Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Bis A, H P/y H : Fluid Statics CL 29
A Bis A, H P/y H : Fluid Statics CL 29
Uploaded by
Javier Rojas PaytanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Bis A, H P/y H : Fluid Statics CL 29
A Bis A, H P/y H : Fluid Statics CL 29
Uploaded by
Javier Rojas PaytanCopyright:
Available Formats
FLUID STATICS Cl 29
2.23
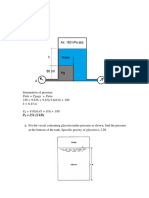
Figure 2-9 shows one pressurized tank inside another. If the sum of the readings of Bourdan gages A and B is
34.1 psi, and an aneroid barometer reads 29.90 inHg, what is the absolute pressure at A, in inHg?
h = p/y
hA + hB = 34.1/[(13.6)(62.4)/(12)1 = 69.44 inHg
(hA).b. = 29.90 + 69.44 = 99.34 inHg
Fig. 2-9
2.24
Determine the heights of columns of water, kerosene (ker), and nectar (s.g. = 2.94) equivalent to 277 mmHg.
040(YHO = (1/40)(YH2o) = (hker)(Yker) = (hnemir)(Ywar)
0.2771(13.6)(9.79)] = (hH2o)(9.79)
0 82
hR2o = 177 m
9 79
0.277[(13.6)(9.79)] = (hker)[( . )( . )1
0.277[(13.6)(9.79)] = (h.)[(2.94)(9.79)1
2.25
hker = 4.59 m
h ,r = 1.28 m
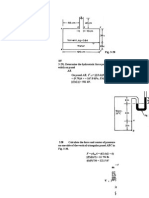
In Fig. 2-10, if h = 25.5 in, determine the pressure at A. The liquid has a specific gravity of 1.85.
p = yh = R1.85)(62.4)1[25.5/12] = 245.3 lb/ft 2 or 1.70 psi
Fig. 2-10
2.26
For the pressure vessel containing glycerin, with piezometer attached, as shown in Fig. 2-11, what is the
pressure at point A?
p = yh = [(1.26)(62.4)1(40.8/12) = 267 lb/ft2
Open to atmosphere
You might also like
- Fluid Statics PDFDocument28 pagesFluid Statics PDFAnthony Leire MontealtoNo ratings yet
- 8 16Document3 pages8 16ejans54No ratings yet
- Hydraulic Engineering Experiment H6: Flow Measurement in Closed ConduitsDocument20 pagesHydraulic Engineering Experiment H6: Flow Measurement in Closed ConduitsKS Chong100% (1)
- Equlibrium Questions (Chem DP HL)Document4 pagesEqulibrium Questions (Chem DP HL)Dea SukrisnaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8-Chemical EquilibriumDocument3 pagesTutorial 8-Chemical EquilibriumNavine NavNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equlibria Test-1Document4 pagesChemical Equlibria Test-1newlifelabsNo ratings yet
- Psychometry Air Conditioning EditDocument33 pagesPsychometry Air Conditioning EditlewisNo ratings yet
- Psycrometric ProcessDocument33 pagesPsycrometric Processmdalt9180No ratings yet
- Principal CH 1.3Document11 pagesPrincipal CH 1.3Zyxw VutNo ratings yet
- Therm DynDocument13 pagesTherm DynSumathi SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Tugas Kelompok 6 PDFDocument10 pagesTugas Kelompok 6 PDFsongjihyo16111994No ratings yet
- CHEM 2820 Problem Set 1Document3 pagesCHEM 2820 Problem Set 1Vicente JonathanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Worked Examples PDFDocument20 pagesThermodynamics Worked Examples PDFJoshua Edokpayi100% (1)
- 2010chem17 PracticeExercise1Document4 pages2010chem17 PracticeExercise1Erika Mae Adoja Espejo100% (1)
- Test, Bansal Chemicalequilibrium PDFDocument18 pagesTest, Bansal Chemicalequilibrium PDFTarun Gupta0% (2)
- Chapter 15 Practice QuestionsDocument17 pagesChapter 15 Practice QuestionsKim LeeNo ratings yet
- Exercises 3: The First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageExercises 3: The First Law of ThermodynamicsAmirali MasoumiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Chemical Equilibrium HWDocument4 pagesChapter 16 Chemical Equilibrium HWAlejo CardoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document7 pagesChapter 2Zadky RiosNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Concept and Factors Affecting EquilibriumDocument4 pagesTopic 1 - Concept and Factors Affecting Equilibriumdeela decemberNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower Selection and SizingDocument30 pagesCooling Tower Selection and SizingGausul Azam100% (1)
- B18pa1 NHN 08 PDFDocument4 pagesB18pa1 NHN 08 PDFMohamed AbdullaNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument2 pagesSolutionBOTU ROHITHNo ratings yet
- CHT I 09Document24 pagesCHT I 09almutaz9879No ratings yet
- ME 306 Tutorial 8 SolDocument2 pagesME 306 Tutorial 8 SolFarzi FarziNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 ThermoDocument1 pageTutorial 5 ThermoAkmar SN MYNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 ThermoDocument1 pageTutorial 5 ThermoAkmar SN MYNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 ThermoDocument1 pageTutorial 5 ThermoAkmar SN MYNo ratings yet
- GASES Free Response WorksheetDocument4 pagesGASES Free Response WorksheetJJNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas (Exercise)Document32 pagesIdeal Gas (Exercise)wacipas172No ratings yet
- Week 11 Solutions - ENB222Document11 pagesWeek 11 Solutions - ENB222Don Wook WonNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap14 P069Document12 pagesThermo 5th Chap14 P069Ahmad AlgarniNo ratings yet
- ch16 CompressDocument2 pagesch16 CompressOlsa NdoshaNo ratings yet
- Airconditioning 002Document24 pagesAirconditioning 002DarklotharNo ratings yet
- CHM092 Tutorial Chapter 4ADocument8 pagesCHM092 Tutorial Chapter 4AvNo ratings yet
- KC and KP Questions EquilibriaDocument8 pagesKC and KP Questions Equilibriakhadijaliyu3No ratings yet
- 53 Page QuestionsDocument53 pages53 Page QuestionssezNo ratings yet
- Drdo Examination Question Paper Year 2009Document19 pagesDrdo Examination Question Paper Year 2009Gaurav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Psi-Ap-Chemistry-Equilibrium-Multiple-Choice 3Document30 pagesPsi-Ap-Chemistry-Equilibrium-Multiple-Choice 3Tricyver ChienNo ratings yet
- Combustion ExamplesDocument5 pagesCombustion ExamplesSameen QaisarNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Chem OpenerDocument5 pagesForm 3 Chem OpenerDenisNo ratings yet
- Phy 1321 Assignment SolutionsDocument2 pagesPhy 1321 Assignment SolutionsNupur VijNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document5 pagesChapter 2Marco LuigiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 and 16 Revision: (104 Marks)Document26 pagesChapter 15 and 16 Revision: (104 Marks)aurennosNo ratings yet
- Mixture and Chemical EquilibriumDocument2 pagesMixture and Chemical EquilibriumAlfieNo ratings yet
- HYDRO 1 - Module 1.4 Hydrostatic Principles (Sample Problems)Document3 pagesHYDRO 1 - Module 1.4 Hydrostatic Principles (Sample Problems)Philip SabadiNo ratings yet
- CHE 122 Written Assignment 4 Chemical EquilibriumDocument6 pagesCHE 122 Written Assignment 4 Chemical EquilibriumRedgraveNo ratings yet
- WORK SHEET - Chemical EquilibriumDocument4 pagesWORK SHEET - Chemical EquilibriumAndrej ZafirovikjNo ratings yet
- 2 Hydrostatics ContinuationDocument5 pages2 Hydrostatics ContinuationPritz Jay Magno TorresNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Maria GaingosNo ratings yet
- 51 PsicrometriciDocument8 pages51 PsicrometriciMiracle LakeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Exercices Enstab Cou SWDocument12 pagesFluid Mechanics Exercices Enstab Cou SWLourenze KigisNo ratings yet
- CombustionDocument35 pagesCombustionallovidNo ratings yet
- NSS Chemistry Part 8 Chemical Reactions and Energy PDFDocument17 pagesNSS Chemistry Part 8 Chemical Reactions and Energy PDF6A(24) Marsh WongNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 1 06Document51 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 1 06Ng Swee Loong Steven100% (2)
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Gas Hydrates 1: Fundamentals, Characterization and ModelingFrom EverandGas Hydrates 1: Fundamentals, Characterization and ModelingDaniel BrosetaNo ratings yet
- Gas Hydrates 2: Geoscience Issues and Potential Industrial ApplicationsFrom EverandGas Hydrates 2: Geoscience Issues and Potential Industrial ApplicationsLivio RuffineNo ratings yet
- 14 Q Chapter 1: DR (0.0402 - 0.0400) /2 0.0001 M A (70 (4.00/100) (4) 0.04398 MDocument2 pages14 Q Chapter 1: DR (0.0402 - 0.0400) /2 0.0001 M A (70 (4.00/100) (4) 0.04398 MJavier Rojas PaytanNo ratings yet
- h19,21 0 - / ' T - T y T,, / ,: MercurDocument2 pagesh19,21 0 - / ' T - T y T,, / ,: MercurJavier Rojas PaytanNo ratings yet
- A Prandtl's Soap-Film Analogy.: Properties of Fluids 0 19Document3 pagesA Prandtl's Soap-Film Analogy.: Properties of Fluids 0 19Javier Rojas PaytanNo ratings yet
- Pa 1 /./ (DVLDR) F W Yv : Properties of Fluids 17 1.98Document2 pagesPa 1 /./ (DVLDR) F W Yv : Properties of Fluids 17 1.98Javier Rojas PaytanNo ratings yet
- Forces On Submerged Plane Areas 73Document2 pagesForces On Submerged Plane Areas 73Javier Rojas PaytanNo ratings yet
- AB. AB, 1 - FabDocument2 pagesAB. AB, 1 - FabJavier Rojas PaytanNo ratings yet
- Properties of Fluids: (P), F W Ma P mIVDocument1 pageProperties of Fluids: (P), F W Ma P mIVJavier Rojas PaytanNo ratings yet
- Gage 2 FTDocument2 pagesGage 2 FTJavier Rojas PaytanNo ratings yet
- (Pply) .+xli2: Kerosene Air TDocument1 page(Pply) .+xli2: Kerosene Air TJavier Rojas PaytanNo ratings yet
- 94Document2 pages94Javier Rojas PaytanNo ratings yet
- 5.50 (A) (B) P Yh A - PR T: F 0 2T - 0 T AsteelasteelDocument1 page5.50 (A) (B) P Yh A - PR T: F 0 2T - 0 T AsteelasteelJavier Rojas PaytanNo ratings yet
- Forces On Submerged Curved Areas 107: 5.333ft 4 .3 3 1 FTDocument2 pagesForces On Submerged Curved Areas 107: 5.333ft 4 .3 3 1 FTJavier Rojas PaytanNo ratings yet