Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem 1. Metallic Bonding
Uploaded by
topbanana09Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem 1. Metallic Bonding
Uploaded by
topbanana09Copyright:
Available Formats
ES174
Example Question 1: Bonding.
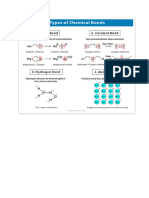
Compare and contrast metallic and covalent primary bonds in terms of
a) The nature of the bond,
b) The valence of the atoms involved, and
c) The ductility of the materials bonded in these ways.
Solutions on next page
Solutions
(a) Metallic bonds are formed between the one or two free electrons of each atom. The free
electrons form a gaseous cloud of electrons that move between atoms. Covalent bonds
involve the sharing of electrons between atoms.
(b) In metallic bonding, the metal atoms typically have one or two valence electrons that are
given up to the electron sea. Covalent bonds form between atoms of the same element or
atoms with similar electronegativities.
(c) Metallic bonds are non-directional. The non-directionality of the bonds and the shielding
of the ions by the electron cloud lead to high ductilities. Covalent bonds are highly
directionalthis limits the ductility of covalently bonded materials by making it more
difficult for the atoms to slip past one another.
You might also like
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- S9Q2T2L2 Types of Chemical BondingDocument37 pagesS9Q2T2L2 Types of Chemical BondingMark Kevin Cagande EscletoNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument9 pagesChemical Bondingangie432meNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Structure of MatterDocument2 pagesBonding and Structure of MatterjuliettekhooNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding (Engineering Chemistry Lecture)Document13 pagesChemical Bonding (Engineering Chemistry Lecture)kiana Jessica MonroeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 21Document16 pagesChemical Bond 21Thanks OdoiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure PDFDocument56 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure PDFAbhishek AgrahariNo ratings yet
- Merged Quiz Concept CheckDocument28 pagesMerged Quiz Concept CheckPatricia Ysabelle YaranonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond TypesDocument5 pagesChemical Bond Typesapi-287081563No ratings yet
- 01-Metallic BondingDocument2 pages01-Metallic BondingNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bond - Definition, Properties, Examples, & Facts - BritannicaDocument7 pagesCovalent Bond - Definition, Properties, Examples, & Facts - BritannicaMuhammad AbdulazizNo ratings yet
- CHEM1030 Atomic and Molecular Theory Lecture 6-7Document17 pagesCHEM1030 Atomic and Molecular Theory Lecture 6-7dopayne7No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding MDocument23 pagesChemical Bonding MnewmowneeshNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Lewis Dot Carbon Hydrogen OxygenDocument17 pagesChemical Bonding: Lewis Dot Carbon Hydrogen OxygenSheila Mae AramanNo ratings yet
- Bonding & Shapes of Mol - CN - STDT2Document3 pagesBonding & Shapes of Mol - CN - STDT2NkemziNo ratings yet
- 2023 Grade 11 Learner Support DocumentDocument131 pages2023 Grade 11 Learner Support DocumentanathinothandoNo ratings yet
- Notes - Chemical BondingDocument14 pagesNotes - Chemical Bonding黄心盈No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Chemical BondingDocument32 pagesLecture 3 Chemical BondingAhmed FouadNo ratings yet
- Material Bonding Character Example: Primary Interatomic Bonds Ionic BondingDocument4 pagesMaterial Bonding Character Example: Primary Interatomic Bonds Ionic BondingCsir RimlaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4: Chemical BondingDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 4: Chemical BondingHikmaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Notes For ExamDocument4 pagesChemical Bonding Notes For ExamMermz96No ratings yet
- Covalent Bond: "Covalent" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument15 pagesCovalent Bond: "Covalent" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeekhadijabugtiNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument53 pagesChemical Bondingpream.s1323No ratings yet
- Presentation of Bonding in SolidsDocument14 pagesPresentation of Bonding in SolidsRohit BiswasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 Atomic Structure and Inter-Atomic Bonding BiomaterialsDocument24 pagesLecture 02 Atomic Structure and Inter-Atomic Bonding BiomaterialsAbdallah ShaatNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1.3 NotesDocument32 pagesChemistry 1.3 NotescheeheNo ratings yet
- Lecture #2. Contact Between Solids. Solid Surfaces. Roughness of Surfaces. Characterization of Surface TopographyDocument10 pagesLecture #2. Contact Between Solids. Solid Surfaces. Roughness of Surfaces. Characterization of Surface TopographyAbdulla CamalNo ratings yet
- Chapt 2 Part 2&3 cmt352Document20 pagesChapt 2 Part 2&3 cmt352Siti Zulaika Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument6 pagesChemical Bonding NotesAyesha Awan100% (1)
- Ionic BondDocument2 pagesIonic BondP. BrucoyNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical BondsDocument8 pagesTypes of Chemical BondsdanNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument22 pagesMetallic BondingnkjkjkjNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document19 pagesCH 12api-256509209No ratings yet
- 1.3. BondingDocument10 pages1.3. BondingdodoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 1Document37 pagesChemical Bonding 1palal123No ratings yet
- Physics 2 SenguptaDocument38 pagesPhysics 2 SenguptaSashank PrayagaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument38 pagesChemical BondingBackup AccountNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 2 AnswersDocument1 pageChemical Bonding 2 Answerssatya176No ratings yet
- Chemical BondDocument8 pagesChemical BondRohan lallNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 PHY 351Document14 pagesTutorial 1 PHY 351MUHAMMAD AMMIRUL HAFIZ MD ZAININo ratings yet
- Atomic Bonding in SolidsDocument3 pagesAtomic Bonding in Solidsazmatshahzad786786No ratings yet
- CB 1Document4 pagesCB 1Mahmudur Rahman27No ratings yet
- Chemical BondDocument1 pageChemical Bonddilwale puchNo ratings yet
- Structure and Bonding IPADDocument4 pagesStructure and Bonding IPADLarissa RubarajNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and BondingDocument15 pagesAtomic Structure and BondingPaidamoyo MunhengaNo ratings yet
- Class 9th Chemistry Unit#4 Structure of MoleculesDocument8 pagesClass 9th Chemistry Unit#4 Structure of MoleculesIrfanullahNo ratings yet
- Islamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyDocument29 pagesIslamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyRayhanuzzaman ShazibNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument2 pagesChemistry NotesSteve Niloy RoyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 2Document32 pagesChemical Bond 2Yak Raj PandeyNo ratings yet
- AQA Chemistry A-Level: 3.1.3: Bonding and StructuresDocument10 pagesAQA Chemistry A-Level: 3.1.3: Bonding and StructuresAshleigh NcubeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsDocument4 pagesLecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsShreyas KamathNo ratings yet
- Lesson No. 3: Inorganic Chemistry (Sci Ac5)Document3 pagesLesson No. 3: Inorganic Chemistry (Sci Ac5)Franklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondDocument10 pagesMetallic BondAbhishek NayakNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Structure PDFDocument14 pagesBonding and Structure PDFWandaNo ratings yet
- Three Types of Chemical BondingDocument97 pagesThree Types of Chemical Bondingriza loveresNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistryzaryabfaraz314No ratings yet
- Lec 2Document43 pagesLec 2SaadFarooqNo ratings yet
- Enlaces Quimicos y Su Influencia en Las Caracteristicas y Propiedades de Los MaterialesDocument10 pagesEnlaces Quimicos y Su Influencia en Las Caracteristicas y Propiedades de Los MaterialesFelipe Alonso Rojas VeraNo ratings yet
- 2 Atomic StructureDocument43 pages2 Atomic StructureRafael ArancibiaNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Document25 pagesInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?lianghoo94No ratings yet
- RSPCA Rabbit Housing AdviceDocument8 pagesRSPCA Rabbit Housing Advicetopbanana09No ratings yet
- 1 PB PDFDocument8 pages1 PB PDFtopbanana09No ratings yet
- Ua035224 Gce Lin Dtprodes Issue 3-2SDocument162 pagesUa035224 Gce Lin Dtprodes Issue 3-2Stopbanana09No ratings yet
- Guide To Citing ReferencesDocument4 pagesGuide To Citing Referencestopbanana09No ratings yet
- ES195 Lab Tensile Testing PDFDocument12 pagesES195 Lab Tensile Testing PDFtopbanana09No ratings yet
- Arguments and ExplanationsDocument4 pagesArguments and Explanationstopbanana09No ratings yet
- CREST Anybody Out ThereDocument4 pagesCREST Anybody Out Theretopbanana09No ratings yet
- UNSC BackgrounderDocument9 pagesUNSC Backgroundertopbanana09No ratings yet
- Keyboard ManualDocument94 pagesKeyboard Manualtopbanana09No ratings yet
- Manuscript PaperDocument1 pageManuscript Papertopbanana09No ratings yet
- GCSE Core ScienceDocument86 pagesGCSE Core Sciencetopbanana09No ratings yet
- E Learning GuideDocument1 pageE Learning Guidetopbanana09No ratings yet
- Manuscript PaperDocument1 pageManuscript Papertopbanana09No ratings yet
- Manuscript PaperDocument1 pageManuscript Papertopbanana09No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityFrom EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressFrom EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Meltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalFrom EverandMeltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- A Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireFrom EverandA Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (129)
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersFrom EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersFrom EverandPhysical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookFrom EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsFrom EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Phase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandPhase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)