Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy and Physiology: Female Reproductive System Structures
Uploaded by
QuinÜQuintana0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views3 pagesap
Original Title
Anatomy and Physiology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentap
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Female Reproductive System Structures
Uploaded by
QuinÜQuintanaap
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
Female Reproductive System
Structures
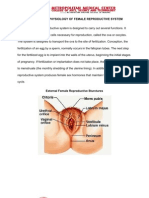
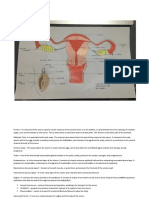
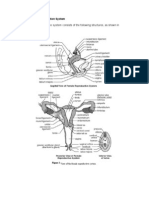
The external genitalia, also called the vulva, includes the mons pubis (a
fatty mound which covers the pubic bone), the labia majora (outer lips of
the vagina), the labia minora (the inner lips of the vagina), the vaginal
opening, the urethral opening (opening of the urethra, a tube which
carries urine from the bladder outside of the body), the clitoris (a small
structure with sensitive nerve endings located within the labia minora, the
sole purpose of which is for sexual arousal and pleasure), and the
perineum (the space between the anus (the rectal opening), and the
vaginal opening).
The internal reproductive anatomy includes the uterus, two ovaries, two
fallopian tubes, the urethra, the pubic bone, and the rectum. The uterus
contains an inner lining called the endometrium (which builds ups and
sheds monthly in response to hormonal stimulation). The lower portion of
the uterus is called the cervix, Cervix is the 3rd lower portion of the uterus,
neck like part (uteri cervix), narrowed where it joins of the top end of the
vagina. Cylindrical in shape and protrudes through the upper anterior
vaginal wall. It has cervical mucus that is made of 90% of water, depending
on the water content which varies during the menstrual cycle that functions
as barrier. It usually contains electrolytes, mainly Calcium, Sodium, and
Potassium, organic components such as amino acids and soluble proteins.
It is also composed of zinc, copper, iron, manganese, and selenium
elements. The cervix also contains a small opening called the os.
Menstrual blood flows through the os into the vagina during menstruation.
Semen travels through the os into the uterus and the fallopian tubes
following ejaculation during sexual intercourse. The cervical os dilates
(opens) during childbirth.
The ovaries, two small almond-shaped structures located on each side of
the uterus, are the female gonads (reproductive glands). Female babies
are born with over 400,000 ova (the gametes, also referred to as egg cells
or oocytes), which are stored in the ovaries. The female body does not
produce any additional ova. The ovaries produce estrogen and
progesterone. The ovaries are close to, but not actually connected to the
fallopian tubes, thin tube-like structures that are the site of fertilization,
the fusion of the male and female gametes.
You might also like
- Bio InfoDocument5 pagesBio InfoSoham MultaniNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System ReportDocument18 pagesReproductive System ReportminnieNo ratings yet
- FemrepnotesDocument38 pagesFemrepnotesLibi FarrellNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document4 pagesScience 10Dawn April sanoyNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument6 pagesBIOLOGYCLANSIE BUXTON CHIKUMBENo ratings yet
- The Female Reproductive System: Niegas, Eunice Ida Marie A. BSN 1-ADocument3 pagesThe Female Reproductive System: Niegas, Eunice Ida Marie A. BSN 1-AEunice Ida Marie NiegasNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesThe Male Reproductive SystemHoney MalabuteNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Reproduction: Female Reproduction Male ReproductionDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Reproduction: Female Reproduction Male ReproductionMhiahLine TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Gender & Society Lo4Document6 pagesGender & Society Lo4Mark Eugene DeocampoNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesThe Reproductive SystemRye ManosNo ratings yet
- Organism Hormones Organ Systems FitnessDocument10 pagesOrganism Hormones Organ Systems FitnessAnonymous 0iY2p9FdNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesMale and Female Reproductive SystemJOSH ELORDENo ratings yet
- Reproductive sy-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesReproductive sy-WPS OfficeAngelo NolealNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesFemale Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyIkea Balhon100% (3)
- Fun With Reproduction: The Big Picture: ReproductionDocument14 pagesFun With Reproduction: The Big Picture: ReproductionAljon AniesNo ratings yet
- Ob Case PressDocument5 pagesOb Case PressHannah Jane PadernalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyLouie Kem Anthony BabaranNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Human Sexual ResponseDocument12 pagesUnderstanding The Human Sexual ResponseMaan JosueNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Document49 pagesAnatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Humraz100% (1)
- Anaphysio (Case Pres)Document7 pagesAnaphysio (Case Pres)Ralph_John_Pac_8337No ratings yet
- Scanned With CamscannerDocument12 pagesScanned With CamscannerDr. Mohammad JamaliNo ratings yet
- Female and Male Reproduvtive SytemDocument4 pagesFemale and Male Reproduvtive SytemAndreiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Sa ScienceDocument15 pagesReviewer Sa Sciencecjosh9975No ratings yet
- Reproductive Nursing SystemDocument17 pagesReproductive Nursing SystemBobby Dwi PutraNo ratings yet
- Liane Ena B. Tabil BSN II MCN (Normal)Document6 pagesLiane Ena B. Tabil BSN II MCN (Normal)ANNooonynmousNo ratings yet
- MCHDocument3 pagesMCHReniella HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemJohn Paulo Morales50% (2)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiologychinchin ramosNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesReproductive SystemJason TaburnalNo ratings yet
- ReproductiveDocument5 pagesReproductiveMaryrose MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Organ in MammalsDocument11 pagesReproductive Organ in MammalstajudeenabdullahaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesReproductive SystemShekinah AsebuqueNo ratings yet
- Presented By, P.Jeyanthi, M.SC (N) I Year Apollo CONDocument67 pagesPresented By, P.Jeyanthi, M.SC (N) I Year Apollo CONPaul AndersonNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesFemale Reproductive System: Anatomy and PhysiologyRyan MulanoNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction and Reproductive HealthDocument16 pagesHuman Reproduction and Reproductive HealthHemanth GowdaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument4 pagesSCIENCEMa. Isabel AtanesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Kenneth MaternalDocument22 pagesAnatomy Kenneth Maternalkennedy14344No ratings yet
- Unit XDocument18 pagesUnit XPreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemArianna Jasmine MabungaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 11 (Reproductive System)Document12 pagesUNIT 11 (Reproductive System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- ReproductiveDocument3 pagesReproductiveJanKennette MangaccatNo ratings yet
- Penis: This Is The Male Organ Used in Sexual Intercourse. It Has Three Parts: The Root, Which Attaches To The Wall of TheDocument1 pagePenis: This Is The Male Organ Used in Sexual Intercourse. It Has Three Parts: The Root, Which Attaches To The Wall of TheAnonymous fI3rSoNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproduction SystemDocument10 pagesThe Female Reproduction Systemrafaelvillacorta100% (1)
- Screenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMDocument127 pagesScreenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMqdvvqvxn7gNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyJustJ ThingsNo ratings yet
- SXSXDocument27 pagesSXSXJoevany E. BigorniaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 7864817067318640141Document55 pagesInbound 7864817067318640141Rijane Mae Castillo GabaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System AnatomyDocument7 pagesReproductive System AnatomyEdDa LaIne TotillaNo ratings yet
- Dana AssignmentDocument10 pagesDana AssignmentDana khalidNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument36 pagesReproductive SystembokkNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Science 10Document22 pagesReproductive Science 10palicpicbea50No ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System (Yuni)Document36 pagesFemale Reproductive System (Yuni)Ayi Abdul BasithNo ratings yet
- Module 1..lesson 1,2&3Document26 pagesModule 1..lesson 1,2&3Carlyn100% (1)
- Chapter: 3. Human Reproduction: The Male Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesChapter: 3. Human Reproduction: The Male Reproductive Systemlogi nageshNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive OrgansDocument39 pagesThe Reproductive OrgansjoaNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction Logo NotesDocument25 pagesHuman Reproduction Logo Notespajice8959No ratings yet
- Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesReview of Anatomy and PhysiologyRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument67 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive Systemannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System and Female Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesMale Reproductive System and Female Reproductive SystemLoriz DoronioNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument3 pagesResumeQuinÜQuintanaNo ratings yet
- Present Medical HistoryDocument1 pagePresent Medical HistoryQuinÜQuintanaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan062014Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan062014QuinÜQuintanaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductionQuinÜQuintanaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanQuinÜQuintanaNo ratings yet
- The Human Brain Project 2014Document2 pagesThe Human Brain Project 2014api-165776946No ratings yet
- Medical Device Quality Systems Manual: A Small Entity Compliance GuideDocument468 pagesMedical Device Quality Systems Manual: A Small Entity Compliance GuideScott BeachNo ratings yet
- BPHDocument57 pagesBPHDiannetotz MoralesNo ratings yet
- Septic Shock PathophysiologyDocument33 pagesSeptic Shock Pathophysiologytummalapalli venkateswara rao67% (3)
- FemaraDocument2 pagesFemaraMyraIntisarNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Wound Healing Activity of Leaves of Crinum AsiaticumDocument5 pagesEvaluation of Wound Healing Activity of Leaves of Crinum AsiaticumxiuhtlaltzinNo ratings yet
- The Teaching HospitalDocument5 pagesThe Teaching Hospitalspurtbd33% (3)
- What Is AsomatognosiaDocument10 pagesWhat Is AsomatognosiaNedima DzaferagicNo ratings yet
- Uji Fagositosis PDFDocument11 pagesUji Fagositosis PDFEno PauzahNo ratings yet
- Easy Health Insurance Claim FormDocument3 pagesEasy Health Insurance Claim FormJanmejay SinghNo ratings yet
- Biology Review Test - Part 2 - Grade 10Document11 pagesBiology Review Test - Part 2 - Grade 10Arhant KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Ability Last enDocument12 pagesAbility Last enzeliteNo ratings yet
- Surgo Fresher's Edition 2013Document24 pagesSurgo Fresher's Edition 2013Surgo GlasgowNo ratings yet
- Methods of Space GainingDocument34 pagesMethods of Space GainingSasikumar Rasappan0% (1)
- Old Age Psychiatry LectureDocument38 pagesOld Age Psychiatry LectureMo 'Fishpondz' IsmailNo ratings yet
- GuidelinesDocument4 pagesGuidelinesChidambaram SeevakanNo ratings yet
- Podj 4 PDFDocument3 pagesPodj 4 PDFNur Sita DewiNo ratings yet
- Knee BiomechanicsDocument32 pagesKnee BiomechanicsnishantsinghbmeNo ratings yet
- Premature Rupture of MembranesDocument38 pagesPremature Rupture of MembranesArwa QishtaNo ratings yet
- ASCP Sttudy GuideDocument12 pagesASCP Sttudy GuideHsin-Hsuan Huang35% (23)
- Sandeep MedicalDocument2 pagesSandeep MedicalSandeep GAMING YTNo ratings yet
- Suffixes and PrefixesDocument2 pagesSuffixes and PrefixesBeckyNo ratings yet
- SPC SoludoxDocument19 pagesSPC SoludoxMihai BirsaNo ratings yet
- Barangay Sta. Cruz Profile 2014Document12 pagesBarangay Sta. Cruz Profile 2014Donnabelle NazarenoNo ratings yet
- DemerolDocument1 pageDemerolCassie100% (1)
- Food Eponyms in Pathology PDFDocument6 pagesFood Eponyms in Pathology PDFJose PhilipeNo ratings yet
- The Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency - Second Edition (BOT-2)Document2 pagesThe Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency - Second Edition (BOT-2)Mikey PanupongNo ratings yet
- NothingNewUnderTheSun Abdul HamidHughesDocument10 pagesNothingNewUnderTheSun Abdul HamidHughesLuisdaniel Martinez AranaNo ratings yet
- Drug Interactions With Antibiotics: August 2018Document4 pagesDrug Interactions With Antibiotics: August 2018Komang SubitaNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure Requirement For B.Pharma & D. PharmaDocument2 pagesInfrastructure Requirement For B.Pharma & D. Pharmaanon_968573480No ratings yet