Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Continuous Assessment 2
Uploaded by
SamCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Continuous Assessment 2
Uploaded by
SamCopyright:
Available Formats
MHJ920505:
Renewable Energy Technology
CW2: Impact of Embedded Generation on the performance Indices of
power system
Allocation of marks:- a-60%, b-40%,
1. Hand-in date: 15th April 2016
The core of your report should not be longer than 4 pages (excluding results/figures) and also
ensure title of coursework, date, your name and matriculation number are included on the front
cover.
2. Introduction
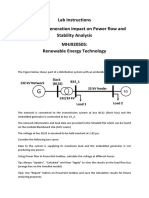
The Figure below shows part of a distribution system with an embedded generator (EG).
The network information and load data are provided in the model which can be found on the
module Blackboard site (GCU Learn).
The voltage at bus B132 (Slack) is assumed to be held constant at 1.02 pu.
3. Tasks
(a)
Consider the following cases:
Case 1) The system is supplying its maximum load and the embedded generator is not
producing any power
Case 2) The system is supplying its minimum load to load 2( which is 20 % of the maximum
load ) and the embedded generator is not producing any power
Case 3) The system is supplying its maximum load and the embedded generator is producing
30 MW active power.
Case 4) The system is supplying its minimum load to load 2( which is 20 % of the maximum
load) and the embedded generator is producing 30MW active power.
I.
Using Power flow in PowerGUI toolbox, calculate the voltage at different buses.
II.
If 5% variation from nominal voltage is acceptable, find the appropriate tap position
of transformer to satisfy this condition.
III.
IV.
Observe the voltage at different bus bars and critically analyze the results.
Using report in Load flow tool, obtain the total production and consumption of
active and reactive power at the network in cases 1 and 3 . Then conclude the active
and reactive power losses in these two cases. Compare and critically analyze the
results.
(b)
Using the power flow tool change the amount of the generated power from EG unit from 0 to
30 MW using steps of 5MW.
I.
II.
III.
Plot the active loss and loading of feeder 33kV versus the EG power generation.
Using smaller steps (1MW) determine the amount of power generation for which
there is no active power flow from B33_1 toward B33_2.
Determine the first hosting capacity when active power losses is a performance index
You might also like
- Lab Instructions 1Document3 pagesLab Instructions 1SamNo ratings yet
- Techno NJR Institute of TechnologyDocument4 pagesTechno NJR Institute of TechnologyIrfanNo ratings yet
- PSASghhggdvDocument6 pagesPSASghhggdvDarshan GowdaNo ratings yet
- KL University Power System Operation & Control AssignmentDocument2 pagesKL University Power System Operation & Control AssignmentVijaya Aditya TadepalliNo ratings yet
- QP Nov - 2010 4 1 Eee PsocDocument8 pagesQP Nov - 2010 4 1 Eee PsocMohammed AlhakeemiNo ratings yet
- IJIRTSV3I2038Document5 pagesIJIRTSV3I2038Tom LoveuNo ratings yet
- EE2404 Power System Simulation Lab ProgramsDocument121 pagesEE2404 Power System Simulation Lab ProgramsSachin Samy0% (1)
- Impact of renewable DG on power systems boundariesDocument10 pagesImpact of renewable DG on power systems boundariesFelipe Antonio SilvaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Power System Economic OperationDocument3 pagesLab 1 - Power System Economic OperationMd Anisur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Emergency Generator Sizing and Motor Starting Analysis: Mukesh Kumar Kirar, Ganga AgnihotriDocument6 pagesEmergency Generator Sizing and Motor Starting Analysis: Mukesh Kumar Kirar, Ganga Agnihotribalwant_negi7520No ratings yet
- X10407EE8702 WatermarkDocument4 pagesX10407EE8702 WatermarkP.Barani Tharan -EEENo ratings yet
- Detailed Analysis of Micro-Grid Stability During Islanding Mode Under Different Load ConditionsDocument9 pagesDetailed Analysis of Micro-Grid Stability During Islanding Mode Under Different Load ConditionsDulal MannaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Nigerian Grid Using MATLABDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Nigerian Grid Using MATLABOgunranti RasaqNo ratings yet
- Challenges_and_Opportunities_of_Rooftop - CopyDocument9 pagesChallenges_and_Opportunities_of_Rooftop - CopyYousup AliNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document21 pagesAssignment 1Ayub Machiri100% (1)
- Investigation On The Dual Functions of Generator As Reactive Power SupportDocument5 pagesInvestigation On The Dual Functions of Generator As Reactive Power SupportJAMESJANUSGENIUS5678No ratings yet
- Emergency Generator Sizing and Motor Starting AnalysisDocument6 pagesEmergency Generator Sizing and Motor Starting AnalysisK.RamachandranNo ratings yet
- 1final Iete - Forth Revision1Document10 pages1final Iete - Forth Revision1Dr. Monika JainNo ratings yet
- Dynamic CompensationDocument6 pagesDynamic Compensationhiabhijit29No ratings yet
- Losses in Electrical Power System Arpapress CompressDocument8 pagesLosses in Electrical Power System Arpapress CompressJean Baptiste nkongoloNo ratings yet
- Ece550 Hw4 AGC f4Document2 pagesEce550 Hw4 AGC f4Swaroop MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Protection and Design of Distributed Energy Generation System (Microgrid)Document6 pagesProtection and Design of Distributed Energy Generation System (Microgrid)Neha BandhuNo ratings yet
- Btech Ee 7 8 Sem Power System Operation and Control A3035 Dec 2018Document2 pagesBtech Ee 7 8 Sem Power System Operation and Control A3035 Dec 2018Raj KamalNo ratings yet
- ECE666 Final Exam 2018 PDFDocument14 pagesECE666 Final Exam 2018 PDFAhmed Khairi100% (1)
- Faculty of EngineeringDocument2 pagesFaculty of Engineeringavinashavi93No ratings yet
- Marine and Offshore Report FinalDocument42 pagesMarine and Offshore Report FinalhasaladNo ratings yet
- Mitigation of Power System Transients in A Multi - Machine System Using STATCOMDocument11 pagesMitigation of Power System Transients in A Multi - Machine System Using STATCOMIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Stat Com SimDocument8 pagesStat Com SimmakroumNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6Document3 pagesAssignment 6ksajj0% (2)
- International Journal of Engineering Research and DevelopmentDocument9 pagesInternational Journal of Engineering Research and DevelopmentIJERDNo ratings yet
- Inverter Based DG Fault CalculationDocument13 pagesInverter Based DG Fault CalculationhassanNo ratings yet
- CDM - Executive Board: Unfccc/CcnuccDocument33 pagesCDM - Executive Board: Unfccc/CcnuccAshokreddy VajralaNo ratings yet
- Psoc-Essay QuestionsDocument2 pagesPsoc-Essay Questionsnarendra kumarNo ratings yet
- Power System Operation QuestionDocument7 pagesPower System Operation QuestionMATHANKUMAR.S100% (1)
- 5th Sem AssignmentDocument6 pages5th Sem AssignmentApoorv Singhal0% (1)
- EXP3 - Symmetrical Fault AnalysisDocument15 pagesEXP3 - Symmetrical Fault AnalysisLee Boon HongNo ratings yet
- PGOC Sample QuestionsDocument2 pagesPGOC Sample Questions2041016166.sourashishpatraNo ratings yet
- Power Flow Analysis of A Continuous Process Plant: (A Case Study)Document4 pagesPower Flow Analysis of A Continuous Process Plant: (A Case Study)hafizgNo ratings yet
- Power System ReliabilityDocument1 pagePower System ReliabilitySrikanth KallakuriNo ratings yet
- Effect of Partial Shading in Grid Connected Solar PV System With FL ControllerDocument10 pagesEffect of Partial Shading in Grid Connected Solar PV System With FL ControllerPtuan ThanhNo ratings yet
- Igbt Based On Vector Control of Induction Motor DriveDocument8 pagesIgbt Based On Vector Control of Induction Motor DriveesatjournalsNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Technical Innovation in Morden Engineering & Science (IJTIMES)Document8 pagesInternational Journal of Technical Innovation in Morden Engineering & Science (IJTIMES)ijtimesNo ratings yet
- Autonomous Three-Phase Induction Generator Supplying Unbalanced LoadsDocument6 pagesAutonomous Three-Phase Induction Generator Supplying Unbalanced Loadsamit621988No ratings yet
- Power System Operation ControlDocument4 pagesPower System Operation Controlvidya_vihar666No ratings yet
- Control Design of Photovoltaic BPSX-60 Using Fuzzy Logic Controller For Low Voltage GridDocument4 pagesControl Design of Photovoltaic BPSX-60 Using Fuzzy Logic Controller For Low Voltage GridMuhammad Reza ImaduddinNo ratings yet
- Suliman Khan, Salim Ur Rehman, Anees Ur Rehman, Hashmat KhanDocument13 pagesSuliman Khan, Salim Ur Rehman, Anees Ur Rehman, Hashmat KhanResky TulfaidahNo ratings yet
- Arduino-based embedded system design and programmingDocument15 pagesArduino-based embedded system design and programmingbinu_10No ratings yet
- Voltage Control Scheme Using Fuzzy LogicDocument6 pagesVoltage Control Scheme Using Fuzzy Logicstudent_ujjwol3163No ratings yet
- Ijest10 02 12 227Document7 pagesIjest10 02 12 227Aroma AamirNo ratings yet
- PSOC Mid 1 QuestionsDocument7 pagesPSOC Mid 1 Questions3nathNo ratings yet
- EET-3415-POWER-SYSTEMS-II- (1)Document3 pagesEET-3415-POWER-SYSTEMS-II- (1)bernardmwangi055No ratings yet
- ECX 4252 AssignmentsDocument6 pagesECX 4252 AssignmentsisuruNo ratings yet
- Improved Grid Integration of Wind Energy SystemDocument5 pagesImproved Grid Integration of Wind Energy SystemVutrieu DinhNo ratings yet
- Understanding Power Quality Based FACTS Using Interactive Educational GUI Matlab PackageDocument24 pagesUnderstanding Power Quality Based FACTS Using Interactive Educational GUI Matlab PackageRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Solar PV PlantDocument9 pagesSolar PV PlantPrashant TrivediNo ratings yet
- Psoc Grand Test-1 QPDocument2 pagesPsoc Grand Test-1 QPsatish reddyNo ratings yet
- Modellinag & Simulation With MiPowerDocument5 pagesModellinag & Simulation With MiPowerAkshay SharmaNo ratings yet
- EE655 Tutorial4 2010Document2 pagesEE655 Tutorial4 2010Devendra PatilNo ratings yet
- Design and Testing of Low Cost Solar Power InverterDocument6 pagesDesign and Testing of Low Cost Solar Power InverterInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- Refelction Report 5th YearDocument27 pagesRefelction Report 5th YearSamNo ratings yet
- Environmental IssuesDocument1 pageEnvironmental IssuesSamNo ratings yet
- DougieDocument1 pageDougieSamNo ratings yet
- CostaDocument1 pageCostaSamNo ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument2 pagesReferencesSamNo ratings yet
- Coursework Cover Sheet: School of Engineering and Built EnvironmentDocument1 pageCoursework Cover Sheet: School of Engineering and Built EnvironmentSamNo ratings yet
- Past Exams Tors Vibs and Solns 1516Document20 pagesPast Exams Tors Vibs and Solns 1516SamNo ratings yet
- Wave Power Feasibility Report for 5000 Household TownDocument1 pageWave Power Feasibility Report for 5000 Household TownSamNo ratings yet
- Dr D R Gordon Matrix Analysis Exam Solutions 2015-16Document35 pagesDr D R Gordon Matrix Analysis Exam Solutions 2015-16Sam100% (2)
- Past Exams Lefm and Solns 1516Document35 pagesPast Exams Lefm and Solns 1516SamNo ratings yet
- ManMat3 CW FlowchartDocument2 pagesManMat3 CW FlowchartSamNo ratings yet
- MyresHill (Trial)Document3 pagesMyresHill (Trial)SamNo ratings yet
- Continuous Assessment 1-HandoutDocument3 pagesContinuous Assessment 1-HandoutSamNo ratings yet
- Man Mat Potential Coursework HelpDocument3 pagesMan Mat Potential Coursework HelpSamNo ratings yet
- Measuring straightness with an autocollimatorDocument4 pagesMeasuring straightness with an autocollimatorSamNo ratings yet
- Refelction Report 5th YearDocument27 pagesRefelction Report 5th YearSamNo ratings yet
- POP Assessment 1 SpreadsheetDocument2 pagesPOP Assessment 1 SpreadsheetSamNo ratings yet
- Model AnswerDocument88 pagesModel AnswerSamNo ratings yet
- ECT - Exam (Practice 2 - SV) 2014-2015Document10 pagesECT - Exam (Practice 2 - SV) 2014-2015SamNo ratings yet