Professional Documents
Culture Documents
sm1 51
Uploaded by
awoods12835Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
sm1 51
Uploaded by
awoods12835Copyright:
Available Formats
PROBLEM 1.
51
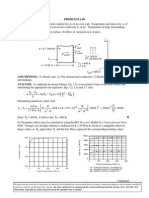
KNOWN: Vertical slab of Woods metal initially at its fusion temperature, Tf, joined to a substrate. Exposed surface is irradiated with laser source, G (W / m 2 ) . FIND: Instantaneous rate of melting per unit area, m (kg/sm2), and the material removed in a m period of 2 s, (a) Neglecting heat transfer from the irradiated surface by convection and radiation exchange, and (b) Allowing for convection and radiation exchange. SCHEMATIC:
Substrate l Gl Woods metal o Tf = 72C h= 33 kJ/kg sf = 0.4 l = 0.4 melt mout , Eout qcv qrad Laser irradation 2 Gl = 5 kW/m Ambient air Tsur 20C =
o
T = 20C h = 15 W/m2K
ASSUMPTIONS: (1) Woods metal slab is isothermal at the fusion temperature, Tf, and (2) The melt runs off the irradiated surface. ANALYSIS: (a) The instantaneous rate of melting per unit area may be determined by applying a mass balance and an energy balance (Equation 1.11c) on the metal slab at an instant of time neglecting convection and radiation exchange from the irradiated surface. m = m - m E - E = E (1a,b) st in out in out st With hf as the enthalpy of the melt and hs as the enthalpy of the solid, we have E = m h s E = m h f st st out out Combining Equations (1a) and (2a,b), Equation (1b) becomes (with hsf = hf hs) m h sf = E = l G l out in Thus the rate of melting is
m = l G l /h sf = 0.4 5000 W/m 2 33,000 J/kg = 60.6 10-3 kg/s m 2 out
(2a,b)
< <
The material removed in a 2s period per unit area is
M = m t = 121 g/m 2 2s out
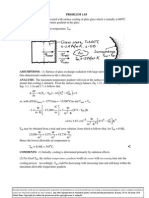
(b) The energy balance considering convection and radiation exchange with the surroundings yields m h sf = l G l - q - q out cv rad
q = h ( Tf - T ) = 15W/m2 K ( 72 - 20 ) K = 780 W/m2 cv
4 q = Tf4 - T = 0.4 5.67 10-8 W/m 2 K [ 72 + 273] - [ 20 + 273] rad 4
)K
= 154 W/m 2
m = 32.3 10-3 kg/s m 2 out
M 2s = 64g/m 2
<
COMMENTS: (1) The effects of heat transfer by convection and radiation reduce the estimate for the material removal rate by a factor of two. The heat transfer by convection is nearly 5 times larger than by radiation exchange. Continued
Excerpts from this work may be reproduced by instructors for distribution on a not-for-profit basis for testing or instructional purposes only to students enrolled in courses for which the textbook has been adopted. Any other reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted by Sections 107 or 108 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without the permission of the copyright owner is unlawful.
PROBLEM 1.51 (Conti.)
(2) Suppose the work piece were horizontal, rather than vertical, and the melt puddled on the surface rather than ran off. How would this affect the analysis? (3) Lasers are common heating sources for metals processing, including the present application of melting (heat transfer with phase change), as well as for heating work pieces during milling and turning (laser-assisted machining).
Excerpts from this work may be reproduced by instructors for distribution on a not-for-profit basis for testing or instructional purposes only to students enrolled in courses for which the textbook has been adopted. Any other reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted by Sections 107 or 108 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without the permission of the copyright owner is unlawful.
You might also like
- Heat Transfer ch-1Document1 pageHeat Transfer ch-1Fawazil NawesNo ratings yet
- Untility Rate Calculation ExamplesDocument11 pagesUntility Rate Calculation Examplesawoods12835No ratings yet
- HW Examples For ESP and Other DevicesDocument69 pagesHW Examples For ESP and Other Devicesawoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 66Document1 pagesm1 66awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 69Document2 pagessm1 69tommypurdueNo ratings yet
- sm1 63Document1 pagesm1 63awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 67Document1 pagesm1 67awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 70Document1 pagesm1 70awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 62Document1 pagesm1 62tommypurdueNo ratings yet
- sm1 68Document1 pagesm1 68awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 61Document1 pagesm1 61awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 52Document1 pagesm1 52awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 60Document2 pagessm1 60awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 65Document1 pagesm1 65tommypurdueNo ratings yet
- sm1 64Document2 pagessm1 64awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 58Document2 pagessm1 58awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 59Document2 pagessm1 59awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 53Document1 pagesm1 53tommypurdueNo ratings yet
- sm1 55Document2 pagessm1 55awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 56Document1 pagesm1 56awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 47Document1 pagesm1 47awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 50Document1 pagesm1 50awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 54Document1 pagesm1 54awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 57Document2 pagessm1 57awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 49Document1 pagesm1 49awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 46Document2 pagessm1 46awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 45Document2 pagessm1 45awoods12835No ratings yet
- Calculating Total Energy Generation Rate and Surface Temperature of Radioactive WastesDocument1 pageCalculating Total Energy Generation Rate and Surface Temperature of Radioactive Wastesawoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 48 PDFDocument2 pagessm1 48 PDFawoods12835No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Grade 12 Enzyme LabDocument25 pagesGrade 12 Enzyme LabKrystalLovejoyNo ratings yet
- De SaltersDocument15 pagesDe SaltersMuhammad Arslaan100% (2)
- Fatigue of MaterialsDocument54 pagesFatigue of Materialsc_gaspard0% (1)
- MHS-15 Prod NoteDocument2 pagesMHS-15 Prod Noteyenlitu50% (2)
- Ganj Ai Bek Irrigation Canal: Tentative Implementation PlanDocument3 pagesGanj Ai Bek Irrigation Canal: Tentative Implementation PlanAbdul Manan AsadzaiNo ratings yet
- (Advances in industrial and hazardous wastes treatment) Chen, Jiaping Paul_ Hung, Yung-Tse_ Shammas, Nazih K._ Wang, Lawrence K._ Wang, Mu Hao Sung-Remediation of heavy metals in the environment-CRC P.pdfDocument541 pages(Advances in industrial and hazardous wastes treatment) Chen, Jiaping Paul_ Hung, Yung-Tse_ Shammas, Nazih K._ Wang, Lawrence K._ Wang, Mu Hao Sung-Remediation of heavy metals in the environment-CRC P.pdfHuỳnh Tấn NhựtNo ratings yet
- Wrangle N 1974Document19 pagesWrangle N 1974KuthuraikaranNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Finished ProductsDocument5 pagesEnhancing Finished ProductsMaricon ChicanoNo ratings yet
- Tips for Treating Your RI DetectorDocument4 pagesTips for Treating Your RI DetectorRaf RafNo ratings yet
- Exp - 2, Extraction Lab - 97-2003Document16 pagesExp - 2, Extraction Lab - 97-2003venu11chemistNo ratings yet
- Lisa Concrete Indonesia ProductsDocument7 pagesLisa Concrete Indonesia ProductskenNo ratings yet
- Accredited: Member: Philippine Association of State Universities and Colleges (PASUC)Document17 pagesAccredited: Member: Philippine Association of State Universities and Colleges (PASUC)Marjorie Ramirez BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Colour Code: Zinc/Zinc-Alloy/Aluminum Continuous Sheet Coating Lines - North AmericaDocument3 pagesColour Code: Zinc/Zinc-Alloy/Aluminum Continuous Sheet Coating Lines - North AmericaHerdisNo ratings yet
- Beton Yol Yapımı (Power Point İngilizce Sunu)Document46 pagesBeton Yol Yapımı (Power Point İngilizce Sunu)Doğan ÖzdemirNo ratings yet
- Basic Knowledge of Discrete Semiconductor Device - Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage Corporation - Asia-EnglishDocument10 pagesBasic Knowledge of Discrete Semiconductor Device - Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage Corporation - Asia-EnglishReetipragya SinghNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Production in Nigeria Using Cocoa Pod Ash As A Catalyst BaseDocument4 pagesBiodiesel Production in Nigeria Using Cocoa Pod Ash As A Catalyst BaseInternational Journal of Science and Engineering InvestigationsNo ratings yet
- Display PDFDocument8 pagesDisplay PDFberktorNo ratings yet
- Carbozinc 858 (3K)Document4 pagesCarbozinc 858 (3K)DuongthithuydungNo ratings yet
- Adjustment of IsotonicityDocument29 pagesAdjustment of IsotonicityHammo Ez AldienNo ratings yet
- Weicco - Flexible Connector PDFDocument2 pagesWeicco - Flexible Connector PDFmsmrizhwanNo ratings yet
- Penetrant Product Brochure EMEARDocument8 pagesPenetrant Product Brochure EMEARChoice OrganoNo ratings yet
- Problem 1.1ADocument23 pagesProblem 1.1AJohnathan Ortega MenesesNo ratings yet
- Goulds Model 3700/3710: High Temperature/High Pressure Process Pumps Designed and Built To Meet Requirements of API-610Document40 pagesGoulds Model 3700/3710: High Temperature/High Pressure Process Pumps Designed and Built To Meet Requirements of API-610Rous MeryNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Diagnostic Exam STEM 12Document11 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Diagnostic Exam STEM 12Neil CorveraNo ratings yet
- FIRE & ARSON INVESTIGATION HISTORYDocument11 pagesFIRE & ARSON INVESTIGATION HISTORYLevy DaceraNo ratings yet
- Zracni Ventil Za RadijatorDocument2 pagesZracni Ventil Za Radijatorshadow_zeNo ratings yet
- 2m-E Static DischargeDocument3 pages2m-E Static DischargeDENNIS JOEL HARICNo ratings yet
- PAULSTRA 04 Sistema de Montaje de ChoqueDocument27 pagesPAULSTRA 04 Sistema de Montaje de ChoqueRajulapati VinodkumarNo ratings yet
- RACOLD Domestic Solar PresentationDocument14 pagesRACOLD Domestic Solar PresentationnagtummalaNo ratings yet
- Sikagard - 700 S: Siloxane Based Water Repellent ImpregnationDocument3 pagesSikagard - 700 S: Siloxane Based Water Repellent Impregnationthe pilotNo ratings yet