArea of BodedthinkiitNo ratings yet
- X 0 M X 0 y N Y: (I.T. Leong) Math 200 in 2010 2010 C 10 7 F 1 / 9Document9 pagesX 0 M X 0 y N Y: (I.T. Leong) Math 200 in 2010 2010 C 10 7 F 1 / 9eouahiauNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Practice Final ExamDocument10 pagesSolutions To Practice Final ExamSchwin W PinkohNo ratings yet
- Double IntegralsDocument4 pagesDouble IntegralsJimuel Adrian Punzalan100% (1)
- Mth301 Mid Fall 2010Document8 pagesMth301 Mid Fall 2010Prince IslamabadNo ratings yet
- Lecture07 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture07 PDFss_nainamohammedNo ratings yet
- 2012 FinalDocument2 pages2012 FinaleouahiauNo ratings yet
- Math 2163, Practice Exam IIIDocument2 pagesMath 2163, Practice Exam IIIhthaier4062No ratings yet
- Very Valuable For Calculus For SurfaceDocument14 pagesVery Valuable For Calculus For Surface吳庭昕No ratings yet
- 29) 6.1 Areas of Plane RegionsDocument6 pages29) 6.1 Areas of Plane RegionsShirley KiangNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Part 3Document13 pagesUnit 2 Part 3Sabu Raj RNo ratings yet
- Assignment4 SolDocument6 pagesAssignment4 SolKush Ganatra ch19b063No ratings yet
- MAM2085F 2013 Exam SolutionsDocument8 pagesMAM2085F 2013 Exam Solutionsmoro1992No ratings yet
- Solutions 1 - MATH221Document5 pagesSolutions 1 - MATH221Ira RasNo ratings yet
- MT261 Tutorial 3Document4 pagesMT261 Tutorial 3Gilbert FuriaNo ratings yet
- Blue Print: Class Xii Maths: Model Question PaperDocument14 pagesBlue Print: Class Xii Maths: Model Question Paperapi-243565143No ratings yet
- Exam - 2013 10 30Document5 pagesExam - 2013 10 30lieth-4No ratings yet
- MATH 2020 B SolutionDocument45 pagesMATH 2020 B SolutionWan Chin ChingNo ratings yet
- HW Apr 20Document2 pagesHW Apr 20AparaNo ratings yet
- Assignment V Intigral CalculusDocument2 pagesAssignment V Intigral CalculusAnonymous 3JcBtYTNo ratings yet
- Assign 4Document1 pageAssign 4Kush Ganatra ch19b063No ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics, IIT Kharagpur MA10002: Mathematics-II Assignment-2 On Integral CalculusDocument1 pageDepartment of Mathematics, IIT Kharagpur MA10002: Mathematics-II Assignment-2 On Integral CalculusSidMadharchodNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument0 pagesPDFPratyush MishraNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Assignment #10, Math 253Document4 pagesSolutions To Assignment #10, Math 253Alex TanNo ratings yet
- Hw6 SolutionDocument4 pagesHw6 Solutionbohoo123No ratings yet
- Assignment3 SolDocument5 pagesAssignment3 SolKalua BhaiNo ratings yet
- Homework09 SolutionsDocument3 pagesHomework09 SolutionsKhaled ChaibNo ratings yet
- Area Theory Notes (MT)Document18 pagesArea Theory Notes (MT)mann123456789No ratings yet
- Term End Examination - May 2013 Course: MAT101 - Multivariable Calculus and Differential Equations Slot: F2+TF2 Class NBR: 3461 Time: Three Hours Max - Marks:100Document2 pagesTerm End Examination - May 2013 Course: MAT101 - Multivariable Calculus and Differential Equations Slot: F2+TF2 Class NBR: 3461 Time: Three Hours Max - Marks:100Pratyush MishraNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Double and Triple Integrals Solutions Math 13, Spring 2010Document8 pagesExercises: Double and Triple Integrals Solutions Math 13, Spring 2010Colls MuntadaNo ratings yet
- Term Test (2005) Sample2Document3 pagesTerm Test (2005) Sample2Peng XuNo ratings yet
- Three Dimensional Coordinate System. Functions of Two Variables. SurfacesDocument5 pagesThree Dimensional Coordinate System. Functions of Two Variables. SurfacesDamaris Kaminza100% (1)
- Vector Fields Line Integrals Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path Conservative Fields and Potential Functions Green's TheoremDocument40 pagesVector Fields Line Integrals Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path Conservative Fields and Potential Functions Green's TheoremeouahiauNo ratings yet
- Outline of Solutions To Homework 1Document3 pagesOutline of Solutions To Homework 1Michel AndradeNo ratings yet
- MA1001-Assg 4Document1 pageMA1001-Assg 4Tony StarkNo ratings yet
- SMA 2116 - Tutotial 1 - 2018Document5 pagesSMA 2116 - Tutotial 1 - 2018PatrickNo ratings yet
- 2013 Homework 04Document2 pages2013 Homework 04eouahiauNo ratings yet
- 2013 Homework 04 PDFDocument2 pages2013 Homework 04 PDFeouahiauNo ratings yet
- Exam - 2012 10 30Document5 pagesExam - 2012 10 30lieth-4No ratings yet
- 2011 (1) Assignment 1 Marking Scheme: School of Mathematical Sciences 2011Document5 pages2011 (1) Assignment 1 Marking Scheme: School of Mathematical Sciences 2011denise323No ratings yet
- Assignment3 SolDocument5 pagesAssignment3 SolKush Ganatra ch19b063No ratings yet
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 1-D Integration and Centroids: Integral of A FunctionDocument3 pages1-D Integration and Centroids: Integral of A Functionshinee_jayasila2080No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes (Chapter 2.2 (A) Double Integrals in Polar Coordinate)Document5 pagesLecture Notes (Chapter 2.2 (A) Double Integrals in Polar Coordinate)shinee_jayasila2080No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes (Chapter 2.2 (A) Double Integrals in Polar Coordinate)Document5 pagesLecture Notes (Chapter 2.2 (A) Double Integrals in Polar Coordinate)shinee_jayasila2080No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes (Chapter 2.3 Triple Integral)Document5 pagesLecture Notes (Chapter 2.3 Triple Integral)shinee_jayasila2080100% (1)
- Lecture Notes (Chapter 3.4 Motion in Plane Curve)Document2 pagesLecture Notes (Chapter 3.4 Motion in Plane Curve)shinee_jayasila2080No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes (Chapter 2.5 Application of Multiple Integral)Document12 pagesLecture Notes (Chapter 2.5 Application of Multiple Integral)shinee_jayasila2080No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes (Chapter 2.4b Spherical Coordinate)Document7 pagesLecture Notes (Chapter 2.4b Spherical Coordinate)shinee_jayasila2080No ratings yet
- NW June P1 2019 MemoDocument6 pagesNW June P1 2019 MemoAsandaNo ratings yet
- Alchem 1090 DDocument10 pagesAlchem 1090 Dmuhammad85No ratings yet
- API 653 Questions Monkey PuzzleDocument5 pagesAPI 653 Questions Monkey PuzzleAnuradha SivakumarNo ratings yet
- Double Corbel PDFDocument5 pagesDouble Corbel PDFSushil Dhungana100% (1)
- 50 Phrasal Verbs (Printing Version)Document3 pages50 Phrasal Verbs (Printing Version)Nagore MonteroNo ratings yet
- Types of Juicers - EditedDocument17 pagesTypes of Juicers - EditedAbdulrehmanNo ratings yet
- Outline Defense FinalDocument5 pagesOutline Defense FinalMelrose LopezNo ratings yet
- MR Bean Is in The Staff Room at School. He Is Making A Cup of Coffee. Miss Smith Comes in ..Document12 pagesMR Bean Is in The Staff Room at School. He Is Making A Cup of Coffee. Miss Smith Comes in ..Sandhya RafiansyahNo ratings yet
- Product Catalogue 01Document11 pagesProduct Catalogue 01Sanja TinaNo ratings yet
- FSC Code Solution For BMW E SeriesDocument21 pagesFSC Code Solution For BMW E SeriesAlex PopaNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 4 - Q2 - W3Document6 pagesDLL - Mapeh 4 - Q2 - W3Janet Escosura Espinosa MadayagNo ratings yet
- Trans-Boundary Fisheries Resources Management (Compatibility Mode)Document16 pagesTrans-Boundary Fisheries Resources Management (Compatibility Mode)KruNont MatchPointNo ratings yet
- Transportation and Highway Engineering PDFDocument3 pagesTransportation and Highway Engineering PDFReymark AbatayoNo ratings yet
- 10.2.2.3 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Single-Area OSPFv2 Instructions - ILMDocument2 pages10.2.2.3 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Single-Area OSPFv2 Instructions - ILMSergio TejedorNo ratings yet
- Esab Cab 460S: A Standard Column and Boom For Flexible Weld MechanizationDocument2 pagesEsab Cab 460S: A Standard Column and Boom For Flexible Weld MechanizationEnaam AtaallahNo ratings yet
- Postgraduate - 19 September 2023Document2 pagesPostgraduate - 19 September 2023Times MediaNo ratings yet
- Dolphs Varnishs Resin ChartDocument3 pagesDolphs Varnishs Resin ChartFernando Rodriguez100% (1)
- Rural Development Hiwre BajarDocument17 pagesRural Development Hiwre Bajarayushnahar16122No ratings yet
- Diamer Bhasha DamDocument14 pagesDiamer Bhasha DamJunaidahmadNo ratings yet
- Café Catula Lunch MenuDocument1 pageCafé Catula Lunch Menuadiejones7No ratings yet
- Annex 11 ITMSprinklersysteminspection 1649142576210Document6 pagesAnnex 11 ITMSprinklersysteminspection 1649142576210AmanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Edexcel CircuitsDocument87 pagesIGCSE Edexcel CircuitsКіра Струлєва ОлексіївнаNo ratings yet
- Airflow in Batch Fluid Bed ProcessingDocument11 pagesAirflow in Batch Fluid Bed ProcessingjokishNo ratings yet
- Amul STP: MissionDocument3 pagesAmul STP: MissionKhushi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Surface Vehicle Recommended PracticeDocument3 pagesSurface Vehicle Recommended PracticeVIGNESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- AWC NDS SUPP - National Design Specification For Wood ConstructionDocument3 pagesAWC NDS SUPP - National Design Specification For Wood ConstructionMichaelNo ratings yet
- Ferrari CMD Sept 2018 - E. Galliera PDFDocument25 pagesFerrari CMD Sept 2018 - E. Galliera PDFSapunaru AndreiNo ratings yet
- Role of Steroids in Critical Care PDFDocument3 pagesRole of Steroids in Critical Care PDFDr.Shilpa JohnNo ratings yet
- Brinsmead Edgard - History of Pianoforte PDFDocument276 pagesBrinsmead Edgard - History of Pianoforte PDFmolesbgNo ratings yet