Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fuel Hot Gases: Conventional Gas Turbine (Recalling)
Fuel Hot Gases: Conventional Gas Turbine (Recalling)
Uploaded by
gthulasi7871260 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views5 pagesThe document describes compressed air energy storage (CAES). It discusses how air is compressed and stored in reservoirs, then expanded through a turbine to release the stored energy during periods of peak demand. It also explains how the heat from compression can be retained in the compressed air or another medium, allowing it to be returned before expansion, which improves efficiency.
Original Description:
EnergyStorage
Original Title
EnergyStorage-1.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes compressed air energy storage (CAES). It discusses how air is compressed and stored in reservoirs, then expanded through a turbine to release the stored energy during periods of peak demand. It also explains how the heat from compression can be retained in the compressed air or another medium, allowing it to be returned before expansion, which improves efficiency.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views5 pagesFuel Hot Gases: Conventional Gas Turbine (Recalling)
Fuel Hot Gases: Conventional Gas Turbine (Recalling)
Uploaded by
gthulasi787126The document describes compressed air energy storage (CAES). It discusses how air is compressed and stored in reservoirs, then expanded through a turbine to release the stored energy during periods of peak demand. It also explains how the heat from compression can be retained in the compressed air or another medium, allowing it to be returned before expansion, which improves efficiency.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Conventional gas turbine (recalling)
fuel
compressed
air
Compressor
Combustion
Chamber
hot
gases
Gas
Turbine
Gen
fresh
air
Prof. R. Shanthini
09 Feb 2013
gases
to the
stack
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)
The above shown CAES system that operates with the excess
generation of a wind farm.
Prof. R. Shanthini
09 Feb 2013
http://www.sc.ehu.es/sbweb/energias-renovables/temas/almacenamiento/almacenamiento.html
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)
Air is compressed and stored in reservoirs, aquifers or
underground cavities.
The stored energy is released during periods of peak demand,
expanding the air through a turbine.
When air is compressed for storage, its temperature will
increase according to
P2
T2 T1
P1
( k 1)
where T is the temperature, P is the pressure, k is the polytropic index of
the expansion, and subscripts 1 and 2 indicate the initial and final state
of compression, respectively.
Prof. R. Shanthini
09 Feb 2013
http://www.sc.ehu.es/sbweb/energias-renovables/temas/almacenamiento/almacenamiento.html
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)
The heat generated can be retained in the compressed air or
in another heat storage medium.
This way, heat can be returned to the air before its expansion
in the turbine.
This method is called adiabatic storage system and achieves
a high efficiency.
However, if the heat generated in compression is lost,
additional heat must be supplied to the air by burning a fuel.
In general, for a given pressure ratio, the work of the turbine is
directly proportional to the absolute temperature of admission.
Prof. R. Shanthini
09 Feb 2013
http://www.sc.ehu.es/sbweb/energias-renovables/temas/almacenamiento/almacenamiento.html
Flywheel Energy Storage (FES)
Conventional flywheel
Prof. R. Shanthini
09 Feb 2013
You might also like
- Two-Stage Air CompressorDocument31 pagesTwo-Stage Air CompressorEjad Afifi33% (3)
- Compressors TeoriDocument41 pagesCompressors TeoriMarcel MrcNo ratings yet
- Tors Assignment 2Document14 pagesTors Assignment 2Leonard ZammitNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Central SystemDocument7 pagesGeothermal Central SystemPaul KwongNo ratings yet
- Super Charging AllisonDocument26 pagesSuper Charging AllisonJonathan Ivor Coetzer100% (4)
- Secondary Air Damper Control in BoilerDocument10 pagesSecondary Air Damper Control in BoilerSourav DasNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air Energy StorageDocument29 pagesCompressed Air Energy StorageharshaNo ratings yet
- Earth BatteryDocument55 pagesEarth BatteryHaris AvNo ratings yet
- Doas DesignDocument4 pagesDoas DesignBill ChambersNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Refrigeration System Utilizing Waste Heat On A ShipDocument49 pagesAnalysis of Refrigeration System Utilizing Waste Heat On A ShipEmmanuel KingsNo ratings yet
- Underground Gas Storage Facilities: Design and ImplementationFrom EverandUnderground Gas Storage Facilities: Design and ImplementationNo ratings yet
- Cold Storage Uses LNG - Design StudyDocument10 pagesCold Storage Uses LNG - Design StudyRatri IrawantiNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Phillips Optimized Cascade and Apci Propane Pre-Cooled Mixed Refrigerant LNG Liquefaction ProcessesDocument8 pagesA Comparative Study of Phillips Optimized Cascade and Apci Propane Pre-Cooled Mixed Refrigerant LNG Liquefaction ProcessesVanessa Ada ElokaNo ratings yet
- Expansion Tank SizingDocument2 pagesExpansion Tank SizingSK NGNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air Energy StorageDocument29 pagesCompressed Air Energy StoragePradeep100% (1)
- Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)Document5 pagesCompressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Maintenance in Our NeighborhoodDocument4 pagesMaintenance in Our NeighborhoodtourramisNo ratings yet
- E Ects of Porous Media Insert On The E Ciency and Power Density High Pressure (210 Bar) Liquid Piston Air Compressor/Expander - An Experimental StudyDocument18 pagesE Ects of Porous Media Insert On The E Ciency and Power Density High Pressure (210 Bar) Liquid Piston Air Compressor/Expander - An Experimental StudyparamopedroNo ratings yet
- Above Ground CAESDocument9 pagesAbove Ground CAESzain ul AbideenNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Energy Storage Alami CAESDocument19 pagesMechanical Energy Storage Alami CAESAndrea La FiuraNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Process in Oil and Gas IndustryDocument20 pagesRefrigeration Process in Oil and Gas IndustrysanjayNo ratings yet
- Caes TechnologyDocument14 pagesCaes TechnologyAnjeri PhelestusNo ratings yet
- About Heat PumpsDocument4 pagesAbout Heat Pumpssumit gulatiNo ratings yet
- Energies 12 00493Document18 pagesEnergies 12 00493abubakar chohaanNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Energy 2019 115993Document37 pages10 1016@j Energy 2019 115993iksan001maulNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage: Mar Ia Soledad Meza CarrilloDocument5 pagesEnergy Storage: Mar Ia Soledad Meza CarrilloSoleMezaNo ratings yet
- Organic Rankine CycleDocument8 pagesOrganic Rankine CycleAytaç ŞanlısoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter One 1.0 Introdiction History of Air Conditioning SystemDocument79 pagesChapter One 1.0 Introdiction History of Air Conditioning Systemikperha jomafuvweNo ratings yet
- Havel - EESAT PaperDocument6 pagesHavel - EESAT PapertfhavelNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics-Ii: Project: Compressed Air EngineDocument7 pagesThermodynamics-Ii: Project: Compressed Air EngineShahzaib Anwar OffNo ratings yet
- Overview of Current Development On Compressed Air Energy Storage - EERA Report 20131 PDFDocument39 pagesOverview of Current Development On Compressed Air Energy Storage - EERA Report 20131 PDFAndrea La FiuraNo ratings yet
- Paper2 Parcial2Document7 pagesPaper2 Parcial2Ishmail VillaNo ratings yet
- A Theoretical and Experimental Study of A Small-Scale Steam Jet RefrigeratorDocument9 pagesA Theoretical and Experimental Study of A Small-Scale Steam Jet RefrigeratorvahidnodetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Refrigeration CyclesDocument14 pagesChapter 10: Refrigeration CyclesGhulam AbbasNo ratings yet
- Tekpanlan Air CompressionDocument2 pagesTekpanlan Air CompressionLiza KandelNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document28 pagesModule 2Naveen S BasandiNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Natural Gas, Optimization of Cogeneration/ Combined Cycle Applications in Campus EnvironmentDocument2 pagesUtilization of Natural Gas, Optimization of Cogeneration/ Combined Cycle Applications in Campus EnvironmentOscar Karim Zapata LiceaNo ratings yet
- Conversion Gate01Document8 pagesConversion Gate01karim karimNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Vehicles 2Document2 pagesHybrid Vehicles 2arif99pakNo ratings yet
- CH - 1Document6 pagesCH - 1Mohamed AbdelRazekNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion and Management: Erren Yao, Huanran Wang, Ligang Wang, Guang Xi, François MaréchalDocument11 pagesEnergy Conversion and Management: Erren Yao, Huanran Wang, Ligang Wang, Guang Xi, François MaréchalrendiNo ratings yet
- Epe 2013101410304374Document5 pagesEpe 2013101410304374Pisindu DanushaNo ratings yet
- Operaciones PT Entrega1Document7 pagesOperaciones PT Entrega1juanita_hidalgoNo ratings yet
- Energy and Exergy Analyses of Cold Thermal Storage Systems: Int. J. Energy Res., 23, 1029) 1038 (1999)Document10 pagesEnergy and Exergy Analyses of Cold Thermal Storage Systems: Int. J. Energy Res., 23, 1029) 1038 (1999)Lia FitrianiNo ratings yet
- ICE-E Info Pack 1 Refrigerant CyclesDocument4 pagesICE-E Info Pack 1 Refrigerant Cycleslethanhvan186No ratings yet
- Ans 1 (A) P-V DiagramDocument4 pagesAns 1 (A) P-V DiagramPardeep8056No ratings yet
- EE Mod2@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument27 pagesEE Mod2@AzDOCUMENTS - inAishwarya ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- REFRIGERATION EarlyDocument21 pagesREFRIGERATION EarlyIrfan FajriNo ratings yet
- AC in An AircraftDocument19 pagesAC in An Aircraftchrisss220No ratings yet
- 2-2 Te-2 GTDocument10 pages2-2 Te-2 GTVamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Technical Review On Study of Compressed Air Vehicle (Cav) : Hemant Kumar Nayak, Devanshu Goswami & Vinay HablaniDocument10 pagesTechnical Review On Study of Compressed Air Vehicle (Cav) : Hemant Kumar Nayak, Devanshu Goswami & Vinay HablaniasasdNo ratings yet
- Conjugate Heat Transfer in AirtoRefrigerant Airfoil Heat ExchangersDocument12 pagesConjugate Heat Transfer in AirtoRefrigerant Airfoil Heat ExchangersMohammed AshiqueNo ratings yet
- Performance Assessment of Wet-Compression Gas Turbine Cycle With Turbine Blade CoolingDocument5 pagesPerformance Assessment of Wet-Compression Gas Turbine Cycle With Turbine Blade Coolingasp9924No ratings yet
- Design, Construction and Testing of An Air-Cycle Refrigeration System For Road TransportDocument8 pagesDesign, Construction and Testing of An Air-Cycle Refrigeration System For Road TransportRafael Andres Albuja Del ValleNo ratings yet
- 2000 Displacement VentilationDocument10 pages2000 Displacement VentilationJavier BaronaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Refrigeration and Air Conditioning PDFDocument5 pagesThesis Refrigeration and Air Conditioning PDFaprilbellhartford100% (3)
- Turbojet EngineDocument33 pagesTurbojet EngineAqish ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Hydronic RecoveryDocument4 pagesHydronic RecoveryKhizerNo ratings yet
- Projet in BriefDocument3 pagesProjet in BriefRavi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Field Of A Sheet Of Charge: Adding the effects of all the strips; dy' ρDocument5 pages2.5 Field Of A Sheet Of Charge: Adding the effects of all the strips; dy' ρgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- 01maxwells Equations5Document5 pages01maxwells Equations5gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations (SI Units) Differential Form: Density of ChargesDocument7 pagesMaxwell's Equations (SI Units) Differential Form: Density of Chargesgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Electromagnetics 1 PDFDocument4 pagesElectromagnetics 1 PDFgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations (SI Units) Differential Form: Density of ChargesDocument3 pagesMaxwell's Equations (SI Units) Differential Form: Density of Chargesgthulasi787126No ratings yet
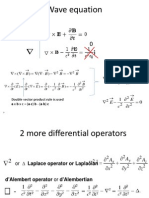
- Differential Operators: A A A A X y ZDocument3 pagesDifferential Operators: A A A A X y Zgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Displacement Current & Maxwell's EquationsDocument4 pagesDisplacement Current & Maxwell's Equationsgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Electric and Magnetic Fields and UnitsDocument3 pagesElectric and Magnetic Fields and Unitsgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Maxwell - Equations 2Document6 pagesMaxwell - Equations 2gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- With This Terminology, We Can Say That:: Line Integrals of Conservative Vector Fields Are Independent of PathDocument6 pagesWith This Terminology, We Can Say That:: Line Integrals of Conservative Vector Fields Are Independent of Pathgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Engine Sealing, Gaskets, and Fastener Torque: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocument5 pagesEngine Sealing, Gaskets, and Fastener Torque: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learninggthulasi787126No ratings yet
- The Following Theorem Says That The Only Vector Fields That Are Independent of Path Are ConservativeDocument4 pagesThe Following Theorem Says That The Only Vector Fields That Are Independent of Path Are Conservativegthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Maxwell - Equations 1Document5 pagesMaxwell - Equations 1gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Choose Any Point (X, Y) in The Disk With X X.: Conservative Vector FieldDocument4 pagesChoose Any Point (X, Y) in The Disk With X X.: Conservative Vector Fieldgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- As Is Independent of Path, It Does Not Matter Which Path C From (A, B) To (X, Y) Is Used To Evaluate F (X, Y)Document5 pagesAs Is Independent of Path, It Does Not Matter Which Path C From (A, B) To (X, Y) Is Used To Evaluate F (X, Y)gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Lithium Ion (Li-Ion) Batteries: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013Document5 pagesLithium Ion (Li-Ion) Batteries: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- We Assume That D Is Open - Which Means That, For Every Point P in D, There Is A Disk With Center P That Lies Entirely in DDocument4 pagesWe Assume That D Is Open - Which Means That, For Every Point P in D, There Is A Disk With Center P That Lies Entirely in Dgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Most Computer Algebra Systems (CAS) Have Commands That Compute The Curl and Divergence of Vector FieldsDocument5 pagesMost Computer Algebra Systems (CAS) Have Commands That Compute The Curl and Divergence of Vector Fieldsgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Notice The Similarity To What We Know From Section 12.4:: A X A 0 For Every Three-Dimensional (3-D)Document5 pagesNotice The Similarity To What We Know From Section 12.4:: A X A 0 For Every Three-Dimensional (3-D)gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- F I J K: X y Z P Q R R Q P R Q P y Z Z X X yDocument6 pagesF I J K: X y Z P Q R R Q P R Q P y Z Z X X ygthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Nickel Metal Hydride (Nimh) Batteries: H) 2 / 1 (Oh E 2 MM O HDocument3 pagesNickel Metal Hydride (Nimh) Batteries: H) 2 / 1 (Oh E 2 MM O Hgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Nickel Cadmium (Nicd) Batteries: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013Document5 pagesNickel Cadmium (Nicd) Batteries: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Sodium Sulphur (Nas) BatteriesDocument4 pagesSodium Sulphur (Nas) Batteriesgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Vector CalculusDocument6 pagesVector Calculusgthulasi787126No ratings yet
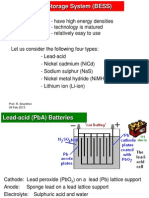
- Lead-Acid (Pba) Batteries: DrawbacksDocument5 pagesLead-Acid (Pba) Batteries: Drawbacksgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Energy Storage 5Document5 pagesEnergy Storage 5gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Battery Electric Storage System (BESS) : - Have High Energy Densities - Technology Is Matured - Relatively Easy To UseDocument6 pagesBattery Electric Storage System (BESS) : - Have High Energy Densities - Technology Is Matured - Relatively Easy To Usegthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Energy Storage 2Document4 pagesEnergy Storage 2gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Flywheel Energy Storage (FES)Document6 pagesFlywheel Energy Storage (FES)gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Mechanical Energy Storage-1Document4 pagesMechanical Energy Storage-1gthulasi787126No ratings yet