Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Handout 3
Uploaded by
mohitnyatiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Handout 3
Uploaded by
mohitnyatiCopyright:
Available Formats
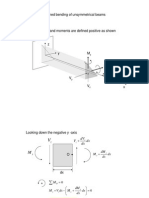
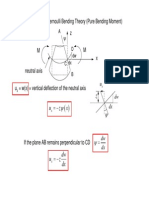
PURE BENDING OF ASSYMETRIC BEAMS * Warping is likely to occur* (BCA pp 151-156)
z
x y
Mz applied alone causes bending in both x-y plane and in x-z plane. So how are the stresses affected?
Notation: radius in x-y plane is Rz; in x-z plane is Ry Beware:this differs from BCA p.151 * What extra stresses does warping cause? To prevent bending in x-z plane requires a moment My: What combination of Mz and My cause Ry = ? x = yE/Rz Mz = Axy dA = (E/Rz)Ay2 dA = (E/Rz) Izz My = Axz dA = (E/Rz)Ayz dA = (E/Rz) Iyz Introduce the product moment of area Iyz relating My to Rz Similarly, for bending only in x-z plane (Rz = infinity), x = zE/Ry My = Axz dA = (E/Ry)Az2 dA = (E/Ry) Iyy Mz = Axy dA = (E/Ry)Azy dA = (E/Ry) Izy If bending occurs in both x-y and y-z planes: x = yE/Rz + zE/Ry My = (E/Ry) Iyy + (E/Rz) Iyz Mz = (E/Ry) Izy + (E/Rz) Izz
y z
THCC/MIG/teaching/handout 3
16
August 2000
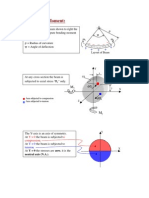
The equations for M in terms of radii R may be rearranged to be equations for R if M is prescribed, as below. M y I zz M z I yz 1 = ; Ry E I yy I zz I 2 yz
M z I yy M y I yz 1 = Rz E I yy I zz I 2 yz
So Ry and Rz can be calculated and used then to calculate x (from previous page). When Iyz = 0, the simple expressions E/R = M/I are regained. AN EXAMPLE: what are max. stresses in the L beam below, made by welding two strips A and B? Position of centroid: A z = A zdA + B zdA (90x10 + 60x10)z = 90x10x5 + 60x10x30; z = 15mm Similarly y = 35mm.
Izz = A y2dA + B y2 dA = (1/12)10x903 + 900x202 +(1/12)60x103 + 600x302 = 151x104 mm4 Similarly Iyy = 41x10 mm
4 4
25 5 35 45 Iyz = A yzdA + B yzdA = y zdz dy + + y zdz dy = 65 15 25 15
(5 15 )(25 65 )/4 + (45 15 )(35 25 )/4 = 45x10 mm If Mz = 2 kNm (= 2x10 Nmm), My = 0 kNm, E/Ry = - (2x10 )(45x10 )/(41x151x10 - 45x45x10 ) = - 2.16 N/mm Similarly, E/Rz = + 1.97 N/mm3 x = yE/Rz + zE/Ry = 1.97y - 2.16z N/mm2 Max. when y = 35mm, z = - 15mm, = 101 MPa
6 4 8 8 6
THCC/MIG/teaching/handout 3
17
August 2000
You might also like
- Torsion in Structural DesignDocument73 pagesTorsion in Structural Designjakeer7100% (1)
- Complex Variables Lecture NotesDocument11 pagesComplex Variables Lecture NotesShan_ShripadNo ratings yet
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- MD 2Document33 pagesMD 2Wilfredo Nieves OsoriaNo ratings yet
- 6 DOF Equations of MotionDocument62 pages6 DOF Equations of Motionmimi_chan_17No ratings yet
- Ec9 Ex94 Beam Column HAZDocument5 pagesEc9 Ex94 Beam Column HAZimotalpNo ratings yet
- SM - Lecture - 6 Simple Bending Theory and Beam DeflectionDocument7 pagesSM - Lecture - 6 Simple Bending Theory and Beam Deflectionsmok38442No ratings yet
- Unsymm BendingDocument29 pagesUnsymm BendingBia MughalNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis SummaryDocument8 pagesStress Analysis SummaryMohammed Taher100% (1)
- Ec9 Ex81 Torsion Open SectionDocument5 pagesEc9 Ex81 Torsion Open SectionimotalpNo ratings yet
- Emw Group Assinment: Members IDDocument17 pagesEmw Group Assinment: Members IDmuseNo ratings yet
- Homework 5 Solutions: 1 Jackson 5.3Document5 pagesHomework 5 Solutions: 1 Jackson 5.3Pavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Solutions A-03 Applied Mechanics: (June 2003)Document24 pagesSolutions A-03 Applied Mechanics: (June 2003)AdzLinkBalaoangNo ratings yet
- Examples That Required For Clutch TopicDocument6 pagesExamples That Required For Clutch TopicDrhaider Khazal100% (1)
- Tutorial With Solution - DiffractionDocument5 pagesTutorial With Solution - DiffractionKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Plane Stress TransformDocument24 pagesPlane Stress Transformsandrock92No ratings yet
- Smith Chart BasicsDocument27 pagesSmith Chart BasicsSebastin SureshNo ratings yet
- 19 Online BlasiusTheoremDocument9 pages19 Online BlasiusTheoremKing TannyNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 NotesDocument36 pagesUnit 4 NotesDamotharan Sathesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Complex Variables and Applications: (Home Work 5 / Due 4.15)Document1 pageComplex Variables and Applications: (Home Work 5 / Due 4.15)negurrasNo ratings yet
- 1.) Reakcije U Osloncima Za Horizontalnu (X-Z) Osu: B Ax 1x 1z 4x 4z Ax 1x 1z 4x 4zDocument6 pages1.) Reakcije U Osloncima Za Horizontalnu (X-Z) Osu: B Ax 1x 1z 4x 4z Ax 1x 1z 4x 4zelma spahicNo ratings yet
- Twisting by Axial LoadsDocument15 pagesTwisting by Axial LoadsVignesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Euler-Bernoulli Bending Theory (Pure Bending Moment) ψ z: dw u z dxDocument13 pagesEuler-Bernoulli Bending Theory (Pure Bending Moment) ψ z: dw u z dxeulerintegralNo ratings yet
- Mec Sol 15Document30 pagesMec Sol 15Vinícius GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Example Contour IntDocument2 pagesExample Contour IntHari B SubediNo ratings yet
- Lec 30Document13 pagesLec 30Shaik MunnaNo ratings yet
- Homework Vector SolnDocument7 pagesHomework Vector SolnReemALMousawiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - 2003 Twist Closed Sections: A) Equilibrium of Wall ElementDocument5 pagesLecture 5 - 2003 Twist Closed Sections: A) Equilibrium of Wall ElementjianjungbdNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line 1Document6 pagesTransmission Line 1Milinda PrabhathNo ratings yet
- Polar Coordinates: Axi-Symmetric ProblemsDocument8 pagesPolar Coordinates: Axi-Symmetric ProblemsalshaijiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Mechanics of Materials: Normal StressDocument18 pagesChapter 2 Mechanics of Materials: Normal StressManoj ManoharanNo ratings yet
- FUNDRAX1Document6 pagesFUNDRAX1kannan100% (1)
- Aisc 360-05-CHAPTER E1-A - SECTION CLASSIFICATIONDocument26 pagesAisc 360-05-CHAPTER E1-A - SECTION CLASSIFICATIONNihesh NNo ratings yet
- Z - TransformDocument26 pagesZ - Transformapi-26581966No ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document14 pagesChapter 13Jimmy ColomboNo ratings yet
- Practical Application 01 W1 ERDocument14 pagesPractical Application 01 W1 ERenrico.michelatoNo ratings yet
- PhasorDocument24 pagesPhasorBryan YaranonNo ratings yet
- Comparative Design of Biaxial RC ColumnsDocument14 pagesComparative Design of Biaxial RC ColumnsMouhamad WehbeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 Drill Solutions Engineering Electromagnetics 7th Edition - William H. Hayt, John A. Buck PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 03 Drill Solutions Engineering Electromagnetics 7th Edition - William H. Hayt, John A. Buck PDFfaqihNo ratings yet
- CDocument17 pagesCaischosNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Lubrication: Q Q R RDocument3 pagesHydrostatic Lubrication: Q Q R RNithesh NitheshbNo ratings yet
- Plane Stress: Notes 10. September 2014Document4 pagesPlane Stress: Notes 10. September 2014grvmaurya999No ratings yet
- Transmission Lines: (Geometric Model)Document11 pagesTransmission Lines: (Geometric Model)Hemanshu DasNo ratings yet
- DSP-3 Z-XformDocument135 pagesDSP-3 Z-Xformnemo41091No ratings yet
- Vector CalculusDocument8 pagesVector Calculusgthulasi789193No ratings yet
- 1-Design of Colnmns + Braced and Un Braced + Lateral Load ErthquakeDocument21 pages1-Design of Colnmns + Braced and Un Braced + Lateral Load ErthquakeheshamNo ratings yet
- MIT2 017JF09 ch10Document11 pagesMIT2 017JF09 ch10Robin SinghNo ratings yet
- A Emc 20Document21 pagesA Emc 20RyanPennNo ratings yet
- Written Lesson: Utkarsh Narayan March 19, 2014Document2 pagesWritten Lesson: Utkarsh Narayan March 19, 2014Prashanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document9 pagesProblem Set 1belderandover09No ratings yet
- Sin X (X +a) Sin X ( X) : Date: October 16, 2002Document6 pagesSin X (X +a) Sin X ( X) : Date: October 16, 2002Daniel Cervantes CabreraNo ratings yet
- ε ∆ L L π r ∆ r π r π r ∆ r r εDocument16 pagesε ∆ L L π r ∆ r π r π r ∆ r r εSAM KUMARNo ratings yet
- S2-1 Beam-14Document12 pagesS2-1 Beam-14abouelrich188No ratings yet
- Exercises: Double and Triple Integrals Solutions Math 13, Spring 2010Document8 pagesExercises: Double and Triple Integrals Solutions Math 13, Spring 2010Colls MuntadaNo ratings yet























































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1714993295?v=1)