Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formula Sheet1
Uploaded by
diptodevilCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formula Sheet1
Uploaded by
diptodevilCopyright:
Available Formats
MIT OpenCourseWare
http://ocw.mit.edu
6.013/ESD.013J Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall 2005
Please use the following citation format:
Markus Zahn, Erich Ippen, and David Staelin, 6.013/ESD.013J
Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall 2005. (Massachusetts Institute
of Technology: MIT OpenCourseWare). http://ocw.mit.edu (accessed
MM DD, YYYY). License: Creative Commons AttributionNoncommercial-Share Alike.
Note: Please use the actual date you accessed this material in your citation.
For more information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit:
http://ocw.mit.edu/terms
6.013 Formula Sheet # 1
Cartesian Coordinates (x, y, z)
f
f
f
ix +
iy +
iz
x
y
z
Ax
Ay
Az
A =
+
+
x
y
z
Az
Ay
Ax
Az
Ay
Ax
+ iy
+ iz
A = ix
y
z
z
x
x
y
f =
Cartesian
x
y
z
ix
=
=
=
=
Cylindrical
r cos
r sin
z
cos ir sin i
=
=
=
=
iy
sin ir + cos i
iz
iz
Cylindrical
r
z
ir
i
iz
=
=
=
=
=
=
Cartesian
p
x2 + y 2
y
tan1 x
z
cos ix + sin iy
sin ix + cos iy
iz
=
=
=
=
=
=
Spherical
r sin
r cos
sin ir + cos i
i
cos ir sin i
Spherical
r
=
=
=
=
Cylindrical
r2 + z 2
cos1 z
=
=
sin ir + cos iz
cos ir sin iz
2f
2f
2f
f =
+
+
2
2
x
y
z 2
Spherical
r sin cos
r sin sin
r cos
sin cos ir + cos cos i
sin i
sin sin ir + cos sin i
+ cos i
cos ir sin i
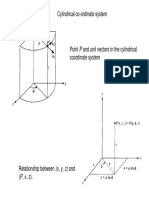
Cylindrical Coordinates (r, , z)
f
1 f
f
ir +
i +
iz
r
r
z
1
1 A
Az
A =
(rAr ) +
+
r r
r
z
" `
#
A
1 Az
Ar
Az
1 rA
Ar
+ i
+ iz
A = ir
r
z
z
r
r
r
2f
2 f
f
1
r
+ 2
+
2 f =
r r
r
r 2
z 2
f =
Spherical Coordinates (r, , )
f
1 f
1 f
ir +
i +
i
r
r
r sin
1 (sin A )
1 ` 2
1 A
A = 2
r Ar +
+
r r
r sin
r sin
#
" `
sin A
1
A
A = ir
r sin
"
`
#
rA
1
1 Ar
1 (rA )
Ar
+ i
+ i
r sin
r
r
r
f
1
1
f
2 f
r2
+ 2
sin
+ 2
2 f = 2
r r
r
r sin
r sin2 2
f =
pCartesian
x2 + y 2 + z 2
z
cos1
x2 +y 2 +z 2
cot1 x
y
sin cos ix + sin sin iy
+ cos iz
i
= cos cos ix + cos sin iy
sin iz
i
=
sin ix + cos iy
Geometric relations between coordinates and unit
and spherical coordinate systems.
ir
=
=
r 2 +z 2
=
i
vectors for Cartesian, cylindrical,
6.013 Formula Sheet # 1
Vector Identities
Maxwells Equations
Integral
Dierential
Boundary Conditions
Faradays Law
R
H
d
E = B
n (E2 E1 ) = 0
L E dl = dt S B dS
t
HAmperes Law
R with Maxwells
R Displacement Current Correction
d
H dl = S Jf dS + dt
D dS H = Jf + D
n (H2 H1 ) = Kf
L
S
d
HGausss Law R
D = f
n (D2 D1 ) = f
H S D dS = V f dV
B dS = 0
B= 0
n (B2 B1 ) = 0
S
Conservation of Charge
H
R
d
Jf + tf = 0
n (J2 J1 ) + tf = 0
S Jf dS + dt V f dV = 0
Usual Linear Constitutive Laws
D = E
B = H
Jf = (E + v B) = E [Ohms law for moving media with velocity v]
(A B) C = A (B C) = (C A) B
A (B C) = B(A C) C(A B)
( A) = 0
(f ) = 0
(f g) = f g + gf
(A B) = (A )B + (B )A + A ( B) + B ( A)
(f A) = f A + (A )f
(A B) = B ( A) A ( B)
(A B) = A( B) B( A) + (B )A (A )B
(f A) = f A + f A
1
(A A)
2
( A) = ( A) 2 A
( A) A = (A )A
Physical Constants
Constant
Symbol
Value
Speed of light in vacuum
c
2.9979 108 3 108
Elementary electron charge
e
1.602 1019
Electron rest mass
me
9.11 1031
Electron charge to mass ratio me
1.76 1011
e
Proton rest mass
mp
1.67 1027
Boltzmann constant
k
1.38 1023
Gravitation constant
G
6.67 1011
Acceleration of gravity
g
9.807
9
Permittivity of free space
0
8.854 1012 10
36
7
Permeability of free space
0
4 10
Plancks constant
h
6.6256 1034
q
0
Impedance of free space
0 =
376.73 120
Integral Theorems
Line Integral of a Gradient
Z b
f dl = f (b) f (a)
a
Divergence Theorem:
Z
I
AdV =
A dS
V
Corollaries
Z
I
f dV =
f dS
S
ZV
I
AdV =
A dS
V
Avogadros number
Stokes Theorem:
I
Z
A dl =
( A) dS
L
Corollary
I
Z
f dl =
f dS
L
6.023 1023
units
m/sec
coul
kg
coul/kg
kg
joule/ K
nt-m2 /(kg)2
m/(sec)2
farad/m
henry/m
joule-sec
ohms
atoms/mole
You might also like
- Laplace Eqn Cartesian CoordsDocument9 pagesLaplace Eqn Cartesian CoordsJoni PhamNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall 2005. (Massachusetts InstituteDocument41 pagesElectromagnetics and Applications, Fall 2005. (Massachusetts InstituteasitiafNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Lasers: The Commonwealth and International Library: Selected Readings in PhysicsFrom EverandEssentials of Lasers: The Commonwealth and International Library: Selected Readings in PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Math AppDocument7 pagesMath Appg3dizeNo ratings yet
- Difference Equations in Normed Spaces: Stability and OscillationsFrom EverandDifference Equations in Normed Spaces: Stability and OscillationsNo ratings yet
- (Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Mit Opencourseware)Document8 pages(Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Mit Opencourseware)asitiafNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- ConstantsDocument23 pagesConstantsJohn JohnNo ratings yet
- 6.641 Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion: Mit OpencoursewareDocument7 pages6.641 Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion: Mit OpencoursewareDevadas MadathilNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 6: The Method of ImagesDocument20 pagesLecture Notes 6: The Method of ImagesZoricaNo ratings yet
- ELEG 413 Spring 2011 Lecture #1Document42 pagesELEG 413 Spring 2011 Lecture #1Jorge Molina MonsivaisNo ratings yet
- Useful Formulas: Appendix ZDocument6 pagesUseful Formulas: Appendix ZSukhmander SinghNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall 2005. (Massachusetts InstituteDocument7 pagesElectromagnetics and Applications, Fall 2005. (Massachusetts InstituteasitiafNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall 2005. (Massachusetts InstituteDocument13 pagesElectromagnetics and Applications, Fall 2005. (Massachusetts InstituteasitiafNo ratings yet
- Chemo MetricsDocument75 pagesChemo MetricsSandy Muay WongsiriNo ratings yet
- Vector Analysis Formulas (Electromagnetic Fields)Document2 pagesVector Analysis Formulas (Electromagnetic Fields)Quý HoàngNo ratings yet
- 6.641 Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion: Mit OpencoursewareDocument8 pages6.641 Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion: Mit OpencoursewareAhmed AiadNo ratings yet
- Equation SheetDocument2 pagesEquation SheetKevin ChauNo ratings yet
- Vector AnalysisDocument72 pagesVector AnalysisAileenMTNo ratings yet
- Emt (Ee) PDFDocument55 pagesEmt (Ee) PDFckvirtualize100% (4)
- IIT-JEE 2004 Mains Questions & Solutions - Maths - Version 2 (The Questions Are Based On Memory)Document15 pagesIIT-JEE 2004 Mains Questions & Solutions - Maths - Version 2 (The Questions Are Based On Memory)AlokShuklaNo ratings yet
- (Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Mit Opencourseware)Document10 pages(Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Mit Opencourseware)asitiafNo ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations and Boundary Conditions: ReviewDocument26 pagesMaxwell's Equations and Boundary Conditions: ReviewtomdarelNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Theory NET-JRF June 2011 - June 2014Document22 pagesElectromagnetic Theory NET-JRF June 2011 - June 2014Abhishek Upadhyay100% (1)
- JD Jackson Solution Chapter 1 and 2Document56 pagesJD Jackson Solution Chapter 1 and 2JYOTIPRASAD DEKA100% (1)
- 6.641 Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion, Spring 2005. (Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Mit Opencourseware)Document13 pages6.641 Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion, Spring 2005. (Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Mit Opencourseware)Arjun ChilukaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fuzzy Set TheoryDocument67 pagesIntroduction To Fuzzy Set TheoryLini IckappanNo ratings yet
- Lec1 PDFDocument47 pagesLec1 PDFPhan Phuong NgocNo ratings yet
- (Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Mit Opencourseware)Document9 pages(Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Mit Opencourseware)asitiafNo ratings yet
- Dirac Oscillator Interacting With A Topological Defect: 10.1103/physreva.84.032109Document6 pagesDirac Oscillator Interacting With A Topological Defect: 10.1103/physreva.84.032109tridevmishraNo ratings yet
- Lecture5 Fuzzy LogicDocument86 pagesLecture5 Fuzzy LogicAnshul PatodiNo ratings yet
- Векторна формула Кiрхгофа у дарвiнiвськiй квазiстатицiDocument23 pagesВекторна формула Кiрхгофа у дарвiнiвськiй квазiстатицiKost' IlyenkoNo ratings yet
- Sohib Ahmed 109Document20 pagesSohib Ahmed 109Sumit KumarNo ratings yet
- Useful Vector Formulae: Appendix ADocument3 pagesUseful Vector Formulae: Appendix AYuvarajaNo ratings yet
- Math102 Equation SheetDocument0 pagesMath102 Equation SheetMaureen LaiNo ratings yet
- Electroquasistatic (EQS) and Magnetoquasistatic (MQS) Fields and Boundary ConditionsDocument12 pagesElectroquasistatic (EQS) and Magnetoquasistatic (MQS) Fields and Boundary ConditionsratansrikanthNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics II Formula Sheet For Mid1Document2 pagesElectromagnetics II Formula Sheet For Mid1wwwakowwwNo ratings yet
- Rumus Matematika Sma InterDocument19 pagesRumus Matematika Sma InterAde JayusNo ratings yet
- Https Doc 00 7g Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentDocument7 pagesHttps Doc 00 7g Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentVignesh RavishankarNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Faraday Effect Produced by A Ring LaserDocument11 pagesGravitational Faraday Effect Produced by A Ring Laserkuntal kumar ghoshNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Fresnel - SlitDocument3 pagesMathcad - Fresnel - SlitAprilMalcolmPhdNo ratings yet
- EC334 AP L01 Arrays PDFDocument27 pagesEC334 AP L01 Arrays PDFjskNo ratings yet
- PH-801: Important Formula: Cartesian Coordinate SystemDocument2 pagesPH-801: Important Formula: Cartesian Coordinate SystemHimadri ChakrabortiNo ratings yet
- 2007-1-Applied Optics 1 PDFDocument274 pages2007-1-Applied Optics 1 PDFUni NgoNo ratings yet
- Elastic Crack Growth in Finite Elements With Minimal Remeshing-Belytschko and Black-1999Document20 pagesElastic Crack Growth in Finite Elements With Minimal Remeshing-Belytschko and Black-1999hahaNo ratings yet
- Exam 2017 SoutionDocument15 pagesExam 2017 SoutionSushil AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Electrodynamics and Relativity: Immediately Not Accelerating NoDocument65 pagesElectrodynamics and Relativity: Immediately Not Accelerating No張恩睿 CHANG,EN-RUEI C24101147No ratings yet
- Wave Equation Applications in Peridynamic Model: Hisham M. Ali HasanDocument5 pagesWave Equation Applications in Peridynamic Model: Hisham M. Ali Hasansar0000No ratings yet
- Holonomic and Nonholonomic ConstraintsDocument20 pagesHolonomic and Nonholonomic Constraintsoltinn0% (1)
- On Approach To Decrease Dimensions of Field-Effect Transistors Framework Element of Sram With Increasing Their DimensionsDocument12 pagesOn Approach To Decrease Dimensions of Field-Effect Transistors Framework Element of Sram With Increasing Their DimensionsijfcstjournalNo ratings yet
- Formula in ElectromagnetDocument5 pagesFormula in ElectromagnetSamir YadavNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall 2005Document24 pagesElectromagnetics and Applications, Fall 2005asitiafNo ratings yet
- OCR GCE G481-G486 Physics Data SheetsDocument8 pagesOCR GCE G481-G486 Physics Data SheetsZak Thomas JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Derivation of Orbits in Inverse Square Law Force Fields: Force Center (Also The Coordinate Center)Document6 pagesDerivation of Orbits in Inverse Square Law Force Fields: Force Center (Also The Coordinate Center)Epic WinNo ratings yet
- Truss MathematicsDocument8 pagesTruss MathematicsOladunni Afolabi100% (1)
- Jest Physics Sample Question PaperDocument3 pagesJest Physics Sample Question PaperSreejith Nhaloor0% (1)
- A.C.T. College of Engineering & Technology: Basic Mathematics Formulae TrigonometryDocument18 pagesA.C.T. College of Engineering & Technology: Basic Mathematics Formulae TrigonometryNilesh Mistry (Nilesh Sharma)No ratings yet
- Physics 1116 Problem Set 1Document3 pagesPhysics 1116 Problem Set 1Somrita BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Normalized Impedance and Admittance Coordinates: Name Title Dwg. NoDocument1 pageNormalized Impedance and Admittance Coordinates: Name Title Dwg. NoRadiah HamdahNo ratings yet
- Naca 4314 Closed TrailDocument2 pagesNaca 4314 Closed TraildiptodevilNo ratings yet
- Matlab Command FunctionsDocument17 pagesMatlab Command FunctionsbehroozfNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Different Types of Transmission Line Transmission Line Per Unit Length Parameters Telegrapher Equation Power FlowDocument15 pagesTransmission Line Different Types of Transmission Line Transmission Line Per Unit Length Parameters Telegrapher Equation Power FlowdiptodevilNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic ExamplesDocument36 pagesElectrostatic ExamplesdiptodevilNo ratings yet
- EEE 402 Exp4Document6 pagesEEE 402 Exp4diptodevilNo ratings yet
- 2 A Ring of Charge PDFDocument3 pages2 A Ring of Charge PDFdiptodevilNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.4: If The Line Charge Density Is Given by (MC/M), Find The Total Charge Distributed On The Y-Axis From yDocument1 pageProblem 4.4: If The Line Charge Density Is Given by (MC/M), Find The Total Charge Distributed On The Y-Axis From yEric KialNo ratings yet
- 4-1 10Document1 page4-1 10diptodevilNo ratings yet
- 4-1 13 PDFDocument1 page4-1 13 PDFdiptodevilNo ratings yet
- Image Charge TheoryDocument4 pagesImage Charge TheoryEd DeldelNo ratings yet
- TFE4120 Electromagnetics - Crash CourseDocument7 pagesTFE4120 Electromagnetics - Crash CoursediptodevilNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Transformation Formula Sheet PDFDocument6 pagesCoordinate Transformation Formula Sheet PDFdiptodevilNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Edit PDFDocument8 pagesLecture 2 Edit PDFdiptodevilNo ratings yet
- 2 A Ring of ChargeDocument3 pages2 A Ring of ChargediptodevilNo ratings yet
- Co OrdinateDocument11 pagesCo OrdinatediptodevilNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.4: If The Line Charge Density Is Given by (MC/M), Find The Total Charge Distributed On The Y-Axis From yDocument1 pageProblem 4.4: If The Line Charge Density Is Given by (MC/M), Find The Total Charge Distributed On The Y-Axis From yEric KialNo ratings yet
- Field and VectoresDocument27 pagesField and VectoresMyameSirameNo ratings yet
- Paper - 2: Full Syllabus Test-1 (Fst-1) - Jee (Advanced)Document21 pagesPaper - 2: Full Syllabus Test-1 (Fst-1) - Jee (Advanced)lol88745No ratings yet
- The Nature of Light and The Principles of Ray Optics-UploadDocument11 pagesThe Nature of Light and The Principles of Ray Optics-UploadEICQ/00154/2020 SAMUEL MWANGI RUKWARONo ratings yet
- Phy 115 Units and DimensionDocument11 pagesPhy 115 Units and DimensionAbraham BanjoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Quantum MechanicsDocument64 pagesModule 2 Quantum MechanicsAkshat GuptaNo ratings yet
- Max Planck: Early LifeDocument2 pagesMax Planck: Early LifeVishal DhekaleNo ratings yet
- Lab5 First DraftDocument5 pagesLab5 First DraftLe VoyageurNo ratings yet
- Quantum ConsciousnessDocument19 pagesQuantum ConsciousnessJaro Neanderthalensis100% (1)
- Search For New Physics With Atoms and MoleculesDocument112 pagesSearch For New Physics With Atoms and MoleculesAnonymous 2ZtL2IL2No ratings yet
- Lab'S Report: SignatureDocument21 pagesLab'S Report: SignatureShayan Ahmad Khattak, BS Physics Student, UoPNo ratings yet
- BohrDocument7 pagesBohrDesita Tri ArifienNo ratings yet
- Determination of Plancks Constant From P PDFDocument10 pagesDetermination of Plancks Constant From P PDFFelipe CeregattiNo ratings yet
- U-2StructureofAtom1 89626Document23 pagesU-2StructureofAtom1 89626Anirudh AshrithNo ratings yet
- Cherenkov RadiationDocument7 pagesCherenkov RadiationManjunath.RNo ratings yet
- Black Holes and The Information ParadoxDocument32 pagesBlack Holes and The Information ParadoxAnonymous BPFIMnCdNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Module 2: Week 2Document16 pagesSecond Quarter Module 2: Week 2Hotdog cheesedogNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual PDFDocument46 pagesLab Manual PDFMnnit Allahabad0% (2)
- Given:: Using The GUESS Method To Solve Problems (Chemistry)Document2 pagesGiven:: Using The GUESS Method To Solve Problems (Chemistry)eric labordoNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Universe: Quarks, Leptons and The Big BangDocument888 pagesUnderstanding The Universe: Quarks, Leptons and The Big BangManjunath.RNo ratings yet
- PhET Simulation - Determination of Planck's ConstantDocument3 pagesPhET Simulation - Determination of Planck's ConstantDaniel CruzNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument15 pagesNCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterVidyakulNo ratings yet
- A Physical Theory of Information vs. A Mathematical Theory of CommunicationDocument10 pagesA Physical Theory of Information vs. A Mathematical Theory of CommunicationMandy DiazNo ratings yet
- Quantum UniversesDocument31 pagesQuantum UniversesRichard Calvin HavensNo ratings yet
- Soal TOEFL 01Document60 pagesSoal TOEFL 01alfiani12No ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument35 pagesClass 12 Physics Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterParvatham VijayNo ratings yet
- Physium For FX-CG EDocument22 pagesPhysium For FX-CG ERohan JacobNo ratings yet
- 1 D Finite Potential WellDocument9 pages1 D Finite Potential WellSubhabrata MondalNo ratings yet
- BSCPH 301Document352 pagesBSCPH 301MohitNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics Unit-2ndDocument18 pagesQuantum Physics Unit-2ndMSONI97No ratings yet
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper Physics Mar 16 Shift 2Document15 pagesJEE Main 2021 Question Paper Physics Mar 16 Shift 2Sanskruti PatilNo ratings yet
- Fred Alan Wolf - The Quantum Physics of Consciousness PDFDocument25 pagesFred Alan Wolf - The Quantum Physics of Consciousness PDFquantumrealm100% (2)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessFrom EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- Chasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombFrom EverandChasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Beyond Weird: Why Everything You Thought You Knew about Quantum Physics Is DifferentFrom EverandBeyond Weird: Why Everything You Thought You Knew about Quantum Physics Is DifferentRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (25)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityFrom EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (76)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (157)
- The Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxFrom EverandThe Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (27)