1.
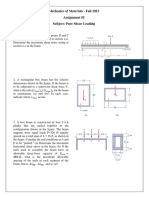
A cantilever beam, 60 mm wide by 200 mm high and 5 m long carries a load that varies uniformly from zero at the free end to 1 kN/m at the wall. (a) Compute the magnitude and location of the maximum shear stress. (b) Determine the type and magnitude of the shear stress in a fiber 40 mm from the top of the beam at a section 3 m from the free end.
Solution: ( )( ) b. Shear stress on a fiber 40 mm from a. Maximum shear stress
Maximum shear occurs at the wall (A)
top of beam, 3 m from free end
( ( ( )( ) ) ( (
) )
( ) ( )
)(
( (
)( ) (
) )
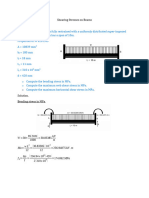
Shear Stress in Beams
�2. A simply supported beam 60 mm wide by 100 mm high and 4 m long, is subjected to a concentrated load of 1 kN at a point 1 m from one of the supports. Determine the maximum shear stress and the shear stress in the fiber 10 mm from the top of the beam at midspan.
Solution: Reactions: RA = kN RB = kN
a.) Maximum shear stress Maximum shear force, V = 0.75 kN ( ) ( )( ) b.) Stress in the fiber 10 mm from top at midspan
( ( ( )( ) ( ) )
)(
Shear Stress in Beams
�3. A simply supported rectangular beam 50 mm wide by 100 mm deep, carries a uniformly distributed load of 1.2 kN/m over its entire length. What is the maximum length of the beam if the flexural stress is limited to 1.0 MPa.
Solution: By symmetry: ( )( ) ( ) ( )
From the V-diagram, Maximum shear force = (600L) N
( ( )(
) )
Shear Stress in Beams
�4. A wooden beam is 150 mm wide by 300 mm deep. The beam is 8 m long which is simply supported at the left end and simply supported 2 m from the right end. It is loaded with a concentrated load P 3m from the left support and a uniformly distributed load on the overhanging and of two meters. If the maximum shearing stress is 1.2 MPa, find the maximum values of w and P that can be applied simultaneousy.
Solution: Reactions: RA(6) = 3P 2w(1) RA = 0.5P 1/3w RB(6) =3P + 2w(7) RB = 0.5P + 14/6(w)
By summing forces to RB from the right of the beam: V = 2w
( ( )( ) )
At P, maximum shear force is: |-0.5P (1/3)w| = 0.5P +(1/3)w ( ( ( )( ( ( )) ) ) )
Shear Stress in Beams
�5. A wooden beam is 150 mm wide by 300 mm deep. The beam is simply supported at the left end and is simply supported x m from the right end. It is loaded with a concentrated load P 3 m from the left support and a uniformly distributed load equal to 10 kN/m on the overhanging end of x meters. If the maximum shearing stress is 2 MPa, find the maximum values of x and P that can be applied simultaneously.
RA(6) = 3P 10x(x/2) RA = 0.5P (5/6)x2
RB(6) =3P + 10(x)(6+x/2) RB = 3P + 60x +5x2 RB = 0.5P + 10x +(5/6)x2
By summing forces to RB from the right of the beam: V = (10x) kN
( ( ) )( )
At P, maximum shear force is: |-0.5P (5/6)x2| =( 0.5P + (5/6)x2 kN) ( ( ) ( )) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( )
Shear Stress in Beams
�6. A rectangular beam 120 mm wide by 400 mm deep is loaded with a uniformly distributed load over its entire length and a concentrated load P, 1 m from the right support. The beam is simply supported over a span of 5 m. if w = 3 kN/m, find P to cause a maximum bending stress of 1 MPa.
Solution: Reactions: ( ) ( )( )( ( ) ) ( )
( ) ( )( )( ( ) Maximum shear force is ( ) ) ( )
( (
( ) )(
)( )
Shear Stress in Beams
�7. A rectangular beam 120 mm wide by 400 mm deep is loaded with a uniformly distributed load over its entire length and a concentrated load P, 1 m from the right support. The beam is simply supported over a span of 5 m. if w = 6 kN/m, find P to cause a maximum shearing stress of 1.20 MPa.
Solution: Reactions: ( ) ( )( )( ( ) ) ( )
( ) ( )( )( ( ) Maximum shear force is ( ) ) ( )
( (
( ) )(
)( )
Shear Stress in Beams
�ASSIGNMENT IN TIMBER DESIGN (SHEAR STRESS) BY BSCE 5B
Engr. Melito Hirondo Instructor
Shear Stress in Beams