Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Final Exam Formu PDF
Final Exam Formu PDF
Uploaded by
JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Final Exam Formu PDF
Final Exam Formu PDF
Uploaded by
JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowCopyright:
Available Formats
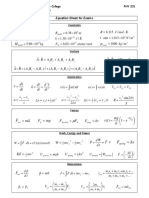
IAP 2006
8.01L SUMMARY OF EQUATIONS
Note: Quantities shown in bold are vectors.
v = dr dt a = dv dt
v = v 0 + at
For constant acceleration a, if at t = 0 r = r0 and v = v0:
r = r0 + v0 t + 12 at 2
v2
Circular motion at constant speed a = r = ! r (Centripetal acceleration, points towards center of circle,
is angular speed in radians per second)
Adding relative velocities ("wrt" is short for "with respect to"):
v A + v B = v A
wrt wrt wrt
B C C
!F = 0 " a = 0 (Newtons first law)
F = ma or F = dp dt (Newtons second law) FAB = FBA (Newtons third law)
p = mv (momentum)
t2 t2 dp
J = ! F dt = ! dt = p2 " p1 (impulse)
t1 t1 dt
!mi ri
rcm = (position of center of mass)
!mi
F = -kx (spring force) f ! N (Friction force relative to Normal force)
GMm
F=! r (gravitational force between two particles)
r2
W = " F ! dr (work done by force F)
Wother = !E = EF " EI E = KE + PE (work-energy theorem)
dU
Fx = ! (force derived from potential energy)
dx
Potential Energies: U = 2 kx (spring force)
1 2
!GMm
U= (gravitational, general) U = mgh (gravitational, near Earth)
r
!= k m x = Acos(!t + " )
(Equations for Simple Harmonic Motion)
v = # A! sin(!t + " ) T = 2$ !
P2 + !gy2 = P1 + !gy1 (Pascals Law: pressure versus height in a liquid with velocity = 0)
P + ! v + ! gy = constant
1
2
2
(Bernoullis equation)
A2 v 2 = A1v 1 (continuity equation)
PV = NkT = nRT (ideal-gas law)
1
2 mv2 = 32 kT (definition of kinetic temperature)
FB = ! f Vf g (buoyancy force, f=fluid displaced)
Quantity Translational Rotational (about axis)
Velocity, acceleration v, a , (v=R, a = R)
Mass M = ! mi I = ! m iRi2
i i
Kinetic energy 1
2 Mv2 1
2 I! 2
Net force ! F ext = Macm " ! ext = I#
i i
Momentum p = mv L = r ! p or L=I
dL
!=r"F= =I# ! = rF sin($ ) = Fr% (torque equations)
dt
L = r ! p L = mvrsin(") (angular momentum of point particle)
L=I (angular momentum for solid object)
I| = Ic .m. + Md 2 (parallel axis theorum)
I = MR
1
2
2
(cylinder around center) I = 25 MR2 (solid sphere around center)
I= 1
12
ML2 (rod around center) I = 13 ML2 (rod around end)
KE = 12 M Tot vCM
2
+ 12 I CM ! 2 (kinetic energy for object moving and rolling)
KE = 12 I Pivot! 2 (kinetic energy for object rotating around a fixed pivot)
Physical Constants:
g = 9.8 m/s2 Use the approximate value g = 10 m/s2 where told to do so.
G = 6.671011 N m2/kg2
k = 1.3810-23 J/K R = 8.31 J/(mol. K)
0 C = 273 K
Density of water = 1,000 kg/m3
Atmospheric pressure = 1.0105 Pa
Conversion reminder:
radians = 180o
Lazy Physicist 's Favorite Angle: (to be used when calculators are not allowed):
36.9o and 53.1o are the angles of a 3-4-5 right triangle so:
sin(36.9) = cos(53.1) = 0.60 cos(36.9) = sin(53.1) = 0.80
tan(36.9) = 0.75 tan(53.1) = 1.33
Other (possibly) Useful Trig Functions:
cos(30) = sin(60) = 3 2 sin(30) = cos(60) = 1 2
cos(45) = sin(45) = 1
2
!b b 2 ! 4ac
Solution to a Quadratic Equation: If ax + bx + c = 0 then x =
2
2a
You might also like
- Formula Sheet For Physics HallidayDocument6 pagesFormula Sheet For Physics HallidayTayyab Chaudhary0% (1)
- SchwartzDocument25 pagesSchwartzAntónio Oliveira100% (1)
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Exam3 FormulasDocument1 pageExam3 FormulasJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- FormulasheetDocument3 pagesFormulasheetAnnypaola MartinezNo ratings yet
- Midterm Review PDFDocument16 pagesMidterm Review PDFMt RushNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument2 pagesPhysics FormulasKristine BalansagNo ratings yet
- Ecor1048 Dyn Formula SheetDocument5 pagesEcor1048 Dyn Formula SheetthatoneafghanakhiNo ratings yet
- Physics Cheat Sheet 1 Units 5 More Motion FormulasDocument1 pagePhysics Cheat Sheet 1 Units 5 More Motion FormulasMuhammad Pathan AbroNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Equations & Formulae For Physics: LTSN Physical Sciences WWW - Physsci.ltsn - Ac.ukDocument5 pagesA Guide To Equations & Formulae For Physics: LTSN Physical Sciences WWW - Physsci.ltsn - Ac.ukseetharamannNo ratings yet
- Formulae SheetDocument4 pagesFormulae SheetOMARNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet PDFDocument3 pagesFormula Sheet PDFMallgi34No ratings yet
- Problems and Solutions Section 1.4 (Problems 1.52 Through 1.65) 1.52Document15 pagesProblems and Solutions Section 1.4 (Problems 1.52 Through 1.65) 1.52RajeshNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet-158Document2 pagesFormula Sheet-158justinkarlpolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Final Exam-Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFinal Exam-Formula SheetJustin DahlmanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To QMDocument3 pagesIntroduction To QMNicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Materi Kuliah 7Document20 pagesMateri Kuliah 7Ikhsan PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Physics Complete Formula Revision (New)Document68 pagesPhysics Complete Formula Revision (New)manas singhNo ratings yet
- Vibrations: and Their Design Requires Consideration To Oscillatory BehaviorDocument25 pagesVibrations: and Their Design Requires Consideration To Oscillatory BehaviorManashaaNo ratings yet
- Exam2 Formulas PDFDocument1 pageExam2 Formulas PDFJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
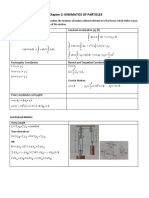
- Chapter 2: Kinematics of Particles: Constrained MotionDocument3 pagesChapter 2: Kinematics of Particles: Constrained MotionRicardo TapiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Work Energy Method in Rigid BodyDocument20 pagesChapter 7 - Work Energy Method in Rigid BodyDivnesh LingamNo ratings yet
- Fis 24Document6 pagesFis 24syafrina novitaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Physics 220 PDFDocument6 pagesFormula Sheet Physics 220 PDFNimish RamtekeNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument14 pagesFormula SheetQER TUGNo ratings yet
- PHYS 101 - General Physics-I, Final ExamDocument8 pagesPHYS 101 - General Physics-I, Final ExamhuuuzenNo ratings yet
- MainDocument2 pagesMainIngoNo ratings yet
- Mechanics: Mechanics Thermal Physics Waves & Optics Electricity & Magentism Modern PhysicsDocument11 pagesMechanics: Mechanics Thermal Physics Waves & Optics Electricity & Magentism Modern PhysicsTibra ArkaNo ratings yet
- 2023 BPH OanswerbookletsDocument18 pages2023 BPH Oanswerbookletsliumeilin20070625No ratings yet
- 2425 Formulas PDFDocument2 pages2425 Formulas PDFNasim AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Physics EquationsDocument3 pagesPhysics Equationsanam abidNo ratings yet
- Tutorial SolutionsDocument67 pagesTutorial SolutionsthewingsmissionNo ratings yet
- Phys303K Dicus Exam4Solutions Spring08Document16 pagesPhys303K Dicus Exam4Solutions Spring08Kayla WorachekNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Circular Motion: Year 5 H2 Physics 2020 Remedial WorksheetDocument3 pagesChapter 6: Circular Motion: Year 5 H2 Physics 2020 Remedial WorksheetMe4d SHiV23No ratings yet
- PHYS220 SFSU FormulaSheetDocument6 pagesPHYS220 SFSU FormulaSheetwizbizphdNo ratings yet
- 3 X 5 Notecardtest 2Document1 page3 X 5 Notecardtest 2ttusigmapiNo ratings yet
- List of Formula MECH 2344Document12 pagesList of Formula MECH 2344hashtagxtahuNo ratings yet
- 1998 FinalDocument11 pages1998 FinalQuynh P. NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17Document21 pagesLecture 17narvan.m31No ratings yet
- OscilatorsDocument21 pagesOscilatorsPepe CruzNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document29 pagesCH 10Ardian20No ratings yet
- HCI H2 PHY P1 Suggested SolutionDocument4 pagesHCI H2 PHY P1 Suggested Solutionllilizheng8No ratings yet
- Lect15 Multiparticle SysDocument22 pagesLect15 Multiparticle SysAldwin Tizon CallosaNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument10 pagesPhysics FormulasFaith Laurence SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Einstein Field Equations (EFE) : 1 - General Relativity OriginsDocument32 pagesEinstein Field Equations (EFE) : 1 - General Relativity Originsapi-457917864No ratings yet
- Revision Notes: M1: Velocity and Displacement VectorsDocument3 pagesRevision Notes: M1: Velocity and Displacement VectorsakilNo ratings yet
- Physics 11 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPhysics 11 Cheat SheetAnshul AhujaNo ratings yet
- Ap Exam Supplement: Specifically Developed For This Year's AP ExamDocument8 pagesAp Exam Supplement: Specifically Developed For This Year's AP ExamGan PentonNo ratings yet
- варианты колебаний Section1 - 4 PDFDocument15 pagesварианты колебаний Section1 - 4 PDFLeo KutsNo ratings yet
- TUT - 06 WorksheetDocument10 pagesTUT - 06 WorksheetSamiul Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Problems and Solutions Section 1.4Document15 pagesProblems and Solutions Section 1.4Haasen Hill100% (1)
- Exam Vibrations and NoiseDocument6 pagesExam Vibrations and NoisejoaoftabreuNo ratings yet
- Equation Reference SheetDocument2 pagesEquation Reference SheetwilliamsmarrenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Number of Electrons 2 N S 2× 1, P 2 ×3, D 2× 5, F 2 ×10Document13 pagesChemistry: Number of Electrons 2 N S 2× 1, P 2 ×3, D 2× 5, F 2 ×10Laissa SerranoNo ratings yet
- Physics 12 Formula SheetDocument3 pagesPhysics 12 Formula SheetJacob TamashiroNo ratings yet
- Equation Sheet 231 PhysicsDocument2 pagesEquation Sheet 231 PhysicsAshlie PolancoNo ratings yet
- Qualifier Study Guide: Office 221 Department of Physics, Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL 32308Document17 pagesQualifier Study Guide: Office 221 Department of Physics, Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL 32308Hussein AlghoulNo ratings yet
- CM Homework 3Document5 pagesCM Homework 3mazhariNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- I Important Rem Nders: Energy and Momentum of RotationDocument1 pageI Important Rem Nders: Energy and Momentum of RotationJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Important Reminders Complete Description of Motion: " # ! " !! !R " !F ! R F Sin (#)Document2 pagesImportant Reminders Complete Description of Motion: " # ! " !! !R " !F ! R F Sin (#)JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Important Reminders Problem-Solving Strategy 4-StepsDocument5 pagesImportant Reminders Problem-Solving Strategy 4-StepsJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Happy Holidays! Happy New Year! Welcome Back! Important Reminders Complete Description of MotionDocument2 pagesHappy Holidays! Happy New Year! Welcome Back! Important Reminders Complete Description of MotionJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Lec 12Document1 pageLec 12JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Lec 31Document1 pageLec 31JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Sit Anywhere. Assigned Seats Will Start This Friday. Pset#1 Due Here Tomorrow at Start of Class. Last LectureDocument1 pageSit Anywhere. Assigned Seats Will Start This Friday. Pset#1 Due Here Tomorrow at Start of Class. Last LectureJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- I Important Rem Nders: G NM KGDocument1 pageI Important Rem Nders: G NM KGJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Lec 29Document1 pageLec 29JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Lec 30Document2 pagesLec 30JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Prs 01 09 06solDocument1 pagePrs 01 09 06solJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- ) Important Reminders Blast From The Past (Early Exam ReviewDocument2 pages) Important Reminders Blast From The Past (Early Exam ReviewJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Lec 20Document1 pageLec 20JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- I Important Rem Nders: Note Distinction Between Mass and WeightDocument2 pagesI Important Rem Nders: Note Distinction Between Mass and WeightJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Lec 13Document1 pageLec 13JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- I Important Rem Nders: 0 V Cos (!) !G V Sin (")Document2 pagesI Important Rem Nders: 0 V Cos (!) !G V Sin (")JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Prs 11 01 05solDocument1 pagePrs 11 01 05solJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- ! V + V + V ! A + A + A: Important Reminders Kinematics: Description of MotionDocument2 pages! V + V + V ! A + A + A: Important Reminders Kinematics: Description of MotionJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- I Important Rem Nders: A Due To On ADocument2 pagesI Important Rem Nders: A Due To On AJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Block A Collides With Block B. After The Collisions The Two Blocks Stick Together. Which of The Following Is True?Document2 pagesBlock A Collides With Block B. After The Collisions The Two Blocks Stick Together. Which of The Following Is True?JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Prs 11 01 05sol PDFDocument1 pagePrs 11 01 05sol PDFJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Prs 11 03 05solDocument1 pagePrs 11 03 05solJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Moves Down The Incline. Which of The Does Not Move at All. Which of TheDocument2 pagesMoves Down The Incline. Which of The Does Not Move at All. Which of TheJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document2 pagesLec 2JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Prs 11 08 05solDocument3 pagesPrs 11 08 05solJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Prs 11 22 05solDocument3 pagesPrs 11 22 05solJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Prs 11 17 05solDocument1 pagePrs 11 17 05solJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Displacement Versus Distance Velocity and Acceleration: Velocity Equal To Zero?Document2 pagesDisplacement Versus Distance Velocity and Acceleration: Velocity Equal To Zero?JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Prs 11 29 05solDocument1 pagePrs 11 29 05solJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- I Important Rem Nders: Constant Velocity Is OK, Accelerated Observer Is NotDocument2 pagesI Important Rem Nders: Constant Velocity Is OK, Accelerated Observer Is NotJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Composites and Their Properties PDFDocument516 pagesComposites and Their Properties PDFCandace Frank100% (1)
- Resato Check ValveDocument4 pagesResato Check ValveSam LarismaNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis Report FBD Vs PBD 1628845299Document103 pagesStructural Analysis Report FBD Vs PBD 1628845299kevinNo ratings yet
- Sae Ams S 13165Document27 pagesSae Ams S 13165sabrunoNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurements: ObjectivesDocument13 pagesFlow Measurements: ObjectivesSaucy MiaNo ratings yet
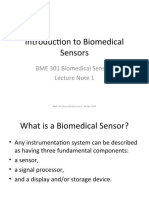
- Introduction To Biomedical SensorsDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Biomedical SensorsAbubakar SadiqNo ratings yet
- Technical Note 4Document3 pagesTechnical Note 4princedottyNo ratings yet
- Volcano Case Studies 5 & 6Document11 pagesVolcano Case Studies 5 & 6Mahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- ME 503-N Manufacturing TechnologyDocument4 pagesME 503-N Manufacturing Technologyhrana287No ratings yet
- CH 08 CDocument30 pagesCH 08 CAnonymous ncBe0B9bNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Laboratory Manual: by Dr. N. Kumara SwamyDocument4 pagesFluid Mechanics and Machinery Laboratory Manual: by Dr. N. Kumara SwamyMD Mahmudul Hasan Masud100% (1)
- Qw-482 Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS) : (See QW-200.1, Section IX, ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code)Document1 pageQw-482 Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS) : (See QW-200.1, Section IX, ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code)linaNo ratings yet
- Am Steel PDFDocument28 pagesAm Steel PDFyogesh vNo ratings yet
- Theory Application and Sizing of Air ValvesDocument9 pagesTheory Application and Sizing of Air ValveskcplemmonsNo ratings yet
- SHMT LAB Assignment Submitted By: Mukhamad Zaman Chatkha 237620 Define PackingDocument5 pagesSHMT LAB Assignment Submitted By: Mukhamad Zaman Chatkha 237620 Define PackingIzza AfaqNo ratings yet
- Group Project DESIGN CASE STUDY FOR POWER TRANSMISSIONDocument14 pagesGroup Project DESIGN CASE STUDY FOR POWER TRANSMISSIONrayan alnoaimiNo ratings yet
- Discovering The Universe Earth and MoonDocument123 pagesDiscovering The Universe Earth and MoonMarcus Skookumchuck VanniniNo ratings yet
- Sika Waterbar®: PVC Waterproofing For Joints in ConcreteDocument12 pagesSika Waterbar®: PVC Waterproofing For Joints in ConcreteKwok MorrisNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment 1 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesSummative Assessment 1 2nd QuarterJudith DurensNo ratings yet
- Principle of DSCDocument10 pagesPrinciple of DSCroopashreems927No ratings yet
- Gravity SettlingDocument10 pagesGravity SettlingNithinKallayil100% (1)
- Chap 1Document15 pagesChap 1darklord338No ratings yet
- Acoutics Answer KeyDocument2 pagesAcoutics Answer KeyDipu GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Padeye - 01Document9 pagesPadeye - 01ramNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Louver Page 1Document1 pageAluminum Louver Page 1Renz ChuaNo ratings yet
- Essential System Phantom Manual - Rev A CompressedDocument36 pagesEssential System Phantom Manual - Rev A CompressedTold Told LeungNo ratings yet
- Ceramic CAD/CAM Materials: An Overview of Clinical Uses and ConsiderationsDocument10 pagesCeramic CAD/CAM Materials: An Overview of Clinical Uses and ConsiderationsNajeeb UllahNo ratings yet
- Effect of Pretreatment Methods On Properties of Natural Fiber Composites A Review - VenkatachalamDocument12 pagesEffect of Pretreatment Methods On Properties of Natural Fiber Composites A Review - Venkatachalamdeathjester1No ratings yet
- Best Practice Guide (Mechanical Insulation)Document158 pagesBest Practice Guide (Mechanical Insulation)Sky LarksNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Reinforced Concrete StructuresDocument44 pagesSeismic Design of Reinforced Concrete Structuresruspra100% (1)