Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concepts of Certain Components
Uploaded by
sudinavada2009Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concepts of Certain Components
Uploaded by
sudinavada2009Copyright:
Available Formats
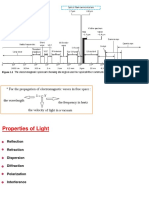
PHYSICAL CONCEPTS OF OPTICAL COMPONENTS 1. Wave plates.
(a) Wave plates change the relative phase between two components of polarization. (b) A linearly polarized light can be converted to circular or elliptical polarization depending upon the phase shift involved. (c) Most widely used wave plates are Full (2), Half () or Quarter(/2) wave plates, which provide phase shifts as indicated in brackets. (d) WPs work on the principle of birefringence shown by materials which offer different RI in two mutually orthogonal directions. (e) When light with certain polarization passes through such material both of its components experience different RI and hence travel at different speeds. Therefore they emerge with a phase difference which in turn causes state of polarization to change. (f) The amount phase difference while the light is travelling through the material is determined by difference in ordinary (no) and extra-ordinary (ne) RI of the material and thickness of the material. 2. Depolarisers. (a) These components transform polarized light into unpolarised state. (b) Strictly speaking the polarization of light is not completely unpolarised but it is randomized creating an overall effect of unpolarisation. (c) The effect is realized by making the light experience different RI while passing through the material. (d) Beam spot size and thickness of material play an important role in determining the degree of depolarisation. 3. Polarisers. (a) Polarisation is the measure of orientation of E vector of light. Polarisers are devices to impart desired polarisation to incoming light. (b) There are various kinds of polarising devices which can be used to create Linear, Circular or Elliptical polarisation. (c) The incoming light is absorbed, reflected, refracted, scattered or transmitted to achieve polarisation. (d) Certain materials like Quartz, Polaroid, Polymers doped with iodine and closely placed wires made of Al or gold are used as polarising devices. (e) In reflection, refraction or transmission type of polarisers birefringence is used as one of the methods for producing polarized light. Wherein depending on, incidence angle light splits into e-ray and o-ray before emerging out of the device and having mutually perpendicular state of polarisation. (f) Circular or elliptical polarisation can be produced by using a combination of linear polarizer and QWP or a variable retarder respectively.
4.
Q Switching. (a) This is the technique used to generate Laser pulses of high peak power. (b) The laser cavity is made to operate under high losses for certain duration of time and thereafter the losses are suddenly brought down to min. level thus a giant pulse emerges. During the period of high loss operation of cavity, a high population inversion achieved through pumping. (c) Therefore the number of species in available at upper laser level continuous to grow beyond its threshold level. (d) The path between two mirrors is blocked and hence roundtrip gain is restricted only to single pass rather than could have been achieved through multiple passes. (e) Thus the accumulation of the excited atoms at ULL and sudden opening of blockage in the gain medium results in oscillations to build up very rapidly and a pulse with very high peak power emerges out of the resonator. (f) The introduction of loss and sudden removal can be implemented using various methods like mechanical, Passive, Electro optic or Acousto-optic shutter with each of the method having its own advantages and disadvantages.
You might also like
- Optical and Microwave Technologies for Telecommunication NetworksFrom EverandOptical and Microwave Technologies for Telecommunication NetworksNo ratings yet
- Abstract - Term Index-Isolators Optical Circulators Faraday RotationDocument4 pagesAbstract - Term Index-Isolators Optical Circulators Faraday RotationGuillermo AramendiNo ratings yet
- Interference in Thin FilmDocument56 pagesInterference in Thin FilmjameshrclassesNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0030402615014394 MainDocument4 pages1 s2.0 S0030402615014394 MainStephanie HellenNo ratings yet
- Anisotropic Diffractive Optical Element For Generating Hybrid-Polarized BeamsDocument8 pagesAnisotropic Diffractive Optical Element For Generating Hybrid-Polarized BeamssankhaNo ratings yet
- Infrared SpectrophotometryDocument22 pagesInfrared Spectrophotometrypako ramaphaneNo ratings yet
- Abramczy@mitr.p.lodz - PL WWW - Mitr.p.lodz - Pl/raman WWW - Mitr.p.lodz - Pl/evuDocument49 pagesAbramczy@mitr.p.lodz - PL WWW - Mitr.p.lodz - Pl/raman WWW - Mitr.p.lodz - Pl/evuChaitanya ShakyaNo ratings yet
- BEC701 - Fibre Optic Communication PDFDocument201 pagesBEC701 - Fibre Optic Communication PDFMax DurendNo ratings yet
- Course 4, Module 7 - Electro-Optic and Acousto-Optic DevicesDocument21 pagesCourse 4, Module 7 - Electro-Optic and Acousto-Optic DevicesИРадојичић100% (2)
- Dragomir N. Neshev Et Al - Observation of Polychromatic Vortex SolitonsDocument3 pagesDragomir N. Neshev Et Al - Observation of Polychromatic Vortex SolitonsTopGunnerzNo ratings yet
- Physics Mu QB Complete SolnDocument60 pagesPhysics Mu QB Complete SolnDivyesha BariNo ratings yet
- CD Ebook PDFDocument11 pagesCD Ebook PDFMauroPellencinNo ratings yet
- Fibre Optic Communication PDFDocument199 pagesFibre Optic Communication PDFBiswarup MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics Part IDocument46 pagesFiber Optics Part ImariahvahNo ratings yet
- Module 4-7 Electro-Optic and Acousto-Optic Devices: General Comments of John SimcikDocument31 pagesModule 4-7 Electro-Optic and Acousto-Optic Devices: General Comments of John SimcikOlugbenga AdeolaNo ratings yet
- Option ADocument13 pagesOption AMartinNo ratings yet
- Haw 2002Document12 pagesHaw 2002Roman TilahunNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics: by Vikas KaduskarDocument81 pagesFiber Optics: by Vikas Kaduskarvpkvikas100% (1)
- Lec 2Document22 pagesLec 2Mahmoud AlsaidNo ratings yet
- 50 Classification of Optical Fibers and Losses in Optical FiberDocument6 pages50 Classification of Optical Fibers and Losses in Optical Fiberaravindsama171No ratings yet
- The Kerr CellDocument9 pagesThe Kerr CellMousumiNo ratings yet
- Tarun Solutions For AOCN QBDocument54 pagesTarun Solutions For AOCN QBTarun Kumar GoyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three-Sources and DetectorsDocument8 pagesChapter Three-Sources and DetectorsOdoch HerbertNo ratings yet
- Fibre Optics PaperhfththtdhdDocument2 pagesFibre Optics PaperhfththtdhdGuillermo AramendiNo ratings yet
- Ieee PaperDocument9 pagesIeee PapermukundNo ratings yet
- Gyroscope Technologies For Space Applications: Armenise@poliba - ItDocument26 pagesGyroscope Technologies For Space Applications: Armenise@poliba - ItAhmed HamoudaNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Intro: - Presentor Muhammad JawadDocument59 pagesOptical Fiber Intro: - Presentor Muhammad JawadMuhammad JawadNo ratings yet
- Sicx1003 Unit 5Document29 pagesSicx1003 Unit 5SimranNo ratings yet
- PpoiDocument8 pagesPpoiKéziaBarretoNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Transmission: Institute of Technical Education and ResearchDocument24 pagesOptical Fiber Transmission: Institute of Technical Education and ResearchTanvi TanayaNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics CommunicationsDocument23 pagesFiber Optics CommunicationsRyan Paul RiwarinNo ratings yet
- Basics of X-Ray DiffractionDocument76 pagesBasics of X-Ray DiffractionAman Mohan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Polarization Measurement (P Hernday)Document26 pagesPolarization Measurement (P Hernday)Zamzuri Abdul KadirNo ratings yet
- d01848 FreezerDocument22 pagesd01848 Freezersrboghe651665No ratings yet
- Infrared SpectrosDocument23 pagesInfrared SpectrosanilNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice: 20-1 Lamps and Lasers: Sources of LightDocument7 pagesMultiple-Choice: 20-1 Lamps and Lasers: Sources of LightBla NkNo ratings yet
- Design and Dynamics Laboratory (ME69035) Submitted by Shaik Sydavali (19ME63R38) E04: Photo Elasticity (Four Point Bending Test)Document16 pagesDesign and Dynamics Laboratory (ME69035) Submitted by Shaik Sydavali (19ME63R38) E04: Photo Elasticity (Four Point Bending Test)sonit7kumarNo ratings yet
- Thermal & Chemical Effects of Current Mag Prop of Matter & EM Waves & Polarisation Principles of CommunicationsDocument28 pagesThermal & Chemical Effects of Current Mag Prop of Matter & EM Waves & Polarisation Principles of CommunicationsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Sunil Vyas, Rakesh Kumar Singh and P. Senthilkumaran - Exotic Vortex Beam Shapes For Optical TrapsDocument4 pagesSunil Vyas, Rakesh Kumar Singh and P. Senthilkumaran - Exotic Vortex Beam Shapes For Optical TrapsKonnasderNo ratings yet
- Solution of Physics SSC-II (3rd Set)Document7 pagesSolution of Physics SSC-II (3rd Set)rabail shahzadNo ratings yet
- Broadband, Single-Layer Dual Circularly Polarized Reflectarrays With Linearly Polarized FeedDocument7 pagesBroadband, Single-Layer Dual Circularly Polarized Reflectarrays With Linearly Polarized FeedTo PhoNo ratings yet
- Photo Conducting Materials PDFDocument18 pagesPhoto Conducting Materials PDFMohanish ShahNo ratings yet
- OPTICAL FIBRE COMMUNICATION Notes PDFDocument18 pagesOPTICAL FIBRE COMMUNICATION Notes PDFAkhil RajuNo ratings yet
- SPIE Frederique-JeanDocument9 pagesSPIE Frederique-JeanMarvin GagarinNo ratings yet
- Homework+4 20220511Document2 pagesHomework+4 20220511許廷睿No ratings yet
- Optics: Quarter-Wavelength and Half-Wavelength PlateDocument10 pagesOptics: Quarter-Wavelength and Half-Wavelength PlatePAULO CESAR CARHUANCHO VERANo ratings yet
- Last Date of Submission: 19 February, 2013 (Tuesday) : ETE/EEE 426 (Section 1) Assignment# 1Document1 pageLast Date of Submission: 19 February, 2013 (Tuesday) : ETE/EEE 426 (Section 1) Assignment# 1Alfred Debashish BhowmickNo ratings yet
- Rte g1Document21 pagesRte g1Ariel Anne Wharlly FiguracionNo ratings yet
- Pres9 WDMDocument26 pagesPres9 WDMPranveer Singh PariharNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics CommunicationsDocument8 pagesFiber Optics CommunicationsKuronix ArcayaNo ratings yet
- Optoelectronics Basics: Advantages of Optoelectronic DevicesDocument44 pagesOptoelectronics Basics: Advantages of Optoelectronic DevicesrafiNo ratings yet
- Probe Signal, and A Continuous Power Wavelength, A2, Called The PumpDocument13 pagesProbe Signal, and A Continuous Power Wavelength, A2, Called The PumpYenny Isabel BetancourtNo ratings yet
- Inverse WKB Method of Refractive Index Profile. A) - Ray AnalysisDocument2 pagesInverse WKB Method of Refractive Index Profile. A) - Ray Analysisnithin_v90No ratings yet
- IA2 SolutionDocument10 pagesIA2 SolutionKaran MNo ratings yet
- OC MCQsDocument43 pagesOC MCQssun ssNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Write Notes On Broadening of Pulse in The Fiber Dispersion?Document17 pagesUnit 3: Write Notes On Broadening of Pulse in The Fiber Dispersion?Kvn NikhilaNo ratings yet
- Dcof Full Notes (Module 4)Document9 pagesDcof Full Notes (Module 4)Minhaj KmNo ratings yet
- ML MedicapsDocument9 pagesML Medicapsgopi raandNo ratings yet
- Module - Iii: Introduction To NaturopathyDocument10 pagesModule - Iii: Introduction To Naturopathysudinavada2009No ratings yet
- Ladakh: The Mystical LandDocument15 pagesLadakh: The Mystical Landsudinavada2009No ratings yet
- SlangsDocument3 pagesSlangssudinavada2009No ratings yet
- Modern Fighter AircraftDocument205 pagesModern Fighter Aircraftapi-1973227094% (17)
- Leave ApplicationDocument1 pageLeave Applicationsudinavada2009No ratings yet
- Yogic Asanas: Module - IDocument15 pagesYogic Asanas: Module - Isudinavada2009No ratings yet
- Module - Iii: Introduction To NaturopathyDocument10 pagesModule - Iii: Introduction To Naturopathysudinavada2009No ratings yet
- Template Railway Reservation FormDocument27 pagesTemplate Railway Reservation Formsudinavada2009No ratings yet
- General AwarenessDocument106 pagesGeneral AwarenessChetan Shetty100% (1)
- IndeginisationDocument10 pagesIndeginisationsudinavada2009No ratings yet
- Students ListDocument2 pagesStudents Listsudinavada2009No ratings yet
- To Develop Animation in Silicon Graphics Workstations Useful For TrainingDocument5 pagesTo Develop Animation in Silicon Graphics Workstations Useful For Trainingsudinavada2009No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentsudinavada2009No ratings yet
- MIS ErpDocument26 pagesMIS Erpsudinavada2009No ratings yet
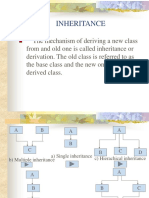
- InheritanceDocument11 pagesInheritancesudinavada2009No ratings yet
- IndeginisationDocument10 pagesIndeginisationsudinavada2009No ratings yet
- Mis IntroDocument16 pagesMis Introsudinavada2009No ratings yet
- TokensDocument11 pagesTokenssudinavada2009No ratings yet
- InheritanceDocument11 pagesInheritancesudinavada2009No ratings yet
- Mis IntroDocument16 pagesMis Introsudinavada2009No ratings yet
- Software Evolution: Machine Language Assembly Language Procedure Programming Object Oriented Programming (OOP)Document17 pagesSoftware Evolution: Machine Language Assembly Language Procedure Programming Object Oriented Programming (OOP)sudinavada2009No ratings yet
- Overview of C++ Overloading: Add (Int, Long) and Add (Long, Int) HaveDocument22 pagesOverview of C++ Overloading: Add (Int, Long) and Add (Long, Int) Havesudinavada2009No ratings yet
- Polymorphism: Function OverloadingDocument4 pagesPolymorphism: Function Overloadingsudinavada2009No ratings yet
- Class Composition: A Shape "Has A" Fixed PointDocument32 pagesClass Composition: A Shape "Has A" Fixed Pointsudinavada2009No ratings yet
- Tutorial 03Document25 pagesTutorial 03sudinavada2009No ratings yet
- Used To Lump Together - Collections of Different Variable Types - So That They Can Be Conveniently Treated As An UnitDocument19 pagesUsed To Lump Together - Collections of Different Variable Types - So That They Can Be Conveniently Treated As An Unitsudinavada2009No ratings yet
- IEG 3080 Tutorial One: Course Outline C++ Basics Data Member & Member Function Constructor & DestructorDocument20 pagesIEG 3080 Tutorial One: Course Outline C++ Basics Data Member & Member Function Constructor & Destructorsudinavada2009No ratings yet
- Inline Functions: Disadv: Code - More MemoryDocument62 pagesInline Functions: Disadv: Code - More Memorysudinavada2009No ratings yet
- The C Language: ProgrammingDocument13 pagesThe C Language: Programmingsudinavada2009No ratings yet
- RAT SpecimenTestPaperDocument6 pagesRAT SpecimenTestPaperPrasad KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- Parable of The Good Shepherd Forerunner CommentaryDocument4 pagesParable of The Good Shepherd Forerunner Commentaryisaac AamagrNo ratings yet
- Family Thesis StatementDocument6 pagesFamily Thesis Statementfc3kh880100% (2)
- Term Paper - JP Rizal LovelifeDocument12 pagesTerm Paper - JP Rizal LovelifeArthur HermiasNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade SyllabusDocument2 pages6th Grade Syllabusapi-252405047No ratings yet
- Energy Healing TherapyDocument11 pagesEnergy Healing Therapyaveellavo100% (1)
- Qualitative Characteristics of Accounting InformationDocument8 pagesQualitative Characteristics of Accounting InformationDiah Ayu KusumawardaniNo ratings yet
- Memory Training ManualDocument43 pagesMemory Training ManualRay Leon86% (7)
- Booke, McLean, Thackeray. The Old Testament in Greek According To The Text of Codex Vaticanus. 1906. Volume 1, Part 2.Document268 pagesBooke, McLean, Thackeray. The Old Testament in Greek According To The Text of Codex Vaticanus. 1906. Volume 1, Part 2.Patrologia Latina, Graeca et OrientalisNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Model To Design Rack and Pinion Ackerman Steering GeomteryDocument5 pagesMathematical Model To Design Rack and Pinion Ackerman Steering GeomteryIntiGowthamSai100% (1)
- Hora Sarvam - Albert Einstein's Horoscope - Some ObservationsDocument4 pagesHora Sarvam - Albert Einstein's Horoscope - Some Observationsbharanivldv9No ratings yet
- Commit30 - Goal Getting GuideDocument4 pagesCommit30 - Goal Getting GuidePongnateeNo ratings yet
- Beyond The Axioms: The Question of Objectivity in MathematicsDocument19 pagesBeyond The Axioms: The Question of Objectivity in Mathematicscpeter9No ratings yet
- Fce Speaking Test ChecklistDocument2 pagesFce Speaking Test Checklist冰泉100% (1)
- Trolldómr in Early Medieval Scandinavia-Catharina Raudvere PDFDocument50 pagesTrolldómr in Early Medieval Scandinavia-Catharina Raudvere PDFludaisi100% (1)
- Slac Eval MayDocument36 pagesSlac Eval MayJMAR ALMAZANNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument32 pagesCase StudyBaby Khor100% (1)
- Subtitle Generation Using SphinxDocument59 pagesSubtitle Generation Using SphinxOwusu Ansah Asare Nani0% (1)
- Demo Day PlaybookDocument30 pagesDemo Day PlaybookChinedu EnekweNo ratings yet
- Surah Taha Tafseer Ayat 2-4Document2 pagesSurah Taha Tafseer Ayat 2-4jader84No ratings yet
- Ethics From The MarginDocument20 pagesEthics From The MarginOvia HerbertNo ratings yet
- Strategy and Tactics of Distributive BargainingDocument58 pagesStrategy and Tactics of Distributive BargainingAnh BVNo ratings yet
- Idiomatic Expressions Module 1Document20 pagesIdiomatic Expressions Module 1Jing ReginaldoNo ratings yet
- G.C.E. (Advanced Level) General EnglishDocument147 pagesG.C.E. (Advanced Level) General EnglishMaliNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Dropout Rate at Secondary School Level in Private Schools of Punjab, PakistanDocument7 pagesFactors Affecting Dropout Rate at Secondary School Level in Private Schools of Punjab, PakistanImran Malik ImranNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten Science Lesson WormsDocument3 pagesKindergarten Science Lesson Wormsapi-402679147No ratings yet
- EuroProB2 Web CoursebookDocument124 pagesEuroProB2 Web Coursebookencipunci100% (1)
- Philosophy 101 Logic: Mr. Timothy Philip MallariDocument41 pagesPhilosophy 101 Logic: Mr. Timothy Philip MallariJohn Estrada TutanaNo ratings yet
- Importance of Research Across FieldsDocument21 pagesImportance of Research Across Fieldsrogelyn samilinNo ratings yet
- Bringing Devi HomeDocument7 pagesBringing Devi Homecharan74No ratings yet
- David Hawkins Lecture Notes On Handling Spiritual ChallengesDocument12 pagesDavid Hawkins Lecture Notes On Handling Spiritual ChallengesTed Carter64% (11)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Chernobyl 01:23:40: The Incredible True Story of the World's Worst Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandChernobyl 01:23:40: The Incredible True Story of the World's Worst Nuclear DisasterRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (264)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldFrom EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessFrom EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- Vibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeFrom EverandVibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Chasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombFrom EverandChasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)