Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nguyen Masters Report16
Uploaded by
PhiPhi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageQ
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentQ
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageNguyen Masters Report16
Uploaded by
PhiPhiQ
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
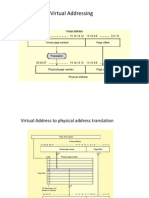
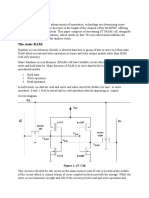
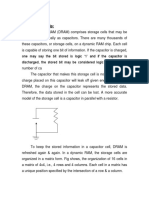
and both true and complementary bit-lines. Figure 2.
2 shows the circuit diagram of a
6T SRAM.
The cell contains a pair of cross-coupled inverters and an access-
transistor for each bit-line as combination read/write port. True and complementary
versions of the data are stored on the cross-coupled inverters. If the data is disturbed
slightly, positive feedback around the loop will restore it to VDD or GND. The wordline in inserted to read or to write the cell.
Figure 2.2: Six-transistor SRAM cell.
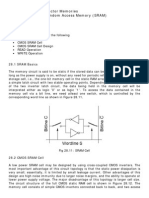
2.2 SRAM Cell Operation:
SRAM operation can be divided into two phases, phase 1 - 1 and phase 2 - 2,
which can be generated from clk and its complement clkb signals. Assume that the
SRAM is pre-charged in phase 2. In phase 1, the SRAM is written, or read by raising the
appropriate word line and either driving the bit lines to the value that should be written or
leaving the bit lines floating and observing which one is pull down. The row and column
are selected by row or column decoders.
Reading a large SRAM array can be slow due the capacitance of the SRAM cells
which are sharing the same bit line.
The sense amplifier circuit (sense amp) can
5
You might also like
- Static RAMDocument235 pagesStatic RAMAnjireddy ThatiparthyNo ratings yet
- DRAM and MOS DRAM CellsDocument13 pagesDRAM and MOS DRAM CellsSiddharth PanditNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Memory OrganizationDocument24 pagesUnit 6 Memory OrganizationAnurag GoelNo ratings yet
- ,hrfikadsz NJSDFMV M VZDocument5 pages,hrfikadsz NJSDFMV M VZpalakNo ratings yet
- SramDocument31 pagesSramParth RamanujNo ratings yet
- VAMSI Kumar SRAMfinalDocument28 pagesVAMSI Kumar SRAMfinalraghuippiliNo ratings yet
- High Speed Applications of Lower Power SRAM CellsDocument10 pagesHigh Speed Applications of Lower Power SRAM CellsshwetabhagatNo ratings yet
- Design of A Low Power SRAM Cell by Tanner Tool 45 NMDocument6 pagesDesign of A Low Power SRAM Cell by Tanner Tool 45 NMEditor IJRITCCNo ratings yet
- Low Power 12T MTCMOS SRAM Based CAMDocument6 pagesLow Power 12T MTCMOS SRAM Based CAMmani_vlsiNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Leakage Power in 8T Sram Cell Using Virtual GroundDocument5 pagesReduction of Leakage Power in 8T Sram Cell Using Virtual GroundSasi Kiran SNo ratings yet
- 6t Sram CellDocument4 pages6t Sram CellKhushi SidNo ratings yet
- Module 5 VLSI Design NotesDocument23 pagesModule 5 VLSI Design NotesUmme HanieNo ratings yet
- Cache PPTDocument20 pagesCache PPTshahida18No ratings yet
- Sram / Dram: PARNEET KAUR (21092003) HARSH NIKETAN DIXIT (21092002) RISHABH MISHRA (21092001)Document10 pagesSram / Dram: PARNEET KAUR (21092003) HARSH NIKETAN DIXIT (21092002) RISHABH MISHRA (21092001)Parneet KaurNo ratings yet
- A Novel Four-Transistor SRAM Cell With Low Dynamic Power ConsumptionDocument5 pagesA Novel Four-Transistor SRAM Cell With Low Dynamic Power ConsumptionDinesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Coa CH3 Q4Document2 pagesCoa CH3 Q4vishalNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of 4Kb Sram Array Cell For The Development of Sram ChipDocument8 pagesDesign and Analysis of 4Kb Sram Array Cell For The Development of Sram ChipRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Flash MemoryDocument68 pagesFlash Memoryshiva100% (1)
- 6T SRAM SimulationDocument9 pages6T SRAM SimulationAzza FaiadNo ratings yet
- SRAMDocument2 pagesSRAMharis123pNo ratings yet
- SRAMReportDocument42 pagesSRAMReportPremkumar ChandhranNo ratings yet
- 6T SRAM Simulation PDFDocument9 pages6T SRAM Simulation PDFAzza FaiadNo ratings yet
- LPVLSIDocument21 pagesLPVLSIagarwaltanujta879No ratings yet
- 6TSRAM Cell ReportDocument15 pages6TSRAM Cell ReportpalakNo ratings yet
- Pardazeshgar Digital Project English TextDocument10 pagesPardazeshgar Digital Project English Textkazem.khaari77No ratings yet
- Low Voltage and Low Power in Sram Read and Write Assist TechniquesDocument9 pagesLow Voltage and Low Power in Sram Read and Write Assist TechniquesIJSTENo ratings yet
- (New Paper On Sram) v39-15Document5 pages(New Paper On Sram) v39-15Pratap SaurabhNo ratings yet
- The International Journal of Engineering and Science (The IJES)Document7 pagesThe International Journal of Engineering and Science (The IJES)theijesNo ratings yet
- SRAM Circuit Design and Operation: Prepared By: Mr. B. H. NagparaDocument49 pagesSRAM Circuit Design and Operation: Prepared By: Mr. B. H. NagparaBharatNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument5 pagesAbstractKurushNishanthNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Memories: VLSI Design (18EC72)Document11 pagesSemiconductor Memories: VLSI Design (18EC72)PraveenNo ratings yet
- Ultra-Low Leakage Static Random Access Memory DesignDocument10 pagesUltra-Low Leakage Static Random Access Memory DesignIJRES teamNo ratings yet
- Sram and Dram L4: Dram: Memory SubsystemDocument17 pagesSram and Dram L4: Dram: Memory SubsystemNeel RavalNo ratings yet
- Pseudo Differential Multi-Cell Upset Immune Robust SRAM CellDocument20 pagesPseudo Differential Multi-Cell Upset Immune Robust SRAM Cellkazem.khaari77No ratings yet
- Figure 1: 6T CellDocument4 pagesFigure 1: 6T CellShehryarNo ratings yet
- ASIC-System On Chip-VLSI Design - SRAM Cell Design PDFDocument8 pagesASIC-System On Chip-VLSI Design - SRAM Cell Design PDFGowtham SpNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3: RA WADocument12 pagesChapter - 3: RA WADinesh SaiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - 1Document65 pagesUnit 4 - 1sparsh kaudinyaNo ratings yet
- Memory Chapter3Document3 pagesMemory Chapter3zhuoyan xuNo ratings yet
- The Memory System PDFDocument38 pagesThe Memory System PDFMeenu RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Column Decoder Using PTL For Memory: M.Manimaraboopathy, S.Sivasaravanababu, S.Sebastinsuresh A. RajivDocument8 pagesColumn Decoder Using PTL For Memory: M.Manimaraboopathy, S.Sivasaravanababu, S.Sebastinsuresh A. RajivInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Power-Gated 9T SRAM Cell For Low-Energy OperationDocument5 pagesPower-Gated 9T SRAM Cell For Low-Energy OperationShital JoshiNo ratings yet
- Sju SRAM IP For DSPSoC ProjectsDocument50 pagesSju SRAM IP For DSPSoC Projectsraymar2kNo ratings yet
- A Combined DOE-ILP Based Power and Read Stability Optimization in Nano-CMOS SRAMDocument6 pagesA Combined DOE-ILP Based Power and Read Stability Optimization in Nano-CMOS SRAMPrateek SinghalNo ratings yet
- Sram Low Power DecoderDocument7 pagesSram Low Power DecoderKedhar MallaNo ratings yet
- Islamic University of Technology: EEE 4483 Digital Electronics & Pulse TechniquesDocument20 pagesIslamic University of Technology: EEE 4483 Digital Electronics & Pulse TechniquesMUHAMMAD JAWAD CHOWDHURY, 180041228No ratings yet
- Memory and Programmable LogicDocument62 pagesMemory and Programmable LogicChandravadhana NarayananNo ratings yet
- Bipolar SramDocument33 pagesBipolar SramRavinder VijayranNo ratings yet
- SRAM Read Write AssistDocument9 pagesSRAM Read Write AssistpradeepkarraNo ratings yet
- Module 6: Semiconductor Memories Lecture 28: Static Random Access Memory (SRAM)Document6 pagesModule 6: Semiconductor Memories Lecture 28: Static Random Access Memory (SRAM)shireesh12345No ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Low Power 6T SRAM Cell in 180nm and 90nmDocument7 pagesPerformance Analysis of Low Power 6T SRAM Cell in 180nm and 90nmDeepika kNo ratings yet
- Array SubsystemDocument29 pagesArray SubsystemMukesh MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document7 pagesLecture 9skdanso1No ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Sense Amplifiers For Sram IJERTCONV4IS32019Document4 pagesComparative Study of Sense Amplifiers For Sram IJERTCONV4IS32019Bhagyavant HanchinalNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Static Random Access Memory (SRAM)Document6 pages3.1 Static Random Access Memory (SRAM)VigneshInfotechNo ratings yet
- COA Module4Document35 pagesCOA Module4puse1223No ratings yet
- IJERM0204055Document5 pagesIJERM0204055Vishnu KSNo ratings yet
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- Power Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignFrom EverandPower Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignBruno AllardNo ratings yet
- Sinh Tong Hop Rna - 2013Document41 pagesSinh Tong Hop Rna - 2013PhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Huong Dan Giai de Thi Minh Hoa THPT Quoc Gia 2020 Mon Toan Cua Bo Giao Duc Va Dao Tao Lan 2Document29 pagesHuong Dan Giai de Thi Minh Hoa THPT Quoc Gia 2020 Mon Toan Cua Bo Giao Duc Va Dao Tao Lan 2PhiPhiNo ratings yet
- CB Acid BazeDocument25 pagesCB Acid BazePhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Nguyen Ly May Bui Trong Hieu Tong Hop de Thi (Cuuduongthancong - Com)Document23 pagesNguyen Ly May Bui Trong Hieu Tong Hop de Thi (Cuuduongthancong - Com)PhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Ky Thuat Sua Chua Xe Dap DienDocument141 pagesKy Thuat Sua Chua Xe Dap DienPhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Bo de On Thi THPT Quoc Gia 2017 Mon Sinh HocDocument329 pagesBo de On Thi THPT Quoc Gia 2017 Mon Sinh HocPhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Giao Trinh An Toan Lao Dong Trong Xay DungDocument152 pagesGiao Trinh An Toan Lao Dong Trong Xay DungPhiPhiNo ratings yet
- 100 Bài Luận Hay Cho Kỳ Thi ĐHDocument106 pages100 Bài Luận Hay Cho Kỳ Thi ĐHPhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Nguyen Van A: Fanpage: 30 Phút Tiếng Anh Mỗi Ngày Website: Langmaster.Edu.VnDocument1 pageNguyen Van A: Fanpage: 30 Phút Tiếng Anh Mỗi Ngày Website: Langmaster.Edu.VnPhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Nguyen Van A: Fanpage: 30 Phút Tiếng Anh Mỗi Ngày Website: Langmaster.Edu.VnDocument1 pageNguyen Van A: Fanpage: 30 Phút Tiếng Anh Mỗi Ngày Website: Langmaster.Edu.VnPhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Lễ Tân Khách SạnDocument2 pagesLễ Tân Khách SạnPhiPhiNo ratings yet