Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EULER - EQ in Cylindrical Cordinates
Uploaded by
spartha_beOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EULER - EQ in Cylindrical Cordinates
Uploaded by
spartha_beCopyright:
Available Formats
Euler equation
EULER EQUATION
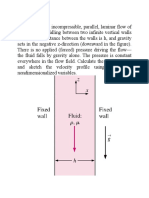
We consider an incompressible , isothermal Newtonian flow (density =const, viscosity
r
=const), with a velocity field V = (u ( x,y,z) , v( x,y,z) , w ( x,y,z))
Incompressible continuity equation:
u v w
+ + =0 eq1.
x y z
Euler equation: r
DV r
vector form: = P + g
Dt
x component:
u u u u P
+ u + v + w = + g x eq2.
t x y z x
y component:
v v v v P
+ u + v + w = + g y eq3.
t x y z y
z component:
w w w w P
+u +v + w = + g z eq4.
t x y z z
Cylindrical coordinates (r , , z ) :
We consider an incompressible , isothermal Newtonian flow (density =const,
r
viscosity =const), with a velocity field V = (u r , u , u z ).
Incompressible continuity equation:
1 (ru r ) 1 (u ) u z
+ + =0 eq a)
r r r z
r-component:
u u u u u2 u P
r + u r r + r + u z r = + g r eq b)
t r r r z r
-component:
u u u u uu u 1 P
+ ur + + r + u z = + g eq c)
t r r r z r
z-component:
u u u u u P
z + ur z + z + u z z = + g z eq d)
t r r z z
You might also like
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Navier Stokes Equation in Cartesian and Polar CoordinatesDocument1 pageNavier Stokes Equation in Cartesian and Polar CoordinatesSayantan Pal100% (1)
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- The Equation of Change: X y Z Through WhichDocument20 pagesThe Equation of Change: X y Z Through Whichsiska pebrianiNo ratings yet
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)From EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)No ratings yet
- Mecánica de Fluidos EjerciciosDocument7 pagesMecánica de Fluidos EjerciciosymailioNo ratings yet
- Tables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39From EverandTables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39No ratings yet
- Acoustics Wave EquationsDocument27 pagesAcoustics Wave Equationszeeshanahmad111No ratings yet
- Chap 02 PropaxDocument32 pagesChap 02 Propaxromy94496No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lesson 11CDocument6 pagesFluid Mechanics Lesson 11CHina MeoNo ratings yet
- MHMT 2017Document9 pagesMHMT 2017SKITTLE BEASTNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics Notes Week 2Document10 pagesAerodynamics Notes Week 2HenryNNo ratings yet
- Gatapov 2005Document8 pagesGatapov 2005KorcaNo ratings yet
- LecturenotesDocument59 pagesLecturenotesTyo Spider-MenkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Navier-Stokes EquationDocument16 pagesChapter 8 Navier-Stokes EquationSyahiran SalehNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics EquationsDocument8 pagesFluid Mechanics EquationsRaman ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Turbulencemodels PDFDocument5 pagesTurbulencemodels PDFPawan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fluid 06Document140 pagesFluid 06Edgar HuancaNo ratings yet
- CmechDocument10 pagesCmechdaskhagoNo ratings yet
- A First-Order Pdes: A.1 Wave Equation With Constant SpeedDocument6 pagesA First-Order Pdes: A.1 Wave Equation With Constant SpeedshayandevNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Control Theory: Introduction To Dynamical SystemsDocument43 pagesNonlinear Control Theory: Introduction To Dynamical SystemsChernet TugeNo ratings yet
- NS .CylindricalDocument2 pagesNS .Cylindricalthakurht2001No ratings yet
- Tehe Net Pressure Force On The Element in The X Direction: Vertikal Dynamic BalanceDocument4 pagesTehe Net Pressure Force On The Element in The X Direction: Vertikal Dynamic BalanceayazamNo ratings yet
- Examples Chap9 2 PDFDocument6 pagesExamples Chap9 2 PDFEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- PH108 - Electricity and Magnetism: Basanta K. NandiDocument21 pagesPH108 - Electricity and Magnetism: Basanta K. Nandiamar BaroniaNo ratings yet
- TUTORIALS 1 (Chap. 1 and Chap. 2) : Exercise 1Document5 pagesTUTORIALS 1 (Chap. 1 and Chap. 2) : Exercise 1Jean LaplaigeNo ratings yet
- Note de Curs-FSIDocument86 pagesNote de Curs-FSICornel BicaNo ratings yet
- Lecture16 Equations IsothermalSystems 3Document11 pagesLecture16 Equations IsothermalSystems 3shubhamNo ratings yet
- Advanced Fluid Mechanics - Chapter 03 - Exact Solution of N-S EquationDocument44 pagesAdvanced Fluid Mechanics - Chapter 03 - Exact Solution of N-S Equationhari sNo ratings yet
- Solucion 01 PDFDocument4 pagesSolucion 01 PDFlibrospiratasNo ratings yet
- 3 Methods To Differentiate Term InsuranceDocument2 pages3 Methods To Differentiate Term InsurancehanNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 Vector Algebra and CalculusDocument2 pagesHomework 2 Vector Algebra and CalculusSwathi BDNo ratings yet
- Rans DerivationDocument16 pagesRans Derivationuday gouthamaNo ratings yet
- MHMT 2018Document10 pagesMHMT 2018SKITTLE BEASTNo ratings yet
- Navier Stokes Equations in Cylindrical CoordinatesDocument8 pagesNavier Stokes Equations in Cylindrical Coordinatesdemichie100% (2)
- Qua Tern IonsDocument10 pagesQua Tern IonsPrashant SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Integral & Differential Form of Energy Equations in Rectangular CoordinatesDocument21 pagesIntegral & Differential Form of Energy Equations in Rectangular CoordinatesSarv JeetNo ratings yet
- Governing Equations For Turbulent FlowDocument15 pagesGoverning Equations For Turbulent FlowRenz Marion CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Intro To SWE Textbook1Document9 pagesIntro To SWE Textbook1AKNo ratings yet
- IX-4.3D-Shape Recognition Based Tactile SensorDocument15 pagesIX-4.3D-Shape Recognition Based Tactile SensorImtiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Physics 2. Electromagnetism: 1 FieldsDocument9 pagesPhysics 2. Electromagnetism: 1 FieldsOsama HassanNo ratings yet
- Math 23 Lecture 1.5 Chain Rule and Implicit Differentiation PDFDocument18 pagesMath 23 Lecture 1.5 Chain Rule and Implicit Differentiation PDFyeahNo ratings yet
- Equations of Turbulent FlowsDocument39 pagesEquations of Turbulent Flowsshehbazi2001No ratings yet
- Solution For Chapter 23: T T' P T' T T' T PDocument8 pagesSolution For Chapter 23: T T' P T' T T' T PSveti JeronimNo ratings yet
- Leyes de ConservacionDocument13 pagesLeyes de ConservacionMario ParedesNo ratings yet
- StrainDocument42 pagesStrainHakim FahmiNo ratings yet
- MIT Numerical PDEDocument119 pagesMIT Numerical PDEKruger JoeNo ratings yet
- 1 XXX 2 Laplace'S Equation: 2.1 Two Dimensional PolarDocument3 pages1 XXX 2 Laplace'S Equation: 2.1 Two Dimensional PolarGovanna StarNo ratings yet
- Continuous Systems ShortDocument2 pagesContinuous Systems ShortShreyansh TibdewalNo ratings yet
- DM M M DT: 2.06 Equation Sheet For Quiz 2 (Spring 2013)Document3 pagesDM M M DT: 2.06 Equation Sheet For Quiz 2 (Spring 2013)Jimmy CarranzaNo ratings yet
- PH424 - Electromagnetic Theory I: Basanta K. Nandi x7560Document30 pagesPH424 - Electromagnetic Theory I: Basanta K. Nandi x7560SupriyoNaskarNo ratings yet
- Fluid Dynamics L02 2002Document20 pagesFluid Dynamics L02 2002Murali KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Solution - Tutorial 4 (24 Feb 2021)Document3 pagesSolution - Tutorial 4 (24 Feb 2021)shubhamNo ratings yet
- AE 301 - Aerodynamics I - Spring 2015 Answers To Problem Set 5Document5 pagesAE 301 - Aerodynamics I - Spring 2015 Answers To Problem Set 5TheTannedFishNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Mass Equation - Di Erential FormDocument4 pagesConservation of Mass Equation - Di Erential FormShawn WaltzNo ratings yet
- Correction To Exercise Class-2Document2 pagesCorrection To Exercise Class-2Tobias HolmNo ratings yet
- Solving PDEsby Partial Integrating FactorsDocument9 pagesSolving PDEsby Partial Integrating FactorsWisal muhammedNo ratings yet
- Derivation of The Lorenz EquationsDocument3 pagesDerivation of The Lorenz EquationsSteven ScottNo ratings yet
- ENS 205 Failure Analysis and PreventionDocument76 pagesENS 205 Failure Analysis and PreventionBolaji Suberu100% (1)
- Rice Pudding Viscosity CHRTDocument1 pageRice Pudding Viscosity CHRTspartha_beNo ratings yet
- R Arfm 90 PDFDocument13 pagesR Arfm 90 PDFPato Patiño MuñozNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem SubjectsDocument3 pages2nd Sem Subjectsspartha_beNo ratings yet
- Rice Pudding Viscosity CHRTDocument1 pageRice Pudding Viscosity CHRTspartha_beNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document2 pagesTutorial 4spartha_beNo ratings yet
- Blasius PDFDocument2 pagesBlasius PDFspartha_beNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1spartha_beNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sol-1Document3 pagesAssignment Sol-1spartha_beNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus Polar Cordni NotesDocument3 pagesVector Calculus Polar Cordni Notesspartha_beNo ratings yet
- Advanced Solid Mechanics U SarvananDocument385 pagesAdvanced Solid Mechanics U Sarvananமாறன் செங்கேணிNo ratings yet
- TensorsDocument116 pagesTensorsUmair IsmailNo ratings yet
- 105106049Document4 pages105106049Siddharth SunejaNo ratings yet
- AM 5030 - Linear Dynamical Systems: Assignment-1Document1 pageAM 5030 - Linear Dynamical Systems: Assignment-1spartha_beNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Automobile SuspensionDocument13 pagesAnalysis of Automobile SuspensionAfeez AzizNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet
- The Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldFrom EverandThe Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- Hero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarFrom EverandHero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonFrom EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (103)
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellFrom EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (81)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelFrom EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Reality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyFrom EverandReality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (24)
- Faster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestFrom EverandFaster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (28)
- Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceFrom EverandPale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (588)
- The Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyFrom EverandThe Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyNo ratings yet
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- The Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaFrom EverandThe Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaNo ratings yet
- How to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerFrom EverandHow to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- A Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsFrom EverandA Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (242)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldFrom EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- How to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerFrom EverandHow to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastFrom EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Broken Money: Why Our Financial System is Failing Us and How We Can Make it BetterFrom EverandBroken Money: Why Our Financial System is Failing Us and How We Can Make it BetterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansFrom EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansNo ratings yet
- Dirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureFrom EverandDirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (125)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationFrom EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- Data-ism: The Revolution Transforming Decision Making, Consumer Behavior, and Almost Everything ElseFrom EverandData-ism: The Revolution Transforming Decision Making, Consumer Behavior, and Almost Everything ElseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (12)