Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Structure of The Atom Dalton's Atomic Theory
Uploaded by
Ruby Go0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesduh
Original Title
Chem14 Notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentduh
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesThe Structure of The Atom Dalton's Atomic Theory
Uploaded by
Ruby Goduh
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
CHAPTER 1 - ATOMIC STRUCTURE
The Structure of the Atom
Dalton's Atomic Theory
The Subatomic Particles
Atomic Number, Mass Number and Isotopes
CHAPTER 1 - ATOMIC STRUCTURE
he Structure of the Atom
alton's Atomic Theory
1. All matter is composed of atoms that are small and indivisible particles
2. Atoms of the same element have identical size, mass, and chemical properties.
However, atoms of different elements do not
3. Atoms combine in a definite ratio of small whole numbers to form a compound
4. During chemcial reaction, atoms are either combined, united, or rearranged, none
are created or destroyed
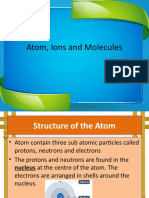
he Subatomic Particles
omic Number, Mass Number and Isotopes
Atoms are identified by their number of protons and neutrons
Atomic Number (Z) = # of protons; fixed and unchanging
Mass Number (A) = protons + neutrons
Mass Number (A) = atomic number + neutrons
In a neutral atom, protons = electrons; atomic number = protons = electrons
A positively charged ion has more protons than electrons
A negatively charged ion has more electrons than protons
charge = algebraic sum of positive charges and negative charges
The atom is the basic unit of an element that can enter into che
Law of Definite Proportions
}
A compound has the same composition regardless of quantity o
Law of Conservation of Mass
}
This is the basis of a balanced equation
Chemical reactions involve orbital electrons only; so there is no
} the number of protons
that can enter into chemical combination
egardless of quantity or source
ns only; so there is no change in
You might also like
- High School Chemistry PDFDocument12 pagesHigh School Chemistry PDFAleph ContinuumNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry - Study GuideDocument79 pagesAP Chemistry - Study GuideRaabiah AzeezNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Unit 1 Molecules Their Interaction Relevant To Biology CSIR UGC NET Life SciencesDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Molecules Their Interaction Relevant To Biology CSIR UGC NET Life SciencesKishan KoyaniNo ratings yet
- QUARTER 1 LESSON 2 Atom Ions and MoleculesDocument60 pagesQUARTER 1 LESSON 2 Atom Ions and MoleculesMichelle De VillaNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument28 pagesAtomic StructureJohn Vince Ramos PapNo ratings yet
- BSAP CurriculumDocument3 pagesBSAP CurriculumRuby Go100% (1)
- Genchem w2 1Document24 pagesGenchem w2 1MonicDuranNo ratings yet
- Basic ChemistryDocument14 pagesBasic ChemistryPitherNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemistry: Class ObjectivesDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry: Class ObjectivesSebastian VillegasNo ratings yet
- GC1-Lesson-3-Atoms-Molecules-and-Ions-2-Daltons-Atomic-TheoryDocument34 pagesGC1-Lesson-3-Atoms-Molecules-and-Ions-2-Daltons-Atomic-TheoryYeri KimNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: The Atomic Structure of MatterDocument3 pagesUnit 1: The Atomic Structure of MatterDanyel Rodriguez RomeraNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Week 1.2Document34 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Week 1.2Giovanni Gumahad Jr.No ratings yet
- Matter and Stoichiometry Chm092 June 2014Document223 pagesMatter and Stoichiometry Chm092 June 2014ida hadiNo ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument4 pagesAtoms and MoleculesHitesh kalraNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure FundamentalsDocument10 pagesAtomic Structure FundamentalsKhin Yadanar KyawNo ratings yet
- Kanav 9a 90040 CH 3 Chem.Document6 pagesKanav 9a 90040 CH 3 Chem.Kanav WallechaNo ratings yet
- Law of Chemical CombinationDocument5 pagesLaw of Chemical CombinationSiddharth SinghNo ratings yet
- Chem ModuleDocument20 pagesChem Modulekeeno manzanoNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules, and IonsDocument30 pagesAtoms, Molecules, and IonsJoel Sevillano BombalesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Periodic TableDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Periodic TableMa. Oliva Diana CastroNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms Amd Molecules NotesDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms Amd Molecules NotesHesandi PeirisNo ratings yet
- ATOMIC STRUCTUREDocument7 pagesATOMIC STRUCTUREcherry shane abanesNo ratings yet
- CHM 092 CHAPTER 1 - Matter &stoichiometryDocument128 pagesCHM 092 CHAPTER 1 - Matter &stoichiometryAisyah NadhirahNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Atoms and Molecules NotesDocument7 pagesGrade 9 Atoms and Molecules NotesAujasvi JainNo ratings yet
- 02-010-21 G8 Atomic Number and Mass NumberDocument3 pages02-010-21 G8 Atomic Number and Mass NumberJose JeramieNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Atoms Molecules NotesDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 9 Atoms Molecules NotesManjot kaurNo ratings yet
- Mass Can Neither Be Created Nor Destroyed in A Chemical Reaction. E.g., A + B C + D Reactants Products Mass of Reactants Mass of ProductsDocument36 pagesMass Can Neither Be Created Nor Destroyed in A Chemical Reaction. E.g., A + B C + D Reactants Products Mass of Reactants Mass of ProductsAnagha PradeepNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2Document24 pagesChemistry Unit 2Auvan HilarioNo ratings yet
- Campbell Lecture Notes Chemistry of LifeDocument42 pagesCampbell Lecture Notes Chemistry of LifeSophia Andrei VillalunaNo ratings yet
- (Independent Activity 1) : 1. AtomDocument3 pages(Independent Activity 1) : 1. AtomRadney Paula Sta MariaNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and Chemical ReactionsDocument51 pagesAtoms, Molecules and Chemical ReactionsDavid PhilemonNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsDocument28 pagesAtoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsCandyAnonymousNo ratings yet
- The Structure of the Atom - Protons, Neutrons, ElectronsDocument13 pagesThe Structure of the Atom - Protons, Neutrons, ElectronsSheena Shane CantelaNo ratings yet
- ATOM Class 7Document23 pagesATOM Class 7Eureka MaterialNo ratings yet
- Eastern Samar National Comprehensive High School Chemistry 1Document3 pagesEastern Samar National Comprehensive High School Chemistry 1Isaac PiaoNo ratings yet
- Meera Class 9 Chemistry NotesDocument11 pagesMeera Class 9 Chemistry Noteslalitha muraliNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument13 pagesChemMj CaraanNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Molecules Class 9 Notes Chapter 3Document7 pagesAtoms and Molecules Class 9 Notes Chapter 3ANAYA SHARANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - ChemistryDocument9 pagesChapter 4 - ChemistryHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Chemical States of Matter: Material Science & Chemistry Week One LectureDocument27 pagesAtomic Structure and Chemical States of Matter: Material Science & Chemistry Week One LectureIbrahim AliNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument58 pagesChemashwin.sp.004No ratings yet
- Structure of An ATOMDocument18 pagesStructure of An ATOMChese Ann PepinoNo ratings yet
- Objective: Topic:ISOTOPESDocument11 pagesObjective: Topic:ISOTOPESMD. ARIFUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesAtoms and Atomic TheorypauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Matter and StoichiometryDocument223 pagesChapter 1 - Matter and StoichiometryJatjediNo ratings yet
- ATOMic StructureDocument5 pagesATOMic Structuretalithaonkabetse723No ratings yet
- Learning about atomic structure and the periodic tableDocument40 pagesLearning about atomic structure and the periodic tableFontanilla, Nathaniel D.No ratings yet
- Dalton S Atomic TheoryDocument1 pageDalton S Atomic TheoryVAIBHAV AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- All Matter in Universe Is Composed Of: AtomsDocument11 pagesAll Matter in Universe Is Composed Of: AtomsmNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory and Atomic Structure 1Document25 pagesAtomic Theory and Atomic Structure 1Mohamed YahiaNo ratings yet
- Additional MathematicsDocument6 pagesAdditional Mathematicslonydon23No ratings yet
- CHEM 11/L Module 2 - Atomic Structure and Periodic TableDocument15 pagesCHEM 11/L Module 2 - Atomic Structure and Periodic TableFrancis RecocoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Atoms ElementsDocument8 pagesLecture 1 Atoms ElementsshanecarlNo ratings yet
- Chemistry FactsheetsDocument415 pagesChemistry FactsheetsAmbrose Aaron DavidNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Ions, MoleculesDocument11 pagesAtoms, Ions, MoleculesGracia Thalia TNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: The Smallest Piece of an ElementDocument23 pagesAtomic Structure: The Smallest Piece of an ElementMd. Mujahid HasanNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules, and Ions LawDocument5 pagesAtoms, Molecules, and Ions LawJohn Mark Clouie PlacaNo ratings yet
- LAMP Application Form A4 FinalDocument3 pagesLAMP Application Form A4 FinalRuby GoNo ratings yet
- 0 Vectors & 1D KinematicsDocument38 pages0 Vectors & 1D KinematicsRuby GoNo ratings yet
- NMAT Answer Sheets Template - ScantronDocument1 pageNMAT Answer Sheets Template - ScantronRuby GoNo ratings yet
- Math 74 2nd Lab DepExDocument1 pageMath 74 2nd Lab DepExRuby GoNo ratings yet
- Application For IAPS Membership As: Local CommitteeDocument4 pagesApplication For IAPS Membership As: Local CommitteeRuby GoNo ratings yet
- Math 74 2nd Lab DepExDocument1 pageMath 74 2nd Lab DepExRuby GoNo ratings yet
- Bio25: Vertebrate Structure & Function: Janice V. NG, MSC Department of Biology, Cas, Upm Sy 2015-2016Document43 pagesBio25: Vertebrate Structure & Function: Janice V. NG, MSC Department of Biology, Cas, Upm Sy 2015-2016Ruby GoNo ratings yet
- M74 Lab1 SampleDocument1 pageM74 Lab1 SampleRuby GoNo ratings yet
- BS Pharmacy Curriculum PDFDocument3 pagesBS Pharmacy Curriculum PDFRuby GoNo ratings yet
- Math 74 Syllabus DetailsDocument4 pagesMath 74 Syllabus DetailsRuby GoNo ratings yet
- Application - Shifees - Transferees 1st Sem 2017 2018Document2 pagesApplication - Shifees - Transferees 1st Sem 2017 2018Ruby GoNo ratings yet
- Troy Justin Go: Search Enroll My Academics My Class Schedule Add Term InformationDocument1 pageTroy Justin Go: Search Enroll My Academics My Class Schedule Add Term InformationRuby GoNo ratings yet
- Math74Lec Derivatives Integrals SummaryDocument2 pagesMath74Lec Derivatives Integrals SummaryKayla JoezetteNo ratings yet
- Bio 22 Syllabus 2say15 16Document4 pagesBio 22 Syllabus 2say15 16Ruby GoNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument1 pageProblem SetRuby GoNo ratings yet
- Expt 9Document3 pagesExpt 9Ruby GoNo ratings yet
- The Austronesian ConnectionDocument11 pagesThe Austronesian ConnectionRuby GoNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge: Chapter V: The Unification of Electricity, Magnetism and LightDocument5 pagesElectric Charge: Chapter V: The Unification of Electricity, Magnetism and LightRuby GoNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge: Chapter V: The Unification of Electricity, Magnetism and LightDocument5 pagesElectric Charge: Chapter V: The Unification of Electricity, Magnetism and LightRuby GoNo ratings yet
- HISTO1 AmericanDocument4 pagesHISTO1 AmericanRuby GoNo ratings yet
- Comm1 Short Essay DraftDocument2 pagesComm1 Short Essay DraftRuby GoNo ratings yet
- Territoriality OutlineDocument2 pagesTerritoriality OutlineRuby GoNo ratings yet
- SOCSCII Debate RulesDocument2 pagesSOCSCII Debate RulesRuby GoNo ratings yet
- Comm1 Short Essay DraftDocument2 pagesComm1 Short Essay DraftRuby GoNo ratings yet
- Term 3Document6 pagesTerm 3Ruby GoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 A Silly PolymerDocument3 pagesExperiment 1 A Silly PolymerRuby GoNo ratings yet
- Partnership Operations Lecture NotesDocument12 pagesPartnership Operations Lecture NotesRuby GoNo ratings yet
- COMM1 Short EssayDocument2 pagesCOMM1 Short EssayRuby GoNo ratings yet