Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heat Khub Valo Cycle PDF
Heat Khub Valo Cycle PDF
Uploaded by
DipayanSeal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagescycle
Original Title
heat khub valo Cycle.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentcycle
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesHeat Khub Valo Cycle PDF
Heat Khub Valo Cycle PDF
Uploaded by
DipayanSealcycle
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
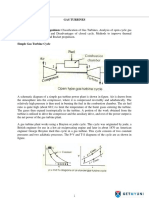
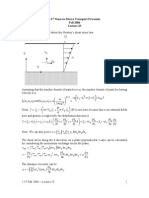
Gas Power Cycles
Prof. U.S.P. Shet , Prof. T. Sundararajan and Prof. J.M . Mallikarjuna
4.9 Lenoir Cycle:
Volume
(a)
2
3
1
Entropy
(b)
Fig.4.9. Lenoir cycle on p-v and T-s diagrams
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Gas Power Cycles
Prof. U.S.P. Shet , Prof. T. Sundararajan and Prof. J.M . Mallikarjuna
The Lenoir cycle consists of the following processes:
Process 1-2: Constant volume heat addition
Process 2-3: Reversible adiabatic expansion
Process 3-4: Constant pressure heat rejection.
No compression process.
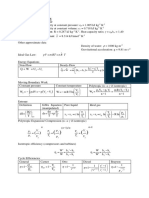
The thermal efficiency can be derived as follows:
th =
C v ( T2 - T1 ) - Cp ( T3 - T1 )
Heat added - Heat rejected
=
Heat added
C v ( T2 - T1 )
T -T
th = 1 - 3 1
T2 - T1
Let,
P2
= rp = Pressure ratio
P1
T2 = rp T1
P
T3
= 3
T2
P2
-1
P
= 1
P2
( )
T3 = T2 rp
1
-1
th
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
-1
1
=
1
( )
= T1 rp rp
1
-1
rp - 1
=1rp - 1
-1
( rp )
( )
= T1 rp
1
-1
You might also like
- Me 2202 Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesMe 2202 Engineering ThermodynamicsDinesh MechNo ratings yet
- Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion 2 Marks All 5 UnitsDocument22 pagesGas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion 2 Marks All 5 UnitsDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap03P061Document22 pagesThermo 5th Chap03P061IENCSNo ratings yet
- Y 240 (3.47) P K Y F PaDocument3 pagesY 240 (3.47) P K Y F PaANER MOHAMED100% (1)
- Single Stage CompressorDocument5 pagesSingle Stage CompressorHaziq HanifahNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab Instructor Manual FinalDocument138 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab Instructor Manual FinalMuhammad Ali100% (1)
- Thermodynamics h2Document209 pagesThermodynamics h2ezoramajnun100% (1)
- Lab Report Triffilliarc PDFDocument17 pagesLab Report Triffilliarc PDFsohail parachaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 FrictionDocument5 pagesTutorial 5 FrictionAjwad HaziqNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Lecture NotesDocument20 pagesIdeal Gas Lecture NotesFlowerNo ratings yet
- RacDocument26 pagesRacgurunakhale123No ratings yet
- HMT - 2 Marks PDFDocument29 pagesHMT - 2 Marks PDFFaiyu MechNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Measurements Lab ManualDocument26 pagesMechanical Measurements Lab ManualseminarprojectNo ratings yet
- Reynold's Number DemonstrationDocument14 pagesReynold's Number DemonstrationKalaiArasanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Advantage of Inclined PlaneDocument4 pagesMechanical Advantage of Inclined PlaneShuja MarwatNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 Solutions - KNLDocument6 pagesAssignment1 Solutions - KNLsaraNo ratings yet
- Free-Samples Amie Chapters Bernoulli S Equation and Their ApplicatiDocument31 pagesFree-Samples Amie Chapters Bernoulli S Equation and Their ApplicatiFei LeeNo ratings yet
- TrifilarDocument11 pagesTrifilarMdnor RahimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Gas DynamicsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Gas DynamicsAswin Varghese TharakanNo ratings yet
- Turbines and Pumps Notes in ThermodynamicsDocument5 pagesTurbines and Pumps Notes in ThermodynamicsJuan HeroNo ratings yet
- The Carnot CycleDocument9 pagesThe Carnot CyclePatrick Antonio Orge ChingNo ratings yet
- Gucor, Rubie-PME 424 Lab. Report 1Document19 pagesGucor, Rubie-PME 424 Lab. Report 1rubie.gucorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Kinematics of Particles Sample ProblemsDocument82 pagesChapter 12 - Kinematics of Particles Sample ProblemsZizhen JiNo ratings yet
- F3 Impact of Jet (Student Copy)Document11 pagesF3 Impact of Jet (Student Copy)Nur Aqilah AdnanNo ratings yet
- Basicthermo Compiled TnshridharDocument129 pagesBasicthermo Compiled Tnshridharsohan2902No ratings yet
- T2 Boyle's Law (Student Copy)Document6 pagesT2 Boyle's Law (Student Copy)afiq9hashim-1100% (1)
- Refrigeration Test Ring.Document12 pagesRefrigeration Test Ring.பிரேம் ஆனந்த்No ratings yet
- 3 Instrumentation - Bridge CircuitsDocument17 pages3 Instrumentation - Bridge CircuitsWanjala WilliamNo ratings yet
- JJ207 Thermodynamic Topic 3 Properties of Pure SubstancesDocument80 pagesJJ207 Thermodynamic Topic 3 Properties of Pure SubstancesAh TiangNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Engg ThermodynamicsDocument47 pagesUnit 1 Engg Thermodynamicsvenkat_mie1080No ratings yet
- Electrical Technology Lab ReportDocument1 pageElectrical Technology Lab ReportHafiffy Kamaruddin100% (1)
- Air ConditioningDocument3 pagesAir ConditioningBoJassim100% (1)
- 4.1 - Understanding Thermal EquilibriumDocument12 pages4.1 - Understanding Thermal EquilibriumsfwongNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Equivalent Circuit Parameters of A Transformer and Calculation of Efficiency and Regulation Using Equivalent CircuitDocument4 pagesDetermination of The Equivalent Circuit Parameters of A Transformer and Calculation of Efficiency and Regulation Using Equivalent CircuitMd Rion100% (1)
- Study of Single Reciprocating Air-CompressorDocument2 pagesStudy of Single Reciprocating Air-Compressorrajivkumardas101No ratings yet
- Estimation of UncertaintiesDocument7 pagesEstimation of UncertaintiesNeelMishraNo ratings yet
- ExperimentsDocument4 pagesExperimentsRohitGuptaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2 E7Document41 pagesThermodynamics 2 E7taya699No ratings yet
- 4 Three Phase Induction Motors 1Document37 pages4 Three Phase Induction Motors 1Terry rickyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Finite Element Method For Solid Mechanics (2016!09!14)Document17 pagesChapter 7 - Finite Element Method For Solid Mechanics (2016!09!14)RickNo ratings yet
- Belt & Rope DrivesDocument26 pagesBelt & Rope Drivesarpit089100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic ConceptsDocument26 pagesChapter 1 Introduction and Basic ConceptsZafirahAhmadFauziNo ratings yet
- External Combustion Engine Valves Gaseous Working Fluid Air Helium HydrogenDocument3 pagesExternal Combustion Engine Valves Gaseous Working Fluid Air Helium HydrogenRakheeb BashaNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer NotesDocument56 pagesApplied Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer NotesS A ABDUL SUKKURNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19-Bulk Deformation Processes IDocument67 pagesChapter 19-Bulk Deformation Processes IMohsin AliNo ratings yet
- CE 02016 p1 24pageDocument93 pagesCE 02016 p1 24pageMd Saiful Islam RajonNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Lab ManualDocument69 pagesDynamics Lab ManualDr. B. Ramesh100% (4)
- Differential Transformation Method for Mechanical Engineering ProblemsFrom EverandDifferential Transformation Method for Mechanical Engineering ProblemsNo ratings yet
- 9 Atkinson CycleDocument3 pages9 Atkinson CyclecaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 4.10 Brayton Cycle (Simple Gas Turbine Cycle) :: Fig.4.10. Brayton Cycle On P-V and T-S DiagramDocument3 pages4.10 Brayton Cycle (Simple Gas Turbine Cycle) :: Fig.4.10. Brayton Cycle On P-V and T-S DiagrammominjeelaniNo ratings yet
- 7 Limited Pressure CycleDocument4 pages7 Limited Pressure CyclecaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics ME250: Submitted ToDocument12 pagesApplied Thermodynamics ME250: Submitted Tomad eye m00dyNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For Exam - April 2022Document5 pagesFormula Sheet For Exam - April 2022philip.groenemeijerNo ratings yet
- Computation of The Compression Factor AnDocument23 pagesComputation of The Compression Factor AnJose Francisco Olivares QuevedoNo ratings yet
- Week 9 NotesDocument2 pagesWeek 9 NotesBowei ZhangNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbines Unit 3: Gas Turbines and Jet Propulsion: Classification of Gas Turbines, Analysis of Open Cycle GasDocument39 pagesGas Turbines Unit 3: Gas Turbines and Jet Propulsion: Classification of Gas Turbines, Analysis of Open Cycle GasJoseph MwansaNo ratings yet
- LS1 - Determination of Jet Velocity and Nozzle EfficiencyDocument9 pagesLS1 - Determination of Jet Velocity and Nozzle EfficiencyfaezahjalalNo ratings yet
- Old Thermo Exam Formula SheetDocument1 pageOld Thermo Exam Formula SheetjonahNo ratings yet
- Handouts PPE Day 3Document4 pagesHandouts PPE Day 3terrence miguel balitaNo ratings yet
- Ideal CyclesDocument2 pagesIdeal CyclesSofia OrjuelaNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Lecture 18Document6 pagesLecture 18captainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004 Guest Lecture by Prof. Mildred S. DresselhausDocument10 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004 Guest Lecture by Prof. Mildred S. DresselhauscaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: F M F F FDocument5 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: F M F F FcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Q FV V: 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document5 pagesQ FV V: 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- Q FV V: 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document7 pagesQ FV V: 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- d dT J Lq L dx dx: q=J (Π - Π) q=J (Π - Π)Document6 pagesd dT J Lq L dx dx: q=J (Π - Π) q=J (Π - Π)captainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document9 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14Document8 pagesLecture 14captainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: I T KXDocument8 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: I T KXcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004 - Lecture 15 Guest Lecture by Prof. DresselhausDocument10 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004 - Lecture 15 Guest Lecture by Prof. DresselhauscaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ae Be CeDocument7 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ae Be CecaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004:) N N N N (NDocument8 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004:) N N N N (NcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document7 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- N F T e U F T F TD D: 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document6 pagesN F T e U F T F TD D: 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: A Wigner-Seitz Primitive Unit CellDocument6 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: A Wigner-Seitz Primitive Unit CellcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: DT Q K T Q DX Q (W/M K (W/M-K) Is Thermal ConductivityDocument5 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: DT Q K T Q DX Q (W/M K (W/M-K) Is Thermal ConductivitycaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ja (j-1) A (j+1) ADocument9 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ja (j-1) A (j+1) AcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: E HN MDocument10 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: E HN McaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: V L KK VKK N VDocument7 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: V L KK VKK N VcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Nlms 2Document7 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Nlms 2captainhassNo ratings yet
- L-05 (GDR) (Et) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document11 pagesL-05 (GDR) (Et) ( (Ee) Nptel)nvnmnitNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-To-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ikn A IkxDocument7 pages2.57 Nano-To-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ikn A IkxcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving On D C Machines PDFDocument16 pagesProblem Solving On D C Machines PDFSelvaraj ParamasivanNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document7 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document6 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Induction Motor: Version 2 EE IIT, KharagpurDocument8 pagesThree-Phase Induction Motor: Version 2 EE IIT, KharagpurHarsh PatelNo ratings yet
- L 07 (GDR) (Et) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document15 pagesL 07 (GDR) (Et) ( (Ee) Nptel)Aneurys DuranNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document8 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- L-44 (GDR) (Et) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document15 pagesL-44 (GDR) (Et) ( (Ee) Nptel)yashaswiyellapragadaNo ratings yet
- Sales Promotion For Reliance Fresh FinalDocument25 pagesSales Promotion For Reliance Fresh FinalSruthz Divakarla100% (1)
- Ap3 Final-Exam EstacioarveeDocument6 pagesAp3 Final-Exam EstacioarveeArvee Rivera EstacioNo ratings yet
- Stuck Pipe Revised 02Document31 pagesStuck Pipe Revised 02BelkhirAouarib100% (2)
- G10 s1 Exam 2016Document10 pagesG10 s1 Exam 2016Roxanne RoxyNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Advertising and PromotionDocument29 pagesUnit 8 Advertising and PromotionAnna ArtamonovaNo ratings yet
- Foww Co-Op Handbook v.1.0 DownloadDocument6 pagesFoww Co-Op Handbook v.1.0 Downloadr4yd3n1No ratings yet
- King of All Days by Hillsong UnitedDocument2 pagesKing of All Days by Hillsong UnitedPaul NietoNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Intro To Proba DistDocument31 pages2.2 Intro To Proba DistQuỳnh Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- MY20 - GLC Coupe - Manual PDFDocument610 pagesMY20 - GLC Coupe - Manual PDFHermawan LesmanaNo ratings yet
- The Eight Extraordinary Qi Vessels and The Twelve Primary Qi ChannelsDocument25 pagesThe Eight Extraordinary Qi Vessels and The Twelve Primary Qi ChannelsJaffer Aftab100% (9)
- 2016 FST 412 Spring Syllabus 3 CRDocument9 pages2016 FST 412 Spring Syllabus 3 CRKenny WuNo ratings yet
- Air Valve CsaDocument1 pageAir Valve Csaمعين عزامNo ratings yet
- Imagery of Light in Abraham Valdelomar'sDocument8 pagesImagery of Light in Abraham Valdelomar'srenatoNo ratings yet
- 1st - 4th Yr Subjects With InstructorDocument6 pages1st - 4th Yr Subjects With InstructorEddie GuiribaNo ratings yet
- PSMA All Members List Region WiseDocument10 pagesPSMA All Members List Region WiseAwais AkramNo ratings yet
- Rail-Steel and Axle-Steel Deformed Bars For Concrete ReinforcementDocument5 pagesRail-Steel and Axle-Steel Deformed Bars For Concrete ReinforcementDarwin DarmawanNo ratings yet
- MCUXpresso SDK API Reference Manual - MKL43Z4Document993 pagesMCUXpresso SDK API Reference Manual - MKL43Z4Deniz KutanNo ratings yet
- GBTS Commissioning Guide (V100R012 - 04) PDFDocument163 pagesGBTS Commissioning Guide (V100R012 - 04) PDFAmine MohamadeNo ratings yet
- Extra Practice Section C: Vocabulary 1Document2 pagesExtra Practice Section C: Vocabulary 1Iggnaciio Moora100% (1)
- IoT Based Car Parking SystemDocument3 pagesIoT Based Car Parking SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Sport - Cardiology Course - Program PDFDocument4 pagesSport - Cardiology Course - Program PDFNico IonaşcuNo ratings yet
- Timbercrete Structural Design-2Document30 pagesTimbercrete Structural Design-2kevin_au18No ratings yet
- Publication PDFDocument44 pagesPublication PDFRika FitriaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map in Tle 7 Subject: Tle Grade Level: Grade 7 TEACHER: Mr. Israel M. MarquezDocument31 pagesCurriculum Map in Tle 7 Subject: Tle Grade Level: Grade 7 TEACHER: Mr. Israel M. MarquezIsrael Marquez0% (1)
- Components of Break-Even Analysis Fixed CostsDocument4 pagesComponents of Break-Even Analysis Fixed CostssuganNo ratings yet
- PDF 20221128 184203 0000Document20 pagesPDF 20221128 184203 0000Ana StolpovencoNo ratings yet
- The Secret To: Japanese SuccessDocument44 pagesThe Secret To: Japanese Successmaria neneng bulakNo ratings yet
- Satisfyer Manual PDFDocument36 pagesSatisfyer Manual PDFOscar TecnobarNo ratings yet
- Sonnet 97 EssayDocument4 pagesSonnet 97 Essaykumar6133No ratings yet