Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Swami Vivekanand Institute of Engineering & Technology: Study and Performance of Domestic Refrigerator
Uploaded by
Dhiraj DhimanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Swami Vivekanand Institute of Engineering & Technology: Study and Performance of Domestic Refrigerator
Uploaded by
Dhiraj DhimanCopyright:
Available Formats
Swami Vivekanand Institute of Engineering & Technology
Chandigarh-Patiala Highway, Sector-8, Ramnagar, Banur, District Patiala (Pb.)
RAC – 601
Page 1 of 4
Study and performance of domestic refrigerator.
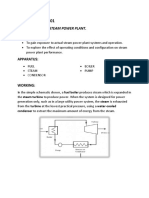
AIM: Study and performance of domestic refrigerator.
APPARATUS: Refrigerator test rig. (Vapour compression cycle)
THEORY:
The refrigerator cycle in vapours forms finds application in countless industrial
and domestic situations through out the world. For examples, the storage and transport of
perishable food stuffs and drugs would be extremely difficult if not impossible without
refrigeration’s. Similarly the efficient operations of offices and factories in many part s of
the world would be impossible without the use of refrigeration plants in air conditioning.
It is for this reason that engineers of many disciplines must have a good working
knowledge of the refrigeration’s cycle .a refrigerator is defined as a machine whose prime
function is to remove heat from a low temperature region. Since the energy extracted
cannot be destroyed, if follows that this energy required to operate the machine, must be
rejected to the surrounding at a higher temperature, if the temperature of the rejections is
high enough to be useful and this is the prime object of the machine, then the machine is
called a HEAT PUMP.
The clausius statement of the second law of the thermodynamics states that heat
will not pass from a cold to a hotter region without an “external agency” being employed.
This external agency may be applied in the form of high-grade energy input of either
“work” or a high-grade heat input. The high-grade heat input may take the form of either
high temperature combustion products, electrical energy (in the form of heat) or solar
energy.
The most common type of refrigerator or heat pump operates on the compression
cycle and requires a work input. The vapour compression refrigeration test rig has been
designed to enables students to safety study in the cycle in details. The test rig requires
220v ac,50c/s supply and fresh water supply connections.
REFRIGERANT USED - R12
REFRIGERATION RATE - 1400w maximum, but varies with the evaporating.
CONDENSATING TEMP. - 50 MAXIMUM
Prepared By Checked By Approved By Effective Date
Lab. Assistant Lab. Incharge HOD
Swami Vivekanand Institute of Engineering & Technology
Chandigarh-Patiala Highway, Sector-8, Ramnagar, Banur, District Patiala (Pb.)
RAC – 601
Page 2 of 4
Study and performance of domestic refrigerator.
EVAPORATING TEMP. - -20C TO +10C. Variable by adjustment of load
and cooling water temp.
COMPRESSOR - hermetically sealed 314l kirloskar
CONDENSER - shell and coil type
EVAPORATOR - compact once through concentric tube with
refrigeration load supplied by separate concentric
heating elements
EXPANSION VALVE - automatic expansion valve with two bypass
capillary circuits.
THERMODYNAMIC ASPECTS OF REFRIGERATIONS:
The second law of thermodynamic includes the statements,” it is impossible to
transfer heat from a region at a low temperature to another at a higher temperature
without the aid of an external agency”.
Refrigerator and heat pumps are examples of machines, which transfer heat from a low to
a high temperature region, and the “external agency” employed, may be either work or
high-grade heat.
The first law of thermodynamics states in a cycle the net heat transfer is equal to
the network transfer. Thus for a refrigerator, heat transfer at low temperature + heat
transfer at high temperature = work done.
In the case of the refrigerator (or heat pump) using a work input, it follows that
heat transfer at low temperature + work input = heat transfer at high temperature .if the
external agency is high grade heat, the heat transfer at low temperature + heat transfer at
high temperatures = 0
A machine whose prime function is to remove heat from a low temperature region
is called the refrigerator.
A machine whose prime function is to deliver heat from a high temperature region
is called the heat pump. From the first law of thermodynamics, it is apparent that
a refrigerator must reject heat at a higher temperature and the heat pump must
Prepared By Checked By Approved By Effective Date
Lab. Assistant Lab. Incharge HOD
Swami Vivekanand Institute of Engineering & Technology
Chandigarh-Patiala Highway, Sector-8, Ramnagar, Banur, District Patiala (Pb.)
RAC – 601
Page 3 of 4
Study and performance of domestic refrigerator.
take in heat at a lower temperature. Thus, there is very little difference between
the two plants, and both useful affects can be obtained from the same unit.
COP:
= Refrigerating effect
Work done
REFRIGERATION LOAD: This is determined by the input to the electric heating
element in the evaporator and is controlled by the heat input control setting. The product
of the voltmeter and ammeter reading gives the evaporator heat input rate.
CONDENSER PRESSURE: The cooling water flow rate and its inlet temperature
controls condensor motor. Reduce the cooling water flow rate to increase the condenser
pressure.
ELECTRIC INPUT: the voltmeter and ammeter indicates the input to the compressor
motor. The electric power input is in the products of volts, amps, and the power factor
applicable (0.8).
TEMPERATURE INDICATORS: the temperature may be measured at six points in
the circuit by selecting station 1-6 and the appropriate temperature scale.
PROCEDURE:
1) Ensure that the operation of the plant is clearly understood.
2) Start the unit and adjust the evaporator heat input control and, to set the
evaporating pressure adjust the condensor cooling water to give the required
condensor pressure and hence saturation temperatures.
3) For performance curves start with a small duty, say 250w and increase this in
increments of about 259w until the maximum duty is reached. The unit will
respond quickly after the load change and stablise within 15 minutes, although it
may take a little longer at light loads. Stability is reached when changes in
pressure temperature, flow, etc have ceased.
4) Reduce the refrigerator load. Switch off mains switch and turnoff the cooling
water.
5) The unit should be started and allowed to stabiles with a refrigeration load of
about 250w.
Prepared By Checked By Approved By Effective Date
Lab. Assistant Lab. Incharge HOD
Swami Vivekanand Institute of Engineering & Technology
Chandigarh-Patiala Highway, Sector-8, Ramnagar, Banur, District Patiala (Pb.)
RAC – 601
Page 4 of 4
Study and performance of domestic refrigerator.
6) In the evaporator, the pressure and temperature are high and the heat has been a
heat input from the electric heating element.
7) In the condenser, the pressure and temperature are high and the heat has been
given up to the cooling water, which has been given up to the cooling water,
which has become warmer.
8) The compressor increases both the pressure and temperature and that the
compressor requires a work input to-do this.
9) Both the pressure and temperature fall across the expansion valve and that no
work transfer involved.
PRECAUTIONS:
1) Do not touch the compressor or the pipelines, which may be hot or cold.
2) Final readings be recorded after steady conditions have reached say after running
for at least 30 minutes at a particular setting of water flow rate and heater
evaporator load.
3) Ensures that water is continuously flowing through the condenser under all
conditions of compressor working.
4) The flow of water should not be permitted to fall below 1lpm.
5) High pressure and low pressure cut out set to shut off all electrical supplies to
motor and evaporator heaters if condenser pressure exceeds 1400 KN-M2.
Reduce the refrigeration load (evaporator heat input control) switch off mains switch
and turn off the cooling water.
Prepared By Checked By Approved By Effective Date
Lab. Assistant Lab. Incharge HOD
You might also like
- Advanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionFrom EverandAdvanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionNo ratings yet
- GeoSource Ultra HydronicDocument28 pagesGeoSource Ultra Hydronicdoina slamaNo ratings yet
- Rac 7th Sem ManualDocument26 pagesRac 7th Sem Manualmanishsingla88No ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Refrigeration and Mechanical Heat Pump ExperimentDocument12 pagesExperiment 1: Refrigeration and Mechanical Heat Pump ExperimentMohamad FaizNo ratings yet
- Rac Lab ManualDocument69 pagesRac Lab ManualHrshita SinghNo ratings yet
- Lab Sheet 2 PDFDocument13 pagesLab Sheet 2 PDFmalaNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Laboratory Unit R715: P.A.Hilton LTDDocument5 pagesRefrigeration Laboratory Unit R715: P.A.Hilton LTDvineet SinghNo ratings yet
- R715-Refrigeration Laboratory UnitDocument3 pagesR715-Refrigeration Laboratory UnitSaud barqNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Evaporative Heat Exchanger IJETT Paper FormatDocument4 pagesPerformance Analysis of Evaporative Heat Exchanger IJETT Paper FormatAnil DubeNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration TutorDocument7 pagesRefrigeration TutorTejas Vibhandik100% (2)
- ME-803 RAC Refrigeration and Air CondtitioningDocument29 pagesME-803 RAC Refrigeration and Air CondtitioningdeepaknayanNo ratings yet
- BATCH 8 Domestic RefrigeratorDocument22 pagesBATCH 8 Domestic RefrigeratorSai RamNo ratings yet
- Two Bearing Housings PD Series SKF ComDocument10 pagesTwo Bearing Housings PD Series SKF ComboroumandNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Chiller SystemDocument45 pagesModule 3 - Chiller Systemmadan karkiNo ratings yet
- Power Consumption Minimisation With Effective Temperature Control in Domestic RefrigeratorDocument3 pagesPower Consumption Minimisation With Effective Temperature Control in Domestic RefrigeratorInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Heat Pump R514: P.A. Hilton LTDDocument4 pagesMechanical Heat Pump R514: P.A. Hilton LTDKarim AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Testing of A Vapor Compression Refrigeration System 1Document12 pagesExperiment 1 Testing of A Vapor Compression Refrigeration System 1Ashley Justine RowanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 2 - Refrigeration - 1Document111 pagesCHAPTER - 2 - Refrigeration - 1Samuel WozabNo ratings yet
- Ice Plant TrainerDocument1 pageIce Plant TrainerVirender RanaNo ratings yet
- 803 Rac (Me-803) Exp. ManualDocument47 pages803 Rac (Me-803) Exp. ManualAnonymous z3RsdPToNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of A Domestic Refrigerator Using Various Alternative ReffrigerantDocument12 pagesPerformance Analysis of A Domestic Refrigerator Using Various Alternative ReffrigerantGulshan SahuNo ratings yet
- Experimental Analysis of Thermoelectric RefrigeratorDocument3 pagesExperimental Analysis of Thermoelectric RefrigeratorBrian GaskarthNo ratings yet
- Technical SeminarDocument19 pagesTechnical SeminarLibinNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of The Performance of An EjeDocument6 pagesAn Analysis of The Performance of An EjeSơn TiếnNo ratings yet
- Water-Cooled Liquid Chiller: $ppmjohdbqbdjuz - L8Document20 pagesWater-Cooled Liquid Chiller: $ppmjohdbqbdjuz - L8Du NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Domestic Refgirator by Using Refrigerants R134a and R600a: Improving and Comparing The Coefficient of Performance ofDocument5 pagesDomestic Refgirator by Using Refrigerants R134a and R600a: Improving and Comparing The Coefficient of Performance ofInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- DB DCLC-R134a-50HzDocument36 pagesDB DCLC-R134a-50Hzrahimi mohamad100% (2)
- Best Practices For Energy Efficient Cleanrooms: Cooling Tower and Condenser Water OptimizationDocument7 pagesBest Practices For Energy Efficient Cleanrooms: Cooling Tower and Condenser Water OptimizationCelrose FernandezNo ratings yet
- The Design and Performance Analysis of Refrigeration System Using R12 & R134a RefrigerantsDocument6 pagesThe Design and Performance Analysis of Refrigeration System Using R12 & R134a RefrigerantsEugine BalomagaNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Thesis StatementDocument7 pagesAir Conditioning Thesis Statementewdgbnief100% (2)
- Design and Performance Analysis of Water Chiller - A ResearchDocument8 pagesDesign and Performance Analysis of Water Chiller - A ResearchDiyar NezarNo ratings yet
- AC Mtce PaperDocument7 pagesAC Mtce PaperSudheer KalarikkalNo ratings yet
- ModellingDocument10 pagesModellingalmadhagiNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 3: Chiller EfficiencyDocument12 pagesActivity No. 3: Chiller EfficiencyAldrian BarachinaNo ratings yet
- Design and Performance Analysis of Water PDFDocument7 pagesDesign and Performance Analysis of Water PDFDiyar NezarNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Thermal Performance of Cooling Tower of A Chiller Plant Using Machine LearningDocument8 pagesPrediction of Thermal Performance of Cooling Tower of A Chiller Plant Using Machine LearningHammad PervezNo ratings yet
- Exp. No. 02 Domestic Refrigerator Test Rig: Pimpri Chinchwad College of Engineering & Research, RavetDocument34 pagesExp. No. 02 Domestic Refrigerator Test Rig: Pimpri Chinchwad College of Engineering & Research, RavetAbcd EfgNo ratings yet
- Lab Heat PumpDocument9 pagesLab Heat PumpShahran IezzatNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document47 pagesPresentation 1Abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- The Study of Evaporative Cooling Technology in Electric and Electronic EquipmentDocument4 pagesThe Study of Evaporative Cooling Technology in Electric and Electronic EquipmentWilliam ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration SystemDocument26 pagesRefrigeration SystemArnob Das100% (1)
- Refrigeration Test RigDocument10 pagesRefrigeration Test Rigakshayarora1909No ratings yet
- AJES Vol.6 No.1 January June 2017 pp.18 22Document5 pagesAJES Vol.6 No.1 January June 2017 pp.18 22Design isotechplNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 RefrigeratorDocument3 pagesLab 2 RefrigeratorMuhammad FasihNo ratings yet
- Miniature Refrigeration SystemDocument7 pagesMiniature Refrigeration SystemRameshkumar RNo ratings yet
- Design of Mechanical Draftcooling Tower and Determination of Thermal EfficiencyDocument7 pagesDesign of Mechanical Draftcooling Tower and Determination of Thermal EfficiencyMoch FaridNo ratings yet
- Adsorption ChillerDocument19 pagesAdsorption Chilleragalvan1311No ratings yet
- Lab Refrigeration N Cooling TowerDocument21 pagesLab Refrigeration N Cooling TowerShahran IezzatNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Lab ManualDocument25 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning Lab ManualShalini Manchikatla100% (4)
- Experimental Investigation On Cascade Refrigeration System With and Without Phase Change MaterialDocument8 pagesExperimental Investigation On Cascade Refrigeration System With and Without Phase Change MaterialijsretNo ratings yet
- Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning: Group MembersDocument23 pagesHeating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning: Group MembersLaiba UzairNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214157X23011085 MainDocument14 pages1 s2.0 S2214157X23011085 MainGerson Tomas Varela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Hot Gas Bypass For RefrigerationDocument5 pagesImplementation of Hot Gas Bypass For RefrigerationhurshawNo ratings yet
- Vapor Jet RefrigeratorDocument11 pagesVapor Jet RefrigeratorAlyan YousafNo ratings yet
- 06E Nomenclature ChartDocument14 pages06E Nomenclature ChartDharani PathyNo ratings yet
- Parametric Analysis OF The Performance OF Heat PipeDocument18 pagesParametric Analysis OF The Performance OF Heat PipeSandeep Pathak0% (1)
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Maths 2Document9 pagesWorksheet Maths 2Dhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Workshop Practice: Course Code: Btmp101-18Document12 pagesWorkshop Practice: Course Code: Btmp101-18Dhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- It Is Concerned With The Study, Design and Application of Equipment, Devices and System Which Use Electricity, Electronics, ElectromagnetismDocument5 pagesIt Is Concerned With The Study, Design and Application of Equipment, Devices and System Which Use Electricity, Electronics, ElectromagnetismDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Workshop Practice: Course Code: Btmp101-18Document10 pagesWorkshop Practice: Course Code: Btmp101-18Dhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Workshop Practice: Course Code: Btmp101-18Document12 pagesWorkshop Practice: Course Code: Btmp101-18Dhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- For PPSDocument57 pagesFor PPSDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet MathsDocument9 pagesWorksheet MathsDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Functions INC: Dr. Pertik GargDocument11 pagesFunctions INC: Dr. Pertik GargDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Metal Cutting ProcessDocument14 pagesLecture 4 Metal Cutting ProcessDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Programming in C: Dr. Pertik GargDocument17 pagesProgramming in C: Dr. Pertik GargDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Workshop Practice: Course Code: Btmp101-18Document12 pagesWorkshop Practice: Course Code: Btmp101-18Dhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 HazardsDocument1 pageUnit 1 HazardsDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank English BTHU101 18Document9 pagesQuestion Bank English BTHU101 18Dhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Programming For Problem Solving BTPS101-18Document2 pagesQuestion Bank Programming For Problem Solving BTPS101-18Dhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air-ConditioningDocument24 pagesRefrigeration and Air-ConditioningDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- For PPSDocument57 pagesFor PPSDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Q T RTH - .: B) Bcad D) Dcba (D) 1 and 4 OnlyDocument2 pagesQ T RTH - .: B) Bcad D) Dcba (D) 1 and 4 OnlyDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Course FileDocument4 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Course FileDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- " Tribology" UNIT:-"3 (Lubrication) Topic: - " Lubrication and Its Types" Name: - "Bashir Ahmad" Semester: - "2 " ROLL NO: - "1933971"Document27 pages" Tribology" UNIT:-"3 (Lubrication) Topic: - " Lubrication and Its Types" Name: - "Bashir Ahmad" Semester: - "2 " ROLL NO: - "1933971"Dhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Boiling and CondensationDocument5 pagesUnit 5 Boiling and CondensationDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- NoiseDocument2 pagesNoiseDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Q T RTH - .: B) Bcad D) Dcba (D) 1 and 4 OnlyDocument2 pagesQ T RTH - .: B) Bcad D) Dcba (D) 1 and 4 OnlyDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Extended SurfacesDocument4 pagesUnit 4 Extended SurfacesDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming Processes - Full PDFDocument91 pagesMetal Forming Processes - Full PDFAnonymous 9xvU1F100% (2)
- New Doc 2020-03-31 14.47.11 PDFDocument4 pagesNew Doc 2020-03-31 14.47.11 PDFDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- " Tribology" UNIT:-"3 (Lubrication) Topic: - " Lubrication and Its Types" Name: - "Bashir Ahmad" Semester: - "2 " ROLL NO: - "1933971"Document27 pages" Tribology" UNIT:-"3 (Lubrication) Topic: - " Lubrication and Its Types" Name: - "Bashir Ahmad" Semester: - "2 " ROLL NO: - "1933971"Dhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- DetailsDocument2 pagesDetailsDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Swami Vivekanand Insitiute of Engg. & Technology Ram Nagr BanurDocument4 pagesSwami Vivekanand Insitiute of Engg. & Technology Ram Nagr BanurDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial SheetsDocument5 pagesTutorial SheetsDhiraj DhimanNo ratings yet
- 10-1-18 M Tech ME 2017 FinalDocument50 pages10-1-18 M Tech ME 2017 FinalIrfanNo ratings yet
- Gas Pool Heaters Melbourne - Sunlover HeatingDocument2 pagesGas Pool Heaters Melbourne - Sunlover HeatingAdam JonesNo ratings yet
- Calorimetry Exercise PDFDocument8 pagesCalorimetry Exercise PDFAmmarmz100% (2)
- Samsung DVM-S (VRF) Catalog Full 2015Document116 pagesSamsung DVM-S (VRF) Catalog Full 2015Hung Tran82% (11)
- Spectrum Chemistry - February 2016 VK Com EnglishmagazinesDocument100 pagesSpectrum Chemistry - February 2016 VK Com Englishmagazinesnandu100% (1)
- Aircond Ref1Document33 pagesAircond Ref1Ghaith AlhadiNo ratings yet
- Stagnation PressureDocument3 pagesStagnation PressureHaider ShahNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics Lab Assignment-3: Mechanical Equivalent of HeatDocument11 pagesThermal Physics Lab Assignment-3: Mechanical Equivalent of HeatMohd Muaaz AnsariNo ratings yet
- Section A: Pengenalan Kepada Sains Topik: Penyiasatan Saintifik (Panduan Guru)Document1 pageSection A: Pengenalan Kepada Sains Topik: Penyiasatan Saintifik (Panduan Guru)Nor Hamizah OmarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Ii Ideal Gases and Their Mixtures: By: Abubeker NDocument23 pagesThermodynamics Ii Ideal Gases and Their Mixtures: By: Abubeker NSidrak MekuriaNo ratings yet
- Chen19111005 M JaishDocument20 pagesChen19111005 M JaishUsama Jahangir KhanNo ratings yet
- BoilersDocument5 pagesBoilersNisarg ModiNo ratings yet
- Thermal PhysicsDocument19 pagesThermal PhysicsMaya SinghNo ratings yet
- HPWH Field Testing Report 1-6-2016Document56 pagesHPWH Field Testing Report 1-6-2016Tommy YoungNo ratings yet
- Part 4-1Document36 pagesPart 4-1doshy89No ratings yet
- Experiment NoDocument5 pagesExperiment NoAbdullah UsmaniNo ratings yet
- 00 - MEP Midterm - Spring 2021 - RDocument25 pages00 - MEP Midterm - Spring 2021 - REngSeham MohamedNo ratings yet
- 102 Na04529a IlzheDocument12 pages102 Na04529a IlzheIstvan MadacsyNo ratings yet
- Continue Practice Exam Test Questions Part 3 of The SeriesDocument8 pagesContinue Practice Exam Test Questions Part 3 of The SeriesKenn Earl Bringino VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Zubadan CopDocument1 pageZubadan CopFlorentin GheorghitaNo ratings yet
- Uvce Be 2nd3rd 4th Year Mech Engg Syl PDFDocument66 pagesUvce Be 2nd3rd 4th Year Mech Engg Syl PDFNAGENDRA0% (1)
- ICE Formula Sheet: P V T P V TDocument3 pagesICE Formula Sheet: P V T P V TAdnan PirbhaiNo ratings yet
- Steam Drive Correlation and Prediction PDFDocument10 pagesSteam Drive Correlation and Prediction PDFEmre CengizNo ratings yet
- Fral FD160 and FD240 Spec SheetDocument1 pageFral FD160 and FD240 Spec SheetmoisturecarevidsNo ratings yet
- Shahjalal University of Science and Technology Dept. of Chemical Engineering and Polymer ScienceDocument7 pagesShahjalal University of Science and Technology Dept. of Chemical Engineering and Polymer ScienceSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Development of A New Alpha Function For The PREOS Comparative Study of Alpha Function Models For Pure Gases and Water-Gas SystemsDocument26 pagesDevelopment of A New Alpha Function For The PREOS Comparative Study of Alpha Function Models For Pure Gases and Water-Gas Systemsmurdanetap957No ratings yet
- Development of Stirling Engine Heat PumpDocument9 pagesDevelopment of Stirling Engine Heat PumpSandra L. Castillo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Set 6 AnsDocument6 pagesSet 6 AnskietNo ratings yet
- Write UpDocument26 pagesWrite UpApple Pear100% (1)
- Adiabatic Process - Physics Olympiads GuideDocument7 pagesAdiabatic Process - Physics Olympiads GuideDiana PonceNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Convection Heat TransferDocument41 pages3.0 Convection Heat Transfershariza91No ratings yet