Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem27 83
Problem27 83
Uploaded by
IENCS0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageThis document discusses the acceleration of a wire as it exits a pool of water. It calculates that: (1) the wire's initial speed was 2.52 m/s based on the distance it fell and acceleration due to gravity, (2) the wire's acceleration was 127 m/s^2 based on the change in speed over a short distance, and (3) using this acceleration and other known values, the resistance of the wire was calculated to be 0.20 ohms.
Original Description:
Original Title
problem27_83
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the acceleration of a wire as it exits a pool of water. It calculates that: (1) the wire's initial speed was 2.52 m/s based on the distance it fell and acceleration due to gravity, (2) the wire's acceleration was 127 m/s^2 based on the change in speed over a short distance, and (3) using this acceleration and other known values, the resistance of the wire was calculated to be 0.20 ohms.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageProblem27 83
Problem27 83
Uploaded by
IENCSThis document discusses the acceleration of a wire as it exits a pool of water. It calculates that: (1) the wire's initial speed was 2.52 m/s based on the distance it fell and acceleration due to gravity, (2) the wire's acceleration was 127 m/s^2 based on the change in speed over a short distance, and (3) using this acceleration and other known values, the resistance of the wire was calculated to be 0.20 ohms.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
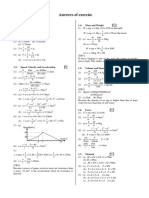
27.83: a) y 0.350 m 0.025 m 0.
325 m, we must subtract off the amount
immersed since the bar is accelerating until it leaves the pools and thus hasn’t reached
v 0 yet.
2
v 2 0 v0 2 gy v0 2 gy.
v0 2(9.8 m/s 2 )(0.325) 2.52 m/s.
b) In a distance of 0.025 m the wire’s speed increases from zero to 2.52 m/s.
v2 (2.52 m / s) 2
a 127 m / s 2 . But
2y 2(0.025 m)
m( g a ) (5.40 10 5 kg) ((127 9.8) m / s 2 )
F ILB mg ma I 7.58 A.
LB (0.15 m) (0.00650 T)
V 1.50 V
c) V IR R I 7.58 A 0.20 .
You might also like
- Hart Chapter 8 SolutionsDocument22 pagesHart Chapter 8 SolutionsCarlos de Castro86% (7)
- Assignment 3Document6 pagesAssignment 3Marlisa Salamat100% (1)
- Muv ExercíciosDocument14 pagesMuv ExercíciosexataNo ratings yet
- Physics - Answers 10-12-1Document4 pagesPhysics - Answers 10-12-1Rabson ZimeranNo ratings yet
- Zatvoreni Kanal-Main Design - RevDocument146 pagesZatvoreni Kanal-Main Design - Revnedi2No ratings yet
- Chapter 25Document22 pagesChapter 25Henry A MelendezNo ratings yet
- Problem27 60Document1 pageProblem27 60IENCSNo ratings yet
- Physics Answers 10-12 TextbookDocument4 pagesPhysics Answers 10-12 TextbookchristophermpidiNo ratings yet
- Rotational Dynamics-08-AnswersheetDocument5 pagesRotational Dynamics-08-AnswersheetRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Tugas TRK AsistenDocument34 pagesTugas TRK Asistennisa methildaarNo ratings yet
- TrabajoDocument4 pagesTrabajoSofía RivasNo ratings yet
- Problem23 74Document1 pageProblem23 74IENCSNo ratings yet
- Application of Spread SheetDocument11 pagesApplication of Spread SheetTrushti SanghviNo ratings yet
- Design of Rectangular Footing PDFDocument10 pagesDesign of Rectangular Footing PDFYedda M IlaganNo ratings yet
- ExmpleDocument3 pagesExmpleNegash Girma TolchaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Soils and Foundations 8th Edition Liu Test BankDocument24 pagesSolution Manual For Soils and Foundations 8th Edition Liu Test BankpatriciaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Soils and Foundations 8Th Edition Liu Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Soils and Foundations 8Th Edition Liu Full Chapter PDFrhonda.mcrae352100% (13)
- Mackintosh Probe RecordDocument4 pagesMackintosh Probe Records0fNo ratings yet
- Ex.-10 (D) MathsDocument4 pagesEx.-10 (D) MathsrrrrNo ratings yet
- Hart Chapter 8 SolutionsDocument15 pagesHart Chapter 8 Solutionsกรพัฒน์ เก่งพานิชNo ratings yet
- Tratamiento de Datos InfDocument9 pagesTratamiento de Datos InfBrandon AfanadorNo ratings yet
- Soil Resistivity CalculationDocument8 pagesSoil Resistivity CalculationVivek ShambharkarNo ratings yet
- @berdasarkan Test LabDocument2 pages@berdasarkan Test LabLulus PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Problem42 41Document1 pageProblem42 41IENCSNo ratings yet
- Answers To Even Numbered ProblemsDocument16 pagesAnswers To Even Numbered ProblemsJonathan Costa CardozoNo ratings yet
- G17 - Dynamics - Rectilinear Motion - ProblemsDocument27 pagesG17 - Dynamics - Rectilinear Motion - ProblemsIsrael MGNo ratings yet
- Linden Comansa 21 LC 290 18T - Loading ChartDocument2 pagesLinden Comansa 21 LC 290 18T - Loading ChartRamez Bou-RizkNo ratings yet
- Capi 9Document32 pagesCapi 9sindynovaperezNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution ControlDocument4 pagesAir Pollution ControlKezia Kusumaningtyas100% (1)
- EE5 Soln Study of EMI AnalysisPlots 1652207439083Document6 pagesEE5 Soln Study of EMI AnalysisPlots 1652207439083The RevolutionNo ratings yet
- G18 - Dynamics - Work and Energy - ProblemsDocument26 pagesG18 - Dynamics - Work and Energy - ProblemsMohammed AlryaniNo ratings yet
- Problem28 48Document1 pageProblem28 48IENCSNo ratings yet
- Graf IceDocument12 pagesGraf IceisspasNo ratings yet
- V2 (m/s) V1 (m/s) P1 (Pa) P2 (Pa) Q (m^3/h) fasumido v (m/s) Re fcalculado L (m) D (m) z1 (m) z2 (m) ε (m) RR=ε/D μ (kg/ (m*s) ) g (m/s^2) ρ (kg/m3) γ (N/m3) ν (m2/s)Document4 pagesV2 (m/s) V1 (m/s) P1 (Pa) P2 (Pa) Q (m^3/h) fasumido v (m/s) Re fcalculado L (m) D (m) z1 (m) z2 (m) ε (m) RR=ε/D μ (kg/ (m*s) ) g (m/s^2) ρ (kg/m3) γ (N/m3) ν (m2/s)DiegoAlexNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Concepts: Chapter - 3Document16 pagesSolutions To Concepts: Chapter - 3Ramesh BadamNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Concepts: Chapter - 3Document16 pagesSolutions To Concepts: Chapter - 3ajay jangirNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Concepts: Chapter - 3Document16 pagesSolutions To Concepts: Chapter - 3Rohit ChattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics-09 - AnswersDocument4 pagesModern Physics-09 - AnswersRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document23 pagesCH 10Amelia RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic LabDocument14 pagesHydraulic LabAbdallah AlhasanNo ratings yet
- Kimia Fisik A 440871 Fadhlih Al-Zaki Sitorus PDFDocument7 pagesKimia Fisik A 440871 Fadhlih Al-Zaki Sitorus PDFFadhlih Al-zakiNo ratings yet
- Problem29 38Document1 pageProblem29 38IENCSNo ratings yet
- Answers To Odd Problems: I F I FDocument5 pagesAnswers To Odd Problems: I F I FJosé Daniel De León VásquezNo ratings yet
- GCI400 SolutionsCh6Document25 pagesGCI400 SolutionsCh6Étienne PaquetNo ratings yet
- Week 1bDocument10 pagesWeek 1bMarck Joseph CabreraNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Excel WorksheetDocument4 pagesNew Microsoft Excel WorksheetarxlanNo ratings yet
- Physics Laboratory Activity 2Document4 pagesPhysics Laboratory Activity 2Mylene NerioNo ratings yet
- AMNO%,-Pqn、P9Gb STUVWX>?YZ (/) ^ - 'abcd # fghi 250: 1,000VAC (1分 4,500VAC (1分Document3 pagesAMNO%,-Pqn、P9Gb STUVWX>?YZ (/) ^ - 'abcd # fghi 250: 1,000VAC (1分 4,500VAC (1分kenny cirino gallegos vicenteNo ratings yet
- 奇數題習題簡答Document17 pages奇數題習題簡答Man Hin TamNo ratings yet
- Teraplast CATALOG TEHNIC 2016 2017 23Document1 pageTeraplast CATALOG TEHNIC 2016 2017 23Paul ItuNo ratings yet
- Set 6 Unit Hydrograph FDocument4 pagesSet 6 Unit Hydrograph FFM burgosNo ratings yet
- Gas AbsorptionDocument4 pagesGas AbsorptionMohammad MdardasNo ratings yet
- Lampiran Tugas IrdrainDocument4 pagesLampiran Tugas IrdrainJessica PrimaulyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4: Filtration & Softening: Water Treatment (Ceng 5403)Document3 pagesAssignment 4: Filtration & Softening: Water Treatment (Ceng 5403)ashe zinab100% (1)
- Beton PrategangDocument30 pagesBeton PrategangNursan MuksinNo ratings yet
- En - Eoliana - Marimi MasurateDocument3 pagesEn - Eoliana - Marimi MasuratePaulHortopanNo ratings yet
- Ftu 3Document7 pagesFtu 3ElizhaWinandaNo ratings yet
- Government Publications: Key PapersFrom EverandGovernment Publications: Key PapersBernard M. FryNo ratings yet
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesFrom Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesNo ratings yet
- Problem21 p102Document1 pageProblem21 p102IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 p100Document1 pageProblem21 p100IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 p101Document1 pageProblem21 p101IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 p105Document1 pageProblem21 p105IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 p104Document1 pageProblem21 p104IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 99Document1 pageProblem21 99IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 94Document1 pageProblem21 94IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 98Document1 pageProblem21 98IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 86Document1 pageProblem21 86IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 89Document1 pageProblem21 89IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 82Document1 pageProblem21 82IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 95Document1 pageProblem21 95IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 93Document1 pageProblem21 93IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 91Document1 pageProblem21 91IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 87Document1 pageProblem21 87IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 88Document1 pageProblem21 88IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 73Document1 pageProblem21 73IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 80Document1 pageProblem21 80IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 85Document1 pageProblem21 85IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 75Document1 pageProblem21 75IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 79Document1 pageProblem21 79IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 74Document1 pageProblem21 74IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 77Document1 pageProblem21 77IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 71Document1 pageProblem21 71IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 72Document1 pageProblem21 72IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 70Document1 pageProblem21 70IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 66Document1 pageProblem21 66IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 64Document1 pageProblem21 64IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 69Document1 pageProblem21 69IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 68Document1 pageProblem21 68IENCSNo ratings yet