Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 7 Lesson 1 Denny
Uploaded by
api-254594631Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 7 Lesson 1 Denny
Uploaded by
api-254594631Copyright:
Available Formats
Name Denny Abragan Date Dec.
8,2013 Class 8
LESSON 1
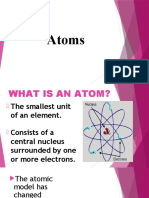
Discovering Parts of an Atom
Directions: Draw an atom model. Use all the terms below to label your drawing. Then write a sentence to
explain each term.
atom electron electron cloud neutron nucleus proton
1. atom - the smallest piece of an element that still represents an element.
2. electron - a particle with one negative charge.
3. electron cloud - an area around an atomic nucleus where an electron is most likely to be located .
4. neutron - a neutral particle that exists in the nucleus of an atom.
5. nucleus - most of an atoms mass and positive charge is concentrated in a small area in the center of the
Atom called the nucleus.
1
Content Vocabulary
Atom
Electron
6. proton - an atomic particle that has one positive charge.
Name Date Class
LESSON 1
Discovering Parts of an Atom
A. Early Ideas About atter
1. any ancient !reek philosophers thought that all matter was made of only four
elements"fire# water# air# and earth .
2. $hese early scientists were not able to test their theories.
3. %emocritus proposed that matter is made of small# indivisible ob&ects
called atomos ' atom .
4. (e proposed that different types of matter are made from
different types of atoms.
B. %altons Atomic odel
1. )ohn %alton proposed the atom theory# which was based
on careful observations and measurements of chemical reactions.
2. %altons theory states that atoms cannot be divided# created #
or destroyed.
3. It also stated that atoms of one element are different from
atoms of other elements .
C. $he Atom
1. A*n+ atom is the smallest piece of an element that still
represents that element.
2. Atoms were first seen by using a*n+ scanning tunneling microscope.
D. $homson"%iscovering Electrons
1. $homson discovered that the rays in a*n+ glass tube were
attracted to a*n+ negative charged plate# which means that the
rays have a*n+ positive charge.
2. $homsons atomic model stated that an atom is a positively charged
sphere with electrons throughout it.
E. ,utherford"%iscovering the -ucleus
.
Lesson Outline
1. ,utherfords student performed an experiment during which they shot
alpha particles into a piece of gold foil.
Lesson Outline continue
2. $he results showed that most of the particles traveled through the foil# but some
bounced to the side # and a few bounced straight back.
3. ,utherfords resulting atomic model proposed that most of an atoms
mass and positive charge is concentrated
in the center of the atom.
a. $he nucleus is the small# positively charged area in the center
of the atom.
b. In the nucleus is the proton # which is an atomic particle
with one positive charge.
!. %iscovering -eutrons
1. )ames /hadwick was one of ,utherfords colleagues.
2. /hadwick discovered the neutron # a neutral particle that exists
in the nucleus of an atom.
". 0ohrs Atomic odel
1. $he atomic model of 0ohrs proposed that
electrons move in circular orbits# or energy levels #
around the nucleus.
2. 1hen energy is added to an atom# electrons move to higher
energy level 2 when energy is released by the electron# it moves back
to a lower level.
3. $he limitation of 0ohrs model is that electrons do not actually move in
circular orbits.
#. $he odern Atomic odel
1. In modern atomic theory# electrons form a*n+ electron cloud # which is
an area around the atomic nucleus in which an electron is likely to be
located.
2. An electron cloud is mostly empty space.
$. Quarks
3
1. 4rotons and electrons are made of smaller parts
called 5uarks .
2. $here are six types of 5uarks.
LESSON 1
Discovering Parts of an Atom
Directions: Use your textbook to respond to each statement.
1. $he table below lists some of the main contributions to the development of the
modern atomic model. 6se the names in the word bank to fill in the table.
Aristotle Bohr Chadwick Dalton
Democritus Rutherford Thomson
Contributor Descri%tion
a. De&ocritus
Greek philosopher who sai that atoms co!l not be i"ie,
create, or estroye.
b. Aristotle
Greek philosopher who tho!ght that matter is mae !p o#
#ire, water, air, an earth.
c. Dalton
$nglish teacher o# the 1%00s who state that matter is mae
o# atoms that cannot be i"ie an that atoms combine in
speci#ic ratios.
. '(o&%son
$nglish scientist who concl!e that cathoe rays are mae
!p o# negati"ely charge particles calle electrons.
e. )ut(er*or
&t!ent o# 'homson who isco"ere that the atom(s mass an
positi"e charge are concentrate in a small area in its center.
*. C(a+ic,
&cientist who isco"ere that the n!cle!s contains ne!trons
in aition to protons.
-. Bo(r
&t!ent o# )!ther#or who state that electrons e*ist in
circ!lar orbits aro!n the n!cle!s.
2. Write a paragraph that describes the modern atomic model.
In the modern atomic model# electrons form an electron cloud. An electron cloud is an area around
an atomic nucleus where an electron is most likely to be located. $he cloud might be denser near the hive
than farther away because the bees spend more tie near the hive. In similar way# electrons constantly
move around the nucleus. It is impossible to know both the speed and the exact location of an electron at
a given moment in time. Instead# scientists only can predict the likelihood that an electron is in a
particular location .
7
Sc(ool to #o&e
Name Date Class
LESSON 1
Discovering Parts of an Atom
.ey Conce%t (ow would you describe the si8e of an atom9
Directions: Each set of items includes one that is larger than the other. Circle the larger item in each set of items.
1. atom neutron
2. 5uark neutron
3. nucleus atom
4. nucleus proton
5. electron cloud atom
6. electron nucleus
/. atom electron
0. proton atom
1. nucleus neutron
12. proton 5uark
Directions: Answer each question on the lines proided.
11. Is it possible to see atoms with your eyes9 Explain.
It is not possible to see atoms with your eyes because they are very small.
:
.ey Conce%t Builer
12. 1hat is an ;$9
;$ < ;canning tunneling microscope2 it uses a tiny metal tip to trace the surface of a piece of matter.
13. (ow have ;$s helped scientists study atoms9
1ith the help of the ;$s# scientists have learned that atoms are not the smallest particles.
=
You might also like
- LB1D3 20220824 Inorganic ChemistryDocument2 pagesLB1D3 20220824 Inorganic ChemistryPhoebe BironNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Module 3, Lesson 1: Atomic TheoryDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Module 3, Lesson 1: Atomic TheoryKeano GelmoNo ratings yet
- Atoms Part 1Document7 pagesAtoms Part 1Franze Nica BacuyagNo ratings yet
- Atom Stations 19-20 Answer SheetDocument6 pagesAtom Stations 19-20 Answer SheetАбдурахман ПсиксNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and IonsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and IonsEugene MacapagalNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Chemistry Atomic Models and Structure of The Atom I. Learning CompetencyDocument8 pagesLesson Plan in Chemistry Atomic Models and Structure of The Atom I. Learning CompetencyLoreen Jane AbogadoNo ratings yet
- Chem Lec ReviewerDocument42 pagesChem Lec ReviewerMaryashlyn NableaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5, The Structure of AtomDocument3 pagesLesson 5, The Structure of AtomRey OrbeNo ratings yet
- History and Models of The Atom: Click On MeDocument26 pagesHistory and Models of The Atom: Click On MeRon Adrian Sarte SebastianNo ratings yet
- History and Models of The Atom: Click On MeDocument26 pagesHistory and Models of The Atom: Click On MeeriksonmurilloNo ratings yet
- History and Models of The Atom: Click On MeDocument26 pagesHistory and Models of The Atom: Click On MeDaniella Ize GordolaNo ratings yet
- Unit FDocument16 pagesUnit FVenkateswara Rao DoodalaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Atomic Theory: ObjectivesDocument19 pages1.1 Atomic Theory: ObjectivesEyad AymanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 History of AtomDocument17 pagesLesson 5 History of AtomTeacher JoanNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 Atoms, Ions and MoleculesDocument14 pagesLESSON 2 Atoms, Ions and MoleculesscientistgenerosoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 4 Structure of AtomDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 4 Structure of Atomnajaf_shaanNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q2 Lesson 1 Atomic Model, Sub Atomic ParticlesDocument29 pagesSci9 Q2 Lesson 1 Atomic Model, Sub Atomic ParticlesFlorenze GonzalesNo ratings yet
- l2.1 Evolution of Atomic ModelDocument33 pagesl2.1 Evolution of Atomic ModelZeke WilliamNo ratings yet
- The History of The Atom Notes - CondensedDocument6 pagesThe History of The Atom Notes - CondensedOin Levney Tecson100% (1)
- The History of The Atom Notes - CondensedDocument5 pagesThe History of The Atom Notes - CondensedMarites AguilarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 11 (Punjab Board)Document583 pagesChemistry Class 11 (Punjab Board)Ali Abbas GilaniNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelsDocument10 pagesAtomic ModelsMuhammad SamyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Modul Theory AtomDocument17 pagesChemistry Modul Theory Atomlevi yunitasariNo ratings yet
- Radiation Production and Characteristics "The Structure of Matter"Document10 pagesRadiation Production and Characteristics "The Structure of Matter"Shara RafisuraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On An AtomDocument6 pagesLesson Plan On An AtomAnonymous ZsTY4mkysTNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Quarter 2-Worksheet 1: The History of AtomDocument7 pagesScience 9 Quarter 2-Worksheet 1: The History of AtomJaimeCrispinoNo ratings yet
- Technical Terms: Charged Particle of An AtomDocument18 pagesTechnical Terms: Charged Particle of An AtomMojere GuardiarioNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 2Document7 pagesPhysical Science Week 2Cyril-J BalboaNo ratings yet
- Panimula: Science 8 3rd April 5-9, 2021Document3 pagesPanimula: Science 8 3rd April 5-9, 2021Michelle Copones LlanesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lesson 2 MADocument3 pagesChemistry Lesson 2 MAarodaina511No ratings yet
- Investigating Atoms and Atomic TheoryDocument34 pagesInvestigating Atoms and Atomic Theorysophia luNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Structure of The Atom Notes Class 9 ScienceDocument47 pagesChapter 4 Structure of The Atom Notes Class 9 ScienceChandan Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory: Students Should Be Able ToDocument34 pagesInvestigating Atoms and Atomic Theory: Students Should Be Able ToRhyz Mareschal DongonNo ratings yet
- History of Atomic Theory NotesDocument22 pagesHistory of Atomic Theory Notesapi-281924829No ratings yet
- Unit 2. The AtomDocument26 pagesUnit 2. The Atomgarciaortegajulia5No ratings yet
- Atoms and The Atomic TheoryDocument47 pagesAtoms and The Atomic TheoryEdgar PeninsulaNo ratings yet
- Investigating Atoms and Atomic TheoryDocument34 pagesInvestigating Atoms and Atomic TheoryyengleeNo ratings yet
- (De Dios) Science ProjectDocument22 pages(De Dios) Science ProjectRoucyzle Ynnah AcidoNo ratings yet
- Admmodule s1112ps Iiib 10Document12 pagesAdmmodule s1112ps Iiib 10Lebz RicaramNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryDocument4 pagesLesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryKokkilaa ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory and ModelsDocument42 pagesAtomic Theory and ModelsJesiah PascualNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 8 ChemistryDocument5 pagesICSE Class 8 ChemistryDoel SenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For FreshmenDocument9 pagesChemistry For FreshmenMeo Angelo AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Foundation &fundamentals of Chemistry Unit: 3 Atomic StructureDocument34 pagesFoundation &fundamentals of Chemistry Unit: 3 Atomic StructurePiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- The History of The Atom - Reforma - Mira - JoyDocument6 pagesThe History of The Atom - Reforma - Mira - JoyVINCENT REFORMANo ratings yet
- PrincesDeGuia - Nuclear ChemistryDocument10 pagesPrincesDeGuia - Nuclear ChemistryRosana BercadesNo ratings yet
- PDF 20221114 080033 0000Document2 pagesPDF 20221114 080033 0000John Marithe PutunganNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument2 pagesReviewerMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- SCH 100 L1Document7 pagesSCH 100 L1nickmcklin7No ratings yet
- AtomsDocument26 pagesAtomsJhul Mhel SonioNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelsDocument26 pagesAtomic ModelsFlitcher Diane PilotonNo ratings yet
- GeneralChemistry Lecture 2Document28 pagesGeneralChemistry Lecture 2biyadgendeshewNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: Describe The Rutherford's Experiments and His Contribution To The Atomic StructureDocument24 pagesObjectives:: Describe The Rutherford's Experiments and His Contribution To The Atomic StructureChalise SupremeNo ratings yet
- Investigating Atoms and Atomic TheoryDocument37 pagesInvestigating Atoms and Atomic TheoryCon AquinoNo ratings yet
- (Joshua) Science ProjectDocument22 pages(Joshua) Science ProjectRoucyzle Ynnah AcidoNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE Chapter 01 3 Cont.Document52 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE Chapter 01 3 Cont.Think Before You ClickNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Atom and Subatomic Particles)Document7 pagesChemistry (Atom and Subatomic Particles)Meo Angelo AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Sweetening by Monoethanolamine ProcessDocument22 pagesNatural Gas Sweetening by Monoethanolamine Processasamad54No ratings yet
- Bisare Small Scale Irrigation ProjectDocument72 pagesBisare Small Scale Irrigation ProjectAbiued EjigueNo ratings yet
- 19.04.20 Sr.N-SUPERCHAINA Jee Adv 2016 P1 GTA-11 (P-1) QP PDFDocument19 pages19.04.20 Sr.N-SUPERCHAINA Jee Adv 2016 P1 GTA-11 (P-1) QP PDFsuryaNo ratings yet
- Causes of EarthquakesDocument8 pagesCauses of Earthquakesdumea paulNo ratings yet
- Liquid Dosage Forms: Course Name: Pharmaceutical Technology-I Course Code: PHRM 3125Document33 pagesLiquid Dosage Forms: Course Name: Pharmaceutical Technology-I Course Code: PHRM 3125Masum HossinNo ratings yet
- PHY12 Review Items Exit ExamDocument26 pagesPHY12 Review Items Exit ExamRigel ZabateNo ratings yet
- Final ProjectDocument22 pagesFinal ProjectDevil KingNo ratings yet
- 37 Boysan - Bawing - Mangrove PDFDocument1 page37 Boysan - Bawing - Mangrove PDFCirilo Jr. LagnasonNo ratings yet
- CompleteDocument36 pagesCompletelarryNo ratings yet
- Galaxy ClassIficationDocument4 pagesGalaxy ClassIficationkNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 206 Advanced Organic Chemistry: Simmons-Smith Reaction: Enantioselective VariantsDocument0 pagesChemistry 206 Advanced Organic Chemistry: Simmons-Smith Reaction: Enantioselective VariantseraborNo ratings yet
- Practical 14 PDFDocument3 pagesPractical 14 PDFSiddharth KumraNo ratings yet
- Altret Industries Private LimitedDocument5 pagesAltret Industries Private LimitedJinalNo ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument8 pagesData AnalysisJosline MuriikiNo ratings yet
- Fe2O3 SourceDocument5 pagesFe2O3 SourceZahid FarooqNo ratings yet
- Sharif 2018Document13 pagesSharif 2018Dost Engineering ServicesNo ratings yet
- Theory and PracticeDocument22 pagesTheory and PracticeBryan Ramirez100% (1)
- International Pharmacopeia - Purified WaterDocument2 pagesInternational Pharmacopeia - Purified WaterFatma AbdelaalNo ratings yet
- The Mole and Chemical Calculations: Pure ChemistryDocument2 pagesThe Mole and Chemical Calculations: Pure Chemistryyuxiang32No ratings yet
- Physical Science - Week 28Document4 pagesPhysical Science - Week 28Mira VeranoNo ratings yet
- Technical Information Sheet 6: Revision 2: 2012Document8 pagesTechnical Information Sheet 6: Revision 2: 2012anon_260328012No ratings yet
- De Leenheer A.p., Lambert W. (Eds.) Modern Chromatographic Analysis of Vitamins, Revised and Expanded (3ed., CRC, 2000) (ISBN 0824703162) (606s)Document606 pagesDe Leenheer A.p., Lambert W. (Eds.) Modern Chromatographic Analysis of Vitamins, Revised and Expanded (3ed., CRC, 2000) (ISBN 0824703162) (606s)Edwin Franco100% (1)
- Q13&14Document2 pagesQ13&14Izzah HzmhNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mix DesignDocument12 pagesConcrete Mix DesignGemechu100% (1)
- Project File LawsDocument5 pagesProject File LawsSonaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Free SilicaDocument2 pagesEffect of Free SilicaHazem DiabNo ratings yet
- Volvo Oil AnalysisDocument5 pagesVolvo Oil Analysisgilar herliana putraNo ratings yet
- Describes The Pattern in The Data?: Diagnostic Test (Grade 5)Document5 pagesDescribes The Pattern in The Data?: Diagnostic Test (Grade 5)Kristine torresNo ratings yet
- Advanced Quantum Field Theory Roberto CasalbuoniDocument261 pagesAdvanced Quantum Field Theory Roberto Casalbuoniapi-3797403100% (1)
- Brooke, Forbes, Richardson, Stacey, and Tatlow: Polyjeuoro-Compounds. ofDocument7 pagesBrooke, Forbes, Richardson, Stacey, and Tatlow: Polyjeuoro-Compounds. ofJeshua CastilloNo ratings yet