Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concreto Pretensado Methods
Uploaded by
Martin Cristobal CupitayOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concreto Pretensado Methods
Uploaded by
Martin Cristobal CupitayCopyright:
Available Formats
Concreto Pretensado
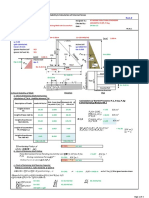
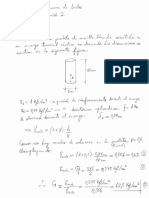
EJEMPLO 1: ton := 1000kgf
L
L := 9m h := = 0.3 m b := 1.00m
30
cota fondo := 6cm
Propiedades de la Seccin :
Solucin: 3
h 4
2 I := b = 225000 cm
A := b h = 0.3 m 12
h
yb := yb = 15 cm yt := h yb yt = 15 cm
2
I 3 I 3
Zt := Zt = 0.015 m Zb := Zb = 0.015 m
yt yb
exc := yb cota fondo = 9 cm
Esfuerzos : Cargas Gravitacionales:
ancho tributario : 5.00m
Peso Propio: ton ton
Wpp := A 2.4 = 0.72
3 m
m
ton ton
Alig Walg := 0.3 4 = 1.2
m m
Muerta ton ton
Wd := 0.1 5 = 0.5
m m
Viva ton ton
WL := 0.4 5 = 2
m m
ton
W := Wpp + Walg + Wd + WL = 4.42
m
2
W L
M := = 44.752 ton m
Momento: 8
M kgf
Esfuerzos: t := = 298.35
Zt 2
cm
M kgf
b := = 298.35
Zb 2
cm
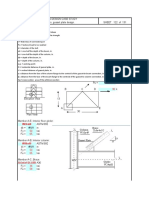
1. METODO CONVENCIONAL:
M
P := = 319.7 ton
Zb 1 +
exc
A Zb
Donde los Esfuerzos por Pretensado Efectivo son :
P kgf P exc kgf P exc kgf
= 106.6 = 191.8 = 191.8
A 2 Zb 2 Zt 2
cm cm cm
Ing. Luis Villena Sotomayor 1
Concreto Pretensado
2. METODO DEL PAR INTERNO
M
P := = 319.7 ton
Zb +
1 exc
A Zb
M
a := = 0.14 m
P e' := a exc = 0.05 m
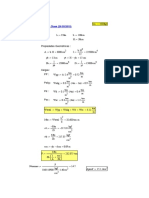
3. METODO DEL CARGA EQUIVALENTE
f := exc = 9 cm 8 P f ton
Wequiv := = 2.841
ton 2 m
W = 4.42 L
m
2
Wequiv L
Mequiv := = 28.769 ton m
8
( M Mequiv)
P := A = 319.7 ton
Zb
Ing. Luis Villena Sotomayor 2
You might also like
- Moving Wheel Loads AnalysisDocument3 pagesMoving Wheel Loads AnalysisAnibal Via EnNo ratings yet
- Anchor Bolt DesignDocument26 pagesAnchor Bolt Designdwicahyo_as100% (1)
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- MDOT GussetPlate LFR Analysis 263315 7Document27 pagesMDOT GussetPlate LFR Analysis 263315 7ankitNo ratings yet
- MDOT GussetPlate LFR Analysis 263315 7Document27 pagesMDOT GussetPlate LFR Analysis 263315 7ankitNo ratings yet
- Frame - Portal and Gable Rigid Plane Frame AnalysisDocument6 pagesFrame - Portal and Gable Rigid Plane Frame Analysisnamasral100% (4)
- AISC Design Guide 29 - Vertical Bracing Connections - Analysis and Design 2 de 2 PDFDocument196 pagesAISC Design Guide 29 - Vertical Bracing Connections - Analysis and Design 2 de 2 PDFMartin Cristobal CupitayNo ratings yet
- Retaining wall check and internal force calculationDocument3 pagesRetaining wall check and internal force calculationjanuarto jamadiNo ratings yet
- Mathcad 13 Column Design PDFDocument34 pagesMathcad 13 Column Design PDFEvilsNo ratings yet
- Gantry GirderDocument38 pagesGantry GirderPiyush Yadav75% (4)
- Gantry GirderDocument38 pagesGantry GirderPiyush Yadav75% (4)
- Transmission Tower Foundation DesignDocument26 pagesTransmission Tower Foundation DesignSara Nuon86% (7)
- NPTEL - Tranmission Tower Design - Facotrs of Safety and LoadDocument70 pagesNPTEL - Tranmission Tower Design - Facotrs of Safety and LoadLakshmi Narayanan100% (3)
- AISC Design Guide 29 - Vertical Bracing Connections - Analysis and Design 1 de 2 PDFDocument195 pagesAISC Design Guide 29 - Vertical Bracing Connections - Analysis and Design 1 de 2 PDFMartin Cristobal CupitayNo ratings yet
- Design-Calculations For Pipelines (Onshore)Document19 pagesDesign-Calculations For Pipelines (Onshore)George100% (1)
- AISC-34 Gusset PlateDocument4 pagesAISC-34 Gusset PlateMartin Cristobal CupitayNo ratings yet
- Crane Runway Girder DesignDocument27 pagesCrane Runway Girder Designyeemonzolo100% (6)
- Determine Active Earth Pressure Using Coulomb TheoryDocument17 pagesDetermine Active Earth Pressure Using Coulomb TheoryAbdullah AzamNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Cracked Rect Section Deflection Analysis of Continuous BeamDocument6 pagesMathcad - Cracked Rect Section Deflection Analysis of Continuous BeamSteven Raynaldo HNo ratings yet
- Design of Stub For Transmission Line TowersDocument26 pagesDesign of Stub For Transmission Line Towersdebjyoti_das_685% (13)
- b= 0.260 m h= 0.186 m α= 35.58 cosα= 0.813: Treppe 1Document6 pagesb= 0.260 m h= 0.186 m α= 35.58 cosα= 0.813: Treppe 1Admir SkenderovicNo ratings yet
- Foundation SpreadsheetDocument5 pagesFoundation SpreadsheetPramita Arif N100% (1)
- Dinding Penahan TanahDocument11 pagesDinding Penahan TanahJoko Sudirmanns SNo ratings yet
- Excel GordingDocument5 pagesExcel GordingRadityo Adhi100% (1)
- 1 Ejemplo1 PDFDocument1 page1 Ejemplo1 PDFAndrew HernandezNo ratings yet
- Design of Long Column Beams in BuildingsDocument25 pagesDesign of Long Column Beams in Buildingsbra22222No ratings yet
- Mathcad - ANALISA KAP SLOOF S2 BNIDocument14 pagesMathcad - ANALISA KAP SLOOF S2 BNIAndre NovanNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - ANALISA KAP SLOOF GUDANGDocument13 pagesMathcad - ANALISA KAP SLOOF GUDANGandre novanNo ratings yet
- Diseño Por FlexionDocument4 pagesDiseño Por FlexionrNo ratings yet
- Conversion from psig to kgf/cm2Document1 pageConversion from psig to kgf/cm2Kauê BrittoNo ratings yet
- False - DISAIN CROSS BEAM JETTY SEBELUM KOMPOSIT 7 APRILDocument11 pagesFalse - DISAIN CROSS BEAM JETTY SEBELUM KOMPOSIT 7 APRILandreNo ratings yet
- Mathcad Sheet of - KpeterDocument3 pagesMathcad Sheet of - KpeterGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Desain Baja FixDocument22 pagesDesain Baja FixRafidah AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Balok Kolom Braced UnDocument3 pagesBalok Kolom Braced UnIkbal ImanudinNo ratings yet
- Dynamic soil foundation analysisDocument3 pagesDynamic soil foundation analysisMarco Novoa MoralesNo ratings yet
- Notes Design Process PDFDocument11 pagesNotes Design Process PDFDak KaizNo ratings yet
- Gas ConstantDocument3 pagesGas ConstantSande NasNo ratings yet
- Gabarito Parcial - Lista 2Document3 pagesGabarito Parcial - Lista 2Paulo Sérgio Zanin JúniorNo ratings yet
- Diseñar La Escalera, Considerando Como Resistencia de Concreto Uso: Biblioteca, Paso P1, Contrapaso CP1Document4 pagesDiseñar La Escalera, Considerando Como Resistencia de Concreto Uso: Biblioteca, Paso P1, Contrapaso CP1Sebastian Gabriel EGUILUZ REYESNo ratings yet
- Losa en Dos Direccion TerminadoDocument16 pagesLosa en Dos Direccion TerminadoJosé Edwar Salas RenteriaNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation & Concrete Column DesignDocument25 pagesPile Foundation & Concrete Column DesignDenden DermawanNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Zabatni Stup3Document10 pagesMathcad - Zabatni Stup3Martin BrnelićNo ratings yet
- Lamp Math Lembaga PDFDocument15 pagesLamp Math Lembaga PDFAndre NovanNo ratings yet
- Muro de Contención en VoladizoDocument4 pagesMuro de Contención en VoladizoERICK IXQUS AMAUTA GUEVARA NEYRANo ratings yet
- PC Viga AceroDocument5 pagesPC Viga AcerocristhianNo ratings yet
- Largest Area of Space Is at The Center Where There Are 23 TubesDocument2 pagesLargest Area of Space Is at The Center Where There Are 23 TubesRenzel ReyesNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITYDocument2 pagesACTIVITYkaren zareth sanchez murciaNo ratings yet
- Pipe 5-6-7Document4 pagesPipe 5-6-7Elago, Justine M.No ratings yet
- Mathcad - SENGKANG SLOOF S-01 GUDANG CMTFDocument4 pagesMathcad - SENGKANG SLOOF S-01 GUDANG CMTFAndre NovanNo ratings yet
- Laporan Baja II Baru1Document30 pagesLaporan Baja II Baru1Syayhuddin Sholeh100% (2)
- SEO-OPTIMIZED TITLEDocument6 pagesSEO-OPTIMIZED TITLEManuel ColmenaresNo ratings yet
- Long Col.Document6 pagesLong Col.HAITHAM ALINo ratings yet
- Practica Numero 3 - Puentes - Alan Angel Chavez IglesiasDocument6 pagesPractica Numero 3 - Puentes - Alan Angel Chavez IglesiasCesar AnthonnyNo ratings yet
- Isolated FDN Design For Isolated Footing CanopyDocument1 pageIsolated FDN Design For Isolated Footing CanopyPatrick TaclibonNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Secondary Beam Design Opening-2Document2 pagesMathcad - Secondary Beam Design Opening-2mrnaeem76No ratings yet
- AISC Design Rules - Allowable Stress Design for Box SectionsDocument3 pagesAISC Design Rules - Allowable Stress Design for Box SectionssereNo ratings yet
- ) Pembebanan Pondasi: Created By: TianDocument35 pages) Pembebanan Pondasi: Created By: TianricopanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Project: Design By: Date: Title: ST1 Building1 Sheet: USE ACI318-99 MaterialDocument32 pagesProject: Design By: Date: Title: ST1 Building1 Sheet: USE ACI318-99 MaterialLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- RISER STRESS ANALYSIS SLEEVE REPAIR PID 152Document2 pagesRISER STRESS ANALYSIS SLEEVE REPAIR PID 152Mahamad Azi Bin IshakNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Puxy - MCD PDFDocument4 pagesMathcad - Puxy - MCD PDFAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Puxy - MCDDocument4 pagesMathcad - Puxy - MCDSandeep BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Problem 1.12 PDFDocument1 pageProblem 1.12 PDFWallace AbreuNo ratings yet
- Calc Steel Metal PerporatedDocument13 pagesCalc Steel Metal PerporatedOecoep Iteem100% (1)
- Slab Analysis: Gato, Jocelyn BSCE-IVBDocument24 pagesSlab Analysis: Gato, Jocelyn BSCE-IVBjoanNo ratings yet
- Solving for the critical bending moment of a reinforced concrete beamDocument2 pagesSolving for the critical bending moment of a reinforced concrete beamSamantha VillaltaNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Sengkang Sloof GudangDocument4 pagesMathcad - Sengkang Sloof Gudangandre novanNo ratings yet
- Desain Upper Structure Disain Pergudangan Sengkang Sloof S1Document4 pagesDesain Upper Structure Disain Pergudangan Sengkang Sloof S1andre novanNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Sengkang Sloof GudangDocument4 pagesMathcad - Sengkang Sloof Gudangandre novanNo ratings yet
- Input Values: Output Values:: Units Converter ForceDocument5 pagesInput Values: Output Values:: Units Converter ForceJeyder GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Kholis Baja 1 PDFDocument22 pagesKholis Baja 1 PDFDwi ArindaNo ratings yet
- Tien Duc: Unofficial SolutionDocument4 pagesTien Duc: Unofficial SolutionMinh DuyNo ratings yet
- Diseño de Escalera - Un Tramo + DescansoDocument6 pagesDiseño de Escalera - Un Tramo + DescansoYessmar Zegarra LopezNo ratings yet
- Breviar - Zid de Sprijin BL 19Document4 pagesBreviar - Zid de Sprijin BL 19Tra ProConsNo ratings yet
- Diseño de Escaleras Predimensionamiento:: LN 1.75 M T Ln/20 T 0.09 M T Ln/25 T 0.07 MDocument5 pagesDiseño de Escaleras Predimensionamiento:: LN 1.75 M T Ln/20 T 0.09 M T Ln/25 T 0.07 MManuel FernandezNo ratings yet
- Theis Jacob DrainageDocument3 pagesTheis Jacob DrainageMartin Cristobal CupitayNo ratings yet
- Resolución de Ecuaciones PolinomicasDocument6 pagesResolución de Ecuaciones PolinomicasMartin Cristobal CupitayNo ratings yet
- LT1 Loading Tree VDEDocument2 pagesLT1 Loading Tree VDEAbdul AzizNo ratings yet
- MonorailDocument14 pagesMonorailAlex GarciaNo ratings yet
- BOLTGRP.xlsDocument18 pagesBOLTGRP.xlscengizNo ratings yet
- "Endplmc9" - End Plate Moment Connections: Program DescriptionDocument21 pages"Endplmc9" - End Plate Moment Connections: Program DescriptionMartin Cristobal CupitayNo ratings yet
- LT1 Loading Tree VDEDocument2 pagesLT1 Loading Tree VDEAbdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Beams On Elastic FoundationDocument15 pagesBeams On Elastic FoundationOmar Eladel Mahmoud100% (2)
- Visweswara Rao 1995Document12 pagesVisweswara Rao 1995Carlos LopezNo ratings yet