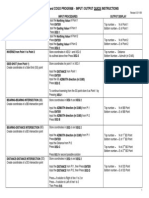
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Radial Survey
Uploaded by
Agustin AndonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Radial Survey
Uploaded by
Agustin AndonCopyright:
Available Formats
A Radial Land Survey
This resource was written by Derek Smith with the support of CASIO New Zealand. It may be
freely distributed but remains the intellectual property of the author and CASIO.
Radial surveys are surveys in which arbitrary points (vertices) are to be located
and connected to a control point. It is assumed that the accuracy of the
survey technique is sufficient to locate any points with acceptable accuracy.
This type of survey is used for general land and seafloor mapping.
Useful Formulae
Sine Rule:
a
sin A
=
b
sin B
=
c
sin C
Cosine Rule: cosC =
a
2
+ b
2
c
2
2ab
Area of a Triangle: A =
1
2
absin C
Cosine Rule: C ab b a c cos 2
2 2 2
+ =
1. Go to the area you are going to measure. Mark a central point on the ground, it will be
labelled A on your ClassPad300. Using an alidade (or compass) to help you draw out radial
lines (spokes), measure the bearings (or angles) from A towards each corner of the area that
you are surveying.
2. Name each corner with a different letter B, C, D,
3. Use the long tape (or accurate, consistent pacing) measure the distance from your central point
A to each vertex. AB, AC, AD,
4. Record these measurements on your ClassPad300
5. You will need to measure and record the sizes of the angles (or bearings), BAC, CAD,
DAE, .
6. Subdivide the area on the diagram into triangles.
7. Calculate the areas of each triangle and confirm lengths of BC, CD, DE, by using of the
Cosine or Sine Rules or Area of a Triangle formulae.
8. Confirm the areas of the triangles formed in the surveyed area when added together equal the
total area.
9. Find distances between opposite vertices.
Example:
Find the area of a piece of the school grounds, labelled ABCDEF (refer to the example sketch shown
below). The following measurements have been collected from a flat area of land:
Length Bearing
AB 25 040
AC 35 100
AD 30 150
AE 33 235
AF 40 265
AG 20 335
Enter this data in to the geometry menu on your ClassPad300, firstly crating the radial lines from
point A and then fixing the lengths and angles by tapping on the attributes you want to fix and
typing in the required measurement and then tapping in the icon so that its background is shaded.
The line AH is illustrating the direction of North so that bearings can also be used (or found).
Practice: Find the area of an irregularly shaped hexagon or other polygon.. Taking appropriate
measurements to calculate lengths and angles in order to find the total area and perimeter of the
hexagonal (or other polygon ) shape.
Point A is located on the geometry page. Form the radial lines required for the hexagon
construction. Tap on the arrow icon (top right) to open page 2.
Tap on the line segment AB and the Classpad300 will display the length in the work box. Enter in
25 and tap on the icon so that its background is shaded, this constrains the length to 25 units.
[Note: You may have to Zoom to fit to see the diagram that you are creating.] See the screensnap
below to alter this window.
Next, begin to set the bearings (or angles) by selecting the radial arms and again changing the
angles displayed in the work box to continue the construction of the hexagon. Displayed below is
the setting of AB to a bearing of 040 by selecting AH and AB. Complete the hexagon by creating
the edges BC, CD, , GB.
Completed hexagon
based on the given
measurements.
Using the geometry tools on page 2 you can find the lengths angles and areas of any aspect of this
constructed hexagon. Some examples are illustrated below.
The total area. Area ABG Area ABC
Fixing the line AH to be
vertical.
Lengths between vertices Selected angles:
CF CE BCD BAD
There are many more pieces of information that you can extract from this radial survey by viewing
the drop down menu on the left on page 2. You can copy and paste or drag and drop the
constructions into the Main icon with the use of the split screen. Have fun!
For further tips, more helpful information and software support visit our website
www.monacocorp.co.nz/casio
You might also like
- MTES1142 Heuristic 2021062310074Document30 pagesMTES1142 Heuristic 2021062310074MT10622 Asma Zulfa Binti Mohd KhairolNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Conceptual FrameworkDocument15 pagesTheoretical and Conceptual Frameworkdrarumugam100% (1)
- SPM QUESTION FORM 4 SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES AND QUADRILATERALSDocument6 pagesSPM QUESTION FORM 4 SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES AND QUADRILATERALSTee Pei LengNo ratings yet
- Logical Agents Apply ReasoningDocument19 pagesLogical Agents Apply ReasoningVuggam VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Translations:: Investigating TransformationsDocument2 pagesTranslations:: Investigating TransformationsMT10621 Wong Yu YanNo ratings yet
- ICT in Malaysian Schools Policy and StrategiesDocument6 pagesICT in Malaysian Schools Policy and StrategiesMisfit XavierNo ratings yet
- Penyelesaian Masalah Matematik Mathematical Problem Solving: MTES3023 Dr. Koay Chen YongDocument40 pagesPenyelesaian Masalah Matematik Mathematical Problem Solving: MTES3023 Dr. Koay Chen YongJeeyin MaryNo ratings yet
- AMATH Solution of TriangleDocument12 pagesAMATH Solution of TriangleLeneNo ratings yet
- Teaching Mathematics EducationDocument21 pagesTeaching Mathematics EducationDerrick Yong Thien Foh0% (1)
- DSKP Mathematics Year 4Document58 pagesDSKP Mathematics Year 4Anonymous HK3LyOqR2gNo ratings yet
- Co-curricular Activities Proposal 2020Document3 pagesCo-curricular Activities Proposal 2020ri.yax3365100% (1)
- Linear ProgrammingDocument13 pagesLinear ProgrammingSuziana MohamadNo ratings yet
- Rubrik Markah Presentation ProjectDocument1 pageRubrik Markah Presentation ProjectKin HamzahNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Report 1Document8 pagesPhysics Lab Report 1Declan Gale Anak DellyNo ratings yet
- Group Vs Individual AssignmentDocument12 pagesGroup Vs Individual AssignmentYvonne TiongNo ratings yet
- TPR2251 Pattern Recognition Assignment: 3.1 Data Collection (4%)Document8 pagesTPR2251 Pattern Recognition Assignment: 3.1 Data Collection (4%)Rez Tamil50% (2)
- Assignment/ Tugasan - BBMP1103 Mathematics For Management Matematik Untuk Pengurusan September Semester 2021Document7 pagesAssignment/ Tugasan - BBMP1103 Mathematics For Management Matematik Untuk Pengurusan September Semester 2021ASHWIN 2629No ratings yet
- Linear Programming SPM 2003 - 2007Document2 pagesLinear Programming SPM 2003 - 2007Rosmizar AhmadNo ratings yet
- (Mai 3.1-3.4) 3d Geometry - TrianglesDocument30 pages(Mai 3.1-3.4) 3d Geometry - TrianglesJuhi KastiyaNo ratings yet
- SMQ3043 Assignment ArticleDocument15 pagesSMQ3043 Assignment ArticleNoor Hidayah Mohd KamalNo ratings yet
- Copper Wire Under Tensile StressDocument2 pagesCopper Wire Under Tensile StressCharith SuriyakulaNo ratings yet
- Csc186topic 1 - Part2Document34 pagesCsc186topic 1 - Part2Nurain DamiaNo ratings yet
- Cel2106 Class Material 1 (Week 1)Document10 pagesCel2106 Class Material 1 (Week 1)WAN NUR AISYAH NADIAH BINTI WAN ZAUKI / UPMNo ratings yet
- Theme: Waves, Light and Optics Chapter 5: WavesDocument17 pagesTheme: Waves, Light and Optics Chapter 5: WavesJacqueline Lim100% (1)
- Ucs102 Entrepreneurship in Asia Assignment - May20 AssignmentDocument5 pagesUcs102 Entrepreneurship in Asia Assignment - May20 AssignmentNUR HABIBAH BT YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Latihan Ulang Kaji Mtes3013 Tajuk3Document1 pageLatihan Ulang Kaji Mtes3013 Tajuk3PeiEnOngNo ratings yet
- Phet Vectors Simulations Lab KeyDocument8 pagesPhet Vectors Simulations Lab Keyapi-259169063No ratings yet
- The Photoelectric Effect and Its Application in The Digital CameraDocument2 pagesThe Photoelectric Effect and Its Application in The Digital Cameraallison125No ratings yet
- Effective Resume WritingDocument21 pagesEffective Resume WritingHarryJoy JackNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Arithmetic ProgressionDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Arithmetic ProgressionFongoh Bobga RemiNo ratings yet
- Mtes3043 Matematik Kewangan. Report - Loan SelectionDocument5 pagesMtes3043 Matematik Kewangan. Report - Loan SelectionainasafiaNo ratings yet
- Edutainment TheoriesDocument3 pagesEdutainment TheoriesJosh Simmons100% (1)
- Pembangunan Modul Kemahiran Berfikir Aras Tinggi DDocument8 pagesPembangunan Modul Kemahiran Berfikir Aras Tinggi DNur Ezzati SulaimanNo ratings yet
- 440Document80 pages440rrrawNo ratings yet
- Skema Kimia K2 Trial SPM MRSM 2019 PDFDocument18 pagesSkema Kimia K2 Trial SPM MRSM 2019 PDFFarhalina Nazira0% (1)
- Additional Mathematics Project Work Index NumberDocument25 pagesAdditional Mathematics Project Work Index NumberUmair Hisham71% (14)
- Non Routine ProblemDocument4 pagesNon Routine ProblemAmmar Imran AnuarNo ratings yet
- Adriana 208098 - g39 - WP Task 1Document16 pagesAdriana 208098 - g39 - WP Task 1adriana syakirahNo ratings yet
- Set A Section A Question 1: Compilation of Trial State Paper 3 QuestionsDocument25 pagesSet A Section A Question 1: Compilation of Trial State Paper 3 QuestionsCart KartikaNo ratings yet
- Revision Test TrigonometryDocument7 pagesRevision Test TrigonometryRNC ArcadeNo ratings yet
- HBSC1103 v2Document6 pagesHBSC1103 v2TAY JIUN HOANG MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 OopDocument17 pagesChapter 4 OopEmy LukaszNo ratings yet
- Kepler-Poinsot Solids NetsDocument26 pagesKepler-Poinsot Solids NetsChia Sheng GoyNo ratings yet
- Ska3023 Instrumentation Analytical Chemistry Exercise 1 Spectroscopy/SpectrometryDocument2 pagesSka3023 Instrumentation Analytical Chemistry Exercise 1 Spectroscopy/Spectrometryhasni ab ghaniNo ratings yet
- Exploratory Factor AnalysisDocument54 pagesExploratory Factor Analysissoumya agrawalNo ratings yet
- Effective Interview AnswersDocument4 pagesEffective Interview AnswersYAN WENHUI / UPMNo ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument11 pagesExerciseHega TarashiniNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Mae576Document10 pagesLesson Plan Mae576Izzaty IhsanNo ratings yet
- Human Respiration Model AnalysisDocument6 pagesHuman Respiration Model Analysiskhairul afzal mokhtarNo ratings yet
- 2016 Melaka Biologi Kertas 2Document17 pages2016 Melaka Biologi Kertas 2Hemanathan HarikrishnanNo ratings yet
- Primary Year 3 SJK SOWDocument150 pagesPrimary Year 3 SJK SOWJoshua100% (1)
- Assignment January 2015 SEMESTERDocument7 pagesAssignment January 2015 SEMESTERAbraham ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Statistics - Part 1Document20 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Statistics - Part 1Faten ZaraNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Heuristics Approaches to Problem SolvingDocument113 pagesModeling and Heuristics Approaches to Problem SolvinglapokNo ratings yet
- Common MisconceptionsDocument16 pagesCommon MisconceptionsfarhalizaNo ratings yet
- January Semester 2015 Hpgd1103 - Curriculum Development Assignment (60%) ObjectiveDocument7 pagesJanuary Semester 2015 Hpgd1103 - Curriculum Development Assignment (60%) ObjectiveAinus SakinahNo ratings yet
- Menurut LimDocument3 pagesMenurut LimmissfhNo ratings yet
- Flow Over An AIRFOILDocument25 pagesFlow Over An AIRFOILMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Extra Problems For Jacobs Using GSPDocument21 pagesExtra Problems For Jacobs Using GSPpeter_ash_4No ratings yet
- C2005 Ukur Kejuruteraan 2Document125 pagesC2005 Ukur Kejuruteraan 2azmir100% (2)
- Civil 3D TutorialsDocument840 pagesCivil 3D TutorialsRebecca ZodinpuiiNo ratings yet
- Calculo PothenotDocument2 pagesCalculo PothenotAgustin AndonNo ratings yet
- Practica Civil 2014Document13 pagesPractica Civil 2014Agustin AndonNo ratings yet
- X y X y R: Calculation of Circle Centre-Point and Radius From Three Points On Circle CircumferenceDocument2 pagesX y X y R: Calculation of Circle Centre-Point and Radius From Three Points On Circle CircumferenceAgustin AndonNo ratings yet
- HP33S Survey Solutions With COGO Code December 11 2009 Rev2!9!11Document9 pagesHP33S Survey Solutions With COGO Code December 11 2009 Rev2!9!11Agustin AndonNo ratings yet
- HP33SCOGO Detailed Instructions 12-11-09Document9 pagesHP33SCOGO Detailed Instructions 12-11-09Agustin AndonNo ratings yet
- Hp-33S Survey and Cogo Program - Input /output Quick InstructionsDocument6 pagesHp-33S Survey and Cogo Program - Input /output Quick InstructionsAgustin Andon100% (1)
- HP 35 Survey Pro Gs EvaluationDocument15 pagesHP 35 Survey Pro Gs EvaluationAgustin AndonNo ratings yet
- RS FX880PDocument11 pagesRS FX880PAgustin AndonNo ratings yet
- 5800 Survey ProgramDocument18 pages5800 Survey ProgramAgustin AndonNo ratings yet
- Mucoindo Prakasa Engineering Company ProfileDocument11 pagesMucoindo Prakasa Engineering Company ProfileAgung WibowoNo ratings yet
- 255 SNN - Training Manual On AutoCAD Civil 3D - SMISDocument57 pages255 SNN - Training Manual On AutoCAD Civil 3D - SMISZac Mweb100% (3)
- BIRD WATCHING IDENTIFICATION METHODSDocument2 pagesBIRD WATCHING IDENTIFICATION METHODSAllian Jaffe50% (4)
- CN 35-2016 New Version of Argonaut Software For Thickness Measurement Reporting PDFDocument2 pagesCN 35-2016 New Version of Argonaut Software For Thickness Measurement Reporting PDFvangeliskyriakos8998No ratings yet
- Lesson 10 - LevelingDocument37 pagesLesson 10 - LevelingJohn Andrei PorrasNo ratings yet
- Curriculam Vitae: VVVVVVVVVVVVVVDocument3 pagesCurriculam Vitae: VVVVVVVVVVVVVVAmzal AhamedNo ratings yet
- BHIMA - M BrochureDocument2 pagesBHIMA - M BrochurePrachi MishraNo ratings yet
- Kerala PSC Engineering Assistant Question PaperDocument16 pagesKerala PSC Engineering Assistant Question Paperelsypeter70No ratings yet
- 86 Devico ProdBrochure - 2008Document9 pages86 Devico ProdBrochure - 2008nidish100% (1)
- Digitals Theodolites Topcon DT 209 SERIESS - TRANSSURVEYDocument4 pagesDigitals Theodolites Topcon DT 209 SERIESS - TRANSSURVEYTRANS SURVEYNo ratings yet
- Quality control of Geophones: A Sensor DeviceDocument5 pagesQuality control of Geophones: A Sensor DeviceAISHUNo ratings yet
- Origin - Destination Survey: Definition, Objective and MethodologyDocument25 pagesOrigin - Destination Survey: Definition, Objective and MethodologyAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Elem Surveying Set 1Document2 pagesElem Surveying Set 1soontobengineer0% (1)
- 001 2017 4 B PDFDocument290 pages001 2017 4 B PDFRachel Du Preez0% (2)
- Eastern Forests Program Timber Trade Survey Final ReportDocument74 pagesEastern Forests Program Timber Trade Survey Final ReportVictor394No ratings yet
- Manual Software LandStar 7 1 2Document115 pagesManual Software LandStar 7 1 2jose de jesus reyes torresNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 148830Document6 pagesG.R. No. 148830Denzel BrownNo ratings yet
- University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering Department of Civil Engineering TechnologyDocument3 pagesUniversity Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering Department of Civil Engineering TechnologyFadzir AmirNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Machinery Condition MonitoringDocument12 pagesGuidelines For Machinery Condition MonitoringArdhiKhurniawanNo ratings yet
- Untitled PDFDocument8 pagesUntitled PDF22100578No ratings yet
- SURVEYING TECHNIQUESDocument6 pagesSURVEYING TECHNIQUESMarijanaJNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering PDFDocument31 pagesCivil Engineering PDFShivangi MishraNo ratings yet
- Area and Volume ComputationsDocument12 pagesArea and Volume ComputationsAndrew SuiterNo ratings yet
- Detection & MappingDocument2 pagesDetection & MappinghsfNo ratings yet
- 8th Social em PDFDocument282 pages8th Social em PDFvidya sagar100% (1)
- GNSS Supported Survey and Open Source Web GIS For ForestDocument21 pagesGNSS Supported Survey and Open Source Web GIS For ForestFabil AlbarruNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Plane Surveying Concepts and TechniquesDocument11 pagesIntroduction to Plane Surveying Concepts and TechniquesVinayaka RamNo ratings yet
- MX - Road Design (Int) V8i Trn011140-Q-z002Document286 pagesMX - Road Design (Int) V8i Trn011140-Q-z002Sangram Mohanty100% (1)
- BV Rules For The Classification of Offshore Units NR445.A1 DT R02 E 2010 - 04Document92 pagesBV Rules For The Classification of Offshore Units NR445.A1 DT R02 E 2010 - 04HIPAPNo ratings yet
- Peta Topografi Kabupaten Banyuwangi / Topography Map of Banyuwangi DistrictDocument1 pagePeta Topografi Kabupaten Banyuwangi / Topography Map of Banyuwangi DistrictRazgriz Riku100% (1)