Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Safety Instruction Sheets For Plant Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines PDF
Safety Instruction Sheets For Plant Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines PDF
Uploaded by
bainOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Safety Instruction Sheets For Plant Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines PDF
Safety Instruction Sheets For Plant Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines PDF
Uploaded by
bainCopyright:
Available Formats
Engineering Encyclopedia
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
SAFETY INSTRUCTION SHEETS FOR PLANT
PIPING AND CROSS-COUNTRY PIPELINES
Note: The source of the technical material in this volume is the Professional
Engineering Development Program (PEDP) of Engineering Services.
Warning: The material contained in this document was developed for Saudi
Aramco and is intended for the exclusive use of Saudi Aramcos employees.
Any material contained in this document which is not already in the public
domain may not be copied, reproduced, sold, given, or disclosed to third
parties, or otherwise used in whole, or in part, without the written permission
of the Vice President, Engineering Services, Saudi Aramco.
Chapter : Mechanical
File Reference: MEX-101.10
For additional information on this subject, contact
PEDD Coordinator on 874-6556
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
MODULE COMPONENT
PAGE
INTRODUCTION .................................................................................................2
DETERMINING THE INFORMATION REQUIRED FOR PLANT PIPING............4
Critical Plant Piping Systems ....................................................................4
Information Contained in Saudi Aramco Form 2821 .................................5
DETERMINING THE INFORMATION REQUIRED FOR CROSS-COUNTRY
PIPELINES ..........................................................................................................7
Information Contained in Saudi Aramco Form 5645-1 ..............................7
Information Contained in Form 5645-1, Cont'd .........................................8
Information Contained in Saudi Aramco Form 5645-2 ..............................9
SUMMARY ........................................................................................................10
Line Identification (Entries 1-6)................................................................11
Equipment Data (Entries 7-16)................................................................11
Operating Limits (Entries 17-28) .............................................................13
Miscellaneous Information (Entries 29-35) ..............................................16
Work Aid 2A: Saudi Aramco Form 5645-1............................................18
Pipeline Identification (Entries 1-12)........................................................18
Equipment Data (Entries 13-24)..............................................................20
Operating Limits (Entries 25-40) .............................................................22
Miscellaneous Information (Entries 41-48) ..............................................25
Work Aid 2B - Saudi Aramco Form 5645-2 .............................................27
Pipeline Identification (Entries 1-9)..........................................................27
Equipment Data (Entries 10-20)..............................................................28
Operating Limits (Entries 21-37) .............................................................29
Operating Limits (Entries 21-37), Cont'd .................................................29
Operating Limits (Entries 21-37), Cont'd .................................................31
Miscellaneous Information (Entries 38-45) ..............................................31
GLOSSARY .......................................................................................................34
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
INTRODUCTION
Safety Instruction Sheets are used to ensure that
operations, maintenance, and inspection personnel will
have adequate information that concerns safe operating
limits, protective devices, any special safety precautions
for specified piping system or pipelines, and other
equipment items in a consistent format. The Saudi
Aramco engineer must know how to complete all the
items on the applicable Safety Instruction Sheet,
including Maximum Allowable Operating Pressure
(MAOP), pipewall thickness, pressure test requirements,
and numerous other items that were previously
discussed in this course. The Saudi Aramco engineer is
responsible for the completion of the form, the audit of
the contents of the form, and ensuring that it is included
in the design package.
The Safety Instruction Sheets applicable to piping
systems are as follows:
Saudi Aramco Form 2821.
Saudi Aramco Forms 5645-1 and 5645-2.
Saudi Aramco Form 2821 is used for plant piping
systems, and Forms 5645-1 and 5645-2 are used for
cross-country pipelines. The extent of their use for these
systems will be discussed in later sections. These forms
provide a permanent record of critical data with regard to
the piping system. In particular, pipe material, design
conditions, thicknesses, MAOP, and safety-valve set
pressures are specified on these sheets. By the time
these forms are completed, the piping system design has
been done, and all the information that is necessary to
complete these forms is readily available. Thus, no
additional engineering is required to complete these
forms.
An engineer can obtain a fairly complete picture of the
design of the piping system from the Safety Instruction
Sheets. The Safety Instruction Sheets are part of the
permanent records for the system and are a critical
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
resource when changes or maintenance are required on
the piping system. These forms must be completed
before the system is put into operation. They are
completed throughout the design of the piping system,
and they are referred to during inspection and testing.
Saudi Aramco Engineering Standard SAES-A-005,
Safety Instruction Sheet, provides requirements and
instructions for the completion of the appropriate form for
a particular situation. SAES-A-005 should be referred to
when a Safety Instruction Sheet is being completed.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
DETERMINING THE INFORMATION REQUIRED FOR PLANT PIPING
Critical Plant Piping Systems
SAES-A-005 requires that Safety Instruction Sheet,
Saudi Aramco Form 2821, be completed for critical plant
piping. A piping system is determined to be critical based
on operational considerations, design conditions that
make it more difficult to design and/or prone to failure, or
safety considerations. A plant piping system is critical if it
meets at least one of the following criteria:
The failure of the system would lead to a major
shutdown of the plant, or shutdown of a major unit
of the plant.
The design temperature is 340C (650F) or higher.
The design pressure is 3,450 kPa (500 psig) or
higher.
The fluid that is contained in the pipe is toxic or very
corrosive.
There is some other specific operating hazard
associated with the system that is not normally
experienced with the usual plant or process lines.
Saudi Aramco Form 2821 is normally not completed for
piping systems that are covered by Piping Material
Specification Classes D, E, F, G, or H of SAES-L-005.
These Specification Classes are relatively mild in nature,
as follows:
Class D Low-Pressure Utilities, Noncorrosive
Class E Low-Pressure Utilities, Corrosive
Class F Nonpressure Sewers
Class G Small Diameter Piping Around Pumps
and Compressors
Class H Low-Pressure Hydrocarbon Service
Refer to SAES-L-005 for the specific service limitations of
these Classes.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
Information Contained in Saudi Aramco Form 2821
Saudi Aramco Form 2821 identifies system design
information for plant piping systems. The design
information that is identified on Saudi Aramco Form 2821
must be determined in order to complete the form. Work
Aid 1 contains a copy of Form 2821 (Figure 1) with each
entry area numbered. Work Aid 1 also contains a
procedure that may be used to complete the form and is
keyed to the numbered areas. Form 2821 identifies four
primary categories of information as follows:
Line Identification Information. These items
identify the line with respect to line number, end
points, fluid service, other reference drawings, and
the industry code that was used for its design.
Equipment Data. These items define the primary
physical design information for the system, such as
diameter, nominal wall thickness, material, and
flange rating. This information helps personnel
define many of the physical characteristics of the
system without the need to locate the detailed
engineering drawings. Additional needed
information can be found as required because the
design drawings are also referenced. All of this
information was determined during the system
design and most was discussed in earlier modules
of MEX 101.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
Operating Limits. These items define the primary
operating limits for the system, such as design
pressure and temperature, MAOP, test pressure,
and the component(s) that limit the system
operation. This information permits personnel to
perform an initial evaluation of the system to
determine its limitations. This may be required if a
rerate is being considered, or if corrosion has
occurred. All of this information was determined
during the system design and most was discussed
in earlier modules of MEX 101.
Miscellaneous Information. This section contains
additional information regarding location,
identification, and locations for the necessary
approvals.
Refer to Work Aid 1 and Figure 1 for the specific
information that is contained in each of these categories
and for a procedure for completing this form.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
DETERMINING THE INFORMATION REQUIRED FOR CROSS-COUNTRY
PIPELINES
In general, Safety Instruction Sheets are prepared for all
flowlines, trunklines, and cross- country pipelines that
carry any fluid. Saudi Aramco Form 5645-1 shall be
completed for all major pipelines. In addition, Saudi
Aramco Form 5645-2 shall be filled out for the same
pipelines to cover tie-in piping, scraper traps and their
appurtenances, jumpovers, flanges, fittings, any special
components, road crossings, and sun pressure relief
valves. Form 5645-2 shall also be prepared for flowlines,
trunklines, testlines, and submarine pipelines. Both
Forms 5645-1 and 5645-2 are to retain the same Saudi
Aramco drawing number when they are used for different
portions of the same general pipeline, but with different
sheet numbers.
When calculations are required to complete the form, the
issuer of the forms must attach a calculation sheet with
each form to help with any later review that might be
required. The calculation sheet shall show the method
that was used to achieve calculated values, such as
formulas, individual variables that are in the formulas with
their units, specific requirements from the relevant
standards, etc.
Information Contained in Saudi Aramco Form 5645-1
Saudi Aramco Form 5645-1 identifies system design
information for cross-country pipelines. The design
information that is identified on Saudi Aramco Form
5645-1 must be determined in order to complete the
form. Work Aid 2A contains a copy of Form 5645-1
(Figure 2) with each entry area numbered. Work Aid 2A
also contains a procedure that may be used to complete
the form and is keyed to the numbered areas. Form
5645-1 identifies four primary categories of information
as follows:
Pipeline Identification Information. This includes
items such as the pipeline's official designation, end
points, fluid service, the year it was built, valve
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
operating diagram reference, the number of sheets
that describe the entire pipeline, reference to the
Forms 5645-2 that are also used for the pipeline,
and the pipeline segment numbers that are covered
by the sheet.
Equipment Data. These items define the primary
physical design information for the pipeline
segments that are covered by a particular sheet.
This includes items such as diameter, nominal wall
thickness, material, flange rating, and whether the
pipeline is buried or aboveground. This information
helps personnel define many of the physical
characteristics of pipelines without the need to
locate the detailed engineering drawings or go into
the field. All of this information was determined
during the pipeline design, and most was discussed
in earlier modules of MEX 101.
Information Contained in Form 5645-1, Cont'd
Operating Limits. These items define the primary
operating limits for the pipeline. This includes items
such as the MAOP of each segment and the overall
system (and the component[s] that limit them), the
Design Factor of each segment, maximum design
temperature, minimum tie-in temperature, minimum
required thickness, and test pressure. This
information permits personnel to perform an initial
evaluation of the pipeline to determine its limitations.
This evaluation may be required if an alternate
operation is being considered, or if corrosion has
occurred. All of this information was determined
during the system design, and most was discussed
in earlier modules of MEX 101.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
Miscellaneous Information. This area contains
additional information regarding location,
identification, and locations for the necessary
approvals.
Refer to Work Aid 2A and Figure 2 for the specific
information that is contained in each of these categories,
and for a procedure for completing this form.
Information Contained in Saudi Aramco Form 5645-2
Saudi Aramco Form 5645-2 identifies system design
information for flowlines, trunklines, testlines, submarine
pipelines, tie-in piping, scraper traps and their
appurtenances, special components, and the other items
that were noted previously. Work Aid 2B contains a copy
of Form 5645-2 (Figure 3) with each entry area
numbered. The design information that is identified on
Saudi Aramco Form 5645-2 must be determined in order
to complete the form. Work Aid 2B also contains a
procedure that may be used to complete the form and is
keyed to the numbered areas.
Saudi Aramco Form 5645-2 identifies the same four
primary categories of information that were discussed for
Saudi Aramco Form 5645-1. However, the specific data
items that are included in the "Equipment Data" and
"Operating Limits" categories are more similar to the
items that are in Form 2821 for plant piping rather than in
Saudi Aramco Form 5645-1; the similarity exists because
the particular pipeline system items for which Saudi
Aramco Form 5645-2 is used are more similar to plant
piping than to cross-country pipelines.
Refer to Work Aid 2B and Figure 3 for the specific
information that is contained in each of these categories
and a procedure for completing this form.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
SUMMARY
Safety Instruction Sheets must be completed before a
piping system can go into operation. For critical plant
piping systems, Form 2821 must be completed. For
cross-country pipelines, Saudi Aramco Forms 5645-1
and 5645-2 must be completed. The completion of these
forms requires the engineer to collect information
regarding system design and operating limits that has
already been determined during detailed engineering.
The collection of data in this manner ensures that
operations, maintenance and inspection personnel have
adequate information in a consistent format.
The next module discusses how to maintain piping and
repair defects after the piping system has been placed in
operation.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
10
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
WORK AID 1:
PROCEDURES FOR DETERMINING THE INFORMATION TO
COMPLETE A SAFETY INSTRUCTION SHEET FOR PLANT
PIPING
Use the following procedure, in conjunction with Figure 1,
to determine the information that is necessary to
complete Safety Instruction Sheet, Form 2821, for critical
plant piping. The identification numbers that are shown in
the following procedure correspond to those shown in
Figure 1. Reference SAES-A-005, Safety Instruction
Sheet, for additional information. Note that by the time it
is necessary to complete Form 2821, engineering has
been completed, all the required information is readily
available, and no new calculations or selections are
needed.
Line Identification (Entries 1-6)
1.
Show the line identification number, such as P28-3A1.
2. & 3.
Indicate where the line starts and ends, such
as Furnace F-201 to Column C-221, Acid
Pumps G-21A/B to Reactor D-21.
4.
Give specific data on the fluid service, such as
reduced crude with acid, vapor, etc.
5.
Indicate the pertinent pipe isometrics, P & ID's,
or other reference drawings that apply to the
particular line.
6.
Show the applicable industry code and year
that was used in the pipe design, such as ANSI
B31.3, 1990.
Equipment Data (Entries 7-16)
Note that there are three columns within the Equipment
Data area. This permits providing information about
three separate pipe sizes or materials that may be within
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
11
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
the same piping system.
7.
Nominal pipe size (NPS).
8.
Pipewall thickness in inches or millimeters.
Note that this is the nominal pipe thickness,
which was discussed in MEX 101.03.
9.
Pipe material specification and grade, such as
A-106, Gr. B, API 5L, Gr. X-42. Material
selection was discussed in MEX 101.02 and
MEX 101.08.
Equipment Data (Entries 7-16), Cont'd
10.
Indicate whether the pipe has a welded
longitudinal seam (such as SAW, ERW), or is
seamless (SMLS).
11.
Flange rating according to ASME/ANSI B16.5.
Selection of the required flange rating was
discussed in MEX 101.04.
12.
Type of flange face, such as raised face (RF),
ring joint (RTJ), or flat face (FF). Flange face
requirements were discussed in MEX 101.04.
13.
Flange material specification and grade, such
as A-105; A-350, Grade LF-2. Flange material
selection was discussed in MEX 101.04 and
MEX 101.08.
14.
Fitting rating, such as Sch. 40 for butt-weldtype fittings, or 3,000 lb. for threaded- or
socket-welded-type fittings. The rating of pipe
fittings was discussed in MEX 101.04 and MEX
101.08.
15.
Fitting material specification and grade, such
as A-105; A-234, Gr. WPB. Fitting material
specification was discussed in MEX 101.04
and MEX 101.08.
16.
Any specific remarks with regard to material,
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
12
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
components, system limitations. Include items
such as the following:
Precautions that are necessary during
operation or tests. For example, the need
to blind-off expansion joints during
hydrostatic tests because they will not
withstand the test pressure, or the need to
add temporary supports during hydrotest.
Special piping components that may be in
the system, such as soft-seat ball valves.
Operating Limits (Entries 17-28)
17. & 18. Indicate the MAOP and temperature for the
lines as one system based on its weakest
point, such as the corrosion condition of the
line, pressure vessels, flanges, etc. MAOP
was discussed in MEX 101.03 and MEX
101.04.
19.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
Enter the actual new test pressure. The test
pressure should be consistent with the
hydrostatic test diagram and SAES-A-004.
Test pressure requirements were discussed in
MEX 101.09.
13
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
Operating Limits, (Entries 17-28), Cont'd
20.
Show the limiting item for the test pressure,
such as flanges, pipewall thickness, pressure
vessel, heat exchanger.
21.
Enter the design pressure, which should be
consistent with SAES-L-002.
22.
Enter the design temperature, which should be
consistent with SAES-L-002.
23.
Indicate the limiting item for the design
pressure, such as pipewall thickness, flanges,
process limitations, or any other limiting item.
24.
Enter the equipment safety valve set pressure,
not greater than that shown under Key Number
21.
25.
Nominal Pipe Size (NPS). Note that there are
three columns for size and for Key Numbers 26
and 27. This permits providing information
about three separate pipe sizes that may be
within the same piping system.
26.
Required minimum wall thickness, tm, for the
pipe. Refer to ASME/ANSI B31.3 and MEX
101.03 for method of calculation.
Note that tm is the retirement wall
thickness, and shall also not be less than
the required wall thickness for mechanical
strength. Refer to Saudi Aramco
Inspection Procedure 01-AIP-02-0, SAESL-006, or the piping specialist in the
Consulting Services Department, for
further explanation. When tm is for
mechanical strength, indicate this in the
remarks section.
27.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
This is calculated based on the nominal wall
thickness of the pipe, minus manufacturing
undertolerance for thickness, and minus the
14
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
value that was determined for Key Number 26.
Note that the corrosion allowance, c, as
determined here, is the remaining pipewall thickness that is above the required
tm. 'c' is not the required corrosion
allowance that was specified as part of
the initial design conditions for the piping
system. If a corrosion allowance is
required, it must be stated in the remarks
area under Key Number 28.
28.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
Add any remarks that pertain to any item or
calculation above. Indicate any items or
hazards which require consideration by
operations, inspection or maintenance
personnel.
15
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
Miscellaneous Information (Entries 29-35)
29.
District and location.
30.
Plant number.
31.
Follow the usual procedure to obtain drawing
numbers.
32.
Include BI and JO under which the equipment
was installed.
33.
Complete this section showing date and name
of originator.
34.
Engineering concurrence as indicated in
Section 4 of this standard plus project manager
or plant manager's approval, as required.
35.
Signature of Facility Engineering Division head.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
16
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
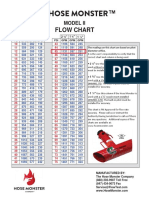
FORM 2821
FIGURE 1
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
17
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
WORK AID 2:
PROCEDURES FOR DETERMINING THE INFORMATION TO
COMPLETE A SAFETY INSTRUCTION SHEET FOR CROSSCOUNTRY PIPELINES
Work Aid 2A:
Saudi Aramco Form 5645-1
Use the following procedure in conjunction with Figure 2
to determine the information that is necessary to
complete Safety Instruction Sheet, Form 5645-1, for
pipelines. The identification numbers that are shown in
the following procedure correspond to those shown in
Figure 2. Reference SAES-A-005, Safety Instruction
Sheet, for additional information. Note that by the time it
is necessary to complete Form 5645-1, engineering has
been completed, all of the required information is readily
available, and no new calculations or selections are
needed.
Pipeline Identification (Entries 1-12)
1.
Give the official designation of the pipeline,
e.g., "Qatif-Ras Tanura Pipeline Number 6"
(QRT-6) and indicate the fluid that is being
handled, such as "stabilized Arabian Light
Crude," "fuel gas," or "water."
2.
Show the name of the pipeline origin, such as
"Qatif Junction."
3.
Show the name of the pipeline termination
point, such as "Ras Tanura."
4.
Indicate the type of fluid that is being handled,
such as Arab Light.
5.
Show the name of the valve operating diagram
of this line, such as "NACRUDE." If not
available, give the P & ID Drawing Number.
6.
Indicate the year in which the line was built.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
18
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
7.
Give the Kilometer Number where the pipeline
begins.
8.
Give the Kilometer Number of the pipeline
where this particular sheet begins. A pipeline
will typically require several Forms 5645-1 to
cover its entire length. This entry defines
where this particular sheet starts.
9.
Show the number of sheets which cover all
major segments of the pipeline to be covered
by Form 5645-1. This entry defines how many
sheets are used for the entire pipeline.
Pipeline Identification (Entries 1-12), Cont'd
10. & 11. Enter the number of the sheet(s) that cover
items which will be covered by Form 5645-2,
as identified above.
12.
Segments of the pipeline are to be numbered
sequentially, i.e., Sheet 1 will show Segments
1-5, Sheet 2 will show Segments 6-10, and so
on. A single pipeline will have multiple
segments.
Note that each segment shall have the same
diameter, wall thickness, material grade,
hydrostatic test pressure, MAOP, Area
Classification, and type of construction. If any
of these characteristics change, a new
Segment Number is to be used. Also, the
portion of the pipeline that is located between
any two major facilities (such as a scraper trap,
pump station, or a junction point) shall be
considered as a separate segment even if it
has the same characteristics as an adjacent
segment.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
19
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
Equipment Data (Entries 13-24)
13.
Nominal or outside diameter.
14.
Nominal wall thickness, with fractions shown in
decimals.
15.
Show the grade of pipe material, such as API
5L, GR. X50. SAMSSs references are not
acceptable.
16.
Enter the starting kilometer location of the
segment.
17.
Enter the ending kilometer of the segment.
18.
Indicate the length of the segment, in feet, as
shown on the layout drawing. Since the actual
routing of the pipe will not necessarily be
straight between kilometer stations, the length
of the pipeline segment is not simply the
difference between the two kilometer markers.
19.
Indicate the length of the segment in
kilometers.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
20
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
Equipment Data (Entries 13-24), Cont'd
20.
Show the process of manufacture for the pipe
(see the mill inspection report).
Seamless (S).
Longitudinally (straight seam) welded submerged-arc (Electricfusion welded) by U-ing, O-ing, Expanding (UOE-EFW).
Longitudinally (straight seam) welded submerged-arc (Electricfusion welded) by Cage Forming (CF-EFW).
Longitudinally (straight seam) welded electric-resistancewelded
(UOE-ERW), (CF-ERW).
Special-welded, submerged-arc (Spiral-EFW).
21.
Indicate the Specified Minimum Yield Strength
in psi, as shown on the mill certificates, for
each item of the purchase order. For example,
41,000 psi.
22.
Indicate the flange rating per ASME/ANSI
B16.5. Selection of the flange rating was
discussed in MEX 101.04.
23.
Show the type of construction for the pipeline
segment as follows:
24.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
B:
Buried
AGR: Restrained Aboveground.
AGN: Nonrestrained Aboveground.
Include any remarks that are related to pipe
material, such as "X65 pipe in Segment 3 is
installed on an experimental basis to check
weldability".
21
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
Operating Limits (Entries 25-40)
25.
Calculate the internal pressure that is required
to develop a hoop stress that is equal to the
Design Factor (DF) multiplied by the Specified
Minimum Yield Strength (SMYS) of the pipe
based on the pipe outside diameter (OD) and
nominal wall thickness (Tn).
MAOP = (DF)(SMYS)(2Tn)/(OD)
If other factors are limiting (such as flange
rating), indicate the lower MAOP and annotate
accordingly. MAOP of a pipe section was
discussed in MEX 101.03.
26.
Indicate the limiting factor of the MAOP, and
whether it is the pipewall thickness or any other
factor, such as flange rating.
27.
Show the Design Factor of the segment, such
as 0.5, 0.6, or 0.72. Design Factor was
discussed in MEX 101.03.
28.
Show the maximum design temperature.
29.
Indicate minimum design tie-in temperatures
specified in the project specification or "scope
of work".
30.
Indicate the allowable bending stress, Sb, per
SAES-L-051 and SADP-L-051. Allowable
bending stress was discussed in MEX 101.07.
31.
Calculate the required minimum wall thickness
of the pipe, Tm, based on the segment MAOP
and the Design Factor, DF. The required
minimum wall thickness of the pipe was
discussed in MEX 101.03.
Tm = (MAOP)(OD) / [2(DF)(SMYS)]
Note that Tm is the retirement wall thickness,
and shall not be less than the required wall
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
22
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
thickness for mechanical strength. Refer to
Saudi Aramco Inspection Procedure 01-AIP02-0, SAES-L-006, or to the piping specialist in
the Consulting Services Department for further
explanation.
32.
Show the actual hydrostatic test pressure of
the particular segment of pipeline that is
performed immediately after construction. The
test pressure must be calculated in accordance
with SAES-A-004, Pressure Testing. Test
pressure requirements were discussed in MEX
101.09.
Operating Limits (Entries 25-40), Cont'd
33.
Show the test date.
34.
Indicate the factor that limits the test pressure,
such as pipewall thickness, flange rating,
branch connection, etc.
Note that entries for revalidation hydrostatic
tests (entries 35-37) are to be completed when
the information is known. The Safety
Instruction Sheet (SIS) is to be updated after
every revalidation test by the responsible
Operations Engineering unit.
35.
Indicate the actual test pressure for the
revalidation test. The test pressure shall be in
accordance with SAES-A-004 and approved by
the responsible Saudi Aramco Engineering
unit.
36.
Show the test date.
37.
Indicate the factor that limits the test pressure.
Note that this does not necessarily have to be
the same item that limited the initial hydrotest
pressure. For example, the original hydrotest
pressure might have been limited by the
flanges. However, corrosion which may have
occurred in the pipe, itself, could make it the
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
23
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
limiting component for a revalidation test.
38.
Indicate the Maximum Allowable Operating
Pressure (MAOP) of the entire pipeline as if
one system, if applicable. This MAOP will be
dictated by the lowest of the MAOP's across
the entire pipeline, or the maximum pressure
that is achievable upstream due to, for
instance, well head or pump shutoff pressure.
If the pipeline does not have one MAOP for the
system, indicate this by "N/A" and give a clear
explanation in the remarks area, such as "the
line is telescoped."
39.
Show the limiting factor that dictates the
system MAOP.
40.
Include any pertinent remarks that will assist
operations, inspection or maintenance
personnel. Any safety hazards for the pipeline
or fluid that is transported should be
mentioned. If the pipeline is constructed such
that the pipe, flanges, valves, or fittings will not
withstand the shutoff pressure of the pump
plus the static head pressure when a
downstream valve is closed, then this hazard
must be clearly highlighted.
Indicate if surge protection system(s) have
been provided. Make reference to any special
operating instructions.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
24
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
Miscellaneous Information (Entries 41-48)
41.
Include the drawing numbers of schematic
layout, P & I diagram, process flow diagram,
hydrostatic test diagram, and hydraulic profile
drawing.
42.
District and/or location and the official pipeline
name, as in Item #1.
43.
Show the Plant No.
44.
Follow the usual procedure to obtain a drawing
number.
45.
Include BI and JO under which the pipeline
was installed.
46.
Complete this section showing the date
prepared and the name of the originator.
47.
Engineering concurrence as indicated in
Section 4 plus Project Manager or Plant
Manager's approval, as required.
48.
Signature of Facility Engineering Division head.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
25
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
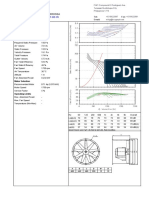
FORM 5645-1
FIGURE 2
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
26
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
Work Aid 2B - Saudi Aramco Form 5645-2
Use the following procedure in conjunction with Figure 3
to determine the information that is necessary to
complete Safety Instruction Sheet, Form 5645-2, for
pipeline tie-in piping, scraper traps and their
appurtenances, jumpovers, as well as flanges, fittings,
any special components, road crossings, sun-pressure
relief valves, flowlines, trunklines, testlines, and
submarine pipelines. The identification numbers that are
shown in the following procedure correspond to those
shown in Figure 3. Reference SAES-A-005, Safety
Instruction Sheet, for additional information. Note that by
the time it is necessary to complete Form 5645-2,
engineering has been completed, all the required
information is readily available, and no new calculations
or selections are needed.
Pipeline Identification (Entries 1-9)
1.-6.
Same as corresponding Key Numbers 1-6 on
Form 5645-1.
7.
Provide adequate information to clearly identify
the equipment; for example, scraper trap, block
valve MOV-123, etc.
8.
Show the location of the equipment by name
and kilometer, such as Qatif Junction, km. 0.0.
In the case of flowlines, testlines, or trunklines,
show the GOSP name at which these lines
terminate.
9.
This section number corresponds to a
numbering system that is adopted in the
pipeline data book. Therefore, this information
must be coordinated with the proponent.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
27
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
Equipment Data (Entries 10-20)
10.
Show the nominal or outside pipe diameter.
List each kind (one diameter, wall thickness
and steel grade) of pipe or fitting once in
separate columns.
11.
Show the nominal wall thickness of pipe,
fractions in decimals.
12.
Show the material, such as carbon steel, alloy,
etc.
13.
Indicate the process of manufacture for the
pipe, such as seamless (S) or EFW, ERW, or
spiral.
14.
Show the pipe material specification and grade,
such as API 5L, Gr. B. SAMSSs references
are not acceptable.
Equipment Data (Entries 10-20), Cont'd
15.
Show the nominal size of flanges and fittings.
16.
Enter the rating per ASME/ANSI B16.5 for
flanges and valves. Selection of the flange
rating was discussed in MEX 101.04.
17.
Enter the type of flange face, such as raised
face (RF) or ring joint (RTJ). Flange facing
was discussed in MEX 101.04.
18.
Enter whether carbon steel or alloy is used for
flanges or fittings.
19.
Specify the ASTM or other specification and
grade of the material used for flanges or
fittings.
20.
List any special piping components that are not
otherwise covered, and include any other
pertinent remarks.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
28
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
Operating Limits (Entries 21-37)
21.
Calculate the Maximum Allowable Operating
Pressure (MAOP) in accordance with the
applicable code, as limited by flanges or by the
nominal pipewall thickness, for materials that
are listed under Key Numbers 10 through 20.
MAOP was discussed in MEX 101.03 and MEX
101.04 for pipe and flanges, respectively.
22.
Show the item that is limiting the MAOP in Key
Number 21.
23.
Show the Design Factor, and give the basis of
the Design Factor in the remarks area in Key
Number 37. The Design Factor was discussed
in MEX 101.03.
24.
Show the design temperature.
25.
Show the actual hydrostatic test pressure of
this particular equipment item that was
performed immediately after construction. The
test pressure must be calculated in accordance
with SAES-A-004, Pressure Testing. Test
pressure requirements were discussed in MEX
101.09. The test pressure of this equipment
item must be equal to or greater than the test
pressure in Key Number 32, Form 5645-1, for
the pipeline segment to which this equipment is
connected.
26.
Show the test date.
Operating Limits (Entries 21-37), Cont'd
27.
Indicate the item (pipeline segment, flange or
special fitting) which limits the test pressure.
Note that entries for revalidation of hydrostatic
tests (entries 28-30) are to be completed when
the information is known. The Safety
Instruction Sheet (SIS) is to be updated after
every revalidation test by the responsible
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
29
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
Operations Engineering unit.
28.
Indicate the actual test pressure for the
revalidation test, which must be in accordance
with SAES-A-004 and approved by the
responsible Saudi Aramco Operations
Engineering unit. The test pressure of this
equipment must be equal to or greater than the
test pressure in Key Number 35, on Form
5645-1, for the segment to which this
equipment is connected.
29.
Show the test date.
30.
Indicate the factor that limits the test pressure.
Note that this does not necessarily have to be
the same item that limited the initial hydrotest
pressure. For example, the original hydrotest
pressure might have been limited by the
flanges. However, corrosion which may have
occurred in the pipe, itself, could make it the
limiting component for a revalidation test.
31.
Indicate the Maximum Allowable Operating
Pressure (MAOP) of the entire pipeline as if
one system. This MAOP is the same as that in
Key Number 38 on Form 5645-1.
In case of flowlines, testlines, or trunklines,
refer to SADP-L-022 for further information.
32.
Show the limiting item for the system MAOP.
In the case where a Saudi Aramco standard
governs, indicate which standard it is and its
date, such as SADP-L-022, 30 August 1985.
33.
Show the set pressure of the safety valve, sunpressure relief valve, pressure switch, or other
safety device if one is included, and if it is
required for routine operation. Confirm this
information with the P & ID.
34.
Enter the nominal size or outside diameter.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
30
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
Operating Limits (Entries 21-37), Cont'd
35.
Calculate Tm based on the system MAOP that
is shown in Key Number 31. If not applicable,
use the MAOP in Key Number 21.
Note that Tm is the retirement wall thickness,
and shall not be less than the required wall
thickness for mechanical strength. Refer to
Saudi Aramco Inspection Procedures 01-AIP02-0, SAES-L-006, or to the piping specialist in
the Consulting Services Department, for further
explanation.
36.
Calculate the corrosion allowance (Tca) which
equals the nominal wall thickness of the pipe
minus Tm that is shown in Key Number 35.
Note that the corrosion allowance, Tca, is the
remaining pipewall thickness that is above the
required Tm. This is not a required corrosion
allowance. If a corrosion allowance is required,
it must be stated (including the referenced
standard) in the remarks area under Key
Number 37.
37.
Include any special remarks regarding safety
hazards in connection with items on the subject
sheet. See the remarks for the main line pipe,
Form 5645-1, Key Number 40.
Miscellaneous Information (Entries 38-45)
38.
Indicate specific drawings for the manifolds,
crossovers, branches, scraper traps, road
crossings, and any items that are covered by
this sheet.
39.
Show the district, area or location, and the
official pipeline, or the equipment name, as
shown in Key Number 1.
40.
Enter the plant number.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
31
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
41.
Follow the usual procedure to obtain a drawing
number.
42.
Include the BI and JO under which the
pipeline/equipment was installed or revised.
43.
Complete this section showing the date
prepared and name of the originator.
44.
Engineering concurrence as indicated in
Section 4, plus Project Manager or Plant
Manager's approval, as required.
45.
Signature of the Facility Engineering Division
head.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
32
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
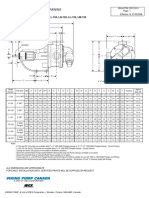
FORM 5645-2
FIGURE 3
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
33
Engineering Encyclopedia
Piping, Pipelines & Valves
Safety Instruction Sheets for Plant
Piping and Cross-Country Pipelines
GLOSSARY
AGN
Nonrestrained Aboveground
AGR
Restrained Aboveground
CF
Cage Forming
EFW
Electric-Fusion Welded
FF
Flat-Face Flange
NPS
Nominal Pipe Size
RF
Raised-Face Flange
RTJ
Ring-Joint Flange
Saudi Aramco
Form 2821
A Safety Instruction Sheet for Plant Piping
Saudi Aramco
Form 5645-1
A Safety Instruction Sheet for Cross-Country
Pipelines
Saudi Aramco
test Form 5645-2
and
A Safety Instruction Sheet for flowlines, trunk lines,
lines, submarine pipelines, tie-in piping, scraper traps
their appurtenances, and special components.
SMYS
Specified Minimum Yield Strength
UOE
U-ing, O-ing, Expanding
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
34
You might also like
- Plastic Pipe Fittings DC-DWVDocument68 pagesPlastic Pipe Fittings DC-DWVAdi KurniaNo ratings yet
- 175 320300Document1 page175 320300sridhar100% (1)
- Valve Selection Types and ClassesDocument71 pagesValve Selection Types and ClassesRaj Bindas100% (2)
- Valve Selection Types and ClassesDocument71 pagesValve Selection Types and ClassesRaj Bindas100% (2)
- Pipe Wall Thickness CalculationDocument79 pagesPipe Wall Thickness CalculationRaj Bindas100% (1)
- Pipe Wall Thickness CalculationDocument79 pagesPipe Wall Thickness CalculationRaj Bindas100% (1)
- 01 Samss 044 PDFDocument11 pages01 Samss 044 PDFAbdul Rahim ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 04-Samss-35 ValvesDocument28 pages04-Samss-35 ValvesNabeel AKNo ratings yet
- 2019 - Saep-1160Document24 pages2019 - Saep-1160smdriyazbashaNo ratings yet
- Inspection & Testing Requirements Scope:: Test and Inspection PerDocument2 pagesInspection & Testing Requirements Scope:: Test and Inspection PerAbu Anas M.SalaheldinNo ratings yet
- 00 SAIP 80 Process Equipment Insp GuideDocument90 pages00 SAIP 80 Process Equipment Insp GuideRaj BindasNo ratings yet
- 00 SAIP 80 Process Equipment Insp GuideDocument90 pages00 SAIP 80 Process Equipment Insp GuideRaj BindasNo ratings yet
- SAES-L-150 PDF Download - Pressure Testing of Plant Pipelines - PDFYARDocument7 pagesSAES-L-150 PDF Download - Pressure Testing of Plant Pipelines - PDFYARZahidRafiqueNo ratings yet
- Flanges Types, Classes and AssemblyDocument65 pagesFlanges Types, Classes and AssemblyRaj Bindas100% (8)
- Gap Control For Socket Weld Back Welded Threaded FittingsDocument12 pagesGap Control For Socket Weld Back Welded Threaded Fittingslaz_k100% (1)
- SAES-L-110 PDF Download - Limitations On Pipe Joints and Components - PDFYARDocument9 pagesSAES-L-110 PDF Download - Limitations On Pipe Joints and Components - PDFYARZahidRafiqueNo ratings yet
- Material SelectionDocument99 pagesMaterial SelectionRaj Bindas100% (8)
- Material SelectionDocument99 pagesMaterial SelectionRaj Bindas100% (8)
- Saep 351Document19 pagesSaep 351QA QC100% (1)
- SAES-L-133 PDF Download - Corrosion Protection Requirements - PDFYARDocument6 pagesSAES-L-133 PDF Download - Corrosion Protection Requirements - PDFYARZahidRafique100% (1)
- API 682 GuidelinesDocument28 pagesAPI 682 GuidelinesSergio Solano100% (3)
- Materials System SpecificationDocument21 pagesMaterials System Specificationnadeem shaikhNo ratings yet
- AE-036411-001 INDEX For Drawing and EquipmentDocument1 pageAE-036411-001 INDEX For Drawing and Equipmentnarutothunderjet216No ratings yet
- Saep 324 PDFDocument13 pagesSaep 324 PDFArvind ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Saic L 2008 PDFDocument4 pagesSaic L 2008 PDFHesham HelalNo ratings yet
- 01 Samss 034Document18 pages01 Samss 034aamirtec301100% (1)
- Saep 347 PDFDocument21 pagesSaep 347 PDFRami ElloumiNo ratings yet
- 1000 Questions and Answers 10Document21 pages1000 Questions and Answers 10Mehboob HassanNo ratings yet
- Saes B 064Document14 pagesSaes B 064Engr HafeezullahNo ratings yet
- ASME B36.10 Ed.2018Document36 pagesASME B36.10 Ed.2018Yasser Abd El FattahNo ratings yet
- 34 Samss 611Document8 pages34 Samss 611naruto256No ratings yet
- Saep 27Document14 pagesSaep 27Abdul Ahad LoneNo ratings yet
- 34 Samss 611Document8 pages34 Samss 611shrikantbelekarNo ratings yet
- Quick Guide For P&ID ReviewDocument7 pagesQuick Guide For P&ID ReviewfloredaNo ratings yet
- 12 Samss 008Document4 pages12 Samss 008Moustafa BayoumiNo ratings yet
- 01-SAMSS-049 Reinforced Thermoset Resin (RTR) Pipe, Fittings and Adhesive Packing, Handling, Transportation and Storage 21-FEB-2012 PDFDocument8 pages01-SAMSS-049 Reinforced Thermoset Resin (RTR) Pipe, Fittings and Adhesive Packing, Handling, Transportation and Storage 21-FEB-2012 PDFasiqnaNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Typical Inspection Plan: Valve Inspection, Testing & Installation SATIP-L-108-01 8-Nov-15 MechanicalDocument12 pagesSaudi Aramco Typical Inspection Plan: Valve Inspection, Testing & Installation SATIP-L-108-01 8-Nov-15 MechanicalAhdal NoushadNo ratings yet
- 00 Saip 12Document8 pages00 Saip 12aamirtec301No ratings yet
- Safety Instruction SheetDocument32 pagesSafety Instruction SheetAdamuNo ratings yet
- Penstock CaalculationDocument3 pagesPenstock CaalculationGertjan DuniceriNo ratings yet
- Saep 322Document18 pagesSaep 322brecht1980100% (1)
- Inspection & Testing Requirements Scope:: Test and Inspection PerDocument2 pagesInspection & Testing Requirements Scope:: Test and Inspection PerZhiguo YangNo ratings yet
- Pew-105.03 (P)Document88 pagesPew-105.03 (P)Raj BindasNo ratings yet
- Pew-105.03 (P)Document88 pagesPew-105.03 (P)Raj BindasNo ratings yet
- 34-Samss-010 2018Document9 pages34-Samss-010 2018asimazami69No ratings yet
- 01-SAMSS-333-HF Welded Line Pipe PDFDocument35 pages01-SAMSS-333-HF Welded Line Pipe PDFmunnaNo ratings yet
- Pipewall Thickness CalculationDocument30 pagesPipewall Thickness CalculationTiu TonNo ratings yet
- SAES-L-310 (Design of Plant Piping)Document30 pagesSAES-L-310 (Design of Plant Piping)Cherukunnon Jubu100% (5)
- Materials System SpecificationDocument9 pagesMaterials System SpecificationFAPM1285No ratings yet
- Engineering Procedure: SAEP-310 13 January 2008 Piping and Pipeline Repair Piping Standards Committee MembersDocument39 pagesEngineering Procedure: SAEP-310 13 January 2008 Piping and Pipeline Repair Piping Standards Committee Membersbrecht1980100% (4)
- Iii. Applicable Codes & Standards For Aramco ProjectsDocument5 pagesIii. Applicable Codes & Standards For Aramco ProjectsZain Ali KidwaiNo ratings yet
- GA DrawingDocument4 pagesGA DrawingGalih PrianggodoNo ratings yet
- 04 Samss 048Document11 pages04 Samss 048Sami100% (1)
- 175 043000Document1 page175 043000Fahad AhmadNo ratings yet
- RBI A Quantitative Soulution Made Practical Lynne KaleyDocument80 pagesRBI A Quantitative Soulution Made Practical Lynne KaleyRaj BindasNo ratings yet
- Pavientadora CAT AP500E and BG500EDocument10 pagesPavientadora CAT AP500E and BG500Ealexander_1985100% (1)
- Saudi Aramco Inspection Checklist: Review of Flange Joint-Gasket Verification and Bolt Tightening ProcedureDocument2 pagesSaudi Aramco Inspection Checklist: Review of Flange Joint-Gasket Verification and Bolt Tightening ProcedureMAZHARULNo ratings yet
- Gate Ece by RK - KanodiaDocument440 pagesGate Ece by RK - KanodiaParitam Soni100% (1)
- Saes L 130Document5 pagesSaes L 130Ahmed Kabel100% (1)
- Saes W 016 PDFDocument10 pagesSaes W 016 PDFRaj AryanNo ratings yet
- Saep 43Document29 pagesSaep 43QcNo ratings yet
- Saep 321Document25 pagesSaep 321AbdullahNo ratings yet
- E PR 250 PDFDocument30 pagesE PR 250 PDFAmirhosein605334No ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Inspection ChecklistDocument3 pagesSaudi Aramco Inspection ChecklistphilipyapNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document28 pagesChapter 4kuma alemayehuNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Inspection ChecklistDocument23 pagesSaudi Aramco Inspection ChecklistjahaanNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Inspection ChecklistDocument8 pagesSaudi Aramco Inspection Checklistnisha_khan0% (1)
- Thickness CalculationDocument6 pagesThickness CalculationBuddy EkoNo ratings yet
- Saep 347Document27 pagesSaep 347Qaiser Mahmood100% (2)
- SAEP-35-N - Valves Handling, Hauling, Receipt Tests and StorageDocument8 pagesSAEP-35-N - Valves Handling, Hauling, Receipt Tests and StorageMuhammad Farukh Manzoor0% (1)
- SAER1972Document9 pagesSAER1972zamil2008No ratings yet
- E PR 230 PDFDocument87 pagesE PR 230 PDFAmirhosein605334No ratings yet
- Sa 1141 PDFDocument66 pagesSa 1141 PDFAwais Tariq100% (2)
- Saudi Aramco Inspection Checklist: Storage and Preservation of Valves SAIC-L-2041 30-Apr-17 MechDocument2 pagesSaudi Aramco Inspection Checklist: Storage and Preservation of Valves SAIC-L-2041 30-Apr-17 Mechsuresh100% (1)
- 01 Samss 029Document15 pages01 Samss 029Cherukunnon Jubu100% (1)
- 175 325100Document2 pages175 325100sridhar100% (1)
- Saep 35Document6 pagesSaep 35hendraox3996No ratings yet
- 01 Samss 010Document11 pages01 Samss 010doyenofcastleNo ratings yet
- 175 012000Document2 pages175 012000Abu Anas M.SalaheldinNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Test Report Temperature Tie-In Welding ReportDocument2 pagesSaudi Aramco Test Report Temperature Tie-In Welding ReportManoj Kumar100% (2)
- Saudi Aramco Typical Inspection Plan Cross Country Above Ground PipeliDocument5 pagesSaudi Aramco Typical Inspection Plan Cross Country Above Ground PipeliShahbaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between MIG and MAGDocument1 pageWhat Is The Difference Between MIG and MAGRaj BindasNo ratings yet
- Appendix KDocument26 pagesAppendix KRaj BindasNo ratings yet
- Pew 105.04 (P)Document174 pagesPew 105.04 (P)Raj BindasNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between MIG and MAGDocument1 pageWhat Is The Difference Between MIG and MAGRaj BindasNo ratings yet
- API570 - Printable Flash CardsDocument45 pagesAPI570 - Printable Flash Cardstipu321100% (2)
- Equipment For SubmergedDocument4 pagesEquipment For SubmergedRaj BindasNo ratings yet
- Pew 209 .02Document59 pagesPew 209 .02Raj BindasNo ratings yet
- TIG Welding: Process CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesTIG Welding: Process CharacteristicsRaj BindasNo ratings yet
- Asme Ix Presentation Summary Oct 2007Document34 pagesAsme Ix Presentation Summary Oct 2007Antonio GraterolNo ratings yet
- MDR CemDocument30 pagesMDR Cemhafizszul AmirushamNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled CondenserDocument7 pagesAir Cooled CondenserSaravanan RagupathyNo ratings yet
- Bulkline 650-1000 IOM ENDocument24 pagesBulkline 650-1000 IOM ENRobert SerafinNo ratings yet
- Rcug-Ahyz1 TC1Document38 pagesRcug-Ahyz1 TC1Site EngineeringtiaNo ratings yet
- Design Standard Gas Piping For Laboratory Facilities: Revisions LogDocument3 pagesDesign Standard Gas Piping For Laboratory Facilities: Revisions LogZineddine ALICHENo ratings yet
- r200 CatalogoDocument2 pagesr200 CatalogoEu_einNo ratings yet
- 1e V09 MPGB 00043Document10 pages1e V09 MPGB 00043mohamed abouraya100% (1)
- Regulador EQA-99-17Document2 pagesRegulador EQA-99-17Ronan CristhiamNo ratings yet
- HM2H Flow Chart GPMDocument1 pageHM2H Flow Chart GPMJishnu MedhiNo ratings yet
- Valvulas de Seguridad Hansen PDFDocument4 pagesValvulas de Seguridad Hansen PDFLuis ReinoNo ratings yet
- Alltech Pump ManualDocument1 pageAlltech Pump ManualGAUTHAMSANo ratings yet
- Valvepedia FEB-2017Document8 pagesValvepedia FEB-2017aliNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Hydraulics QuizDocument11 pagesMaintenance Hydraulics QuizArshad MullaNo ratings yet
- KA Series PDFDocument8 pagesKA Series PDFsancsa_74No ratings yet
- SpesifikasiDocument3 pagesSpesifikasiIhsannrNo ratings yet
- Mac 2009Document60 pagesMac 2009Ridwan Pramudya100% (1)
- 1.EPV NORTH SEA Exploded PartviewDocument45 pages1.EPV NORTH SEA Exploded PartviewPSC RFQNo ratings yet
- Prosintech CatalogDocument6 pagesProsintech CatalogDeepak PatelNo ratings yet
- FNDWRRDocument3 pagesFNDWRRsranjeitNo ratings yet
- Tecnidro - FirefightingDocument4 pagesTecnidro - FirefightinggtecnidroNo ratings yet
- MVAC Duct Pressure Drop (Reference Summary)Document19 pagesMVAC Duct Pressure Drop (Reference Summary)Cheng Chun TingNo ratings yet
- Larossa: Company Date Philippines 1773 Tunasan Muntinlupa City FAPI Compound E Rodriguez AveDocument1 pageLarossa: Company Date Philippines 1773 Tunasan Muntinlupa City FAPI Compound E Rodriguez AveasdzxcNo ratings yet
- Dimensiones de Bomba Viking L124Document1 pageDimensiones de Bomba Viking L124nerio gerardinoNo ratings yet