Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Non-Magnetic Motors: Main Articles:, and
Uploaded by
raviOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Non-Magnetic Motors: Main Articles:, and
Uploaded by
raviCopyright:
Available Formats
Non-magnetic motors[edit]
Main articles: Electrostatic motor, Piezoelectric motor and Electrically powered spacecraft
propulsion
An electrostatic motor is based on the attraction and repulsion of electric charge. Usually,
electrostatic motors are the dual of conventional coil-based motors. They typically require a highvoltage power supply, although very small motors employ lower voltages. Conventional electric
motors instead employ magnetic attraction and repulsion, and require high current at low
voltages. In the 1750s, the first electrostatic motors were developed by Benjamin Franklin and
Andrew Gordon. Today the electrostatic motor finds frequent use in micro-electro-mechanical
systems (MEMS) where their drive voltages are below 100 volts, and where moving, charged
plates are far easier to fabricate than coils and iron cores. Also, the molecular machinery which
runs living cells is often based on linear and rotary electrostatic motors. [citation needed]
A piezoelectric motor or piezo motor is a type of electric motor based upon the change in shape
of a piezoelectric material when an electric field is applied. Piezoelectric motors make use of the
converse piezoelectric effect whereby the material produces acoustic or ultrasonic vibrations in
order to produce a linear or rotary motion. In one mechanism, the elongation in a single plane is
used to make a series stretches and position holds, similar to the way a caterpillar moves. [citation
needed]
An electrically powered spacecraft propulsion system uses electric motor technology to propel
spacecraft in outer space, most systems being based on electrically powering propellant to high
speed, with some systems being based on electrodynamic tethers principles of propulsion to the
magnetosphere.[87][citation needed]
See also[edit]
Electronics portal
Energy portal
Electric generator
Goodness factor
Motor capacitor
Notes[edit]
1.
Jump up^ Ganot provides a superb illustration of one such early electric motor designed
by Froment.[19]
2.
Jump up^ The term 'electronic commutator motor' (ECM) is identified with the heating,
ventilation and air-conditioning (HVAC) industry, the distinction between BLDC and BLAC being in
this context seen as a function of degree of ECM drive complexity with BLDC drives typically
being with simple single-phase scalar-controlled voltage-regulated trapezoidal current waveform
output involving surface PM motor construction and BLAC drives tending towards more complex
three-phase vector-controlled current-regulated sinusoidal waveform involving interior PM motor
construction.[61]
3.
Jump up^ The universal and repulsion motors are part of a class of motors known as AC
commutator motors, which also includes the following now largely obsolete motor types: Singlephase - straight and compensated series motors, railway motor; three-phase - various repulsion
motor types, brush-shifting series motor, brush-shifting polyphase shunt or Schrage motor, FynnWeichsel motor.[62]
You might also like
- API Recommended Practice For ESPDocument104 pagesAPI Recommended Practice For ESPMaghfiraRamadhani100% (1)
- Science - Grade 10: Electricity and MagnetismDocument16 pagesScience - Grade 10: Electricity and MagnetismJames AlforteNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor ReportDocument23 pagesElectric Motor ReportAnfield Faithful67% (3)
- ProjectDocument25 pagesProjectAsif MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Ac Motors Technical ReportDocument12 pagesGroup 2 Ac Motors Technical Reporttristan jeff bautistaNo ratings yet
- Report Analog IC DesignDocument2 pagesReport Analog IC DesignAvinash GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2 Comparing Electric Machine Sys-TemsDocument6 pages2 Comparing Electric Machine Sys-TemsAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Study of Electricity Generated by Ceiling Fan & Car WheelDocument6 pagesStudy of Electricity Generated by Ceiling Fan & Car WheelSaru TVNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor: History and DevelopmentDocument22 pagesElectric Motor: History and DevelopmentVijay MishraNo ratings yet
- Electric MotorDocument2 pagesElectric MotorLAKSHYA SINGHNo ratings yet
- DC Motor WikiDocument55 pagesDC Motor Wikisupratim05No ratings yet
- Ion PropDocument3 pagesIon PropxionNo ratings yet
- For Other Kinds of Motors, See - For A Railroad Electric Engine, SeeDocument6 pagesFor Other Kinds of Motors, See - For A Railroad Electric Engine, SeeSubramanian SakthivelNo ratings yet
- Electrical Generator: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesElectrical Generator: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSalooNo ratings yet
- Building Science Electrical / HVACDocument16 pagesBuilding Science Electrical / HVACManjeet CinghNo ratings yet
- Electric Generator GutulescuDocument7 pagesElectric Generator GutulescuDaniel MariusNo ratings yet
- Ele3114 EvolutionsDocument8 pagesEle3114 EvolutionsKawooya CharlesNo ratings yet
- Eee 2303 Electrical MachinesDocument7 pagesEee 2303 Electrical MachinesKOSGEI CORNELLIUS KIPTANUI EE102/G/5632/18No ratings yet
- Electric Motors of Use As Given at The W PDFDocument399 pagesElectric Motors of Use As Given at The W PDFjimNo ratings yet
- Compilations of Assignment EE330-ACDCDocument173 pagesCompilations of Assignment EE330-ACDCDECIPOLO, KENNETH JOHN E.No ratings yet
- Electrical Machine II: EEEEC11 (3 - 0 - 2) Semester 4Document250 pagesElectrical Machine II: EEEEC11 (3 - 0 - 2) Semester 4sanjoni.jainNo ratings yet
- Electricity Generation From Speed BreakerDocument44 pagesElectricity Generation From Speed Breakerdilliprout.caplet2016No ratings yet
- 1.0 Origin and History of AC GeneratorsDocument58 pages1.0 Origin and History of AC GeneratorsAlfred AgihNo ratings yet
- Lecture#10: Storey: Electrical & Electronic Systems © Pearson Education Limited 2004Document9 pagesLecture#10: Storey: Electrical & Electronic Systems © Pearson Education Limited 2004Hassnain MassidNo ratings yet
- AC GeneratorDocument16 pagesAC Generatorsheikhiyad60No ratings yet
- Concept of Power SystemDocument29 pagesConcept of Power SystemZiyad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document19 pagesModule 3Pragati ShindeNo ratings yet
- Electric EngineDocument2 pagesElectric EngineOpreanDan100% (1)
- Electrical MotorDocument3 pagesElectrical MotorPrakashPrakashNo ratings yet
- Project Documentation For Multilevel InvertersDocument89 pagesProject Documentation For Multilevel InvertersAnonymous hm7nSy1ebNo ratings yet
- Referat BuzoDocument11 pagesReferat BuzoAnaNo ratings yet
- QUIZ#1 - REGIO, Clim Jobert L.Document8 pagesQUIZ#1 - REGIO, Clim Jobert L.Clim RegioNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion: 1. Enumerate and Discuss The Different Forms of Energy Conversion. (Site 10 Examples)Document6 pagesEnergy Conversion: 1. Enumerate and Discuss The Different Forms of Energy Conversion. (Site 10 Examples)ooweemgeeNo ratings yet
- Altena TorDocument8 pagesAltena TorJb EnarioNo ratings yet
- An AC GeneratorDocument2 pagesAn AC Generatorthunderj43No ratings yet
- KronDocument4 pagesKronDeepak Singh100% (1)
- Types of Electrical Motors1Document12 pagesTypes of Electrical Motors1AnilNo ratings yet
- Ac Motor: Motor System Level DiagramDocument3 pagesAc Motor: Motor System Level DiagramDan ZkyNo ratings yet
- DC MotorsDocument1 pageDC MotorsЕри БгNo ratings yet
- Generating Electricity by Using Exhaust GasDocument4 pagesGenerating Electricity by Using Exhaust GasAnonymous j0aO95fgNo ratings yet
- Assgnment MachineDocument5 pagesAssgnment MachineNur AfiqahNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document2 pagesExperiment 2Anthony John Camacho ReburianoNo ratings yet
- Extra Notes DCmotorsDocument19 pagesExtra Notes DCmotorsashikinNo ratings yet
- DC Machines and DrivesDocument10 pagesDC Machines and DrivesMahadev KovalliNo ratings yet
- Multipurpose Machines Using Scotch Yoke MechanismDocument36 pagesMultipurpose Machines Using Scotch Yoke Mechanismnithinkenator88% (16)
- Electrical MachinesDocument38 pagesElectrical Machineshephzi28No ratings yet
- Study of Variable Frequency Drives VDocument22 pagesStudy of Variable Frequency Drives VManjiri PhadnisNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroductionjayantabhbasuNo ratings yet
- Electric Generator: Specialized Types of GeneratorDocument3 pagesElectric Generator: Specialized Types of GeneratorErRANaveenNo ratings yet
- Classification or Types of Motor: Electric CurrentDocument2 pagesClassification or Types of Motor: Electric CurrentSrini Vasan100% (1)
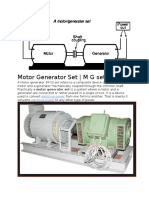
- Motor-Generator - WikipediaDocument7 pagesMotor-Generator - Wikipediahema FawzyNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Simulation StudyDocument10 pagesExperimental and Simulation Studyمحمد عامرNo ratings yet
- SM Report HandoutDocument4 pagesSM Report HandoutShang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor Drive Analysis Using LabVIEWDocument26 pagesThree-Phase Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor Drive Analysis Using LabVIEWCarlos Roberto Amaya Rodriguez100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Electrical MachineDocument27 pagesChapter 5 Electrical MachineBirhex FeyeNo ratings yet
- The Use of Electric Motors For The Propulsion of Seagoing VesselsDocument23 pagesThe Use of Electric Motors For The Propulsion of Seagoing Vesselspal_malayNo ratings yet
- Electric Motors (English Project) PDFDocument10 pagesElectric Motors (English Project) PDFAvramov Iulian Cristian50% (2)
- Motor Study Material: UniversalDocument1 pageMotor Study Material: UniversalDinesh VelNo ratings yet
- Alternator - WikipediaDocument35 pagesAlternator - Wikipediajoseph5689No ratings yet
- Subtructure WorksDocument1 pageSubtructure WorksRazakMaidenNo ratings yet
- Ac/Dc Machines: Electromechanical Energy ConversionDocument20 pagesAc/Dc Machines: Electromechanical Energy ConversionAshner NovillaNo ratings yet
- Integration of Large Scale Wind Energy with Electrical Power Systems in ChinaFrom EverandIntegration of Large Scale Wind Energy with Electrical Power Systems in ChinaNo ratings yet
- PEECC Equipment ListDocument1 pagePEECC Equipment ListraviNo ratings yet
- Dielectrics: Charge Storage Principles of Different Capacitor Types and Their Inherent Voltage ProgressionDocument3 pagesDielectrics: Charge Storage Principles of Different Capacitor Types and Their Inherent Voltage ProgressionraviNo ratings yet
- CT 1Document2 pagesCT 1raviNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentraviNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Types: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument1 pageCapacitor Types: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaraviNo ratings yet
- Zebra ACSR ConductorsDocument3 pagesZebra ACSR ConductorsraviNo ratings yet
- Rolling Stock: This Article Is About Train Cars. For The Genre of Motorsports, SeeDocument3 pagesRolling Stock: This Article Is About Train Cars. For The Genre of Motorsports, SeeraviNo ratings yet
- Type MDocument2 pagesType MraviNo ratings yet
- Acsr (Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced) : You Are HereDocument1 pageAcsr (Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced) : You Are HereraviNo ratings yet
- Type E: Learn MoreDocument6 pagesType E: Learn MoreraviNo ratings yet
- Type A: Here HereDocument3 pagesType A: Here HereraviNo ratings yet
- Neutral Return Currents Through The Ground: Three PhaseDocument1 pageNeutral Return Currents Through The Ground: Three PhaseraviNo ratings yet
- Baffle Placement For A RefractorDocument5 pagesBaffle Placement For A RefractorLuizNo ratings yet
- CPC 100 User Manual ENUDocument77 pagesCPC 100 User Manual ENUSujoy PaulNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Electrolysis. AQA OCR Edexcel. QuestionsDocument4 pagesGCSE Chemistry Electrolysis. AQA OCR Edexcel. QuestionsRhona MatahariNo ratings yet
- Tutorial: Lecture Delivered By: Anusha VaddeDocument5 pagesTutorial: Lecture Delivered By: Anusha Vaddevaddeanusha203100% (1)
- Esprit Series Lead-Acid Battery ChargersDocument2 pagesEsprit Series Lead-Acid Battery ChargersbtiscribdNo ratings yet
- CO278-279 Solenoid RelayDocument3 pagesCO278-279 Solenoid RelayAdasson BravoNo ratings yet
- Ar2 Doc 006 0004 00 Earthing Design Calc (Substation) Rev CDocument17 pagesAr2 Doc 006 0004 00 Earthing Design Calc (Substation) Rev CmbnuguidNo ratings yet
- Relay Catalogue PDFDocument44 pagesRelay Catalogue PDFMohammad Tabrez Alam100% (2)
- ANSI C84.1-1995 Electric Power Systems and Equipment Voltage Ratings (60 Hertz)Document24 pagesANSI C84.1-1995 Electric Power Systems and Equipment Voltage Ratings (60 Hertz)Alejandro UshiñaNo ratings yet
- Samsung HPS5033Document147 pagesSamsung HPS5033Omar CastilloNo ratings yet
- Deh 1900r/Xu/Ew5Document64 pagesDeh 1900r/Xu/Ew5roca9oNo ratings yet
- Satip-X-600-02 Rev 1 For CP SystemDocument4 pagesSatip-X-600-02 Rev 1 For CP SystemSaleem MohammedNo ratings yet
- L931 ManualDocument29 pagesL931 ManualYesid Luna100% (1)
- Exp 4 Hall EffectDocument10 pagesExp 4 Hall EffectNischayNo ratings yet
- MFIE Analysis and Design of Ridged Waveguide PDFDocument7 pagesMFIE Analysis and Design of Ridged Waveguide PDFవేలుసామి లింగాసామిNo ratings yet
- Ii-1 MCQDocument2 pagesIi-1 MCQMofazzal Hossain KhondekarNo ratings yet
- 72gf66e PDFDocument56 pages72gf66e PDFAutogrederNo ratings yet
- INSTALLATION MANUAL OF 525Document63 pagesINSTALLATION MANUAL OF 525Wajaht Ali100% (1)
- Blackbody Radiation PDFDocument23 pagesBlackbody Radiation PDFShweta Sridhar100% (1)
- EE6201-Circuit Theory PDFDocument18 pagesEE6201-Circuit Theory PDFKevin EstaNo ratings yet
- Specification Including GTP of Energy MetersDocument113 pagesSpecification Including GTP of Energy MetersBijuNo ratings yet
- WWW - Iranswitching.Ir: Ac/Dc Switch Mode Power Supply Design GuideDocument1 pageWWW - Iranswitching.Ir: Ac/Dc Switch Mode Power Supply Design GuidedraNo ratings yet
- Syllabus UEE001 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERINGDocument2 pagesSyllabus UEE001 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERINGWarden Hostel GNo ratings yet
- Power Meter DPM-C530 User ManualDocument114 pagesPower Meter DPM-C530 User ManualPablo CallaNo ratings yet
- Apgenco Ae Electronics SyllabusDocument3 pagesApgenco Ae Electronics SyllabusDhanu NetintiNo ratings yet
- SuperconductorsDocument31 pagesSuperconductorsnitibodhe100% (1)
- Chang 2016Document9 pagesChang 2016Muhammad Fahmi Syawali RizkiNo ratings yet
- NFBUP NFXUP S-Sub1 PDFDocument2 pagesNFBUP NFXUP S-Sub1 PDFMihai Butnaru-PaladeNo ratings yet