Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anti-TB Drugs
Uploaded by
Mohd Fadhli0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
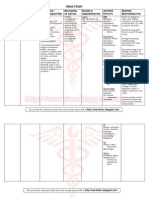
23 views1 pageThis document summarizes common side effects and management strategies for several drugs used to treat tuberculosis, including rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, ethambutol, streptomycin, amikacin, and capreomycin. Side effects include rash, liver dysfunction, flulike symptoms, urine discoloration, drug interactions, fever, hepatitis, neuropathy, seizures, and ototoxicity. Management involves monitoring for side effects through lab tests and patient education, limiting dosages, and stopping the drug if side effects appear.
Original Description:
Original Title
Anti-TB drugs
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes common side effects and management strategies for several drugs used to treat tuberculosis, including rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, ethambutol, streptomycin, amikacin, and capreomycin. Side effects include rash, liver dysfunction, flulike symptoms, urine discoloration, drug interactions, fever, hepatitis, neuropathy, seizures, and ototoxicity. Management involves monitoring for side effects through lab tests and patient education, limiting dosages, and stopping the drug if side effects appear.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views1 pageAnti-TB Drugs
Uploaded by
Mohd FadhliThis document summarizes common side effects and management strategies for several drugs used to treat tuberculosis, including rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, ethambutol, streptomycin, amikacin, and capreomycin. Side effects include rash, liver dysfunction, flulike symptoms, urine discoloration, drug interactions, fever, hepatitis, neuropathy, seizures, and ototoxicity. Management involves monitoring for side effects through lab tests and patient education, limiting dosages, and stopping the drug if side effects appear.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
DRUGS SIDE EFFECTS MANAGEMENT
Rash Observe patient/stop drug if significant
Liver dysfunction Monitor AST/limit alcohol consumption/monitor for hepatitis symptoms
Flulike syndrome Administer at least twice weekly/limit dose to 10 mg/kg (adults)
Red-orange urine Reassure patient
Drug interactions (induce P450 - ↑ elimination
RIFAMPIN
anticoagulant & contraceptive; ↑ urinary excretion of Consider monitoring levels of other drugs affected by rifampin, especially with
methadone – precipitate methadone withdrawal; contraceptives, anticoagulants, and digoxin / avoid use with protease inhibitors
pseudomembranous colitis)
Fever, chills Stop drug
Light-chain protenuria
Monitor AST/limit alcohol consumption/monitor for hepatitis symptoms /
Hepatitis educate patient / stop drug at first symptoms of hepatitis (nausea, vomiting,
ISONIAZID anorexia, flulike syndrome)
(cause pyridoxine Peripheral neuritis Administer vitamin B6
deficiency due to Optic neuritis Administer vitamin B6/stop drug
competition with Seizures; insomnia; restlessness; urinary retention;
Administer vitamin B6
pyridoxal phosphate psychoses
for enzyme Allergy – fever; skin rash
apotryptophanase) Hemolysis in G6PD deficiency
Inhibit metabolism of Phenytoin
SLE-like syndrome
Monitor AST/limit daily dosage to 15–30 mg/kg/discontinue with signs or
Hepatitis symptoms of
PYRAZINAMIDE
hepatitis
Hyperuricemia
Monitor uric acid level only in cases of gout or renal failure
(inhibit uric acid excretion by kidney)
Use 25 mg/kg daily only for first 2 months (except in drug-resistant
Optic neuritis tuberculosis), then use lower daily dose (15 mg/kg) when possible / monitor
ETHAMBUTOL
(+ red-green colour blindness; reduce visual acuity; visual acuity (eye chart) and red-green color vision (Ishihara Color Book) at
retinal damage) baseline and with any visual complaint / educate patient / stop drug at first
change in vision, get ophthalmologic evaluation
Limit dose and duration of therapy as much as possible/avoid daily therapy in
patients >50 years old/monitor BUN and serum creatinine levels and possibly
STREPTOMYCIN,
conduct audiometry before and as needed during therapy/question patient
AMIKACIN, Ototoxicity, renal toxicity
regularly about tinnitus, dizziness, vertigo, and decreased hearing/measure
CAPREOMYCIN
serum drug levels if possible/educate patient/stop drug at first development of
adverse effect (usually tinnitus)
You might also like
- Medication CardsDocument5 pagesMedication CardsAndrew Harrison Lewis0% (1)
- Trade/Generic Name Classification Action of Medication Dosage/Route/ Frequency Indications For Use (Patient Specific)Document16 pagesTrade/Generic Name Classification Action of Medication Dosage/Route/ Frequency Indications For Use (Patient Specific)lightzapNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyRye IbarraNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument1 pageAcetazolamideKyuSheenNo ratings yet
- Medication Cards Table Form Up To p.38Document38 pagesMedication Cards Table Form Up To p.38enf.mayara90No ratings yet
- Anti TB Drug TableDocument2 pagesAnti TB Drug TableMuba ShirNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic DrugsDocument43 pagesAntiepileptic DrugsdrpraneethpremkumarNo ratings yet
- Camuso OtcDocument15 pagesCamuso Otcapi-548307464No ratings yet
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingDocument1 pageAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Anti-Tuberculosis AgentsDocument15 pagesAnti-Tuberculosis AgentsNick van ExelNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument43 pagesDrug Studyapi-3818438100% (2)
- PRN Medications: Indications & UseDocument23 pagesPRN Medications: Indications & Usedis_is_me100% (1)
- Adverse Drug ReactionsDocument29 pagesAdverse Drug ReactionsMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- AcetaminophenDocument3 pagesAcetaminophenShaira Tan100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY Week 4Document4 pagesDRUG STUDY Week 4Sheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Medication Sheet TMDocument4 pagesMedication Sheet TMapi-544317178No ratings yet
- 7-Lipid DisorderDocument6 pages7-Lipid DisorderApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShane Arroyo100% (1)
- Atazanavir SulfateDocument5 pagesAtazanavir SulfateGLen CaniedoNo ratings yet
- IsoniazidDocument2 pagesIsoniazidMichael Kuzbyt100% (1)
- Furosemide HaloperidolDocument6 pagesFurosemide HaloperidolLady Lou ArmadaNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument13 pagesDrugsJune DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- BenazeprilDocument2 pagesBenazeprilFeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- Year 2: PBL 2: JaundiceDocument74 pagesYear 2: PBL 2: JaundiceyaneemayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyDiana Laura LeiNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide (Reglan)Document1 pageMetoclopramide (Reglan)ENo ratings yet
- Anti Tuberculosis AgentsDocument15 pagesAnti Tuberculosis Agentsejg26100% (1)
- Drug Study For SLEDocument28 pagesDrug Study For SLERomwella May AlgoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - IbuprofenDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Ibuprofenanon-326479No ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Setera Case 8Document10 pagesDRUG STUDY Setera Case 8Ceria Dorena Fe SeteraNo ratings yet
- MM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM MDocument9 pagesMM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM M배기숭No ratings yet
- Prescribed Medication: Information Leaflet PriorDocument4 pagesPrescribed Medication: Information Leaflet PriorHavier EsparagueraNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations ParacetamolDocument7 pagesName of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations ParacetamolAnne Monique Moran OngjocoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument43 pagesDrug StudyMamot MotNo ratings yet
- Medication Generic/Brand Classification Nursing Implications (3) Dosage Route Schedule /time Desired Effect Side Effects (3) TeachingDocument5 pagesMedication Generic/Brand Classification Nursing Implications (3) Dosage Route Schedule /time Desired Effect Side Effects (3) TeachingrunnermnNo ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis Drug TherapyDocument2 pagesMultiple Sclerosis Drug Therapyampogison08No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyKyle Margaret FloresNo ratings yet
- HF and CAD Case ScenarioDocument17 pagesHF and CAD Case ScenarioElla Neiza AngelesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CompilationDocument9 pagesDrug Study CompilationRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- HI Drug Study - v.3Document13 pagesHI Drug Study - v.3Mary Claire AbenidoNo ratings yet
- Verapamil HCLDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- LisinoprilDocument3 pagesLisinoprilLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Drug Study TBDocument5 pagesDrug Study TBSanvar Mal SoniNo ratings yet
- Mobic Drug CardDocument1 pageMobic Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Drug Name (Generic & Brand) : Ondansetron HCLDocument6 pagesDrug Name (Generic & Brand) : Ondansetron HCLnetanya DoanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Drug CardsDocument32 pagesNursing Drug CardsJenna Rasmussen100% (3)
- TOP DRUGS - Doc Version 1Document12 pagesTOP DRUGS - Doc Version 1Charme Jean RaygonNo ratings yet
- Anti TB DrugsDocument22 pagesAnti TB DrugsIsmael JaaniNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 4C Case 2 Final PDFDocument18 pagesDrug Study 4C Case 2 Final PDFRegine Kate JuntoNo ratings yet
- Short Case TBDocument15 pagesShort Case TBLateefah TalalNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification and Mode of Action Adverse Effects/precautions Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesName of Drug Classification and Mode of Action Adverse Effects/precautions Nursing ConsiderationsDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Hydrochlorothiazide ThiazideDocument1 pageHydrochlorothiazide ThiazideE100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY - FurosemideDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - FurosemideVANESSA PAULA ALGADORNo ratings yet
- Drug 25Document17 pagesDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- KK Bab 2Document5 pagesKK Bab 2Lidya Elizabeth LieNo ratings yet
- Top DrugsDocument12 pagesTop DrugsStephanie Villanueva AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Fixcom 4® (Tab) : Natrapharm Natrapharm Anti-TB AgentsDocument13 pagesFixcom 4® (Tab) : Natrapharm Natrapharm Anti-TB AgentsApril_Jane_Nat_8299No ratings yet
- Dosage: Route:: Mycobacterium TuberculosisDocument21 pagesDosage: Route:: Mycobacterium TuberculosisLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- Socsci 1Document27 pagesSocsci 1Bernardo Villavicencio VanNo ratings yet
- 30 Days To Better Habits - Examples DatabaseDocument9 pages30 Days To Better Habits - Examples DatabaseAlysia SiswantoNo ratings yet
- Empirically Supported Complexity: Rethinking Evidence-Based Practice in PsychotherapyDocument6 pagesEmpirically Supported Complexity: Rethinking Evidence-Based Practice in PsychotherapyPedro VargasNo ratings yet
- 05-S-2019 Dengue Ordinance of Barangay San CarlosDocument6 pages05-S-2019 Dengue Ordinance of Barangay San CarlosRonel Rosal MalunesNo ratings yet
- Curriculum VitaeDocument2 pagesCurriculum VitaeHORT SroeuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Basic Epidemiology in IPC - HFDB TemplateDocument29 pagesChapter 1 Basic Epidemiology in IPC - HFDB TemplateNylamor LicayNo ratings yet
- RejectedDocument2 pagesRejectedAutismeyeNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Assistant - JDDocument5 pagesHealthcare Assistant - JDM LubisNo ratings yet
- School Form 2 (SF2) Daily Attendance Report of LearnersDocument2 pagesSchool Form 2 (SF2) Daily Attendance Report of LearnersRommel Urbano YabisNo ratings yet
- Sample I-Search Paper 2014Document7 pagesSample I-Search Paper 2014univfi12100% (3)
- List of ClinicsDocument44 pagesList of ClinicswoodksdNo ratings yet
- Mapeh Pre PostDocument6 pagesMapeh Pre PostCathy Fern GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Killua Workout PDFDocument7 pagesKillua Workout PDFRazor. Wolf.100% (1)
- The History of The Dentistry Con Correcciones (Martin Eduardo Rojas Ochoa)Document2 pagesThe History of The Dentistry Con Correcciones (Martin Eduardo Rojas Ochoa)Maria Fernanda GarciaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Health PsychologyDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Health PsychologyUm Ar100% (1)
- VIVA PresentationDocument26 pagesVIVA PresentationWgr SampathNo ratings yet
- Memorandum: Philippine National Police Training Institute Regional Training Center 8Document2 pagesMemorandum: Philippine National Police Training Institute Regional Training Center 8DUN SAMMUEL LAURENTENo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument50 pagesTraumatic Brain InjuryDavide LeeNo ratings yet
- Mind Maps of PV Basics by Amrita AkhouriDocument92 pagesMind Maps of PV Basics by Amrita Akhourib00403007No ratings yet
- Queen - My Melancholy Blues (Piano Sheet Music)Document27 pagesQueen - My Melancholy Blues (Piano Sheet Music)Kamil Iżykowski0% (3)
- Tren Dan Isue Water BirtDocument14 pagesTren Dan Isue Water Birtijal_cakepNo ratings yet
- Nutritional AssessmentDocument45 pagesNutritional AssessmentalweenarNo ratings yet
- Scholarship Application: 2012 Global Youth ForumDocument4 pagesScholarship Application: 2012 Global Youth ForumNadhira AfifaNo ratings yet
- To Infinitive Ing VerbsDocument5 pagesTo Infinitive Ing VerbsrosarioNo ratings yet
- Health Education Feb. 23, 2024Document2 pagesHealth Education Feb. 23, 2024Ma. Jhysavil Arcena100% (1)
- Unit 11: Develop Professional Supervision Practice in Health and Social Care or Children and Young People's Work SettingsDocument4 pagesUnit 11: Develop Professional Supervision Practice in Health and Social Care or Children and Young People's Work SettingsMalgorzata MarcinkowskaNo ratings yet
- Arriesgado-Sevilleno National High School Locso-An, Placer, Masbate Quarter 2-Assessment 2Document1 pageArriesgado-Sevilleno National High School Locso-An, Placer, Masbate Quarter 2-Assessment 2Caloña Piañar JinelynNo ratings yet
- SDS N 7330 NorwayDocument15 pagesSDS N 7330 NorwaytimbulNo ratings yet
- Ocular Melanoma - Lex and TommyDocument16 pagesOcular Melanoma - Lex and Tommyapi-447472585No ratings yet
- 01 Manajemen Risiko Klinik (MRK)Document32 pages01 Manajemen Risiko Klinik (MRK)irmaNo ratings yet